Radiographic Interpretation of Mixed LesionDental Radiology
د. شهرزاد ساميBroken Roots
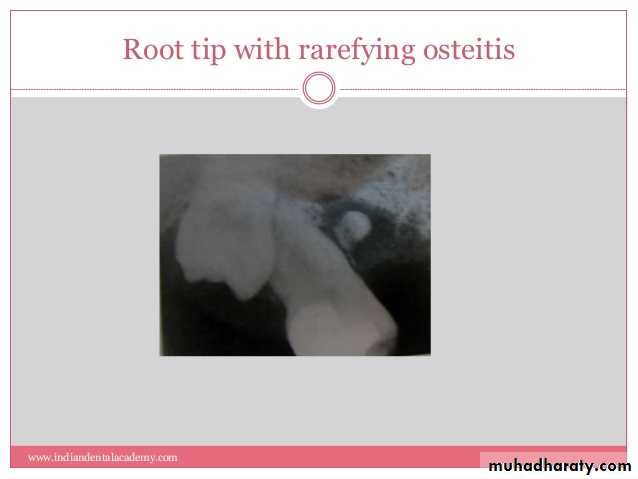
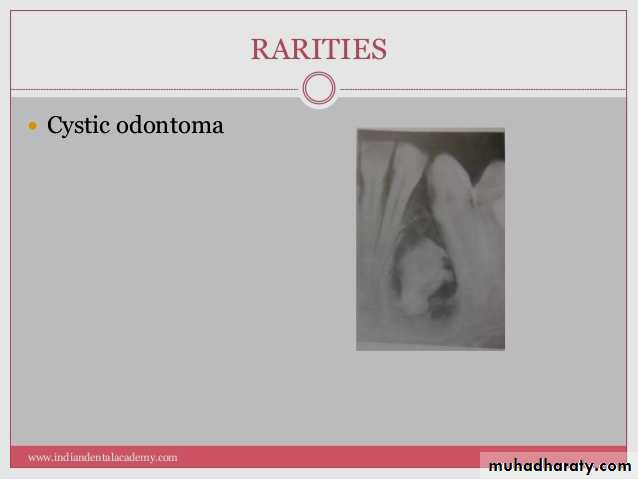
Secondary infection of broken roots produces a partly radiolucent and partly radiopaque (mixed) lesions. The clinical history, location, and appearance of radiopaque area is assist in arriving at the correct diagnosis.Cystic odontoma
The compound and complex odontoma are lesion of slow growth and are radiopaque, on rare occasions one of them may undergo a cystic changer. Under these circumstances a odontoma is surrounded by a radiolucency and called cystic odontomaCalcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumors (CEOT), Pindborg Tumors
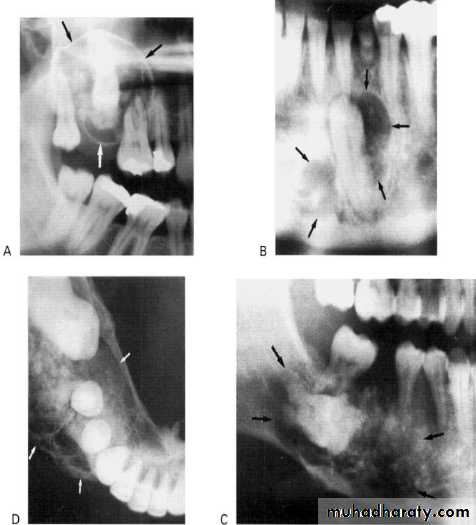
This rare odontogenic tumour usually presents in the premolar/molar region of the mandibleAppearance: They can be either monolocular or multilocular, but tend to remain relatively small although they can cause expansion of surrounding cortical bone. They are often associated with an unerupted tooth.
Outline: The lesion tends to be of variable definition and cortication but is frequently scalloped.
Radiodensity: They are often radiolucent in their early stages; then numerous scattered radiopacities usually become evident within the lesion, often most prominent around the crown of any associated unerupted tooth. This appearance is sometimes described as driven snow.
Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour (AOT
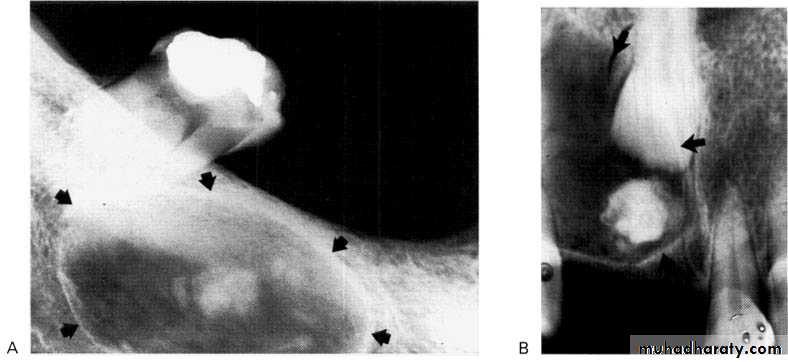
• Site: Anterior maxilla — incisor/canine region, occasionally anterior mandible.• Shape: — Monolocular
— Round or oval — Often surrounds an entire unerupted tooth.
• Outline: — Smooth and well defined
— Well corticated.
Radiodensity: — Initially radiolucent, but small opacities (snow flakes) within the central radiolucency may be seen peripherally as the lesion matures.
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst (Gorlin Cyst)
It presents typically as a radiolucency resembling other odontogenic cysts, but, as it develops, a variable amount of calcified material becomes evident, scattered throughout the radiolucency. The opacities can range from small flecks to large masses.
Shape: Variable, but usually monolocular.
Outline: — Smooth, well defined
— Often corticated.
Radiodensity: — Initially radiolucent but in more advanced stages contains a variable amount of calcified radiopaque material of tooth-like density.
Fibro-cemento-osseous Lesions
The term fibrocemento- osseous lesion are defined as skeletal disorders in which bone is replaced by fibrous tissue which in turn is replaced by mineralized tissue (bone and/or cementum) to a varying degree as the lesions age.Although these lesions are radiolucent in their early stages, they are commonly seen clinically as variably radiopaque lesions.
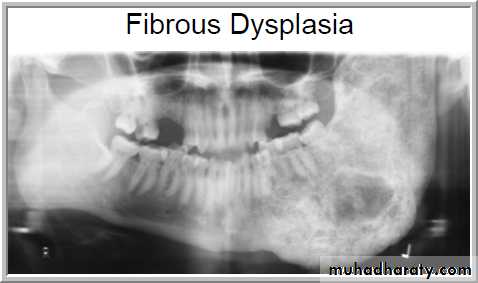
Fibrous Dysplasia
Fibrous dysplasia is considered to represent a developmental tumour-like lesion. Most cases (approx. 80%) are monostotic (limited to a single bone, often the jaw).
• Shape: Round.
•Outline: — Poorly defined
— Not corticated.
Radiodensity: — Initially radiolucent
— Gradually becomes opaque to produce the typical ground glass, orange peel and finger print appearances resulting from superimposition of many fine, poorly-calcified bone trabeculae arranged in a disorganized fashion.
— Continuing to become more opaque with age.
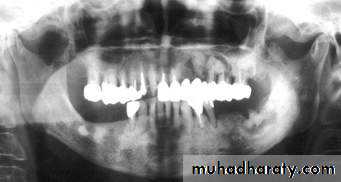
Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia
Shape: — Multiple— Round, but frequently coalesce
Outline: — Smooth
— Moderately well defined
— Occasionally corticated.
Radiodensity: — Early stage — multiple Radiolucencies
— Intermediate stage — multiple radiolucencies with gradually increasing patchy internal opacities
— Late stage — multiple irregular dense radiopacities with individual lesions, sometimes surrounded by a thin radiolucent line.
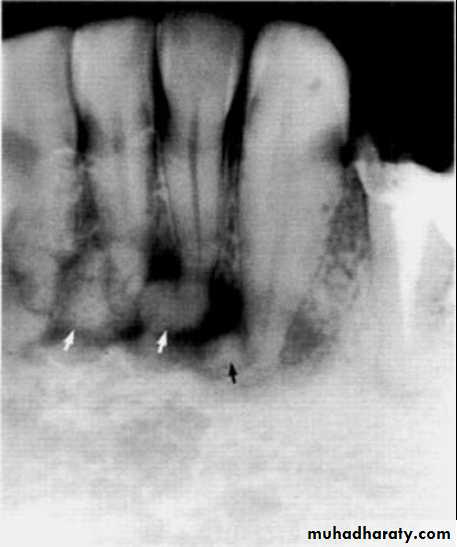
Periapical Cemento-osseous Dysplasia
Site: Apices of vital lower incisor teeth.Shape: — Round, monolocular
— Often multiple.
Outline: —Poorly defined
— Not corticated.
Radiodensity: — Early stage — radiolucent
— Intermediate stage — radiolucent with patchy opacity within the radiolucency
— Late stage — densely radiopaque but surrounded by a thin radiolucent line.