Odontogenic infections
2020-2019Infection: The invasion and multiplication of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites(pathogenic ) that are not normally present within the body .
Inoculation : is the entry of pathogenic microbes into the body prior to disease occurrence .
Opportunistic infection : is type of infection caused by microorganisms which are not normally pathogenic (opportunistic microorganism) ,but in some circumstances (like immunodeficiency) become pathogenic .
Introduction and terminology
Inflammation : is the reaction of the body to the irritant (trauma, heat, pathogens….. etc. ), it is a vascular and connective tissue reaction causing tissue exudate of high protein and cell content to collect , thus limiting the irritant and eliminating its harmful effect.
Cardinal signs of inflammation are : calor (hot) dalor (pain) ruber (red) tumor (swelling) and finally loss of function
Acute Inflammation : is the early or immediate reaction of the body to the irritant( trauma, heat, pathogens….. etc. ),it is associated with the typical (cardinal) sign of inflammation. If not managed well within 5-7 day , it may become either subacute or chronic.
Subacute Inflammation : is a transitional phase between acute and chronic phase , with low grade inflammatory response ( as Subacute pericoronitis).
Chronic Inflammation : is the prolonged inflammatory response that involves a progressive change in the type of cells present at the site of inflammation. It is characterized by the simultaneous destruction and repair of the tissue from the inflammatory process with slight clinical signs and symptoms.
Pus : thick, opaque, usually yellowish white fluid matter formed in association with inflammation caused by the invasion of the body by infective microbes(such as bacteria). It is composed of degenerating leukocytes tissue debris, and living or dead microorganisms and their toxins
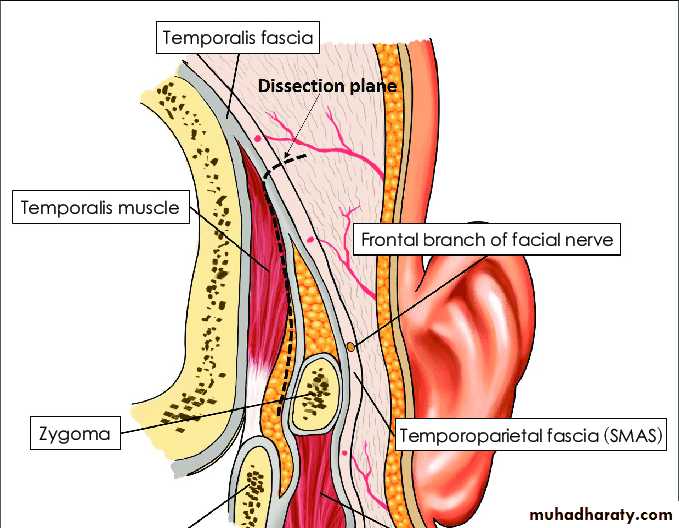
Fascia : is a band or sheet of connective tissue , mainly collagen, beneath the skin that attaches , stabilizes encloses and separates muscles and other internal organs. It is classified into superficial and deep fasciae.
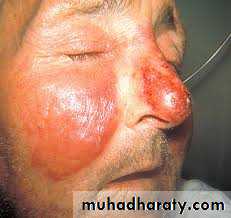
Abscess : a localized collection of pus in the tissues of the body, often accompanied by signs of inflammation and frequently caused by bacteria .The region is fluctuant and fluid felt when pressed with a red zone of inflammation around .It is generally a feature of staphylococci infection. Abscess usually require incision and drainage as the best treatment option.
Cellulitis: is a diffuse inflammation through out soft tissue space and along fascial plane (no localization) (no pus) , it may or may not end with pus and abscess formation. It is generally a streptococci infection feature and may resolve by a suitable antibiotic prescription.
Abscess
Cellulitis
Bacteremia : is the presence of bacteria in the bloodstream. Bacteremia may result from ordinary activities (such as vigorous tooth brushing), dental or medical procedures, or from infections (such as pneumonia or a urinary tract infection).Septicemia : ( blood poisoning) is the presence and persistence of pathogenic microorganisms and /or their toxins in the blood . It is life-threatening condition and requires immediate treatment and if not treated it may progress to death
Pyemia : is the presence of pus in the blood as a foci or multiple abscesses
Empyema : is the presence of pus in normal cavities of the body ( as nasal sinuses, pleural cavity)
Infection in orofacial region :
The main causes :
1. Non-vital teeth . 2. Pericoronitis. 3.Periodontitis. 4. Periapical lesions (cyst, granuloma, etc…) which may be infected secondarily . 5. Postsurgical infection.
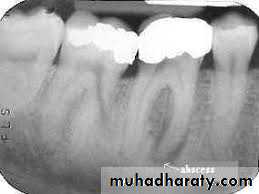
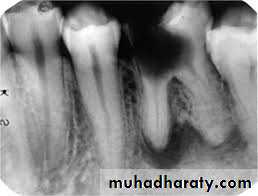
Periapical (dentoalveolar, dental) abscess: Is the collection of pus at the apex of a non-vital tooth. ( Acute, Chronic and subacute)
Phoenix abscess: is acute exacerbation of a chronic periapical abscess.
• 1- Pain.• In the initial phase the pain is dull and continuous and worsens during percussion of the responsible tooth or when it comes into contact with antagonist teeth.
• If the pain is very severe and pulsates, it means that the accumulation of pus is still within the bone or underneath the periosteum.
• Relief of pain begins as soon as the pus perforates
• the periosteum and exits into the soft tissues.
Local symptoms of acute dento- alveolar abscess.
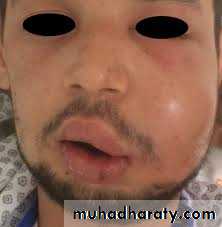
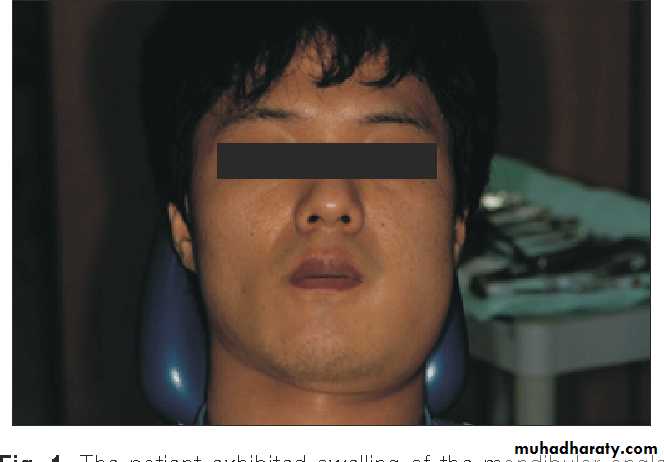
• 2- Edema. Edema appears intraorally or extraorally and
• it usually has a buccal localization and more rarely• palatal or lingual. Usually the edema is soft with redness of the mucosa or the skin. During the final stages, the swelling fluctuates, especially at the mucosa of the oral cavity. This stage is considered the most suitable for incision and drainage of the abscess.
3- Other Symptoms. There is a sense of elongation of the responsible tooth and slight mobility; the tooth feels extremely sensitive to touch,
4- difficulty in Swallowing and eating is also observed.
•
Systemic symptoms( constitutional )
The systemic symptoms usually observed are: fever, which may rise to 39–40 °C, chills, malaise with pain in muscles and joints, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.The laboratory tests show leukocytosis and increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Complications
If the inflammation is not treated promptly, the following complications may occur: trismus, lymphadenitis at the respective lymph nodes, osteomyelitis, bacteremia and septicemia.
Radiographically, in the acute phase, no signs are observed at the bone (which may be observed 8–10 days later), unless there is recurrence of a chronic abscess, where upon osteolysis is observed.
Radiographic verification of a deeply carious tooth or restoration very close to the pulp, as well as thickening of the periodontal ligament, are data that indicate the causative tooth.
Phoenix abscesses demonstrate the outline of the original chronic lesion, with or without an associated ill-defined bone loss.
Clinically , periapical abscesses may have one or all of these clinical presentations:
1. intra-alveolar.2. sub-periosteal.
3. submucoasl.
4. subcutaneous
Thanks