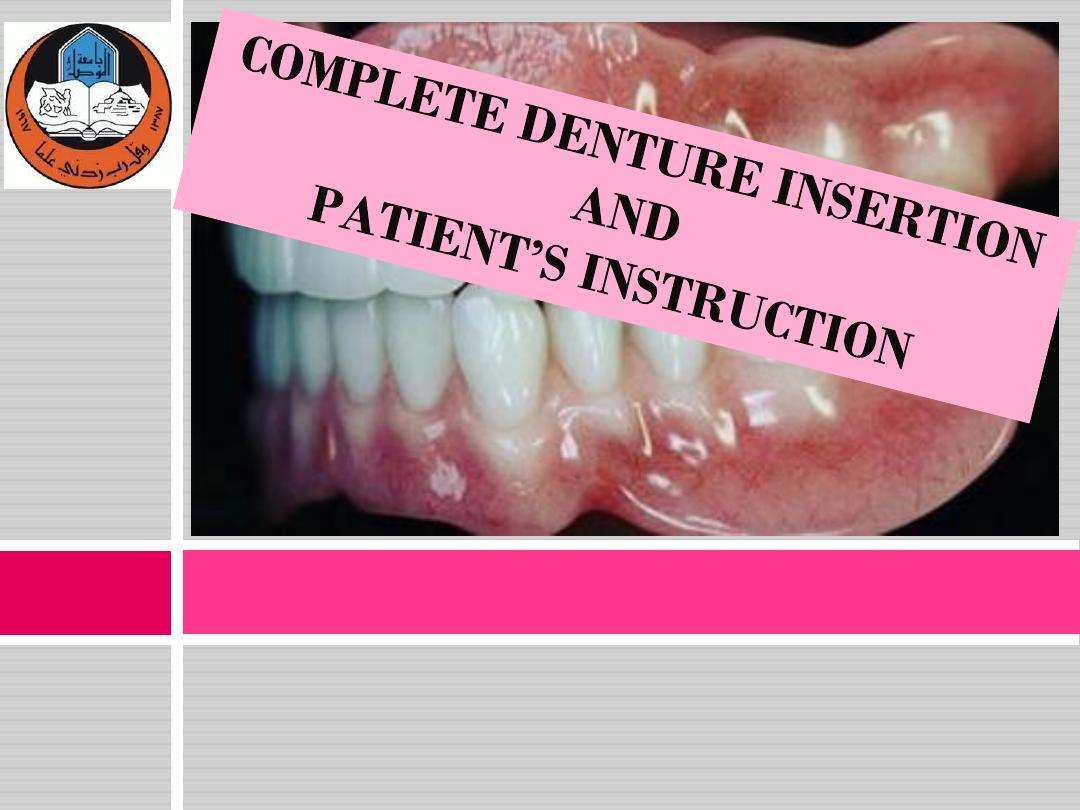
Prosthodontics Dep. / College of Dentistry/ University of Mosul
Dr. Inas Aziz M. Jawad

outlines
Patient Education and Motivation
CD Insertion Procedure
CD Patient’s Instructions

Objectives of CD treatment
The finished denture must fulfill :
1.
Physical needs required to perform adequate
functions (mastication and speech) and to preserve the
remaining oral related structures.
2.
Physiological needs to maintain the health and comfort
of the mouth and the TMJ and to improve the general
systemic health.
3.
Psychological needs to restore esthetics and to
improve the general self-esteem of the patient.
Patient Education and Motivation:
House Classification
Patient’s oral and general conditions

Dentist need to spend time in educating and recalling the patient
for complete denture as it will lead to success of denture.
Words of encouragement are very important to ensure success.
The dentist should inspect the patient’s mental attitude from the
beginning of treatment. In addition, it’s the responsibility of the
dentist to acquire about the oral and general (systemic) status of
the patient to direct the patient expectance about the denture
prognosis.
Patient’s Mental Attitude: All patients have a “threshold of
acceptability” that determines their response to denture insertion.
This threshold acceptability differs according to the patient’s
mental attitude. The House Classification, given by Dr. Milus House
of complete denture patients’ mental attitudes is as follows:

House Classification:
1. The Philosophic Patient:
(i) Accepting of dentist and oral
condition.
(ii) Ideal attitude for successful
treatment provided the bio-mechanical
factors are reasonable.
2. The Indifferent Patient:
(i) Little concern about oral health and
dentist.
(ii) Treatment insisted on by a
significant other.
(iii) Gives up easily
3. The Critical Patient:
(i) Finds fault with everything.
(ii) Directs the treatment.
(iii) Usually have poor health leading
to poor personality.
(iv)Medical consultation advisable
before treatment.
4. The Skeptical Patient:
(i) Previous bad experience with
dentist/dentures.
(ii) Poor health and unfavorable oral
conditions for fabrication of dentures.
(iii)Often have a series of personal
tragedies.
Patient’s oral and general conditions complicating use
of complete denture:
Educating a prospective denture patient about his/her oral status
and systemic conditions as they apply to his/ her is absolutely
necessary.
1) Diabetes mellitus: Diabetic patients show an abnormally high
rate of bone resorption with decreased tissue tolerance and
delayed wound healing. Such patients should be informed about
frequent oral examinations, denture adjustments and relines
along with effective oral hygiene.
2) Arthritis: These patients should be made aware that occlusal
relationship may change as a result of their disease and that
limited jaw function may follow.

Patient’s oral and general conditions complicating use
of complete denture:
3) Anemias: Mucositis, glossitis and angular cheilitis decrease the
tolerance to a foreign body in the mouth. Patients should be
counseled about the diet and pharmacotherapy.
4) Neuromuscular disorders: Lack of neuro-motor skill and
control can result in instability of the denture base. The use of a
denture adhesive may be advised in this type of patients.
5) Menopause: Post-menopausal osteoporosis results in excessive
alveolar bone resorption and chronic tenderness of oral tissues.
This condition requires diet modification pharmacotherapy and
use of soft liner.

Patient’s oral and general conditions complicating use
of complete denture:
6) Other conditions:
i.
Patients who have problems where surgery is either
contraindicated or surgery cannot be performed can
complicate the use of dentures.
ii.
Patients who cannot control tongue and jaw movements due
to wasting or muscular incoordination.
iii.
Macroglossia or microglossia can result in loss of peripheral
seal and loss of retention and stability.
iv.
Patients with lack of mental capacity to adjust to the
treatment.
Denture Insertion Procedure
Tools and materials required
methods

Denture insertion represents the culmination of a
series of carefully considered and exacting
procedures. It is also the moment eagerly awaited by
the patient, who has co-operated in both time and
effort toward this event.
Denture insertion
appointment requires
amply repaying the skill
and training of the dentist
and the patience of the
patient.
Tools and Materials required:
Articulator
Pressure indicating
(disclosing) paste
(PIP)
Rubber bowl
mouth wash
Hand mirror
The finished
Complete dentures
study casts
Straight handpiece and
burs
Occlusal indicating wax
Articulating paper
Mouth mirror
napkin
Note: dentures should be
soaked in water for 72 hrs
prior to their insertion to
remove majority of residual
monomer.
Methods
I- Extraoral examination of the finished denture prior to its
insertion:
Before the insertion appointment, dentures are inspected to
determine the following:
a) That the polished surfaces are smooth and devoid of scratches.
b) That no imperfections on
tissue surface remain.
c) That the borders are sound
with no sharp angles in the
border areas.

Methods
II- Intraoral examination of the finished denture :
a)
Location and relief of pressure areas in denture base.
b)
Identification and reduction of overextended borders.
c)
Evaluation of retention and stability.
d)
Evaluation of esthetics, facial contours and phonetic
e)
Refinement of occlusion.
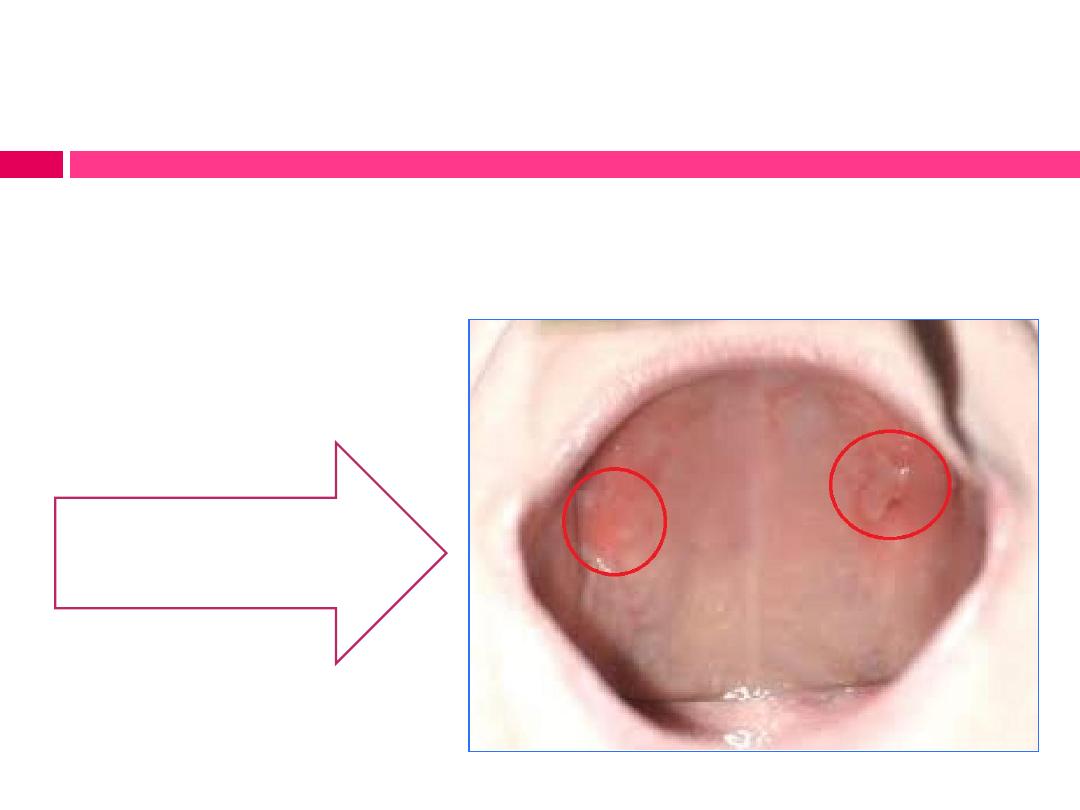
Location and relief of pressure areas in denture base:
Small areas of excess pressure can disrupt occlusal harmony or
lead to ulceration that erodes patient acceptance of the
prosthesis.
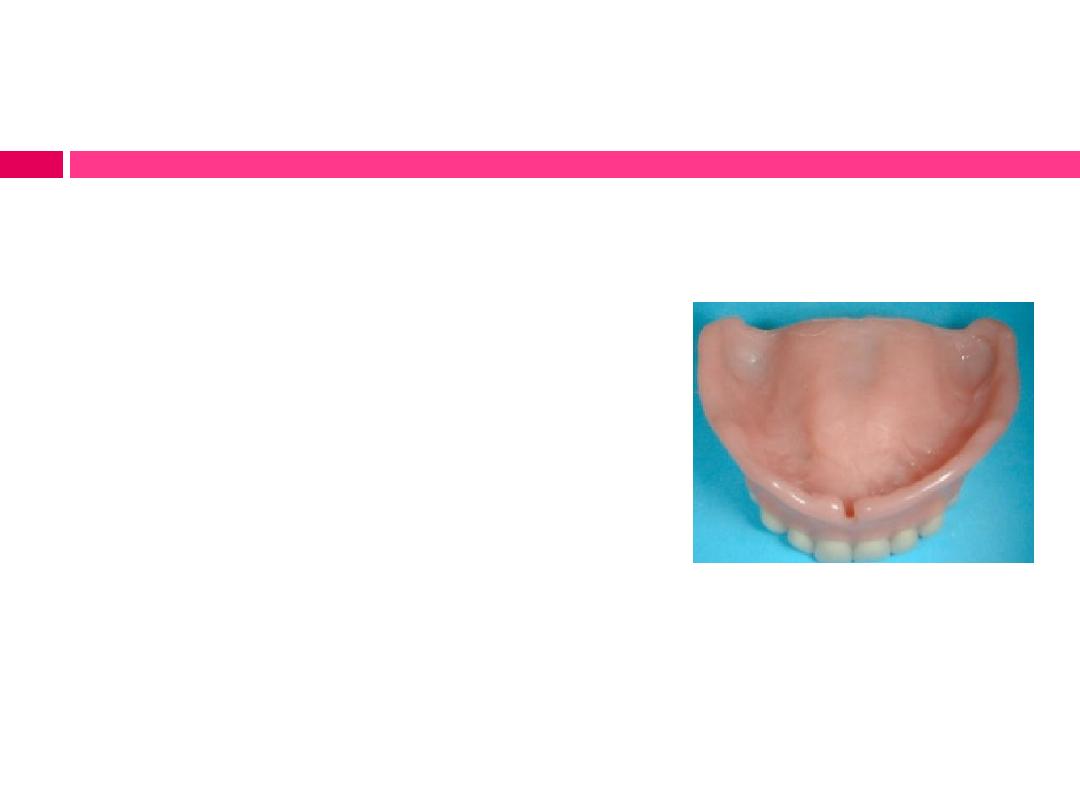
Mucosal ulceration due to
pressure areas of maxillary
denture
Location and relief of pressure areas in denture base:
Procedure:
A)- Before inserting the denture,
dry it, paint the entire tissue side
with a thin coat of (PIP), leave
streaks.
B) - Then insert the denture with
gentle pressure and remove it.
The paste will be dragged from the
denture base in pressure areas
which include: tissue undercuts,
exostosis or areas of bone covered
with tissue that is not displaceable,
such as mid-palatal suture.
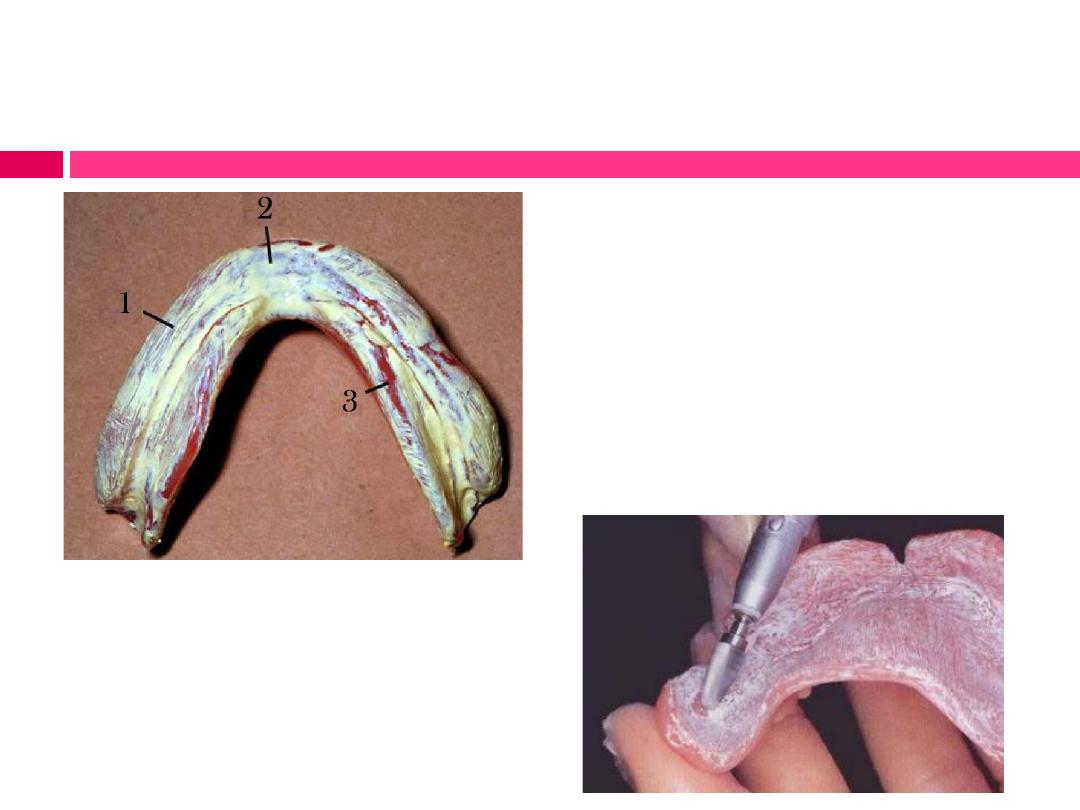
Location and relief of pressure areas in denture base:
These areas indicate:
1- streaks still present indicate no contact
2 – no streaks present indicate normal
contact
3 – no paste indicates impingement
(pressure areas)
C)- These areas of impengment
should be relieved by grinding
with an acrylic bur and then
smoothened.
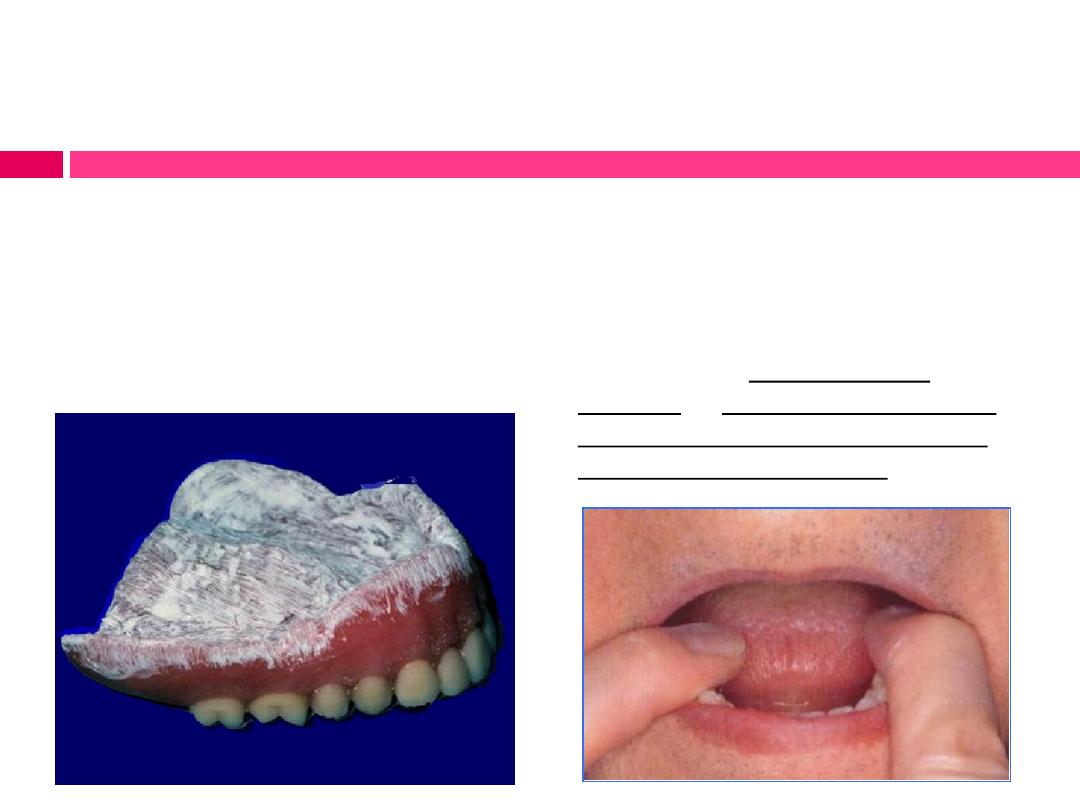
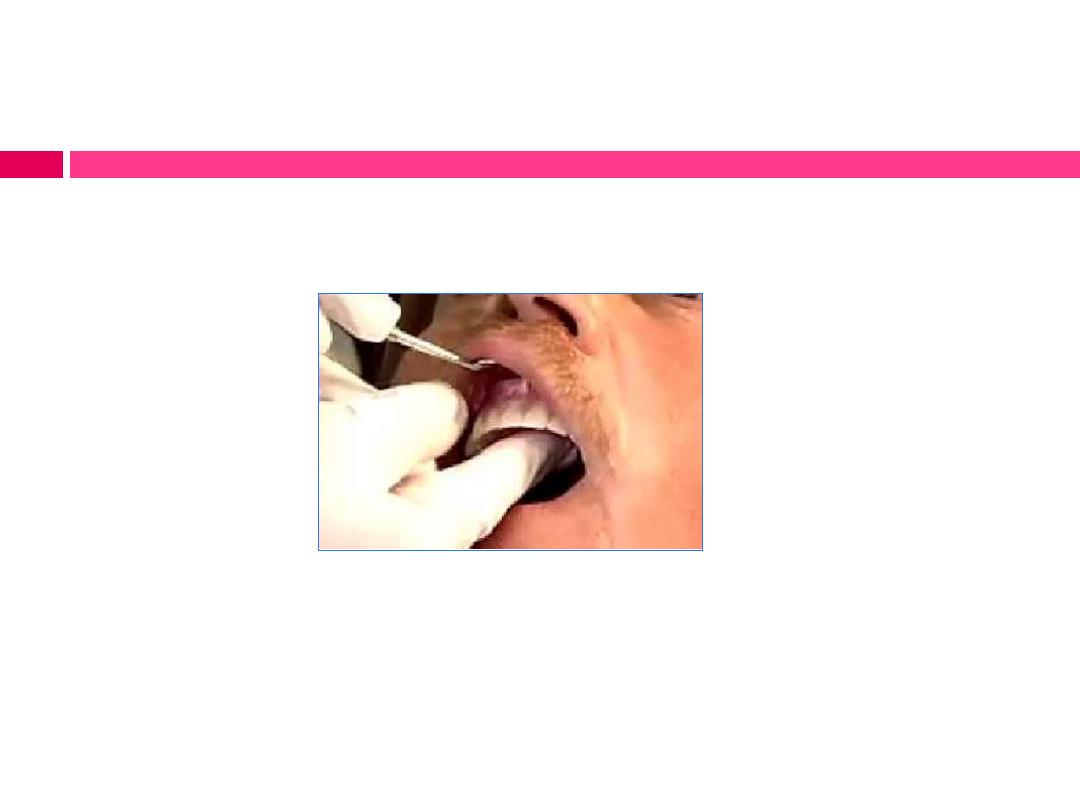
Identification and reduction of overextended borders:
1) The border extensions and contour
are compatible with the available
spaces in the vestibules.
2) The borders are properly relieved to
accommodate the frenum attachments
and the reflection of the tissues in the
hamular notch area.
3) The dentures are stable during speech
and swallowing.
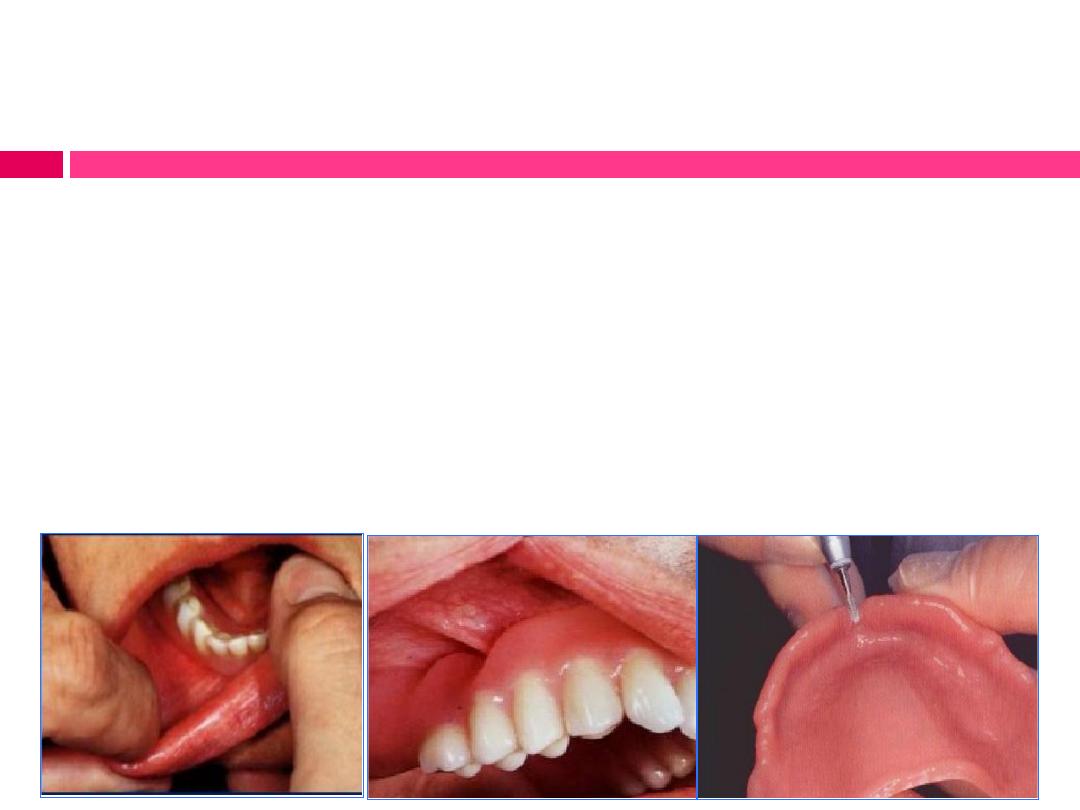
Identification and reduction of overextended borders:
Procedure:
1)
Stretch patient’s lips and cheeks
2)
Apply disclosing wax to the borders of the denture. Instruct
the patient to open the jaws as in yawning, push the lower
jaw forward, and move the lower jaw from right to left.
3)
Relieve any existing over extensions by grinding; polish the
relieved area.
Evaluation of denture support:
Procedure:
Seating the denture in its place and apply finger pressure in a tissue-
ward direction alternately on one posterior occlusal section
(unilaterally) and then on the other.
When evaluating support, occlusal contact should not be used to apply
force, since it would superimpose any occlusal discrepancy that may
exist.
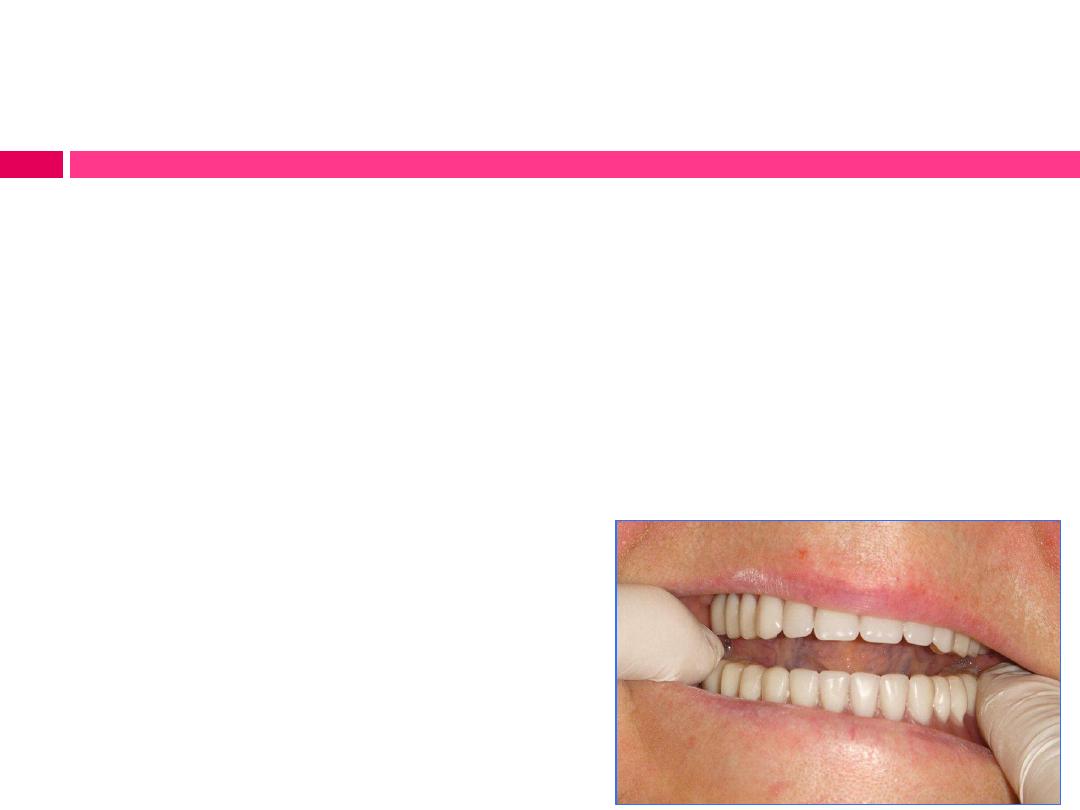
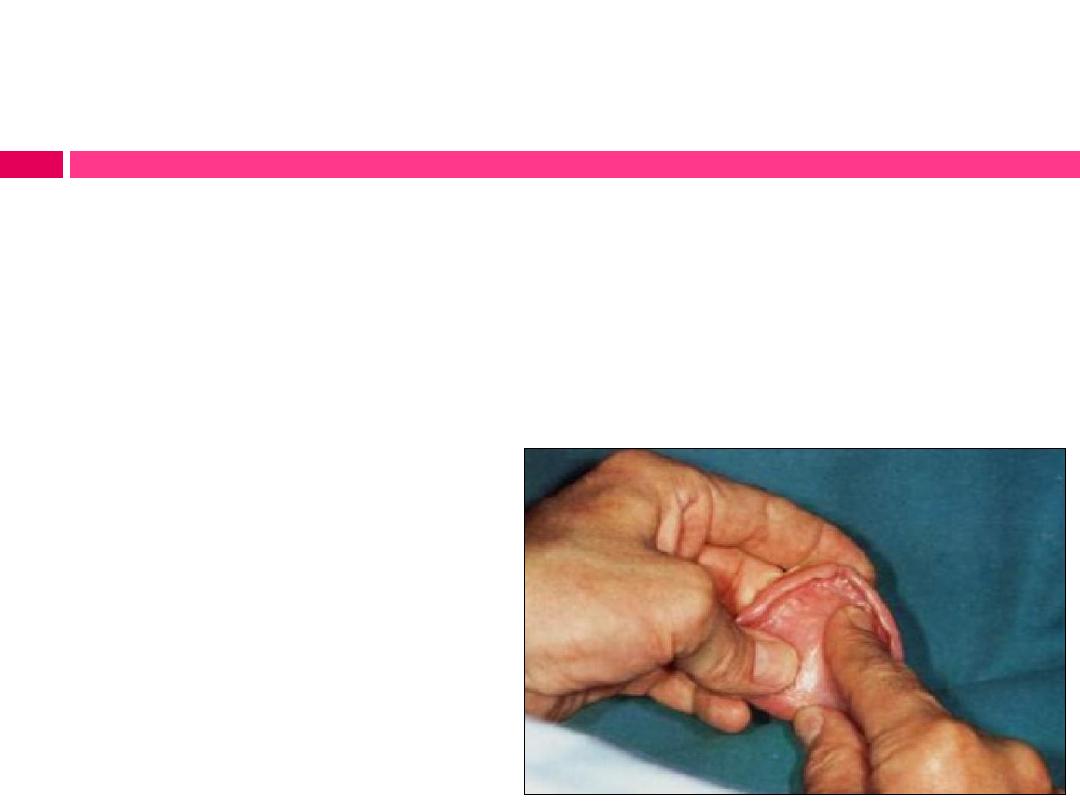
Evaluation of stability:
Procedure:
To check the stability of maxillary denture, grasp the denture and
attempt to rotate or displace it laterally. The amount of movement must
be considered relative to the shape and character of the supporting
structures.
To evaluate the stability of lower denture, apply pressure on premolar
and molar region on one side of arch, rise of denture on the other
side indicates instability.
The causes could be:
(i) Teeth set outside the ridge or lack of
denture base on pressure side.
(ii) Under-extended flange on the non-
pressure side.
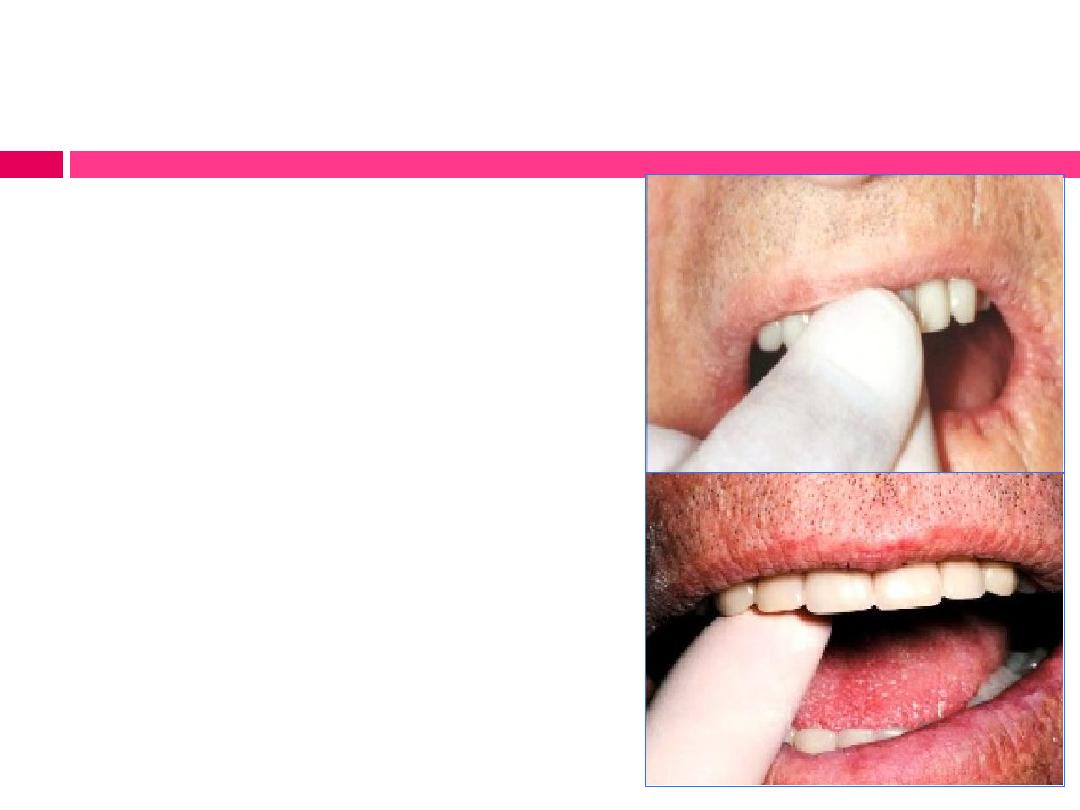
Evaluation of retention:
Maxillary denture retention:
a) Grasp the incisors and pulled
downward between thumb and
forefinger to inspect the anterior
retention, there should be resistance to
displacement.
b) Apply upward and outward
pressure on the canine at one side to
inspect the seal at the tuberosity area
on opposite side.
Evaluation of retention:
c) Apply an upward and forward force on the palatal aspect of the
anterior teeth to inspect the efficiency of posterior border seal.
d) Apply buccal force on palatal aspect of the posterior teeth on one
side to inspect the degree of border seal on the opposite side of
mouth.

Evaluation of retention:
Mandibular denture retention:
a) gently push against the facial surfaces of the mandibular
incisors backward. The denture should not become dislodged.
b) apply a downward and forward force on the lingual aspect
of the anterior teeth to inspect the retention in the posterior
portions.

Evaluation of retention:
Both retention and stability can be evaluated
further by placing a trial addition of low-fusing
modeling compound on the suspected area of
deficiency. An increase in retention or stability or
both after this temporary addition confirms the
location of the deficiency and indicates that
improvement can be made.
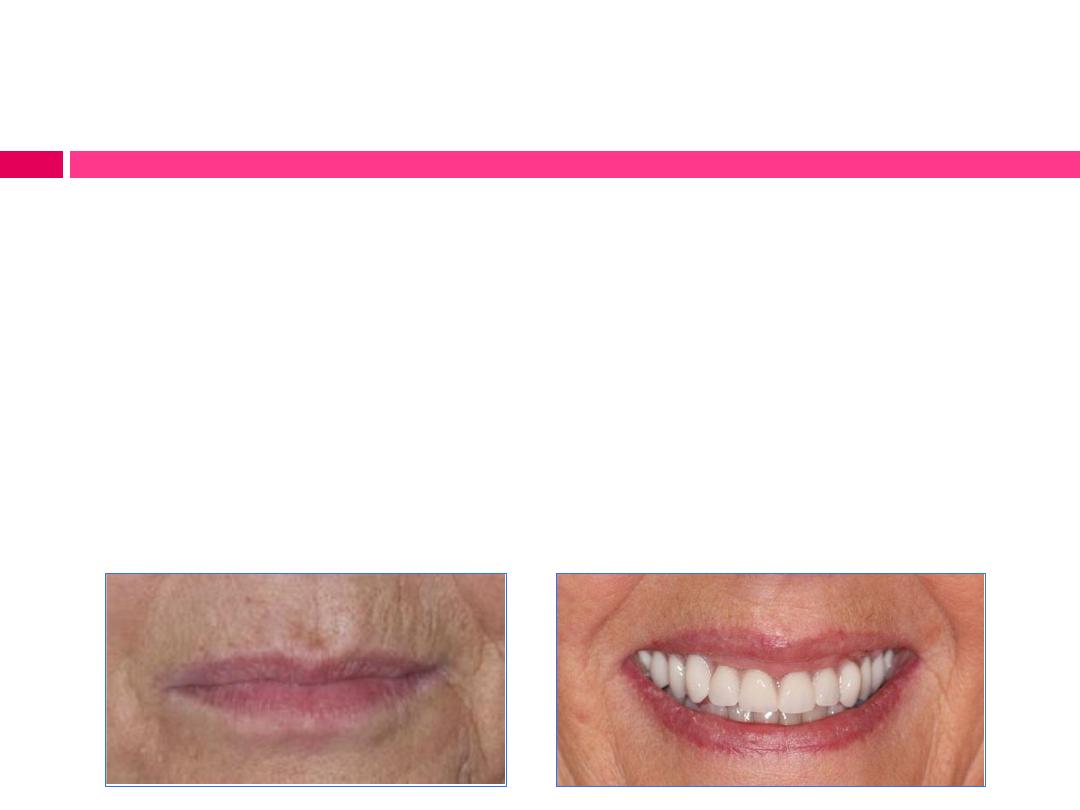
Evaluation of esthetics, facial contours and phonetic:
(i) Esthetic requirements are met.
(ii) Predetermined occlusal vertical dimension is
maintained.
(iii) Predetermined freeway space is evident.
(iv) Patient has relative phonetic freedom.

Refinement of occlusion:
It is difficult to see occlusal discrepancies intraorally
with complete dentures because of the resiliency and
displaceability of the supporting tissues tend to permit
the dentures to shift. Therefore, minor interferences may
be corrected at this stage to insure:
i.
Centric occlusion demonstrates repeatable maximum
intercuspation of maxillary and mandibular teeth.
ii.
All eccentric relations demonstrate bilateral balance
occlusion. (Optional)

Refinement of occlusion:
A variety of techniques can be employed
for checking the dentures’ occlusion.
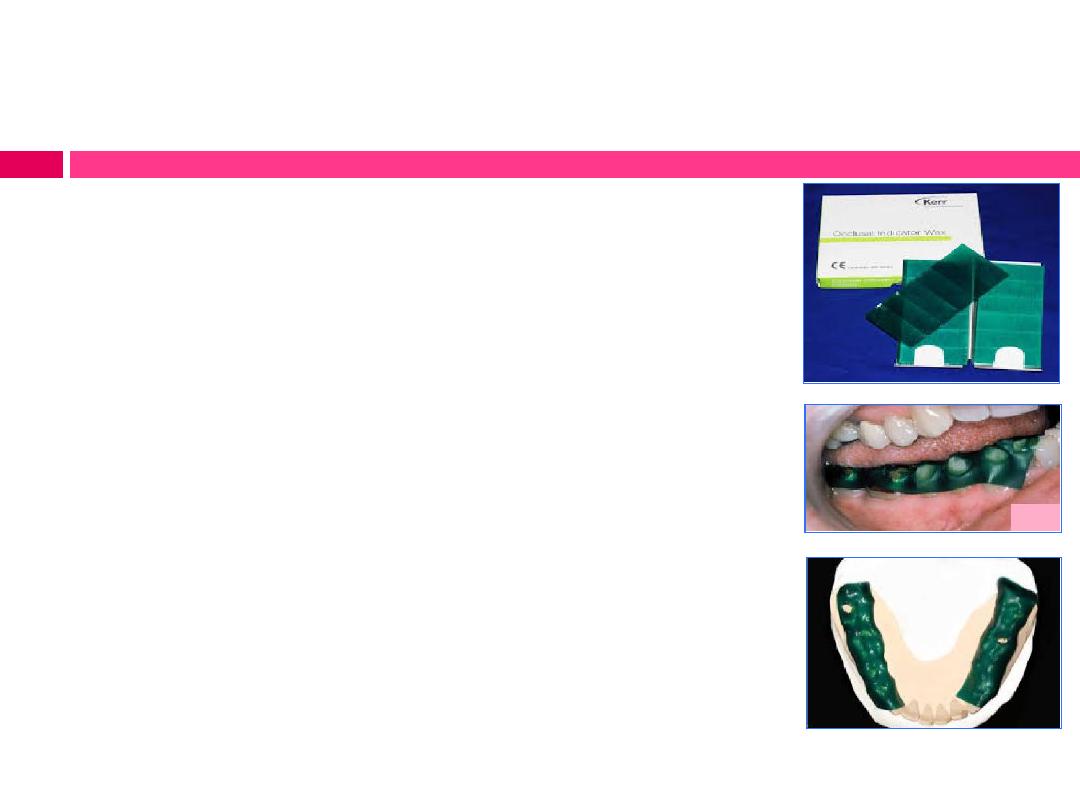
A) Checking the occlusion with wax:
Occlusal indicator wax is a soft, dark wax
with an adhesive surface that is applied to
the mandibular posterior occlusal surfaces
bilaterally. Areas where the wax penetrated
represent premature contacts (heavy occlusal
contacts)and should be adjusted, after which
the occlusion is checked again. This process
continues until all contacts represent similar
degrees of penetration into the wax.
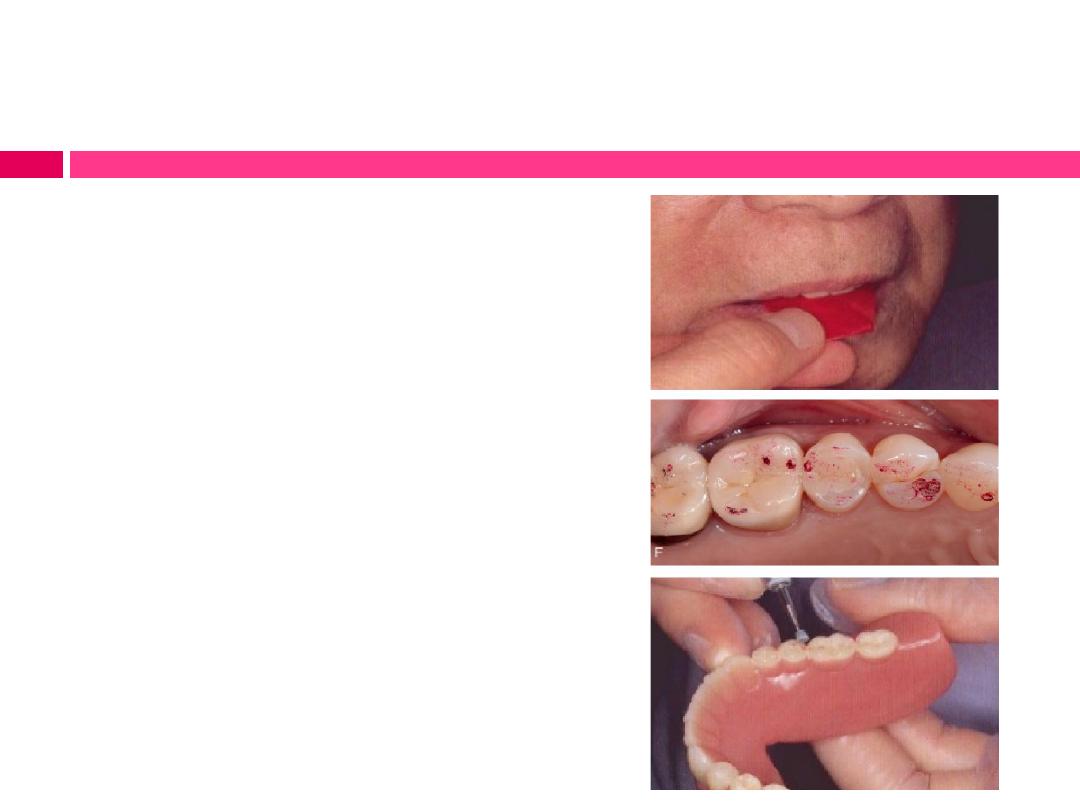
Refinement of occlusion:
B) Checking the occlusion with
articulating paper:
Two pieces of occlusal marking paper
or a single “horseshoe” articulating
paper is inserted intraorally, placed
over the mandibular teeth and the
patient is instructed to gently bite
together once and release.
The dark contact marks should be
recognized as pre-maturities, adjusted
and the occlusion checked again. This
process continues until the desired
pattern is achieved.

Refinement of occlusion:
C) If contacts still only appear
unilaterally or bilaterally but exclusively
anteriorly or exclusively posteriorly, a
laboratory remount will be required for
proper adjustment of both centric and
eccentric contacts.
CD Patient’s Instructions

The insertion appointment is the time to educate the
patient on how to properly care for the new
dentures.
Whenever possible, the patient should be provided
with printed material summarizing the most
important spoken instructions.
More important is the need for the patient to
understand the limitations of the denture service and
to comprehend the use and care of dentures.

The list of instructions should include:
Habituation
Eating habits
Speech
Denture’s home care.

Habituation:
1)
Initially the denture will feel strange and bulky and
the facial expression may seem slightly altered and it
takes time for the muscles and lips to relax and
assume their natural position around the dentures.
2)
Patient’s mouth and tongue have to get adjusted to the
denture.
3)
Soon after the insertion of dentures, salivary flow is
stimulated which declines after 2-3days unless
something is physically wrong with the dentures which
can cause irritation.

Eating habits
Learning to eat with dentures takes time and requires
positive effort from the patient side.
1)
Eat slowly and cut food into small pieces.
2)
not to chew hard in the first few days and avoid sticky
food.
3)
chew on both sides over the back teeth.
4)
Try to chew vertically (up and down) rather than
horizontally (side to side).
5)
not to drink water by lifting the tumbler but drinking
by sipping.

Speech
1)
Speaking with the dentures normally requires
some practice and patience.
2)
read aloud in front of a mirror and repeat the
words those which are difficult to pronounce.
3)
With passage of time patient's speech with
denture will be better than without denture.

Denture’s home care
The patient should be instructed to do the following:
1) How to insert denture? It does not matter which prosthesis,
upper or lower, should be inserted first unless there is virtually no
retention to the maxillary denture. In this case the mandibular
denture should be inserted first.
2) How to remove denture? break the seal by running one or both
fingers along the full length of the flanges or by puffing out the
cheeks.
3) Thoroughly rinse the mouth and denture after every meal and
after soaking.

4) clean the denture “outside of the mouth” daily by soaking and
brushing with an effective, nonabrasive denture cleanser and soft
brush, and keep cloth in the wash basin so, if denture will fall then
it won’t break.
5) Avoid using of any abrasive or detergents or hot water (above
70° C), in cleaning the denture because this will craze the denture
surface resulting in a bleached appearance.
6) never wear denture at night and should store denture in cold
water.
7) It is recommended that dentures should not be worn
continuously (24 hours per day) in an effort to reduce or minimize
denture stomatitis.

8) store denture in water at night to avoid warping.
9) massage the gums for few minutes with fingers after removing
the denture.
10) Dentures should be cleaned annually by a dentist or dental
professional using ultrasonic cleansers to minimize biofilm
accumulation over time.
11) Patients who wear dentures should be checked annually by
the dentist for maintenance of optimum denture fit and function,
for evaluation for oral lesions and bone loss and for assessment of
oral health status.

THANK YOU



