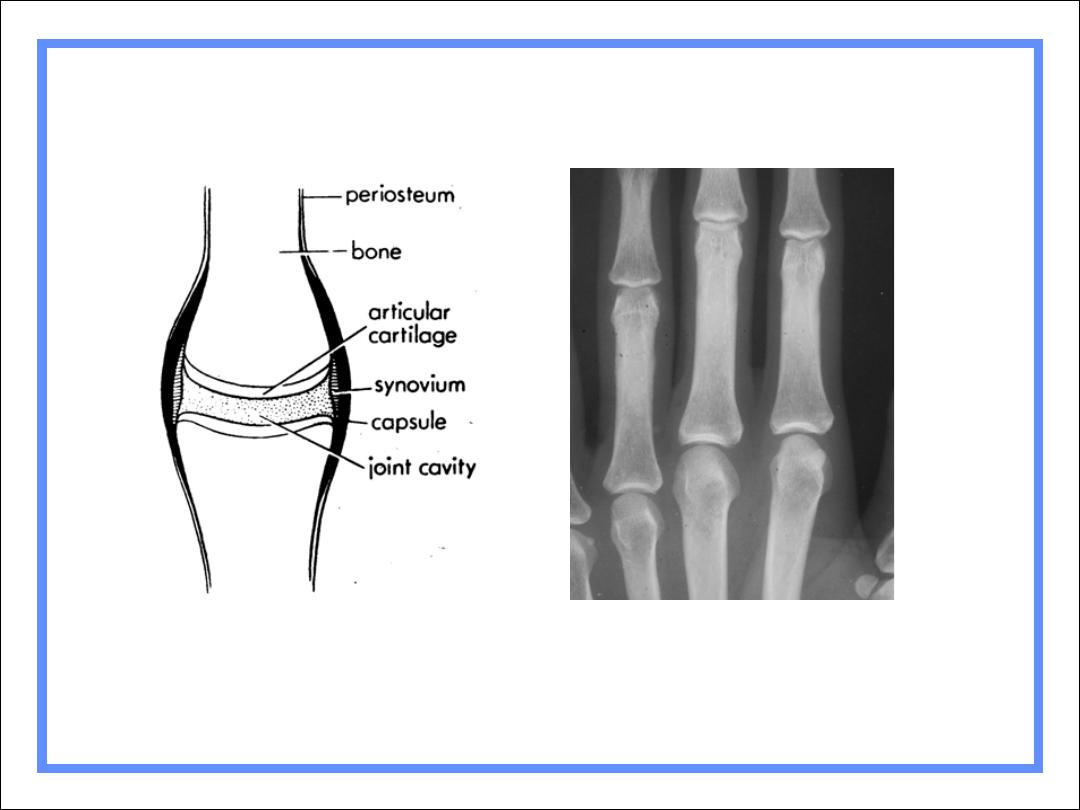
Normal articular cortex
Normal joint

Joint disease
•
1-degenerative disease (osteoartheritis )
2- inflammatry disease (still disease ,RA)
3-infective disease (septic artheritis ,TB artheritis )
4-malignant disease (synovioma )
5-traumatic disease
6-congenital disease (displacement hip)
7-abnormal trabecular patteran (behejet disease)
Classification
Hypertrophic
Hallmarks
Bone production
Sclerosis
Infectious
Hallmark
Destruction of articular cortex
Erosive
Hallmark
Erosions
Hypertrophic Arthritis
Degenerative arthritis(osteoartheritis)
Primary
Secondary
Charcot arthropathy
1º Degenerative Arthritis
Intrinsic degeneration of articular
cartilage
Excessive wear and tear
Most commonly hips and knees
Less commonly shoulders and elbows
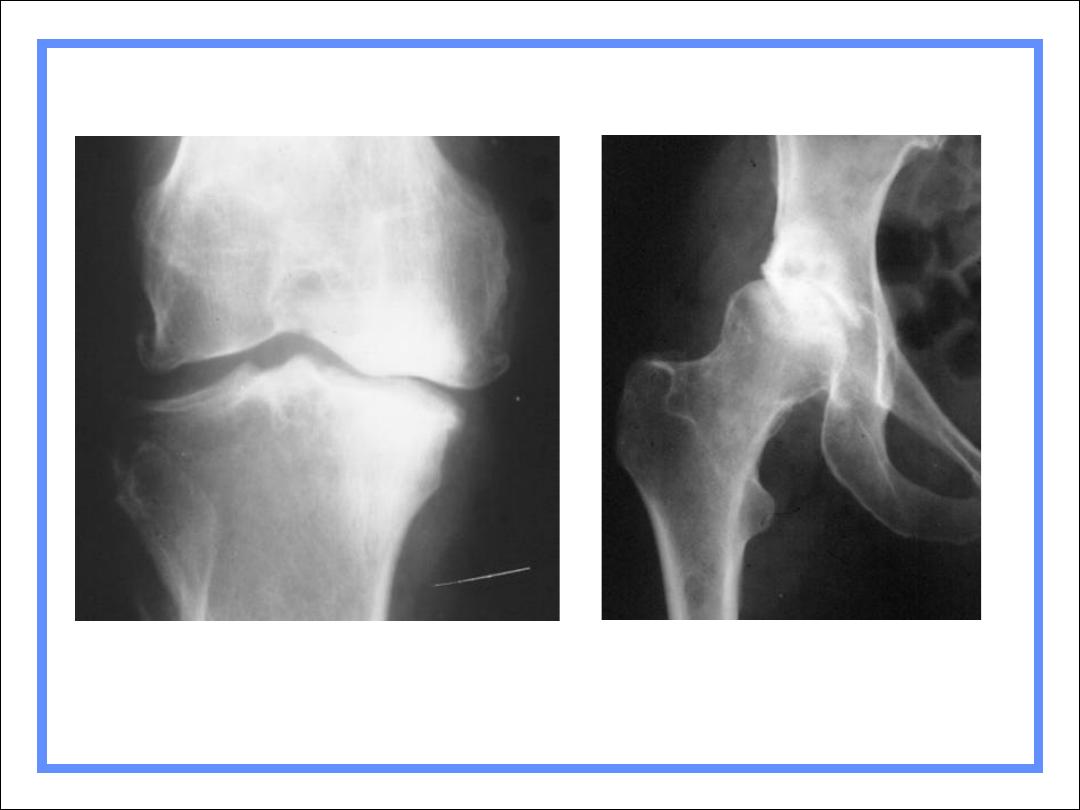
1º DJD of knees affects medial,
weight-bearing surface
1º DJD of hips affects superior,
weight-bearing surface
2º Degenerative Arthritis
Another process destroys articular
cartilage
Degenerative changes supervene
How to recognize
Atypical locations (
knee)
Atypical appearance (
Marked DJD of 1 hip)
Atypical age (
DJD in 20 year-old)
2º Degenerative Arthritis
Causes
Trauma
Infection
Avascular necrosis
CPPD
RA
Hemophilia

Osteoartheritis (degenerative
joint disease):
•
RADIOLOGICAL SIGN :
1-normal bone density(no osteoporosis)
2-narrowing of the joint space maximal at weight
bearing site
3- subchondral sclerosis and cyst may be seen
4-osteolytic lesion
5-sclerosis of the bone is a prominent feature
6-osteophyte formation
7-loose bodies

osteoarthritis
•
1-bone appearing closer to each other ,the joint
space narrow
•
2-cysts:as the body responds to cartilage
destruction and attempts to stabilize the joint , cyst
or fluid filled cavities can form in the bone
•
3-uneven joints
•
4- bony spurs
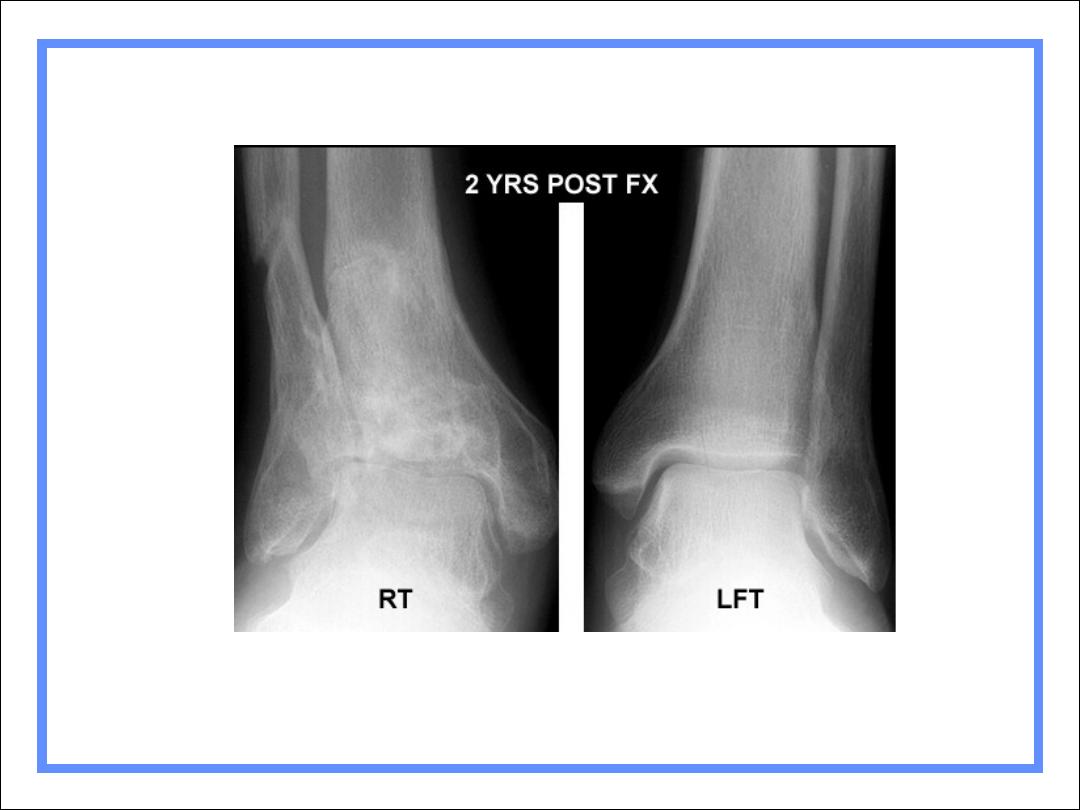
2º DJD of right ankle following fracture
R3

Charcot’s Arthropathy
•
Neuroarthropathy
•
Cuases:
•
1-DM
•
2-Syphilis
•
3-alcoholism
•
4-renal dialysis
•
5-spinal cord injury
Charcot’s Arthropathy
General
Disturbance in sensation leads to
multiple microfractures
Pain sensation intact from muscles and
soft tissue
Causes
Shoulders – syrinx, spinal tumor
Hips – tertiary syphilis, diabetes
Feet – diabetes
Charcot’s Arthropathy
Findings
X-ray findings
Fragmentation
Soft tissue swelling
Destruction of joint
Sclerosis
Osteophytosis
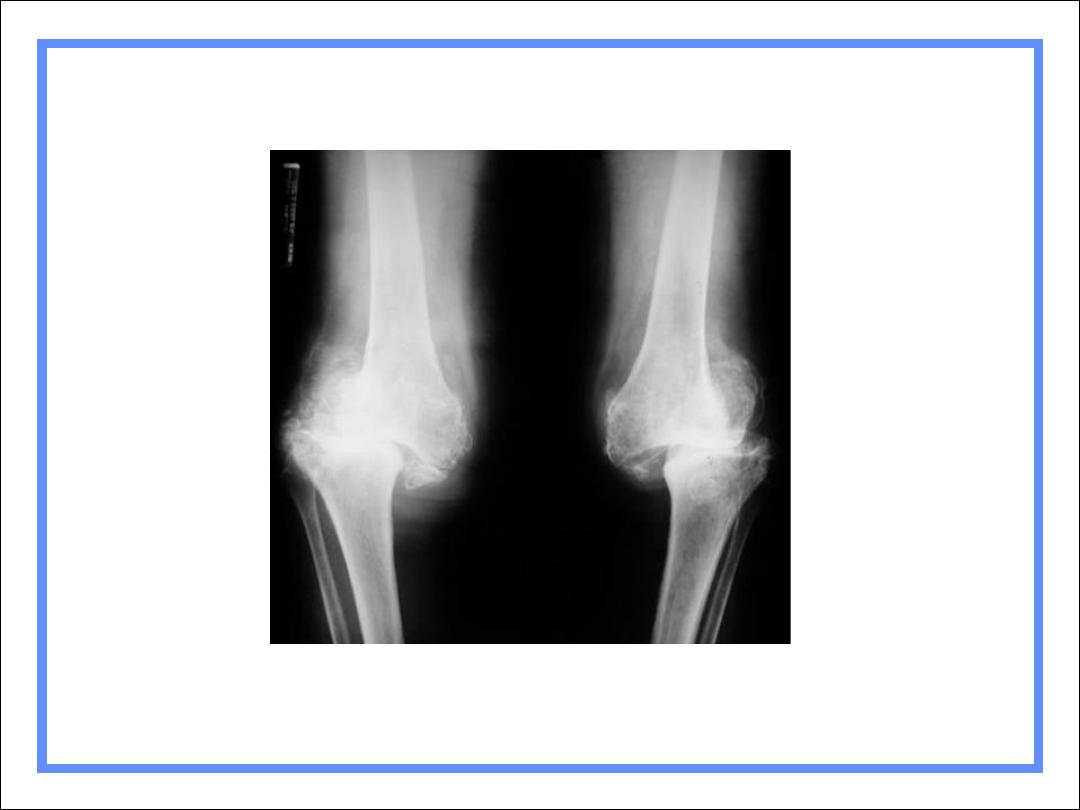
Charcot’s Knees-Diabetes
Infectious Arthritis
More common in adults
Usually from local trauma-surgery or accident
Children get osteomyelitis
Destruction of articular cartilage & cortex
Tends to affect one joint (DDx from gout)
Fingers from human bites
Feet from diabetes
Infectious Arthritis
Causes
Usually staph - “early” destruction of
articular cortex
Rapid course (unlike most arthritides)
TB spreads via bloodstream from lung
More protracted course
In children, spine most common; in adults,
knee
Severe osteoporosis
Healing with ankylosis common in both
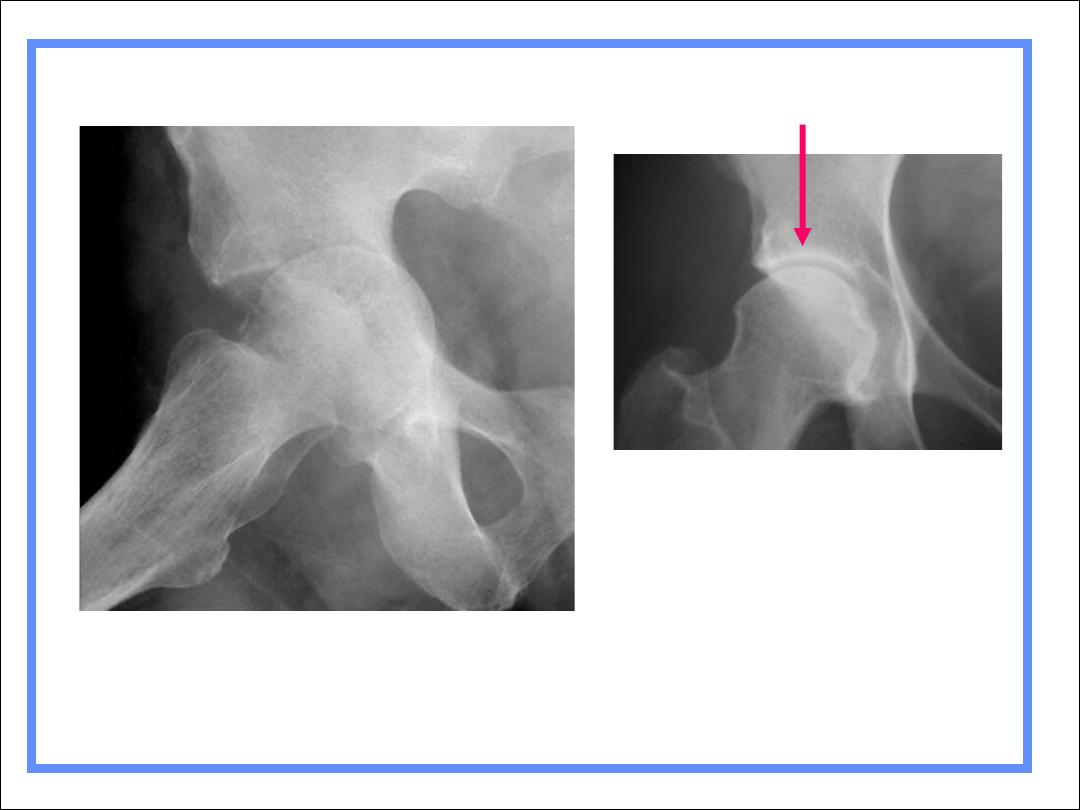
Septic arthritis of hip with
pathologic fracture
R3
Normal hip
Acetabular white line
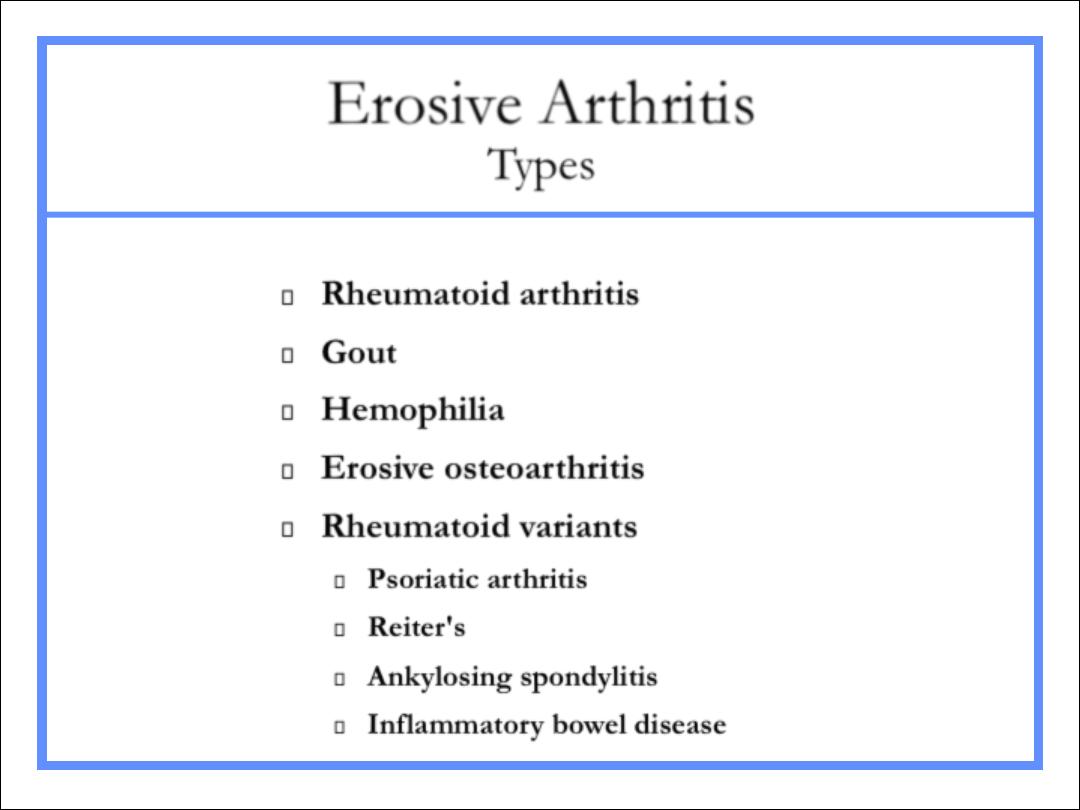
Erosive Arthritis
Types
Rheumatoid arthritis
Gout
Hemophilia
Erosive osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid variants
Psoriatic arthritis
Reiter's
Ankylosing spondylitis
Inflammatory bowel disease
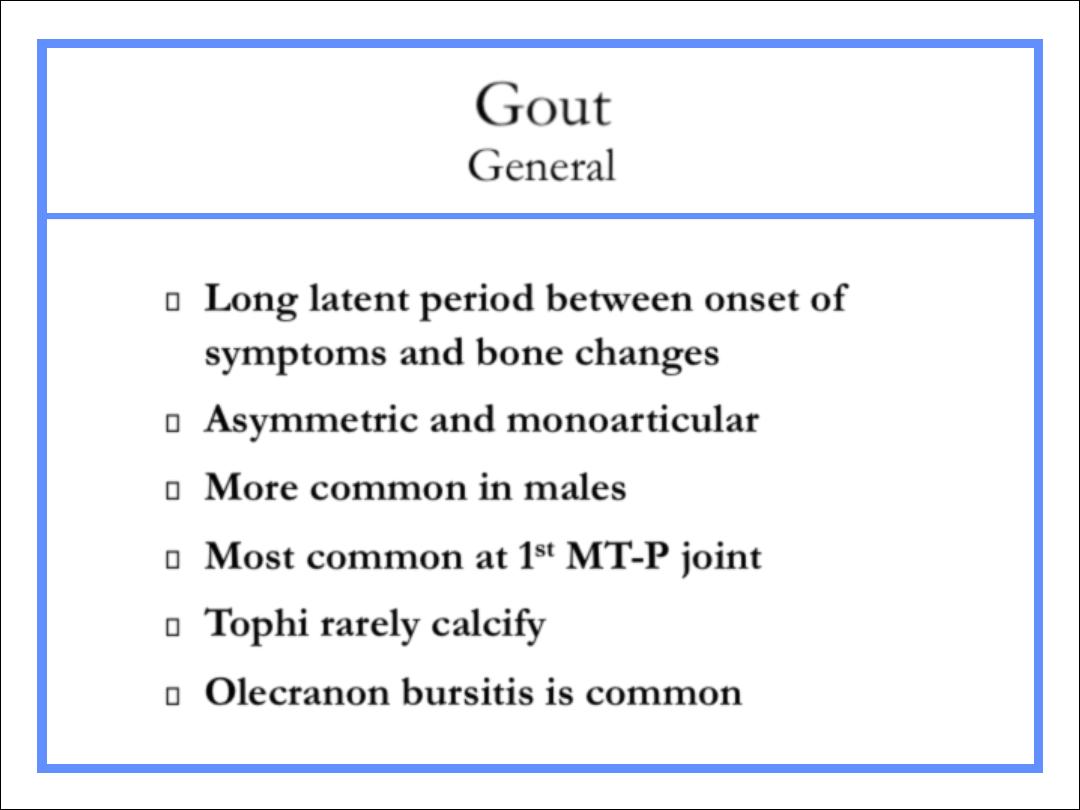
Gout
General
Long latent period between onset of
symptoms and bone changes
Asymmetric and monoarticular
More common in males
Most common at 1
st
MT-P joint
Tophi rarely calcify
Olecranon bursitis is common
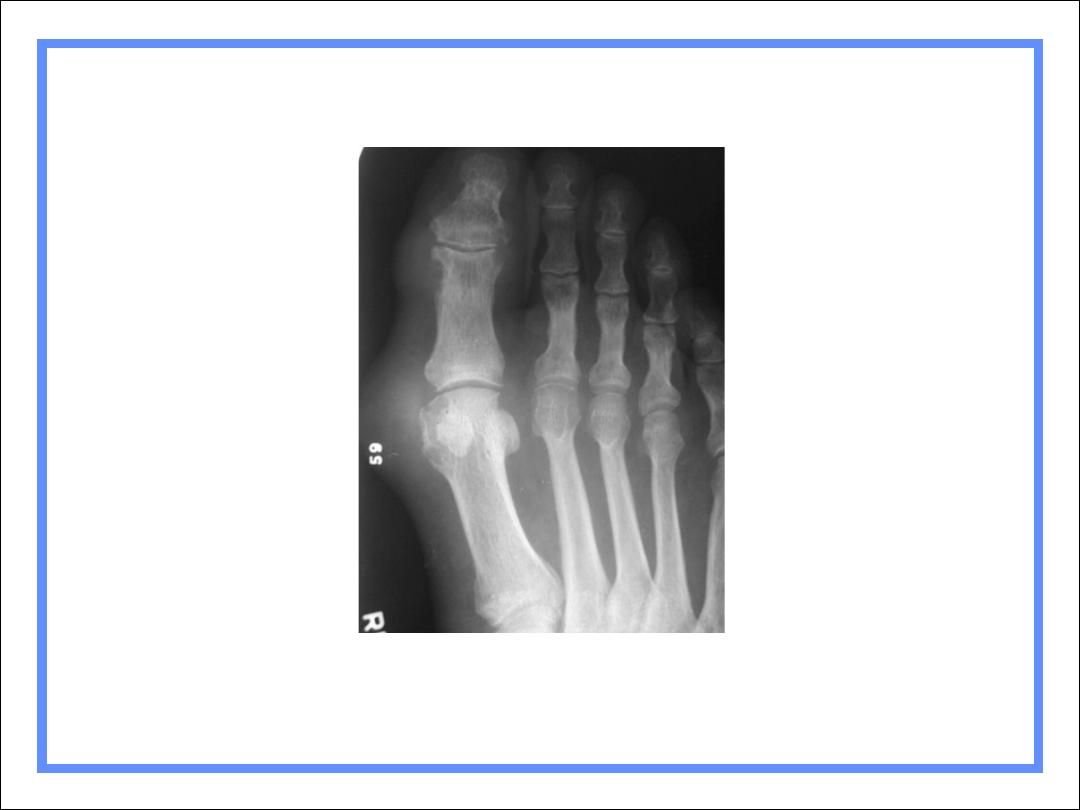
Gout
Findings
Juxta-articular erosions
Sharply marginated with sclerotic rims
Overhanging edges (rat-bites)
No joint space narrowing until later
Little or no osteoporosis
Soft tissue swelling
Tophi not calcified
Gout
R3

Rheumatoid artheritis
•
RADIOLOGICAL SIGN :
1-generalzed osteopenia
2-swelling of the soft tissue around
3-articular erosion
4- sometime the joint ligment may undergo softening
or complete cut
Rheumatoid Arthritis
General
Bilaterally symmetrical
Earliest change: MCP, PIP, ulnar styloid
Radiocarpal jt most commonly narrowed
Periarticular demineralization
Begins MCP jts of 1
st
and 2
nd
fingers
Large joints usually no erosions
Rheumatoid Arthritis
General
Can lead to 2º DJD
Marked narrowing of joint space with
intact articular cortex, think of RA
Little or no sclerosis
Especially, hips and knees
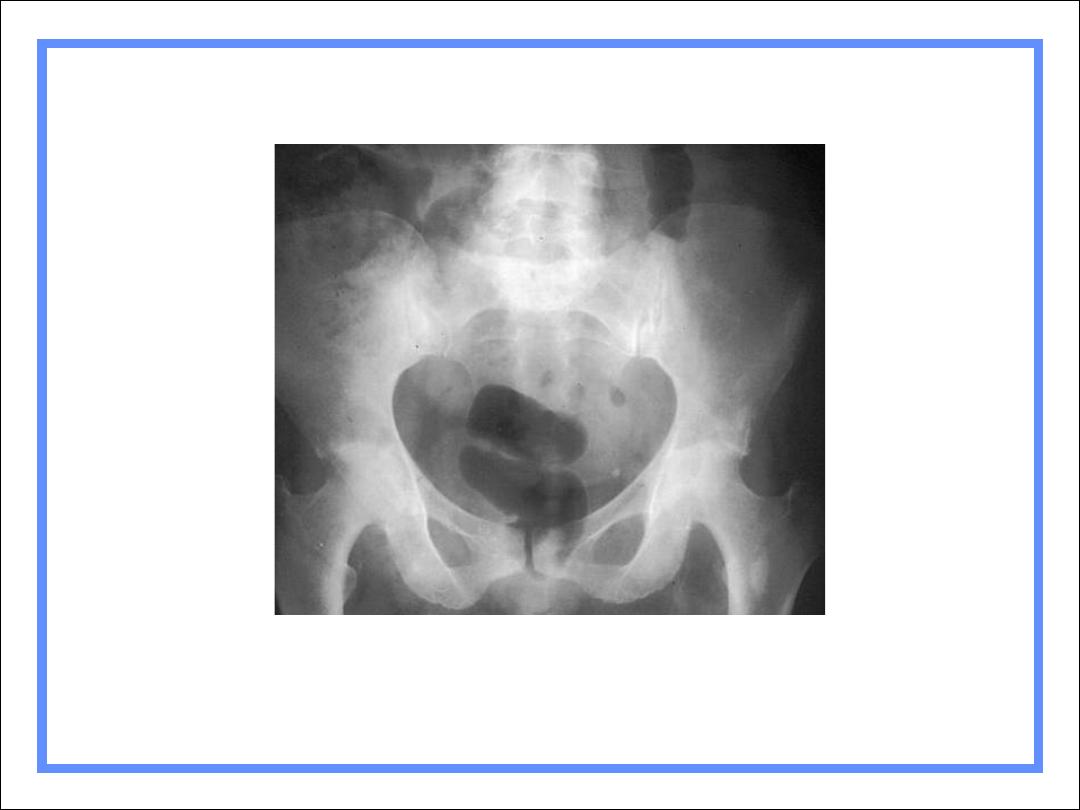
RA of Hips – Marked narrowing, little
sclerosis
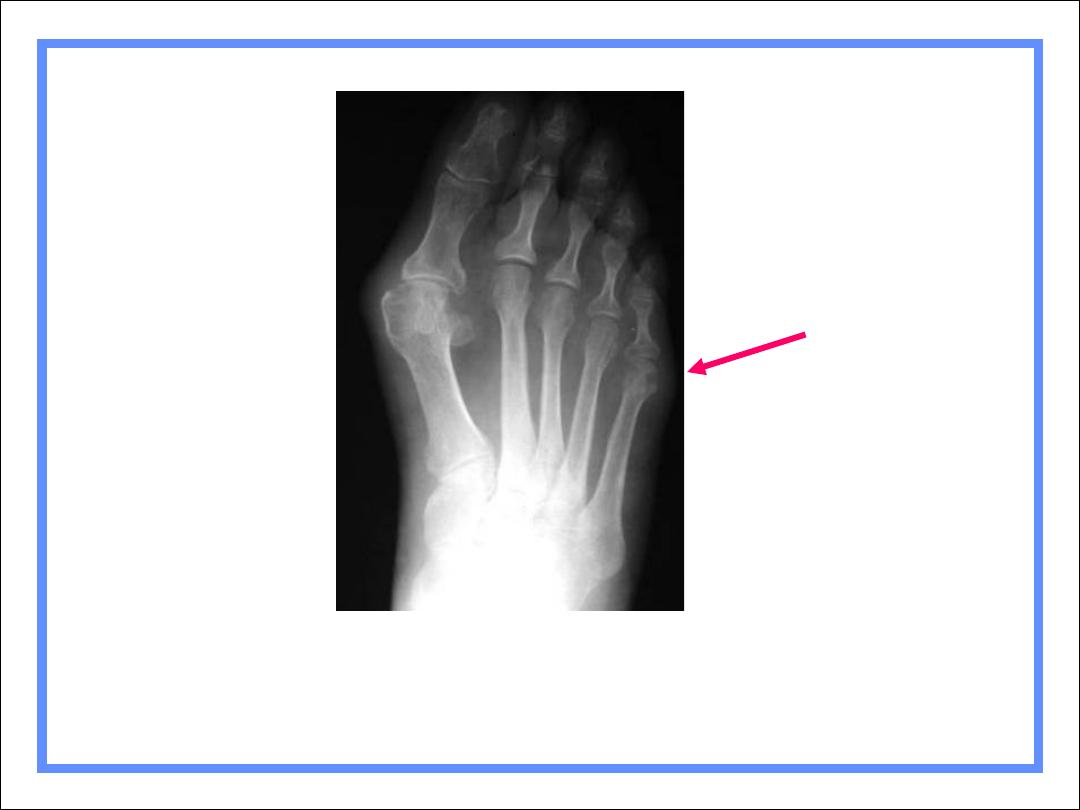
RA of Foot
RA usually
involves 5
th
MT-P joint
first
Psoriatic Arthritis
Almost always accompanies skin
disease, especially nail changes
Involves DIP joints of hands > feet
Cup-in-pencil deformity
Resorption of terminal phalanges
No osteoporosis
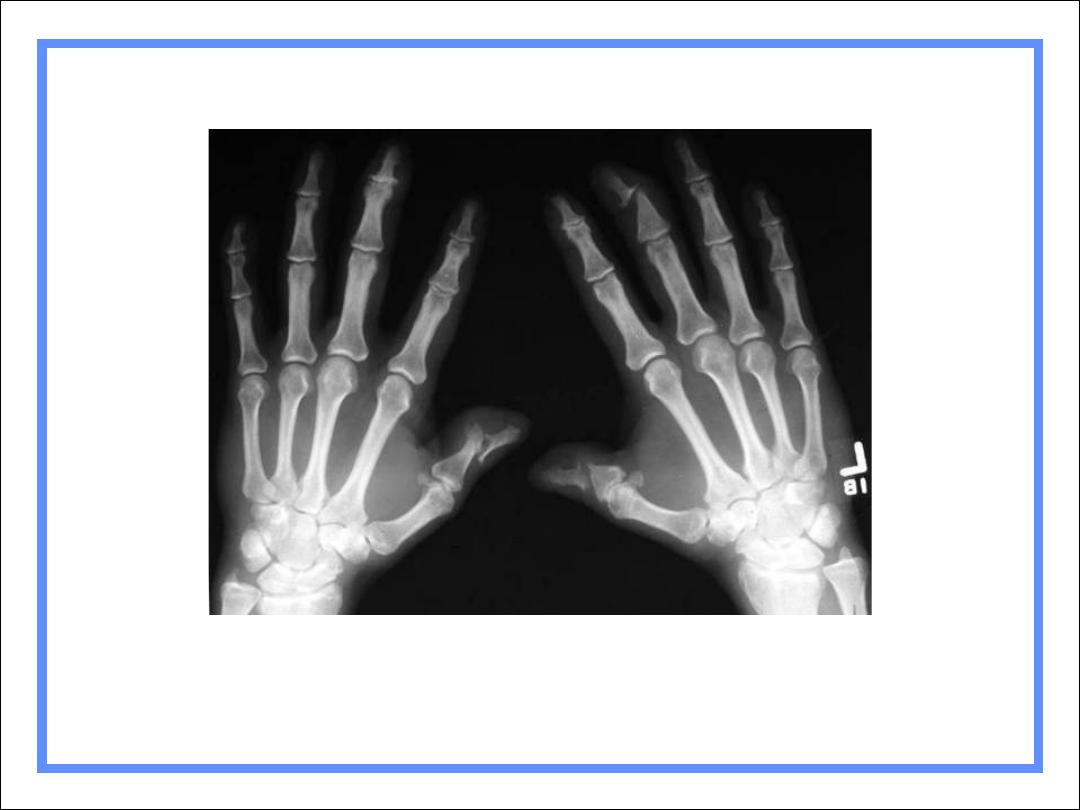
Psoriasis of hands
Reiter’s Syndrome
Urethritis, arthritis (50%) & conjunctivitis
Periostitis at sites of tendinous insertion
Whiskering
Like DISH, ankylosing spondylitis
Affects feet more than hands .
Resembles RA
Reiter’s also has osteoporosis
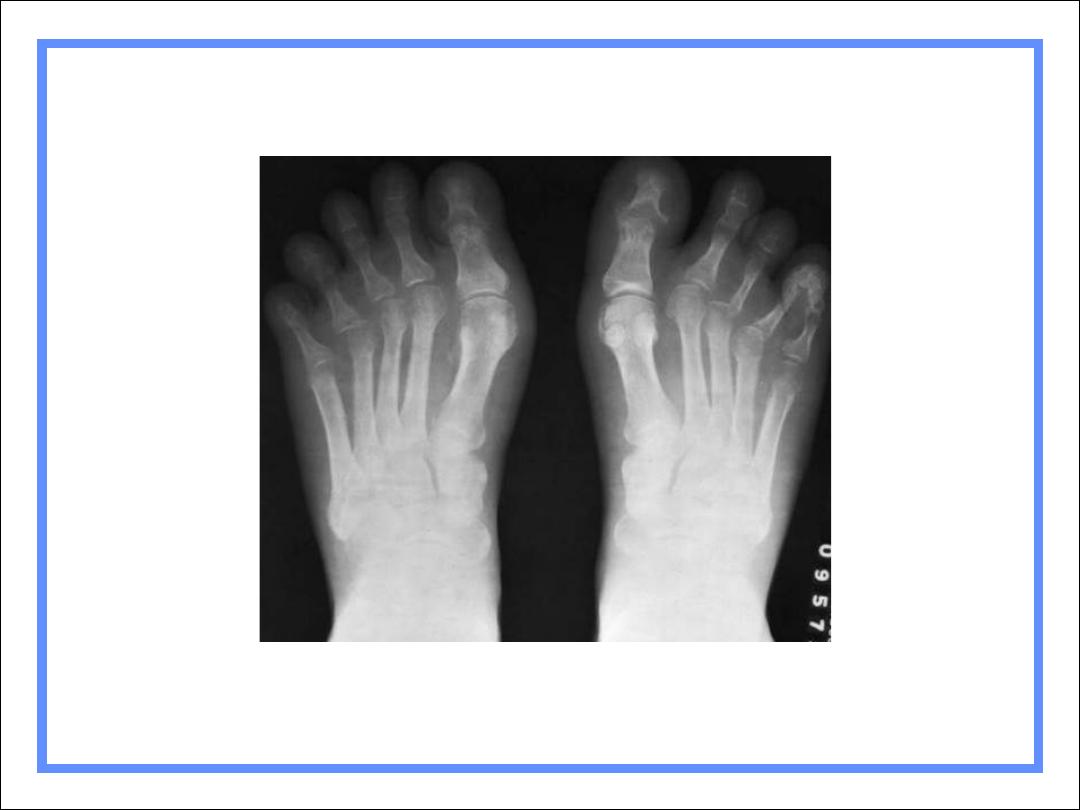
Reiter’s Syndrome
R3
Ankylosing Spondylitis
HLA-B27 positive
B/L SI arthritis
Squaring of vertebral bodies
Bamboo-spine from continuous
syndesmophytes
Peripheral large joint erosive arthritis
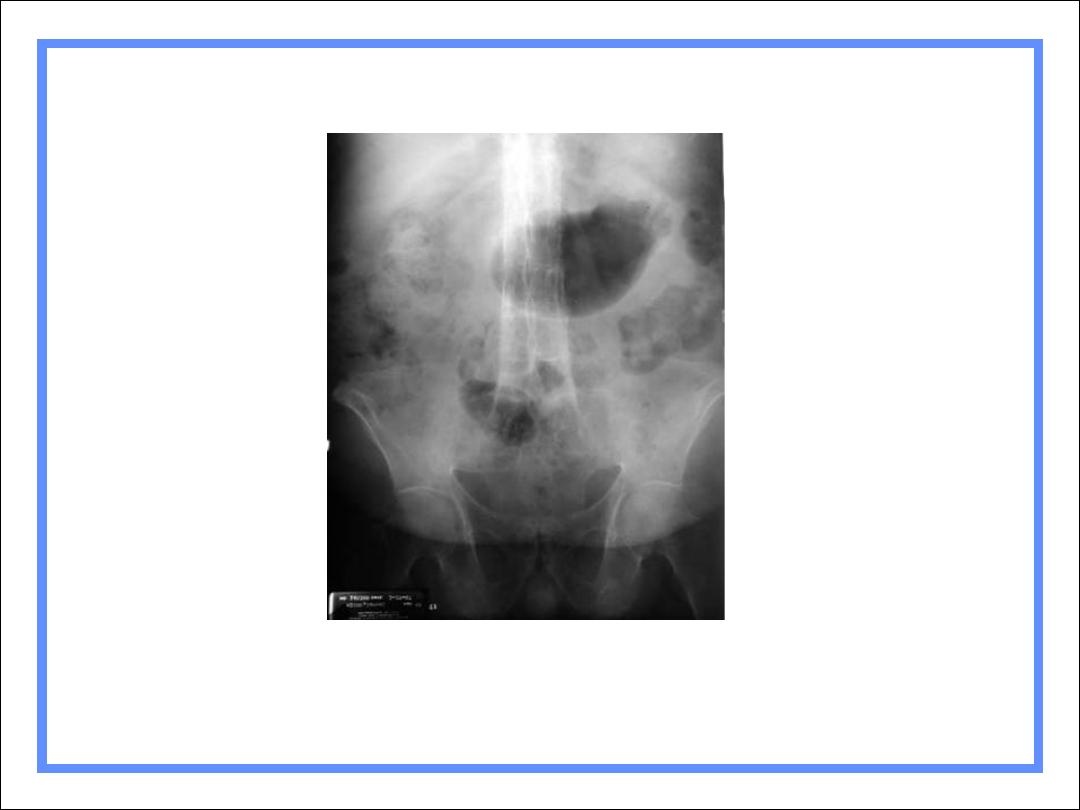
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Can occur with either Crohn’s or UC
More common with UC
Looks like AS in spine
Asymmetric sacroiliitis
Like psoriasis, TB
Peripheral joint STS without erosions
Hemophilia
General
Usually seen in large joints
Hemorrhage produces synovitis which
leads to pannus
Incites hyperemic response
Bone resorption and remodeling
Especially in open epiphyses
DDx: JRA
Hemophilia
Findings
Overgrowth of epiphyses
Resorption of secondary trabeculae
Longitudinal striations
Widening of interconylar notch of knee
Joint effusion
Hemosiderin deposit around joint
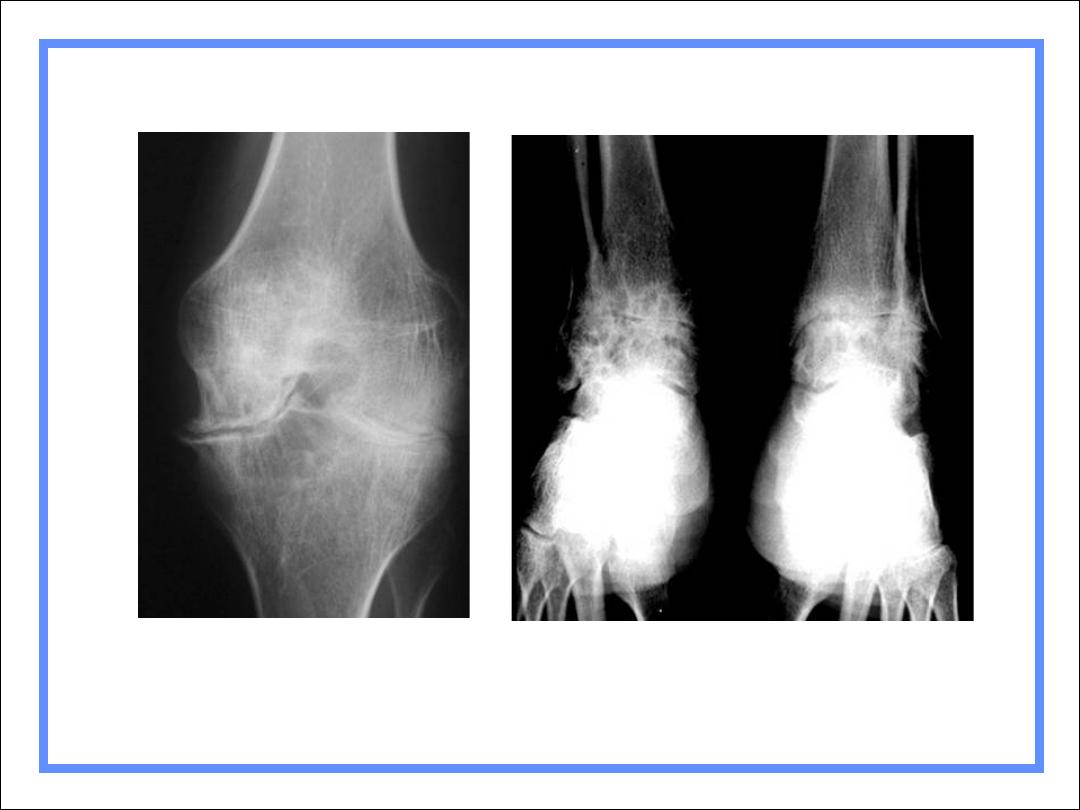
Hemophiliac Arthropathy
R3
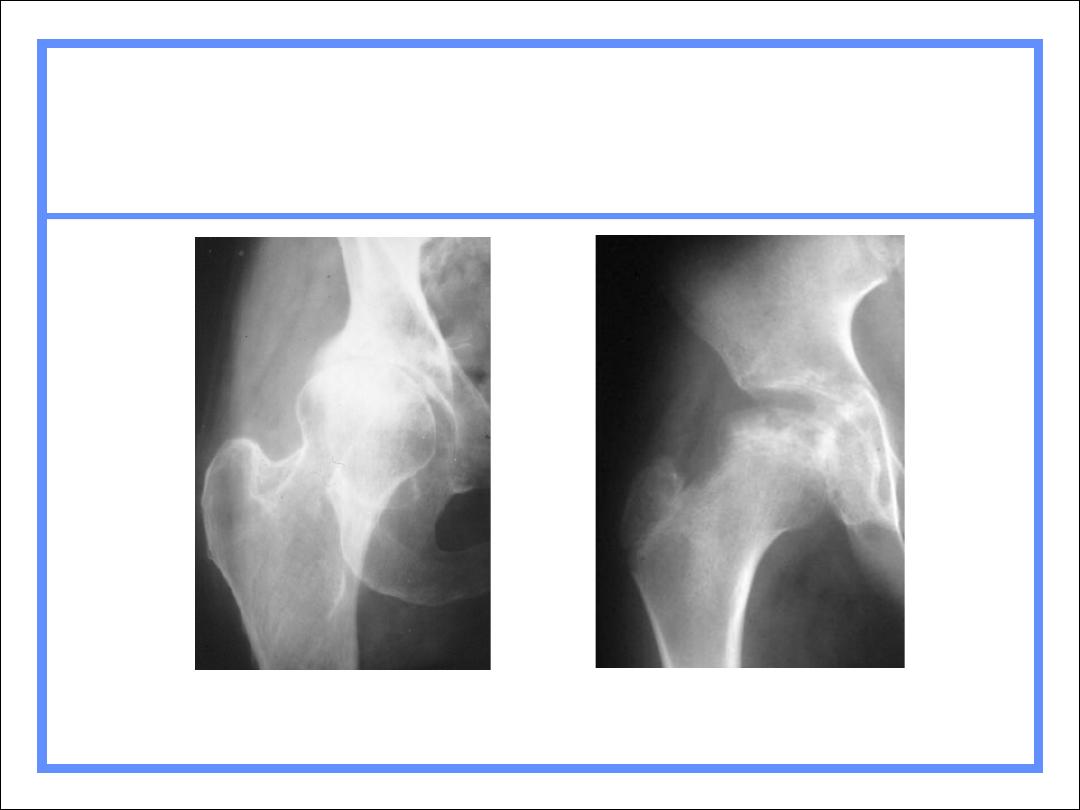
Arthritis or Not
AVN
DJD

hyperparathyrodium
•
Generalzed decrease in bone density
•
Subperiosteal bone resorption
•
Soft tissue calcification
•
Brown tumours

THANK YOU
