
Cardiovascular
system
lecture 6
Dr. Noor


When a person is at rest, the heart pumps only 4 to
6 liters of blood each minute. During strenuous
exercise, the heart may be required to pump four to
seven times this amount..

The basic means by which the volume pumped by
the heart is regulated are
(1) intrinsic cardiac regulation of pumping in
response to changes in volume of blood flowing
into the heart and
(2) control of heart rate and strength of heart
pumping by the autonomic nervous system

The amount of blood pumped by the heart each
minute is normally determined almost entirely by
the rate of blood flow into the heart from the veins,
which is called
venous return.
While the volume
of
pumped from the left
per
beat
called
stroke volume (SV)

That is, each peripheral tissue of the body controls
its own local blood flow, and all the local tissue
flows combine and return by way of the veins to the
right atrium. The heart, in turn, automatically
pumps this incoming blood into the arteries so that
it can flow around the circuit again.

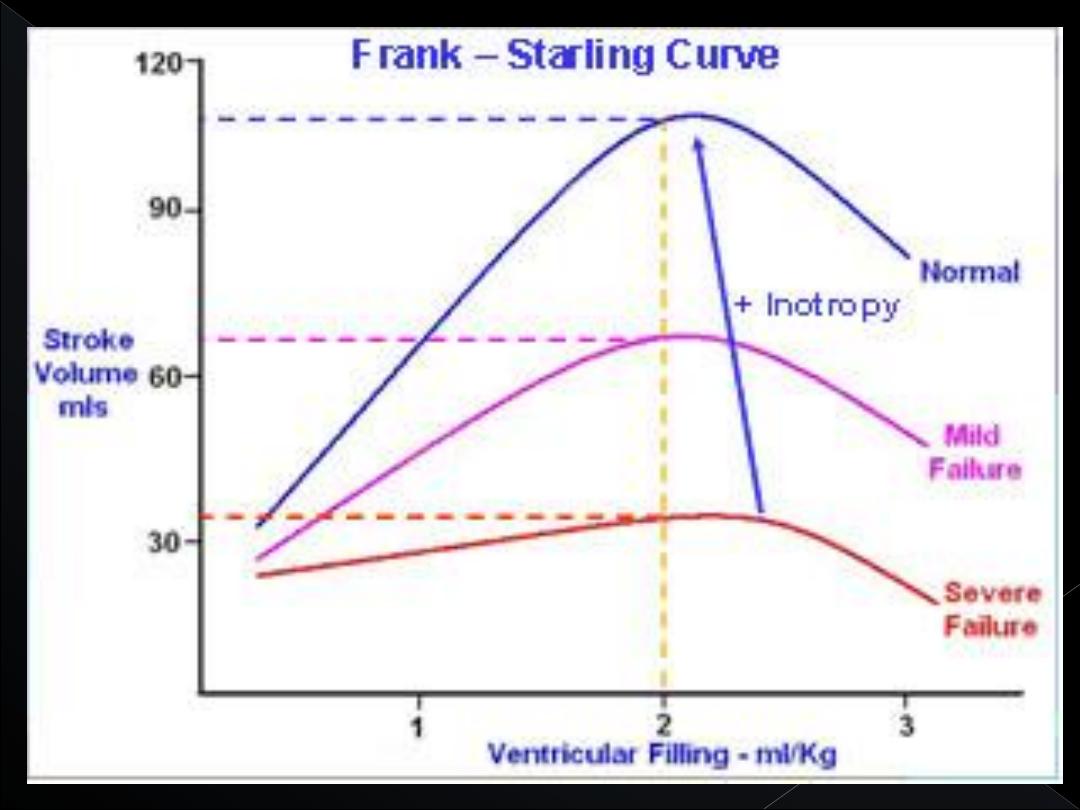
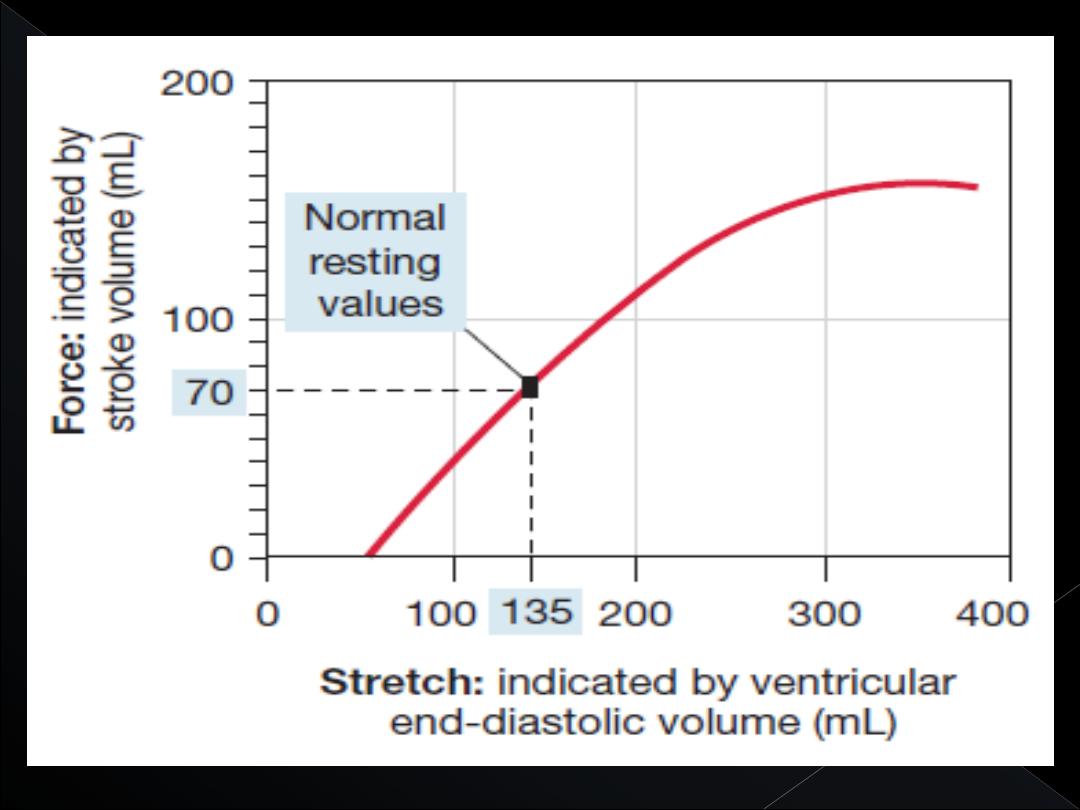
This intrinsic ability of the heart to adapt to
increasing volumes of inflowing blood is called
the
FrankStarling mechanism of the heart

Basically, the Frank-Starling mechanism means that
the greater the heart muscle is stretched during
filling, the greater is the force of contraction and the
greater the quantity of blood pumped into the aorta.
Or, stated another way:
Within physiological limits,
the heart pumps all the blood that returns to it by
way of the veins.

When an extra amount of blood flows into the
ventricles, the cardiac muscle itself is
stretched to greater length. This in turn causes
the muscle to contract with increased force
because the actin and myosin filaments are
brought to a more nearly optimal degree of
overlap for force generation.

In addition to the important effect of lengthening the
heart muscle, still another factor increases heart
pumping when its volume is increased. Stretch of
the right atrial wall directly increases the heart rate
by 10 to 20 per cent; this, too, helps increase the
amount of blood pumped each minute, although its
contribution is much less than that of the Frank-
Starling mechanism.
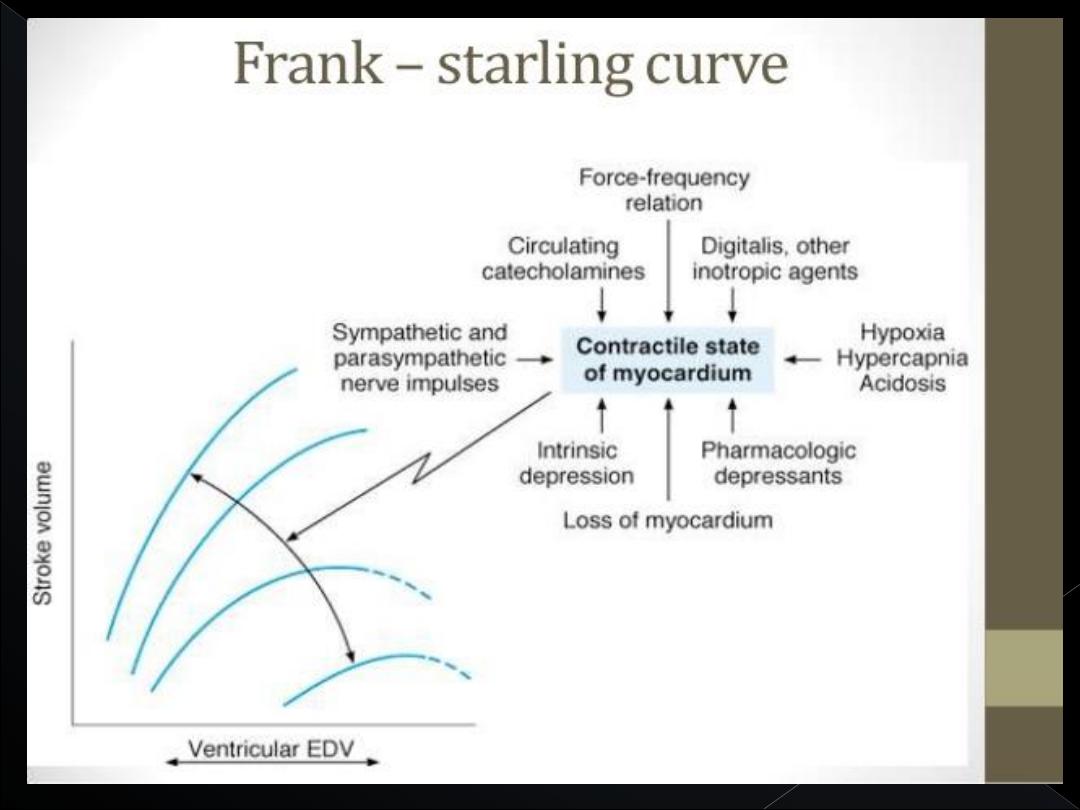


The pumping effectiveness of the heart also is
controlled by the sympathetic and
parasympathetic (vagus) nerves, which
abundantly supply the heart.
.

The amount of blood pumped each minute
(cardiac output)
often can be increased more than
100 per cent by sympathetic stimulation. By
contrast, the output can be decreased to as low as
zero or almost zero by vagal (parasympathetic)
stimulation

Strong sympathetic stimulation can increase the
heart rate in young adult humans from the normal
rate of 70 beats per minute up to 180 to 200 and,
rarely, even 250 beats per minute.

Also, sympathetic stimulation increases the force of
heart contraction to as much as double normal,
thereby increasing the volume of blood pumped and
increasing the ejection pressure.

Conversely, inhibition of the sympathetic nerves to
the heart can decrease cardiac pumping to a
moderate extent in the following way: Under
normal conditions, the sympathetic nerve fibers to
the heart discharge continuously at a slow rate that
maintains pumping at about 30 per cent above that
with no sympathetic stimulation.

Therefore, when the activity of the sympathetic
nervous system is depressed below normal, this
decreases both heart rate and strength of ventricular
muscle contraction, thereby decreasing the level of
cardiac pumping as much as 30 per cent below
normal.

Strong stimulation of the parasympathetic nerve
fibers in the vagus nerves to the heart can stop the
heartbeat for a few seconds, but then the heart
usually “escapes” and beats at a rate of 20 to 40
beats per minute as long as the parasympathetic
stimulation continues

In addition, strong vagal stimulation can decrease
the strength of heart muscle contraction by 20 to 30
per cent.
The vagal fibers are distributed mainly to the atria
and not much to the ventricles, where the power
contraction of the heart occurs.This explains the
effect of vagal stimulation mainly to decrease heart
rate rather than to decrease greatly the strength of
heart contraction.

Nevertheless, the great decrease in heart rate
combined with a slight decrease in heart
contraction strength can decrease ventricular
pumping 50 per cent or more.

Excess potassium in the extracellular fluids
causes the heart to become dilated and flaccid
and also slows the heart rate. Large quantities
also can block conduction of the cardiac
impulse from the atria to the ventricles
through the A-V bundle.

Elevation of potassium concentration to only 8 to
12 mEq/L—two to three times the normal value—
can cause such weakness of the heart and abnormal
rhythm that this can cause death.

These effects result partially from the fact that a high
potassium concentration in the extracellular fluids
decreases the resting membrane potential in the
cardiac muscle fibers.
As the membrane potential decreases, the intensity
of the action potential also decreases, which makes
contraction of the heart progressively weaker.

Effect of Calcium Ions.
An excess of calcium ions causes effects almost
exactly opposite to those of potassium ions, causing
the heart to go toward spastic contraction.
This is caused by a direct effect of calcium ions to
initiate the cardiac contractile process.

Conversely, deficiency of calcium ions causes
cardiac flaccidity, similar to the effect of high
potassium. Fortunately, however, calcium ion levels
in the blood normally are regulated within a very
narrow range.
Therefore, cardiac effects of abnormal calcium
concentrations are seldom of clinical concern.

Increased body temperature, as occurs when one
has fever, causes a greatly increased heart rate,
sometimes to as fast as double normal. Decreased
temperature causes a greatly decreased heart rate,
falling to as low as a few beats per minute when a
person is near death from hypothermia in the body
temperature range of 60° to 70°F.

. These effects presumably result from the fact that
heat increases the permeability of the cardiac muscle
membrane to ions that control heart rate, resulting in
acceleration of the self-excitation process.

Contractile strength of the heart often is enhanced
temporarily by a moderate increase in temperature,
as occurs during body exercise, but prolonged
elevation of temperature exhausts the metabolic
systems of the heart and eventually causes
weakness. Therefore, optimal function of the heart
depends greatly on proper control of body
temperature by the temperature control mechanisms
.


Q2 \\ Pulmonary congestion typically indicate
the right ventricle problem :
A. True
B. False

Given
these valves:
1. aortic semilunar valve
2. bicuspid (mitral) valve
3. pulmonary semilunar valve
4. tricuspid valve.
Arrange them in the order in which an erythrocyte
pass through them after returning to the heart from
the left arm
.
A. 1,2 3,4
B. 2,3,1,4
C. 3,1,2,4
D. 3,4,2,1
E. 4,3,2,1

