
Perinatal asphyxia occurs when antepartum,
intrapartum, neonatal, or a combination of
these events result in hypoxia and ischemia of
the brain and other organs.

ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY(H.I.E.):
-
HYPOXIC
means decreased arterial
Hypoxia
concentration of oxygen.
means blood flow to cells or organs that
Ischemia
is insufficient to maintain their function.
is an important cause of permanent
H.I.E.
damage to C.N.S. tissues that may result in
neonatal death or manifest later as cerebral palsy
(C.P.) or developmental delay.

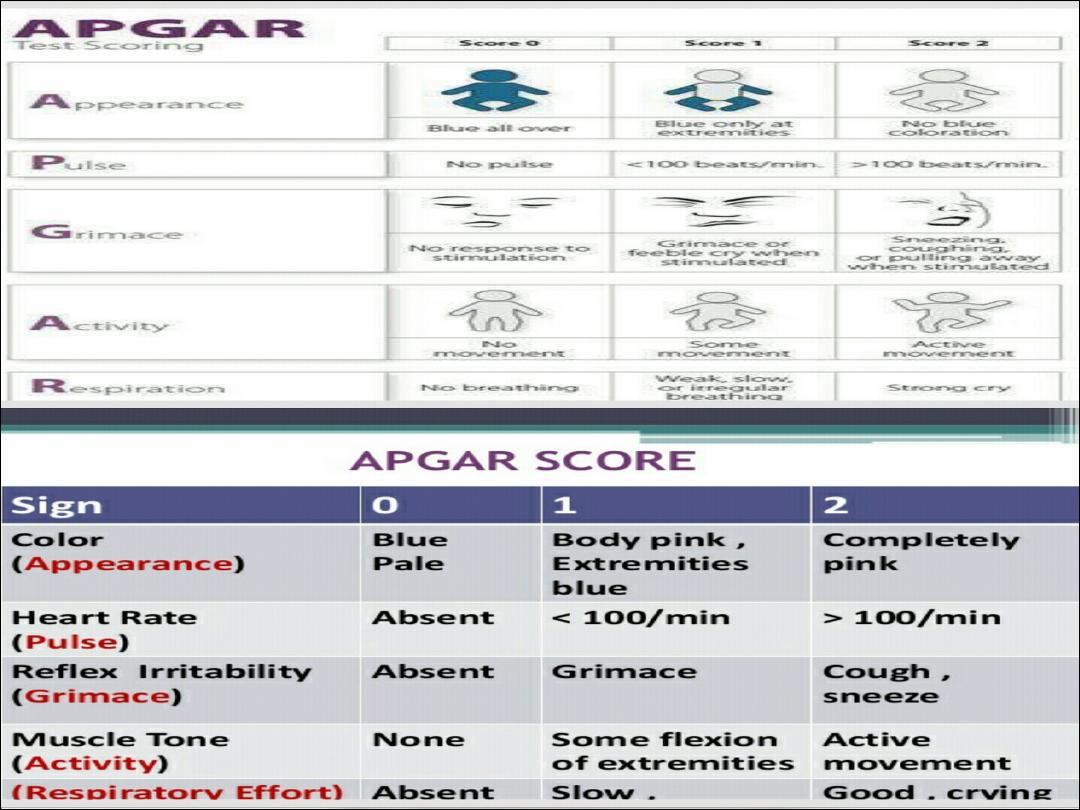
1. Umbilical cord arterial PH < 7.
2. APGAR score of 0-3 for > 5 minutes.
3. Neonatal neurological
manifestations(convulsions, coma,
hypotonia).
4. Multisystem organ dysfunction.

1. Inadequate oxygenation of maternal
blood e.g. G.A., cyanotic heart disease.
2. Low maternal BP e.g. shock.
3. Uterine tetany (excess oxytocin).
4. Premature separation of the placenta.
5. Compressed umbilical cord.
6. Post maturity and placental infarction.

1. Very low APGAR score.
2. Acidotic infants.
3. Those who require
cardiopulmonary resuscitation.

1. Before delivery :
eclampsia, uterine infections, bleeding, anemia.
2. During labor :
premature or prolonged labor,
mal-presentation, G.A.


1. Fetal asphyxia.
2. Maternal G.A.
3. Maternal sedation with morphine or
pethidine within the last 4 hours.
4. L.B.W. & Prematurity.
5. Difficult or traumatic delivery.

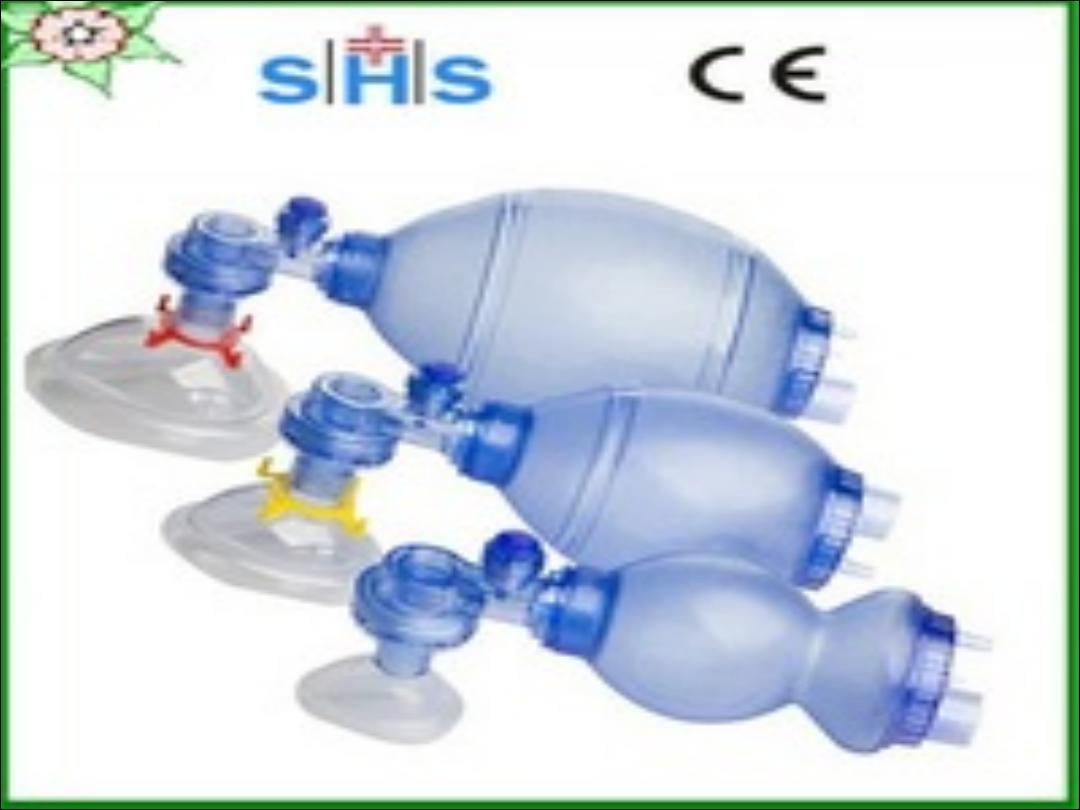
7 or > 7 : No resuscitation.
5-6 : Bag and mask.
4 or< 4 : Endotracheal intubation.


1. Cerebral hypoxia.
2. Convulsions.
3. I.V.H.
4. Renal failure.
5. Anoxic cardiomyopathy.
6. N.E.C.
7. Metabolic(hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia,
inappropriate A.D.H. secretion).

TERM OUTCOMES AFTER H.I.E. :
-
LONG
1. Cognition and developmental delay
2. Learning difficulties
3. Cerebral palsy
4. Vision defects
5. Epilepsy
6. Hearing loss

1.Treatment of cerebral edema:
a. Correct hypoxia & acidosis.
b. Control convulsions (in 20-50% of HIE cases).
c. Restrict i.v. fluid to 60 ml/kg/day.
d. Mannitol 5ml/kg/dose over 20 minutes can be
repeated 4 times a day.
e. Dexamethasone 1 mg loading dose then
0.3 mg/kg 8 hourly for 3 days.
f. Hyperventilation.

2. Maintain normal cerebral tissue perfusion
e.g.by giving blood to prevent neuronal damage.
3. Maintain renal function
e.g.by furosemide and dopamine. 4.
Stop oral feeding for 4-7 days. 5.
Treat secondary infections. 6.
Thermal regulation.
7.
Physiotherapy. 8.
Drugs which inhibit or destroy oxygen free radicals e.g.
allopurinol.
9.Magnesium to block glutamate receptors (which is a
powerful neurotoxin).
10.Induced Hypothermia
Cooling to 33.5c is thought to be protective in
newborns mainly by reducing brain perfusion and
metabolism. It is either total body or selective head
hypothermia.
