Development of the Face
•
The development of the face occurs mainly between 5 – 8 weeks
The lower jaw (mandible) is the first to form (4th week)
The facial proportions develop during the fetal period (9th week to birth)
During infancy & childhood, following the development of teeth and paranasal sinuses, the facial skeleton increases in size and contribute to the definitive shape of the face
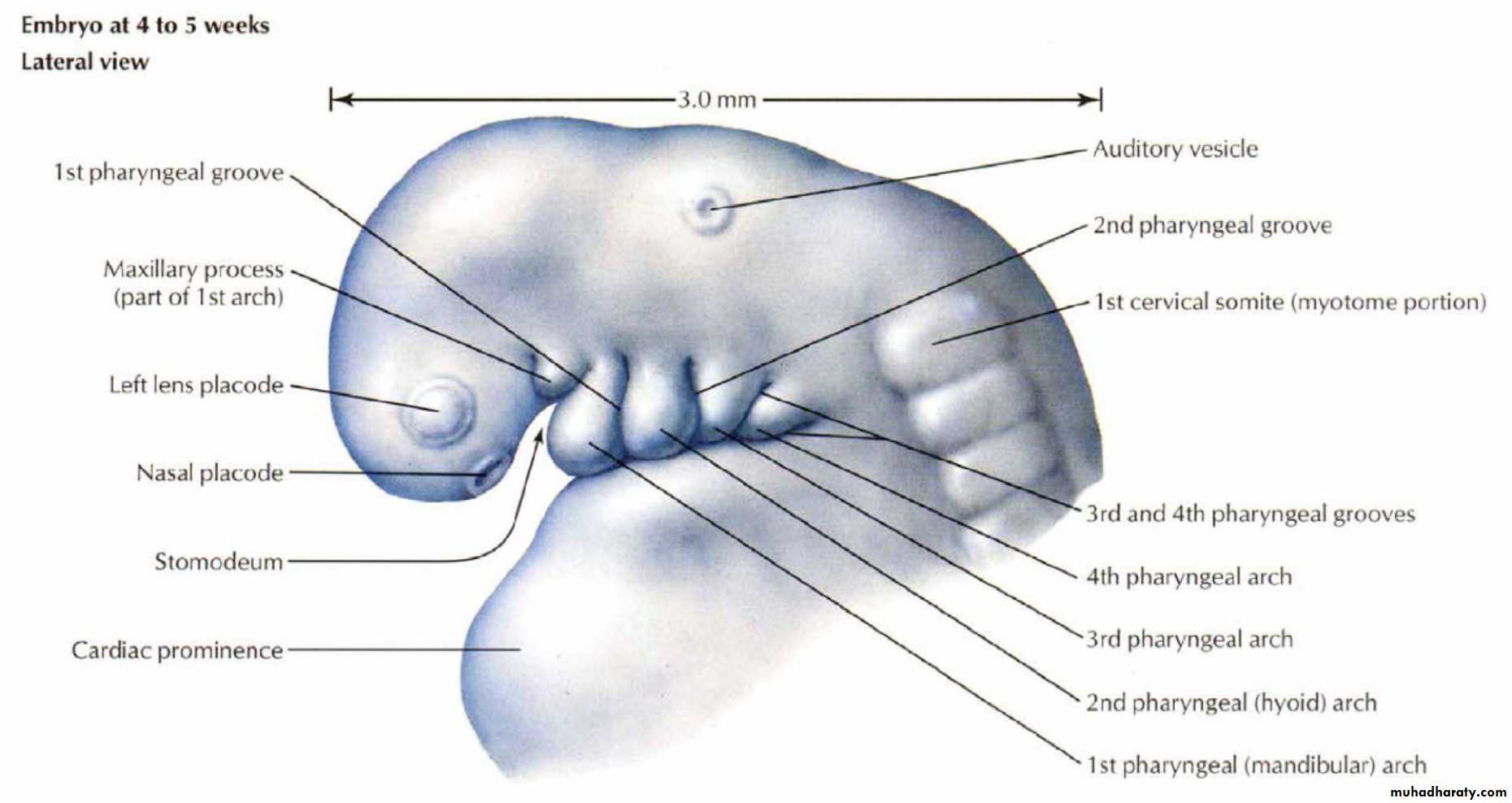
Embryo at 4 - 5 weeks (Lateral view)
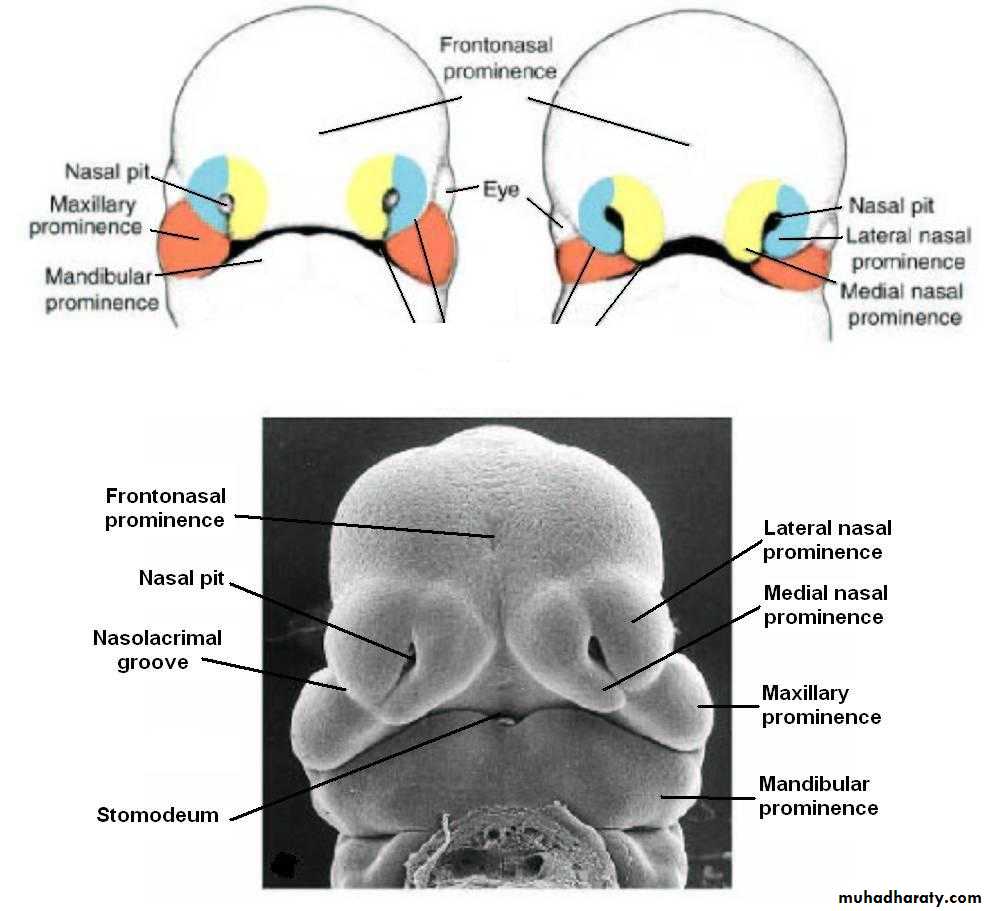
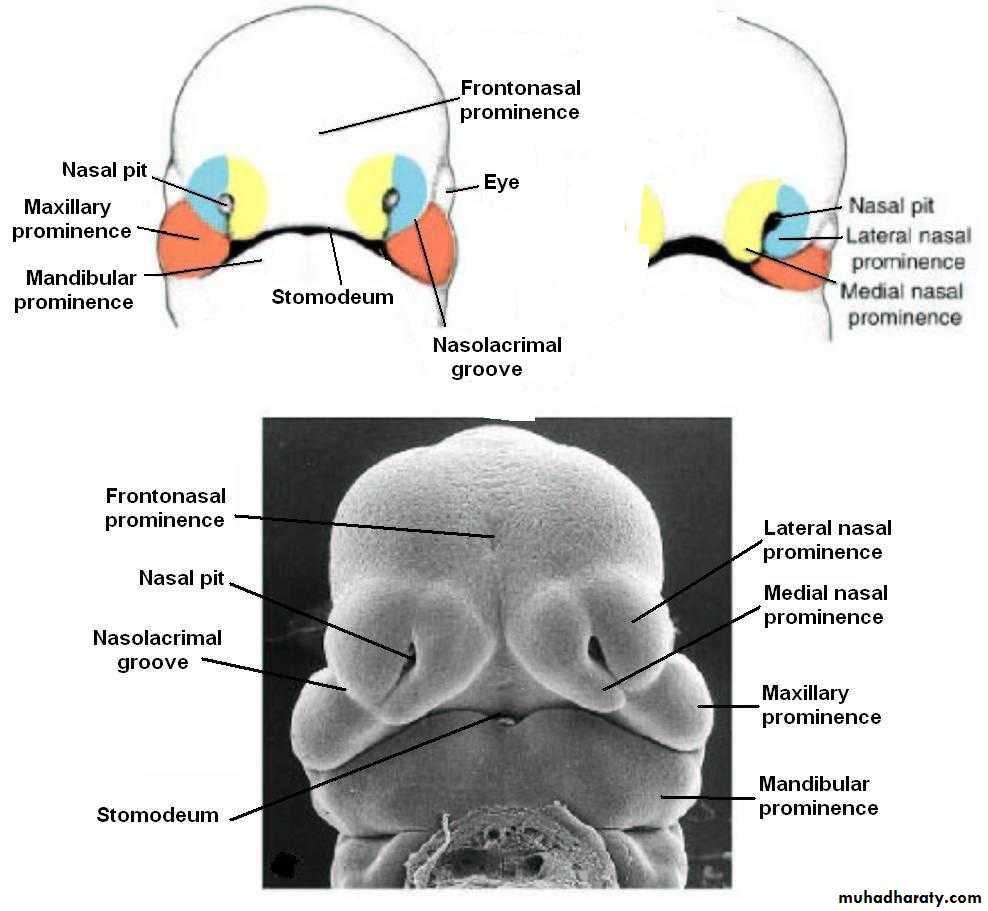
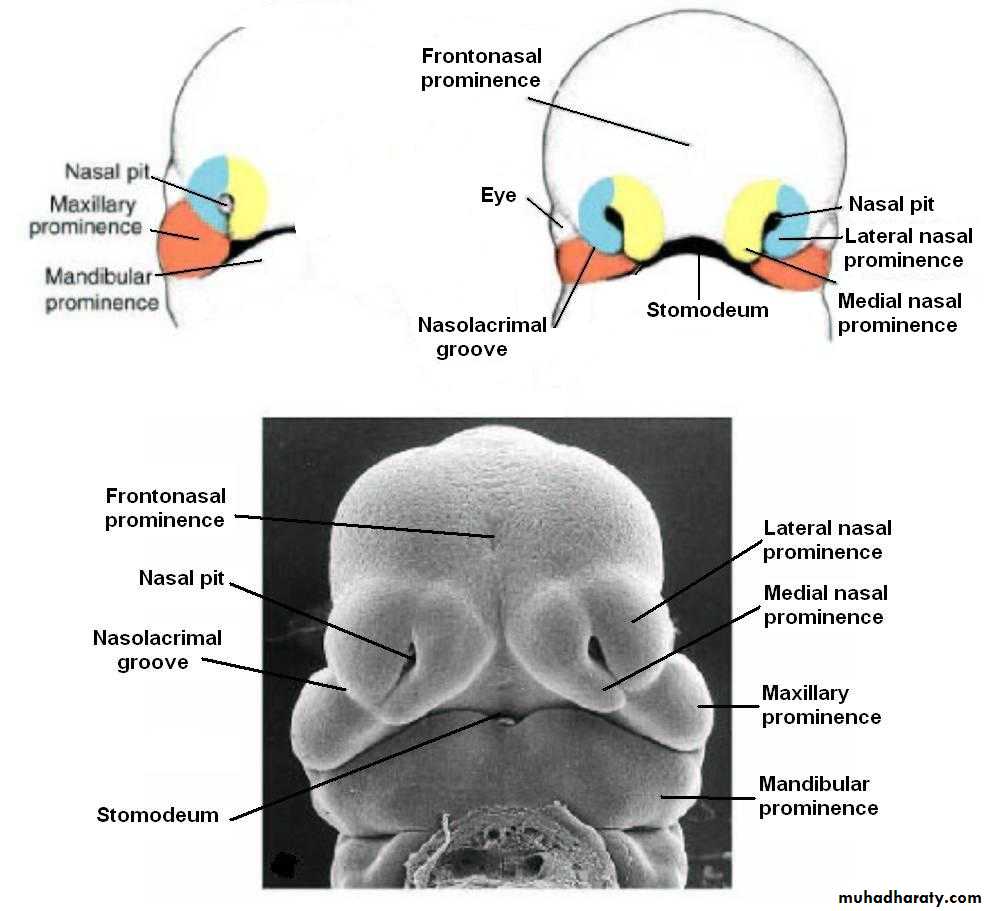
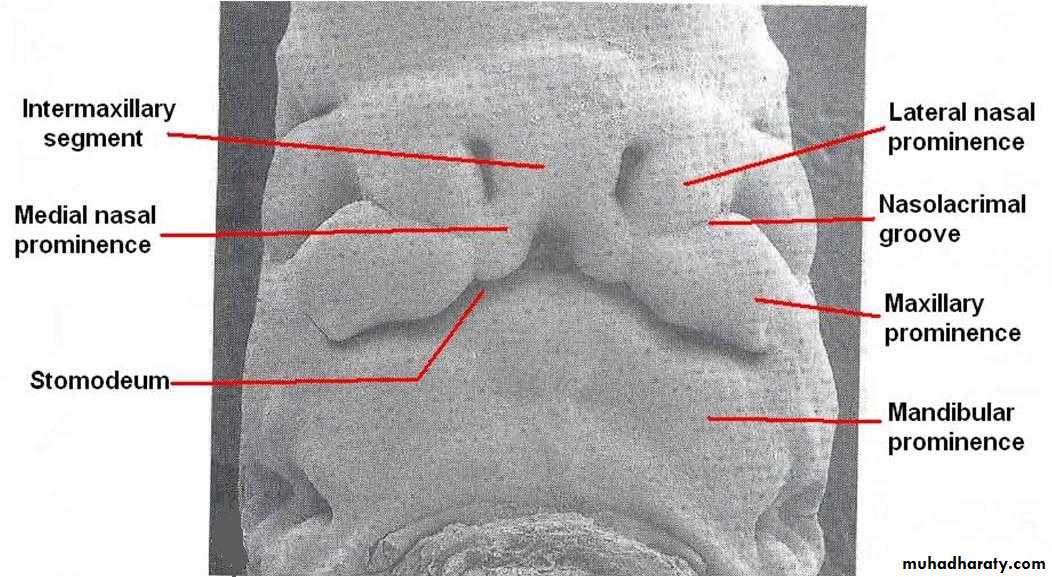
Early in the 4th week, five primordial swellings consisting primarily of neural crest-derived mesenchyme appear around the stomodeum and play an important role in the development of face
Stomodeum
1 Frontonasal prominence
2 Maxillary prominences2 Mandibular prominences
The single frontonasal prominence ventral to the forebrain
The paired maxillary prominences develop from the cranial part of first branchial archThe paired mandibular prominences develop from the caudal part of first branchial arch
Lateral view
Stomodeum
An ectoderm lined depression
Separated from the primitive pharynx by the buccopharyngeal (oropharyngeal) membrane
The membrane later breaks down and stomodeum opens into the pharynx
Forms the vestibule of the oral cavity
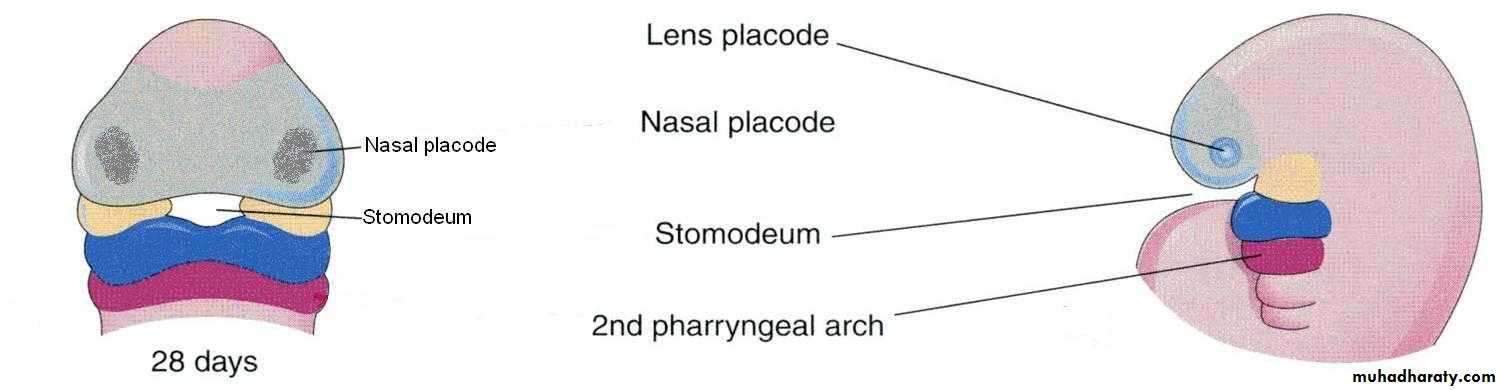
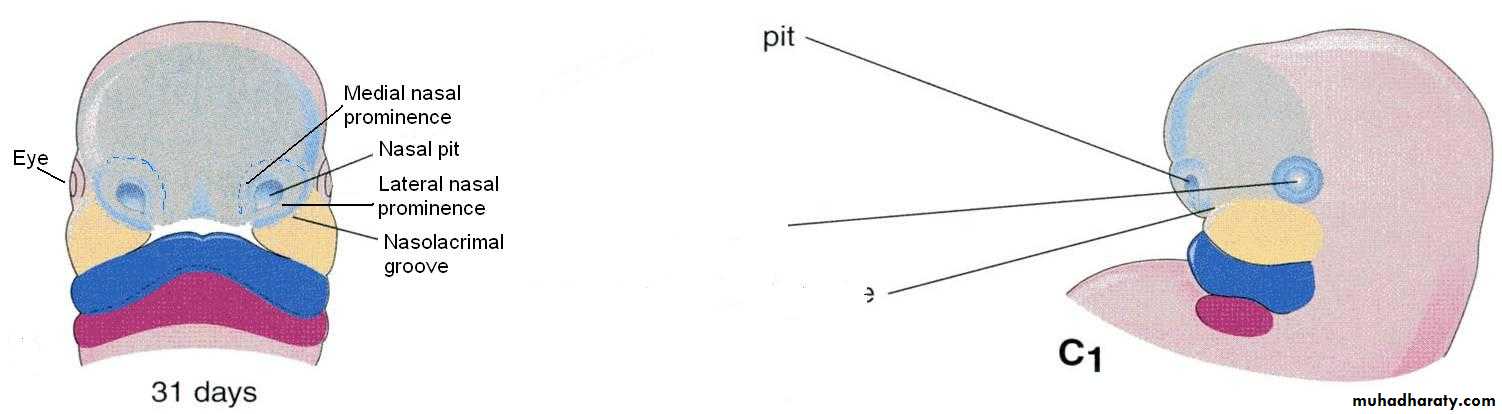
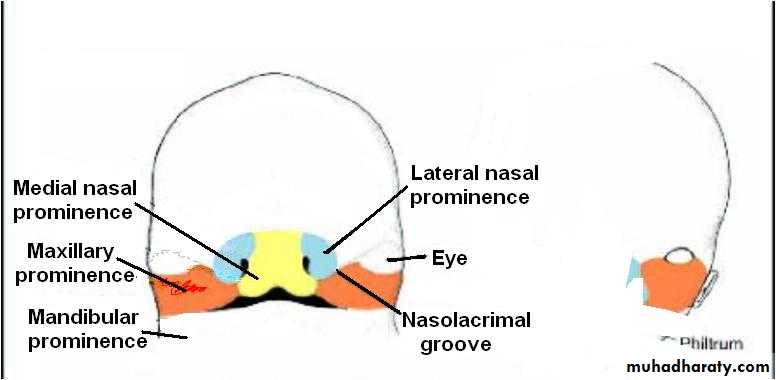
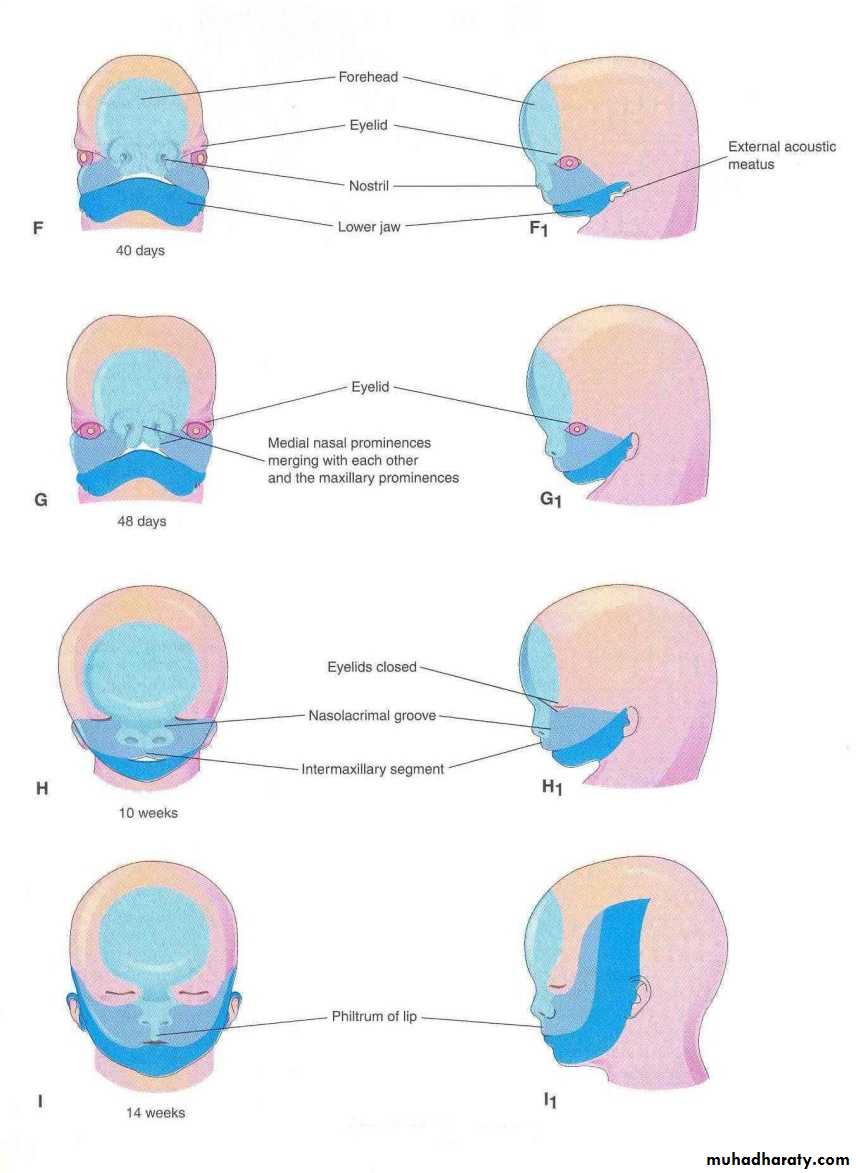
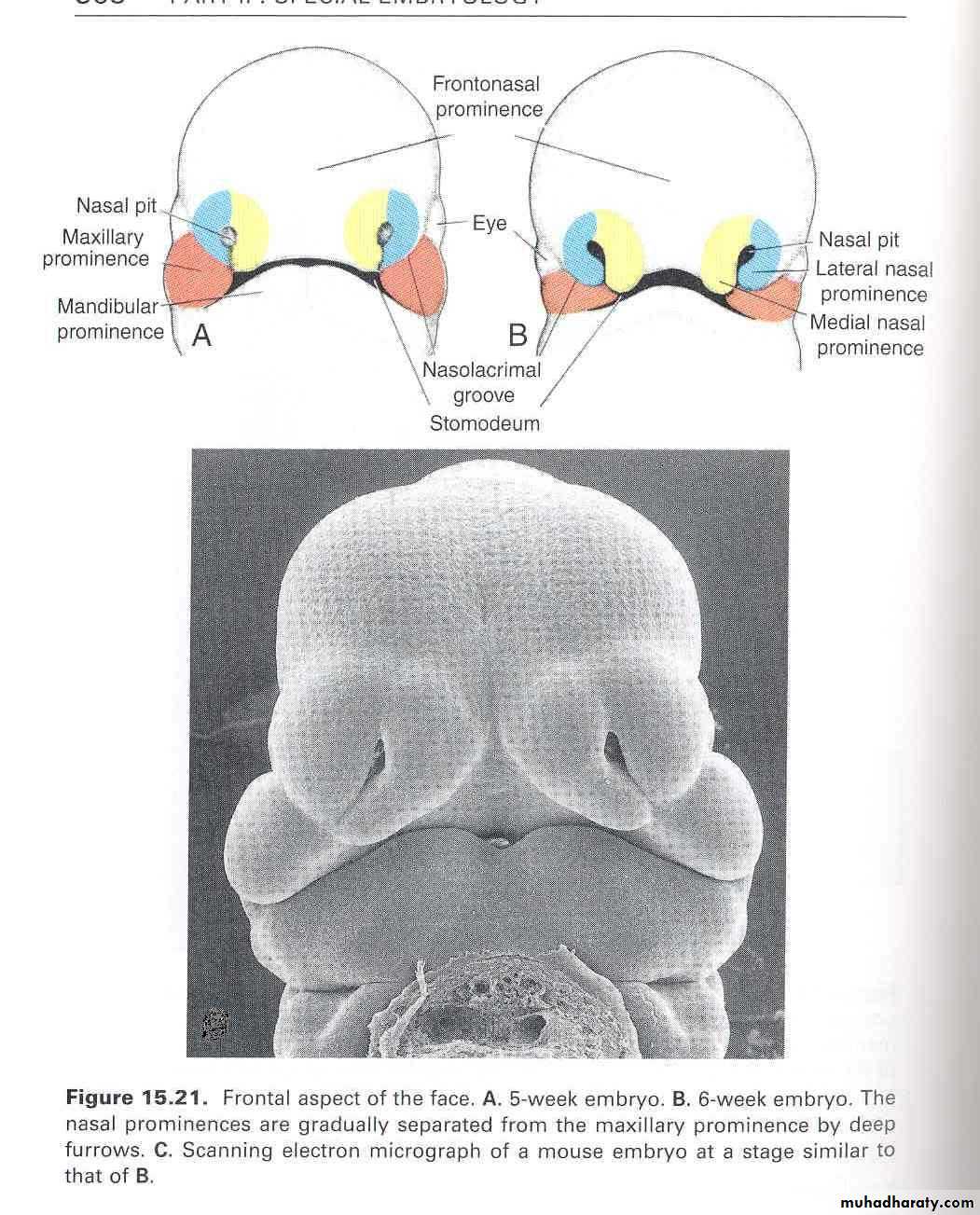
By the end of 4th week, bilateral oval-shaped ectodermal thickenings called ‘nasal placodes’ appear on each side of the lower part of the frontonasal prominence
Nasal placodes are primordia of the nose and nasal cavities.
Frontonasal prominence
Mesenchymal cells proliferate at the margin of the placodes and produce horse-shoe shaped swellings around these.
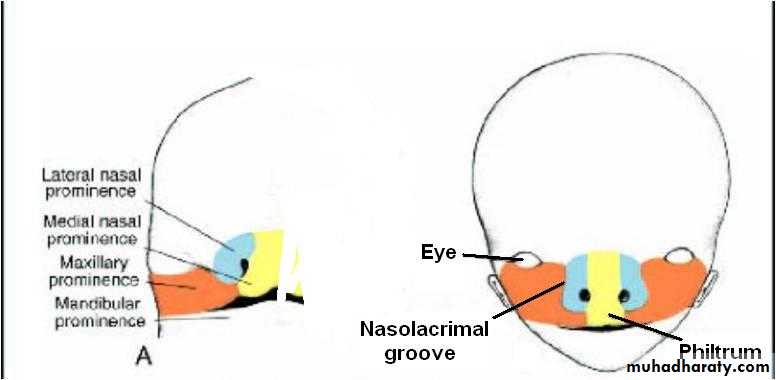
The sides of these swellings are called ‘medial’ and ‘lateral’ nasal prominences
The placodes now lie in the floor of a depression called ‘nasal pits’
Each lateral nasal prominence is separated from the maxillary swelling by nasolacrimal groove
embryo: 6 weeks
The maxillary prominences continue to increase in size and:
Laterally, merge with the mandibular prominences to form the cheekMedially, compress the medial nasal prominences toward the midline and finally fuses with these to form the upper lip.
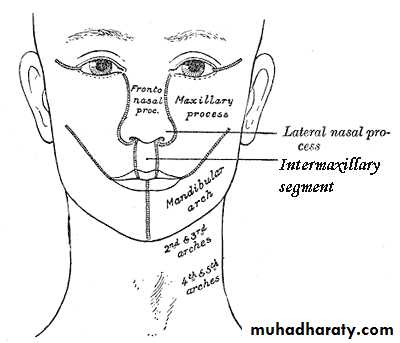
The upper lip is formed by the two medial nasal prominences & the two maxillary prominences
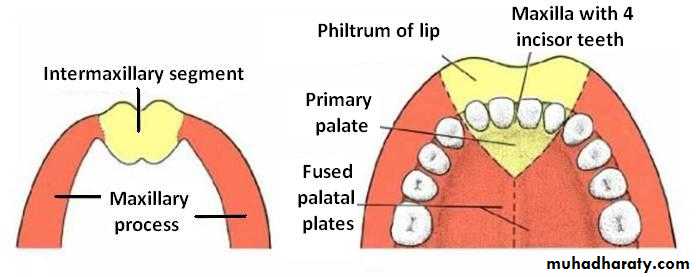
The medial nasal swellings enlarge, grow medially and merge with each other in the midline to form the intermaxillary segment
Human embryo: 7 weeks
Intermaxillary Segment
Gives rise to the:Philtrum of lip
Premaxillary part of the maxilla, that bears the upper 4 incisors and the associated gums
Primary palate (region of hard palate just posterior to the upper incisors)
Besides the fleshy derivatives, the facial prominences also give rise to bones of the facial skeleton
The mesenchyme from the 1st & 2nd pairs of pharyngeal arches invade the facial prominences and give rise to the muscles of mastication and muscles of facial expression respectively
The frontonasal prominence forms the:
Forehead and the bridge of the noseFrontal and nasal bones
The maxillary prominences form the:
Upper cheek regions and most of the upper lip
Maxilla, zygomatic bone, secondary palate
Derivatives of Facial Components
The mandibular prominences fuse and form the:
Chin, lower lip, and lower cheek regionsMandible
The lateral nasal prominences form the alae of the nose
The medial nasal prominences fuse and form the intermaxillary segment
Development of the Nasal Cavity & Paranasal Sinuses
With the formation of the medial and lateral nasal prominences, the nasal placodes lie in the floor of depressions called the nasal pits
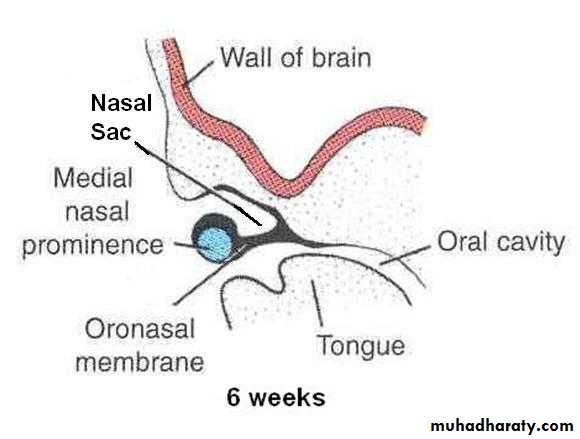
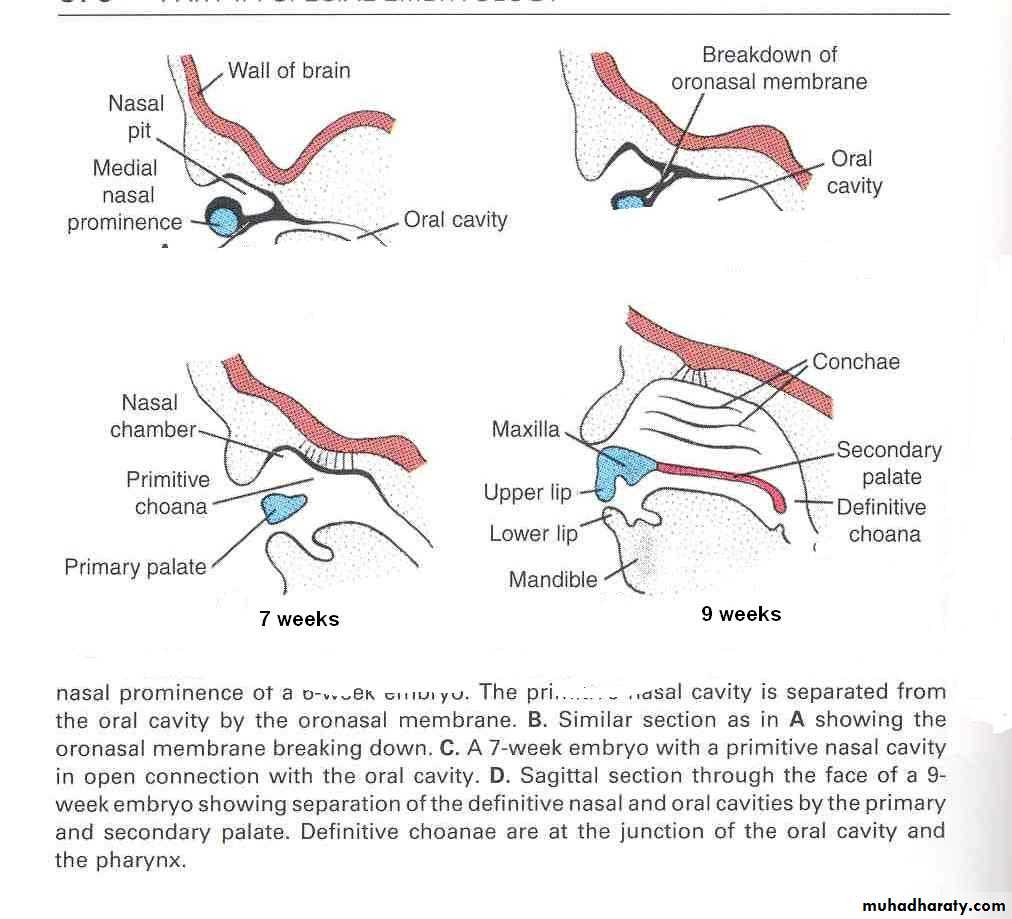
By the end of 6th week, nasal pits deepen and form nasal sacs
Each nasal sac grows dorsocaudally, ventral to the developing brain
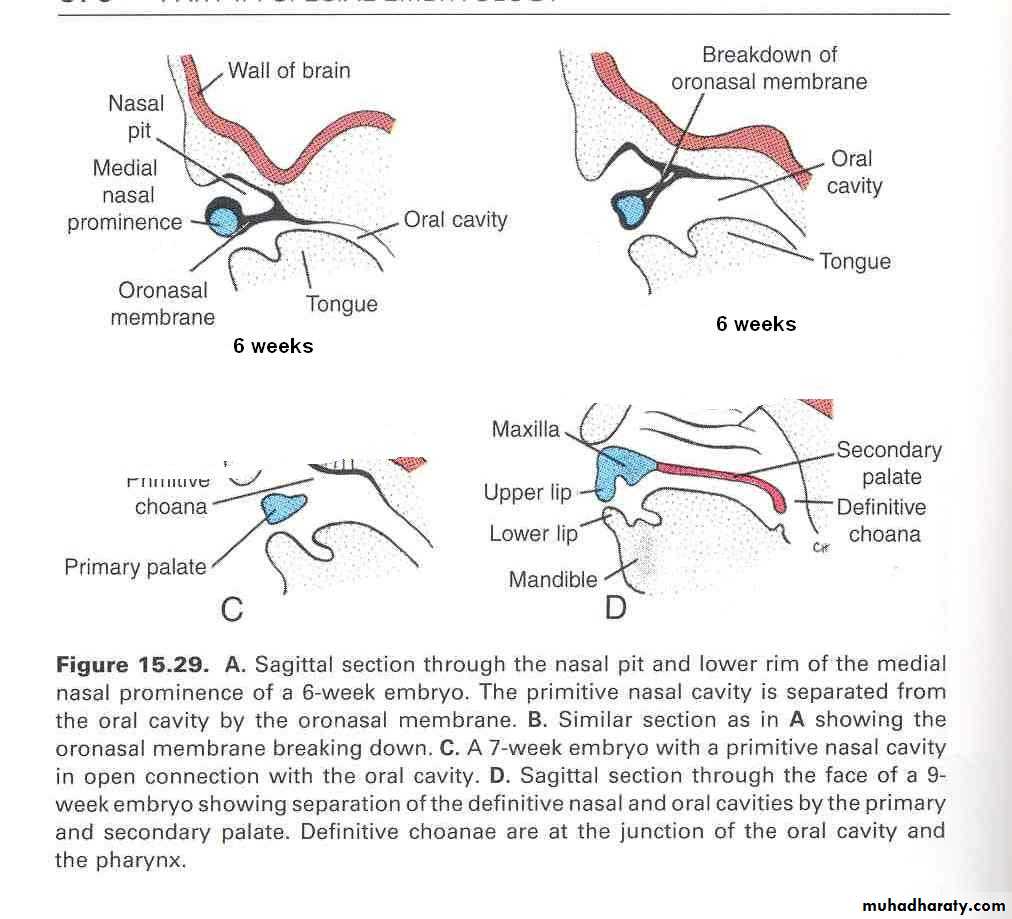
Initially the nasal sacs are separated from the oral cavity by oronasal membrane.
The oronasal membrane ruptures by the 7th week, communicating the primitive nasal cavities with the oral cavityThe nasal septum develops as a downgrowth from the internal parts of merged medial nasal prominences
Fuses with the palatine process in 9-12 weeks, superior to the hard palate primordium
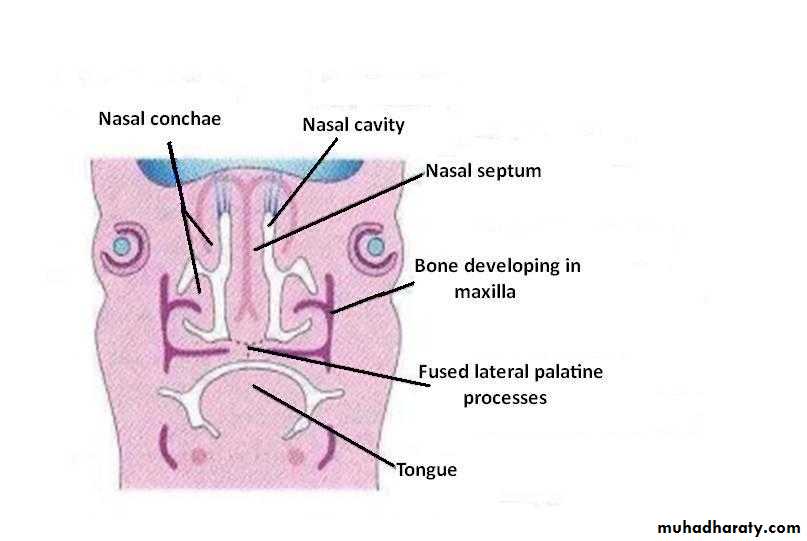
The superior, middle and inferior conchae develop on the lateral wall of each nasal cavity
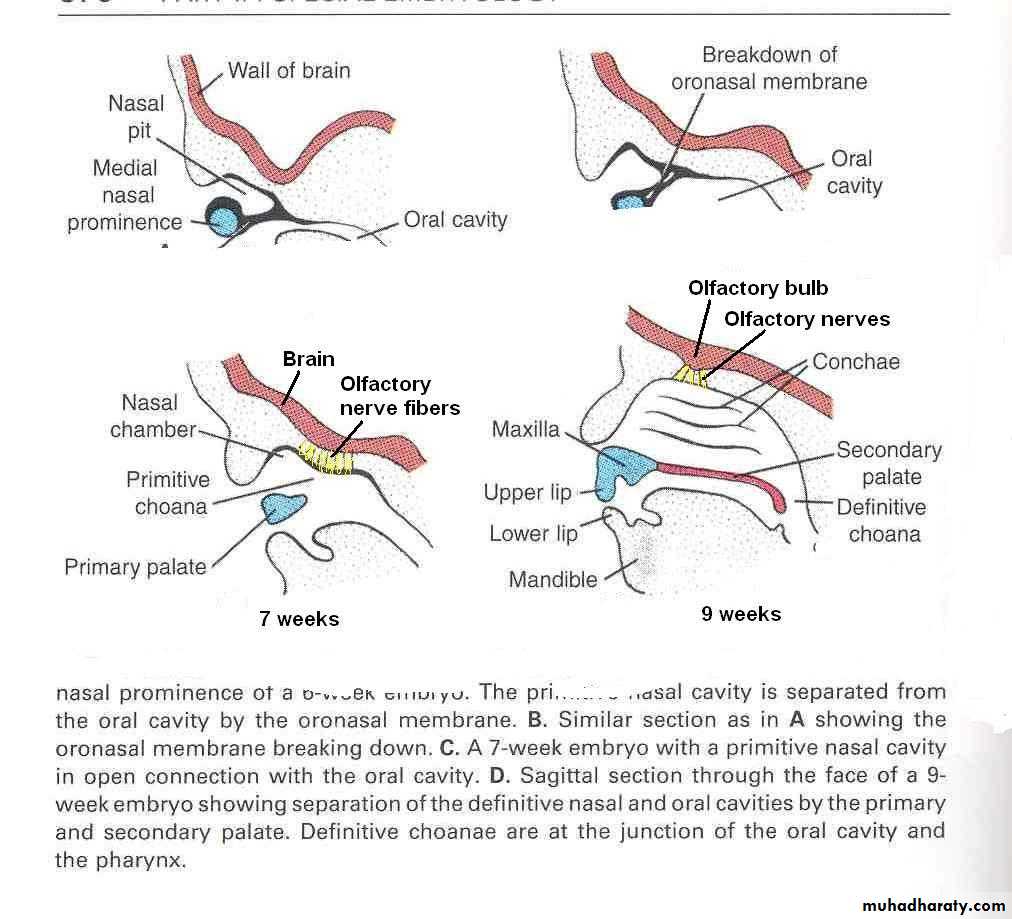
The ectodermal epithelium in the roof of each nasal cavity becomes specialized as the olfactory epitheliumThe olfactory cells of the olfactory epithelium give origin to olfactory nerve fibers that grow into the olfactory bulb
The paranasal sinuses develop as diverticulae of the walls of the nasal cavity
Maxillary sinuses and few anterior & posterior ethmoidal air cells develop in fetal lifeFrontal and sphenoidal sinuses develop after birth
E
M
From a 3 months old fetus, showing ethmoid & maxillary sinuses
Nasolacrimal duct
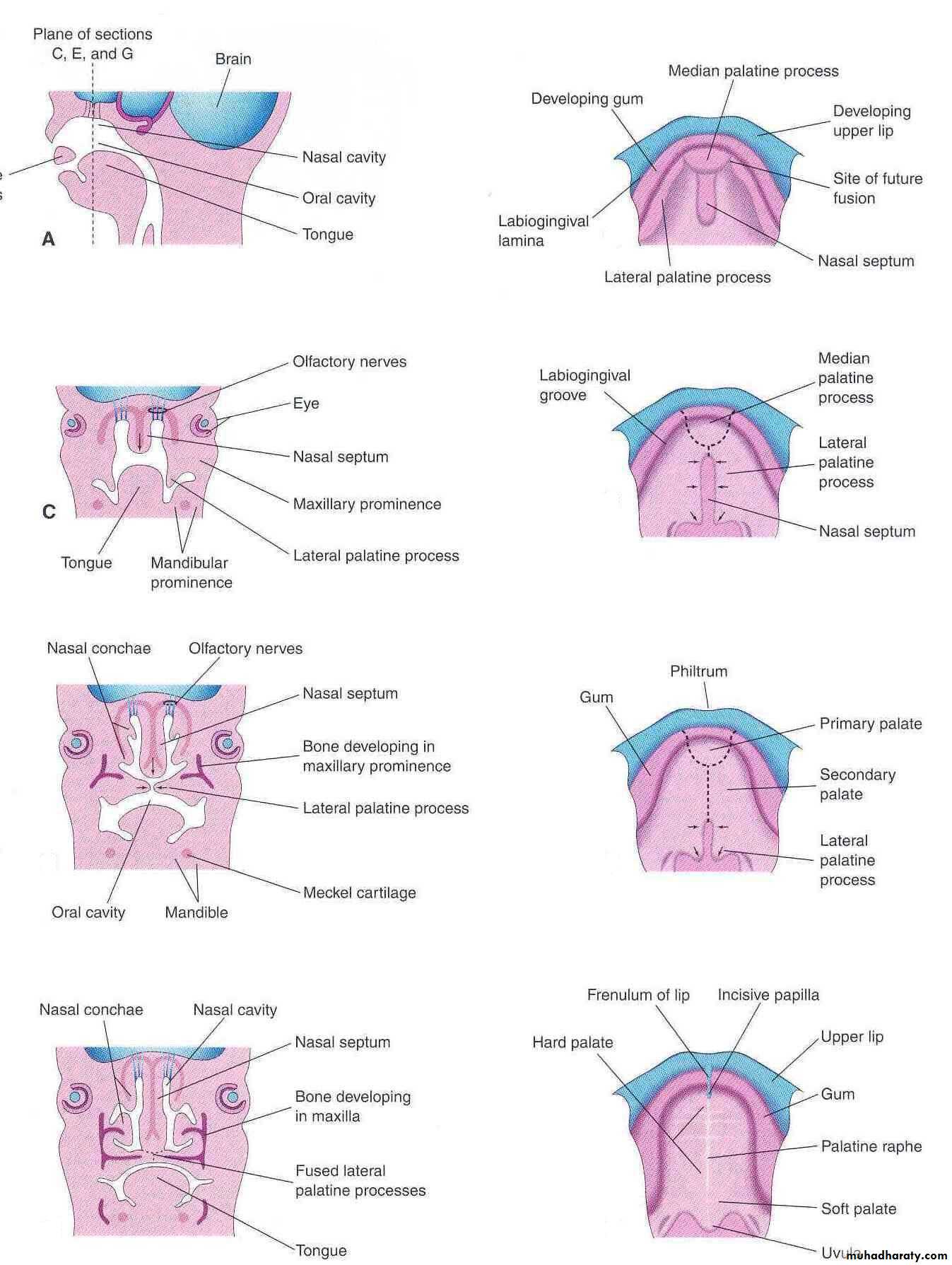
Development of Palate (Palatogenesis)
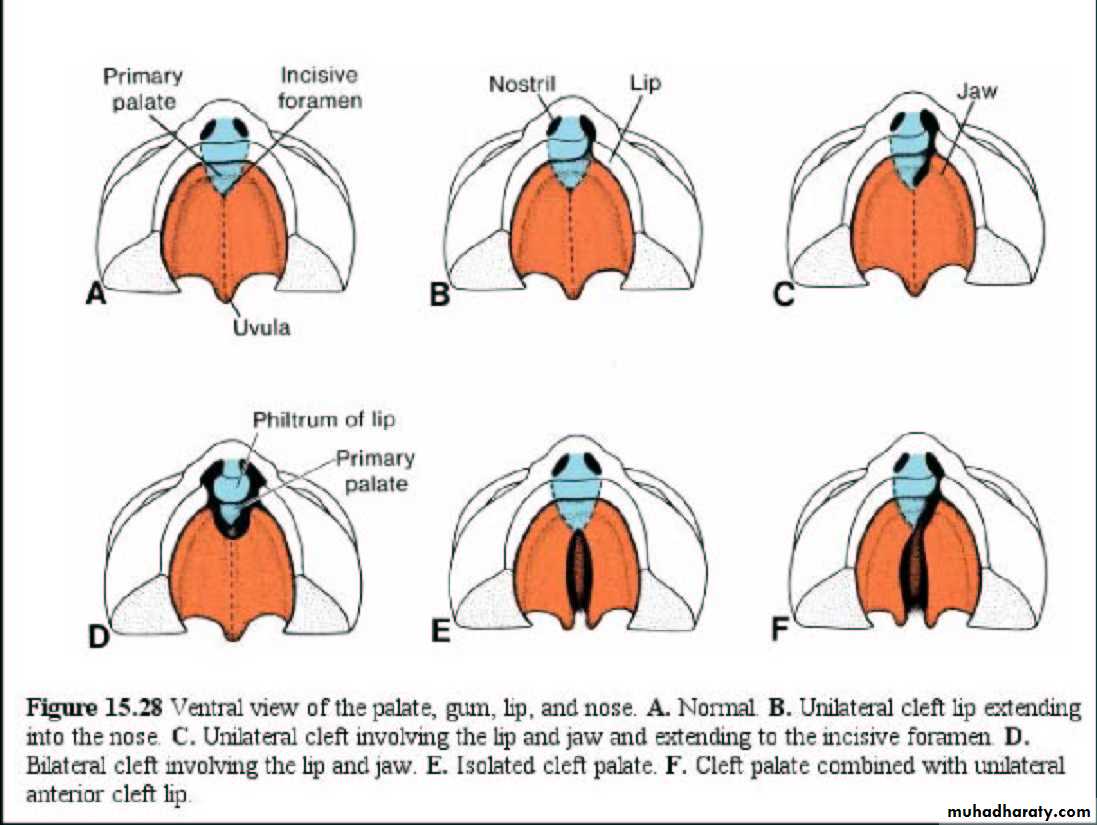
The palate develops from two primordia:
The Primary palateThe Secondary palate
Begins at the end of the 5th week
Gets completed by the end of the 12th weekThe most critical period for the development of palate is from the end of 6th week to the beginning of 9th week
Palatogenesis
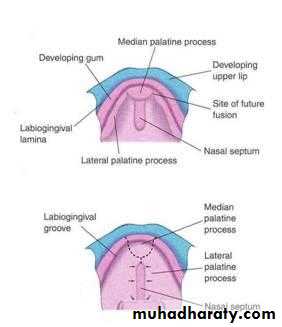
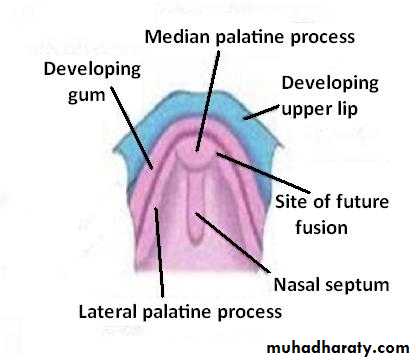
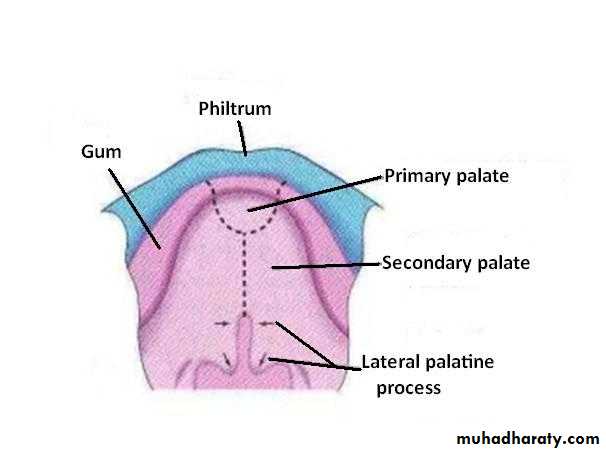
The Primary Palate
Begins to develop:Early in the 6th week
From the deep part of the intermaxillary segment, as median palatine process
Lies behind the premaxillary part of the maxilla
Fuses with the developing secondary palate
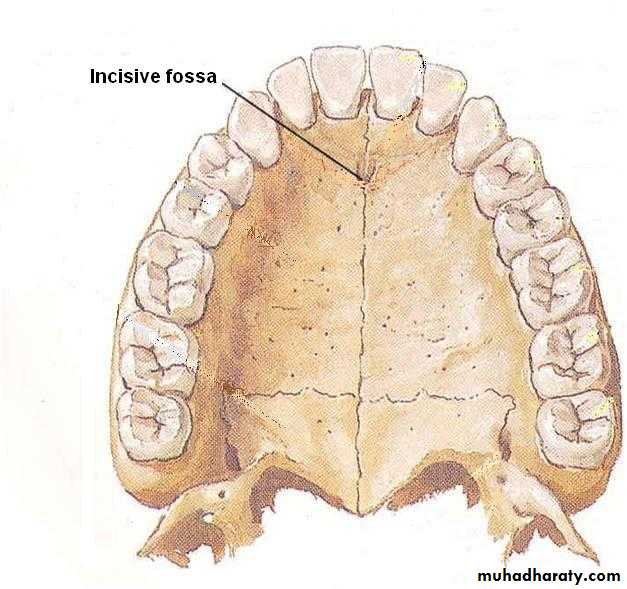
The primary palate represents only a small part lying anterior to the incisive fossa, of the adult hard palate
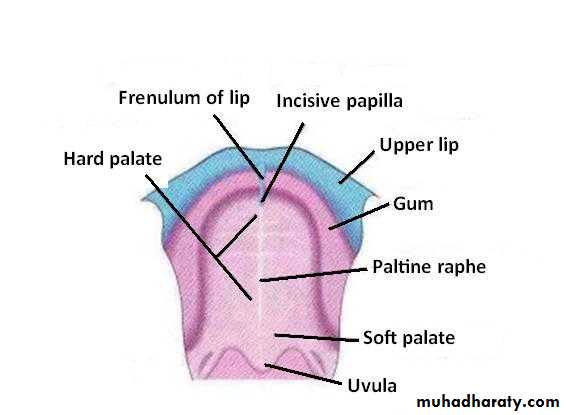
Hard palate
Primary palateSoft palate
Secondary palate
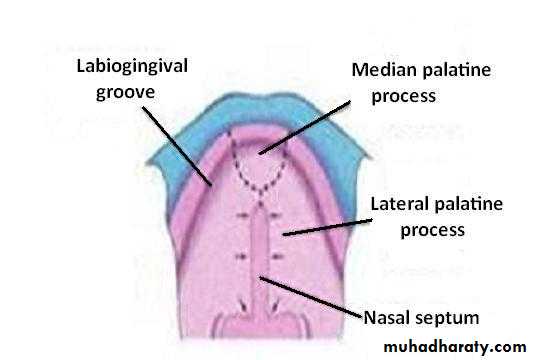
The Secondary Palate
Is the primordia of hard and soft palate posterior to the incisive fossaBegins to develop:
Early in the 6th week
From the internal aspect of the maxillary processes, as lateral palatine process
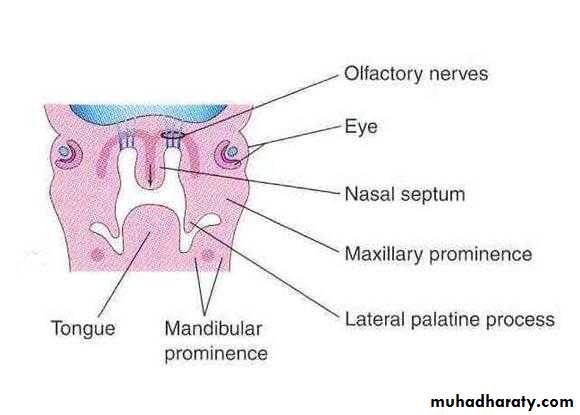
In the beginning, the lateral palatine processes project inferomedially on each side of the tongue
With the development of the jaws, the tongue moves inferiorly.
During 7th & 8th weeks, the lateral palatine processes elongate and ascend to a horizontal position above the tongue
Tongue
Gradually the lateral palatine processes:
Grow medially and fuse in the median planeAlso fuse with the:
Posterior part of the primary palate
&
The nasal septum
Fusion with the nasal septum begins anteriorly during 9th week, extends posteriorly and is completed by 12th week
Bone develops in the anterior part to form the hard palate. The posterior part develops as muscular soft palate
Changes in Face during Fetal period
Mainly result from changes in the proportion & relative positioning of facial structuresIn early fetal period the nose is flat and mandible underdeveloped. They attain their characteristic form during fetal period
The enlargement of brain results in the formation of a prominent forehead
Eyes initially appear on each side of frontonasal prominence move medially
Ears first appear on lower portion of lower jaw, grow in upper direction to the level of the eyes
Anomalies related to Face, Nose & Palate
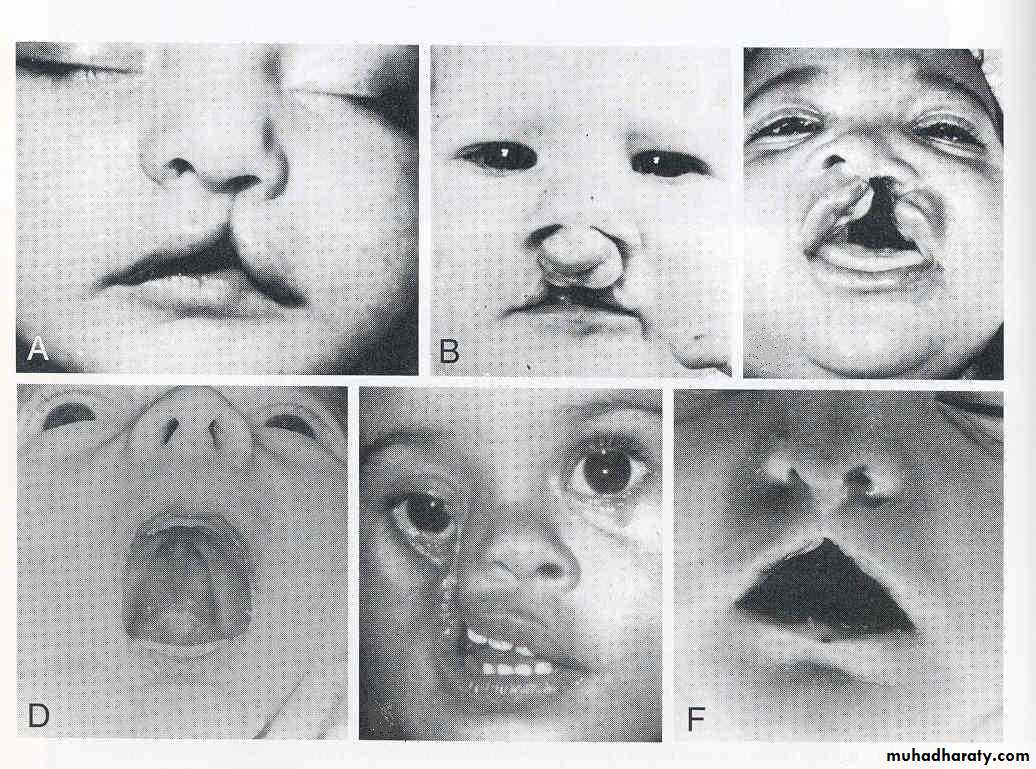
Facial clefts Failure of the embryonic facial prominences to fuse properly
May be unilateral or bilateralMay involve:
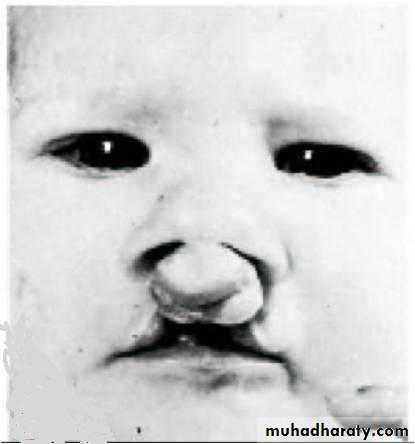
Lips only: Cleft lip
Palate only: Cleft palate
Lip & palate: Cleft lip & palate
Region of nasolacrimal groove: Facial clefts
Lead to difficulty in breathing feeding sucking swallowing
&speech
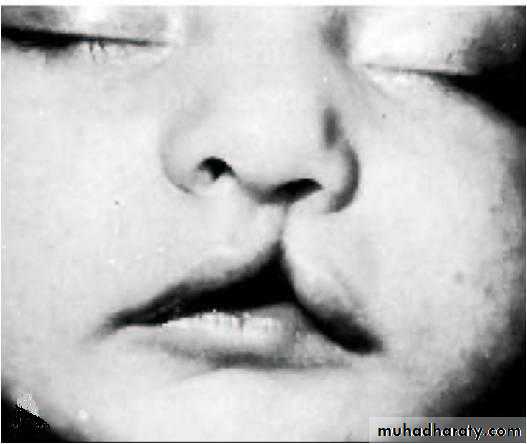
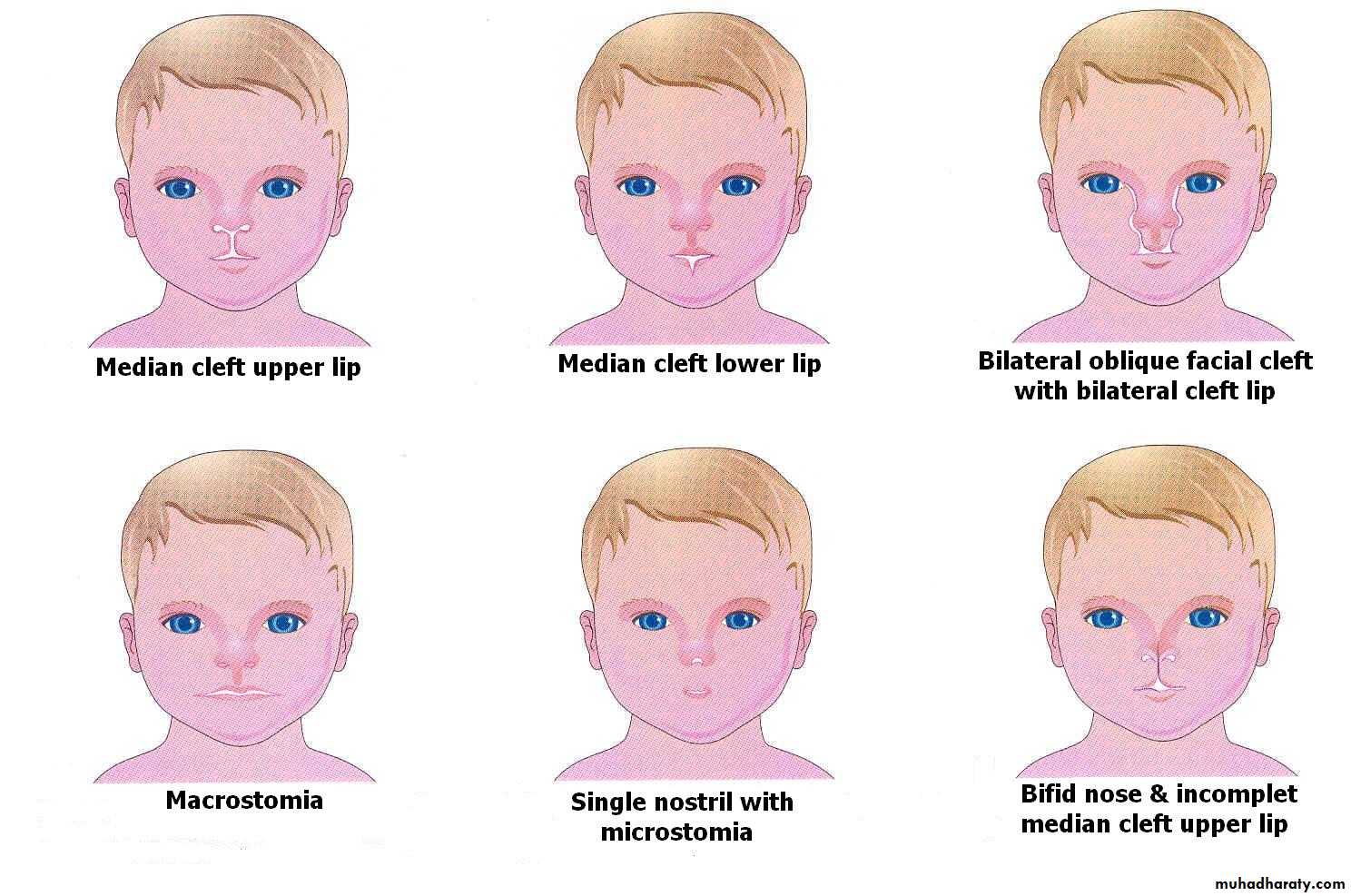
Median cleft lip: results from failure of the medial nasal prominences to merge and form the intermaxillary segments
Unilateral cleft lip: result from failure of the maxillary prominence to merge with the medial nasal prominence on the affected side
Bilateral cleft lip: results due to failure of maxillary prominences to meet and unite with the medial nasal prominences on both sides
Median Cleft lip
Unilateral cleft lipBilateral cleft lip
2. Oblique facial cleft: results from failure of the maxillary prominence to fuse with the lateral nasal prominence
3. Cleft palate leaves the nasal and oral cavities connected & results in nursing problem for the new born
May be:
Anterior/posterior to incisive foramen
Unilateral/bilateral
Isolated/associated with cleft lips