Fertilization

FERTILIZATION
Fertilization, the process by which male and female gametes fuse, occurs in the ampullary
region of the uterine tube. This is the widest part of the tube and is close to the ovary.
Spermatozoa may remain viable in the female reproductive tract for several days.
Movement of sperm from the cervix to the uterine tube occurs by muscular contractions of
the uterus and uterine tube and very little by their own propulsion .
The trip from cervix to oviduct can occur as rapidly as 30 minutes or as slow as 6 days.
.
Spermatozoa are not able to fertilize the oocyte immediately upon arrival in the female
genital tract but must undergo
(1) capacitation and (2) acrosome reaction
Capacitation is a period of conditioning in the female reproductive tract that in the
human lasts approximately 7 hours. Much of this conditioning during capacitation
occurs in the uterine tube and involves epithelial interactions between the sperm and
the mucosal surface of the tube.
During this time, a glycoprotein coat and seminal plasma proteins are removed from
the plasma membrane that overlies the acrosomal region of the spermatozoa. Only
capacitated sperm can pass through the corona cells and undergo the acrosome
reaction.

Acrosome reaction, which occurs after binding to the zona
pellucida, is induced by zona proteins, the release of enzymes
needed to penetrate the zona pellucida, including
acrosin- and
trypsin-like substances.
The phases of fertilization include
●
Phase 1, penetration of the corona radiata
●
Phase 2, penetration of the zona pellucida
●
Phase 3, fusion of the oocyte and sperm cell membranes
●
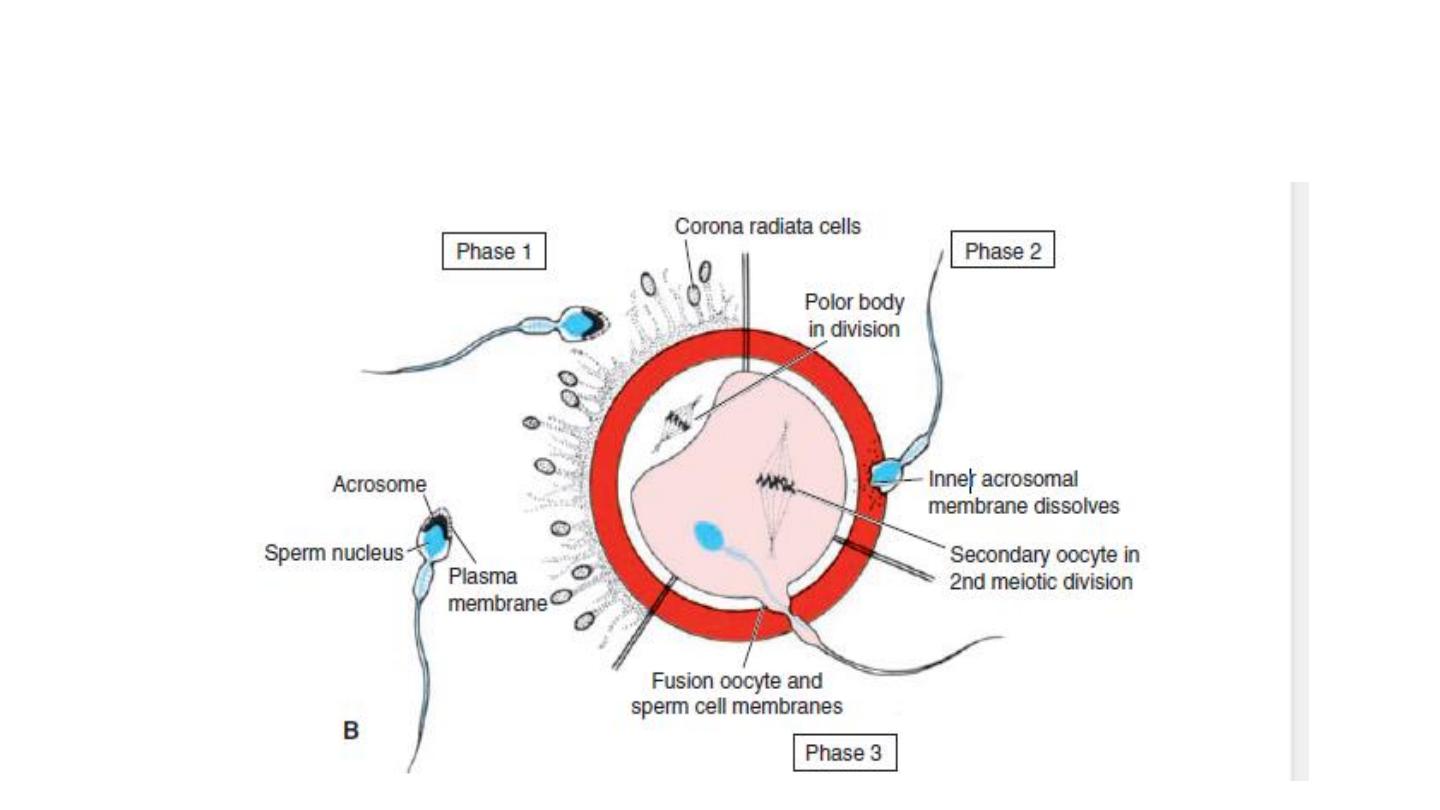

As soon as the spermatozoon has entered the oocyte, the egg
responds in three ways:
1-
Cortical and zona
reactions. These reactions prevent polyspermy
(penetration of more than one spermatozoon into the oocyte).
2
–Resumption of second meiotic division. The oocyte finishes its meiotic
division immediately after entry of the spermatozoon, and forms the female
pronucleus.
3
–Metabolic activation of the egg.The activating factor is probably carried
by the spermatozoon ,the head of the sperm separates from the tail, swells,
and forms the male pronucleus.

The main results of fertilization are
1-
Restoration of the diploid number of chromosomes, half from the father
and half from the mother. Hence, the zygote contains a new combination of
chromosomes different from both parents.
2-
Determination of chromosomal sex. An X-carrying sperm produces a
female (XX) embryo, and a Y-carrying sperm produces a male (XY) embryo.
3-
Initiation of cleavage. Without fertilization, the oocyte usually degenerates
24 hours after ovulation.
