
1
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
Lecture 1- Neurophysiology Dr. Noor Jawad
2
nd
stage Saturday 15 / 2 / 2020
……………………………………………………………………
Nervous system
Objectives :
1.what is the nervous system ? parts of nervous system?
2. what are the areas for language comprehension, word
formation?
The nervous system is the part of an animal's body that coordinates
its actions and transmits signals to and from different parts of its
body. In vertebrate species it consists of two main parts,
the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous
system (PNS).
The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists
mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers
or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body.
Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are
called motor or efferent nerves,while those nerves that transmit
information from the body to the CNS are
called sensory or afferent. Most nerves serve both functions and
are called mixed nerves.
The PNS is divided into a) somatic and b) autonomic nervous
system, and c) the enteric nervous system. Somatic nerves mediate
voluntary movement. The autonomic nervous system is further
2
subdivided into the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous
systems. Both autonomic and enteric nervous systems function
involuntarily. Nerves that exit from the cranium are called cranial
nerves while those exiting from the spinal cord are called spinal
Physiological anatomy of cerebral cortex
The functional part of the cerebral cortex is a thin layer of neurons
covering the surface of all the convolutions of the cerebrum. This
layer is only 2 to 5 millimeters thick, with a total area of about one
quarter of a square meter. The total cerebral cortex contains about
100 billion neurons.
Figure below shows the typical histological structure of the
neuronal surface of the cerebral cortex, with its successive layers
of different types of neurons. Most of the neurons are of three
types: (1) granular (also called stellate), (2) fusiform, and (3)
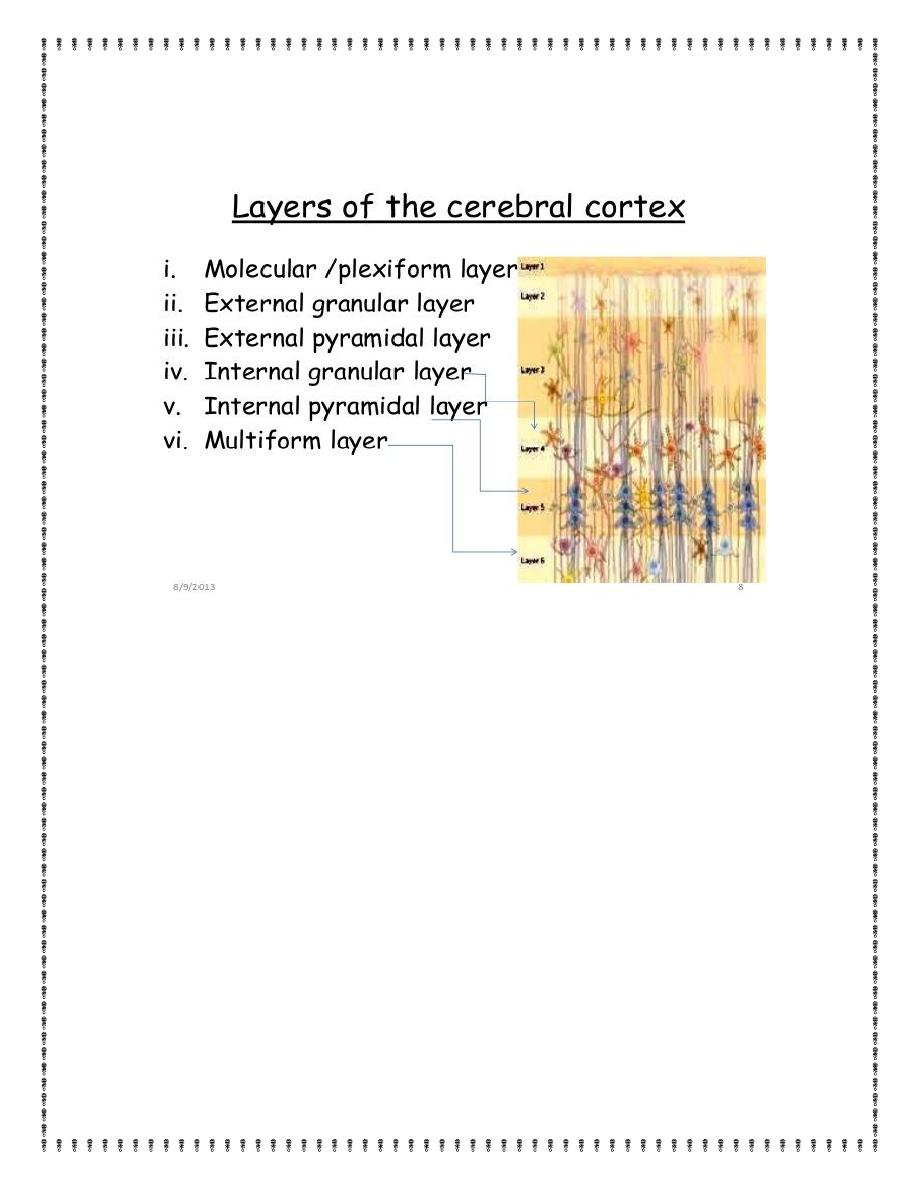
3
pyramidal, the last named for their characteristic pyramidal shape.
The granular neurons generally have short axons and, therefore,
function mainly as interneurons that transmit neural signals only
short distances within the cortex. Some are excitatory, releasing
mainly the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate, whereas others
are inhibitory and release mainly the inhibitory neurotransmitter
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
The pyramidal and fusiform cells give rise to almost all the output
fibers from the cortex. The pyramidal cells, which are larger and
more numerous than the fusiform cells, are the source of the long,
large nerve fibers that go all the way to the spinal cord.
