1
Introduction
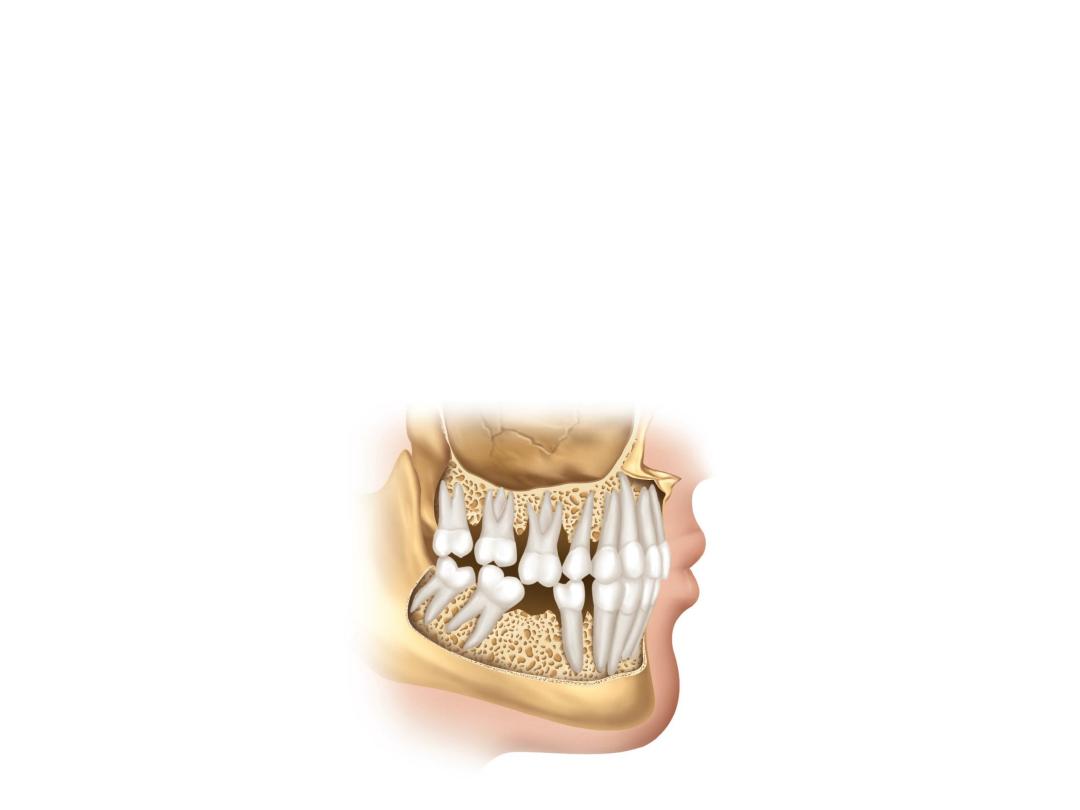
Teeth are designed for the lifetime but often patients lose teeth partially or
completely because of causes such as dental caries, periodontal problems, accidental
trauma, etc. Replacing missing teeth is important to the patient’s general health as
well as to the health of his/her other teeth. Not only does the patient lose chewing
ability when a tooth is lost, but if it is not replaced, it can cause other teeth to be lost,
tipped or crowded and create subsequent problems.
2
Introduction
Dentistry has undergone many changes during the past quarter century;
however, no changes have been more profound than those in the field of
implant dentistry.
3
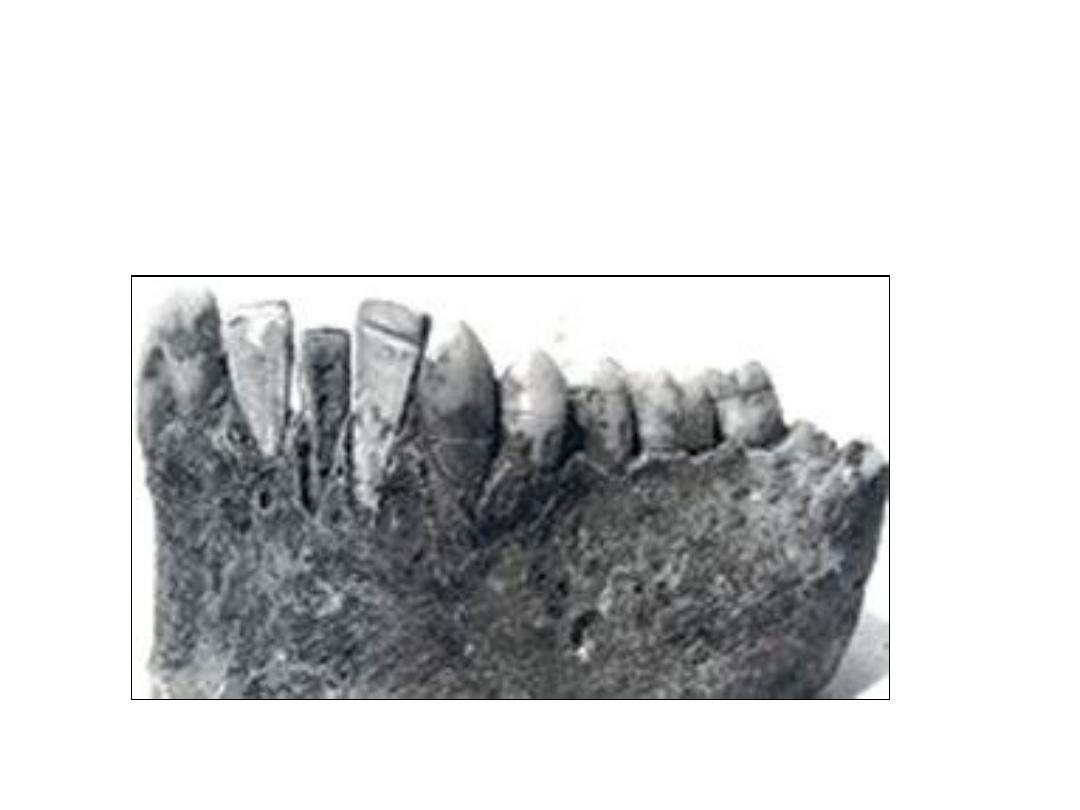
Replacing lost teeth with a bone anchored device is not a new
concept, it has been an aspiration of humankind for centuries.
Mayan dental implants from 600 AD
4
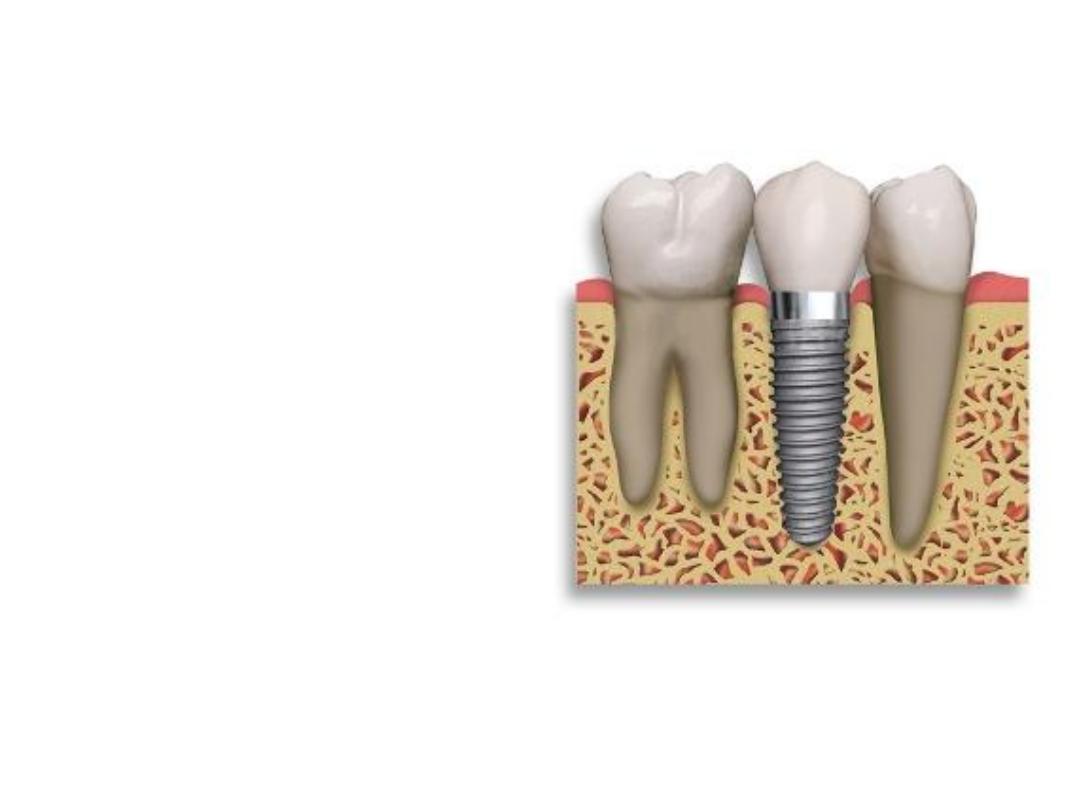
Careful selection of patient
and treatment planning is the
critical step in the prevention
of
iatrogenically
induced
damage
during
implant
treatment.
Introduction
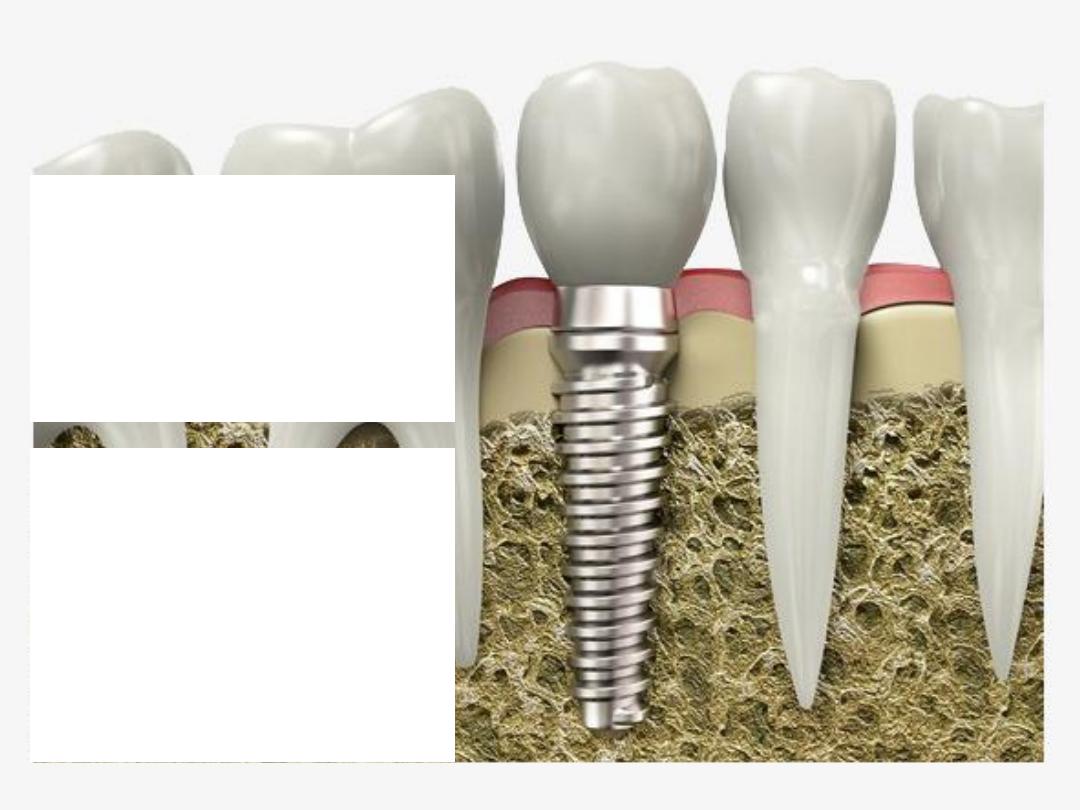
Definition of dental implant
“Dental implant is an artificial
dental root that is surgically
inserted into the jaw bone and
that can be used by the dentist
as platform to support a dental
prosthesis such as a crown,
bridge, denture or to act as an
orthodontic anchor.”
“Dental implant is an alloplastic
and
biocompatible
material
placed into (endosseous) or onto
(subperiosteal) the jawbone to
support a fixed prosthesis, or to
stabilize removable prosthesis.”

6
ADVANTAGES OF IMPLANT
• To overcome the drawbacks of removable
prosthesis.
• To maintain of height and width of bone.
• Ideally esthetic tooth positioning.
• Improved psychological health and Quality of life.
• Increase stability in chewing.
• Increase retention.
• Eliminates need to involve adjacent teeth.
7
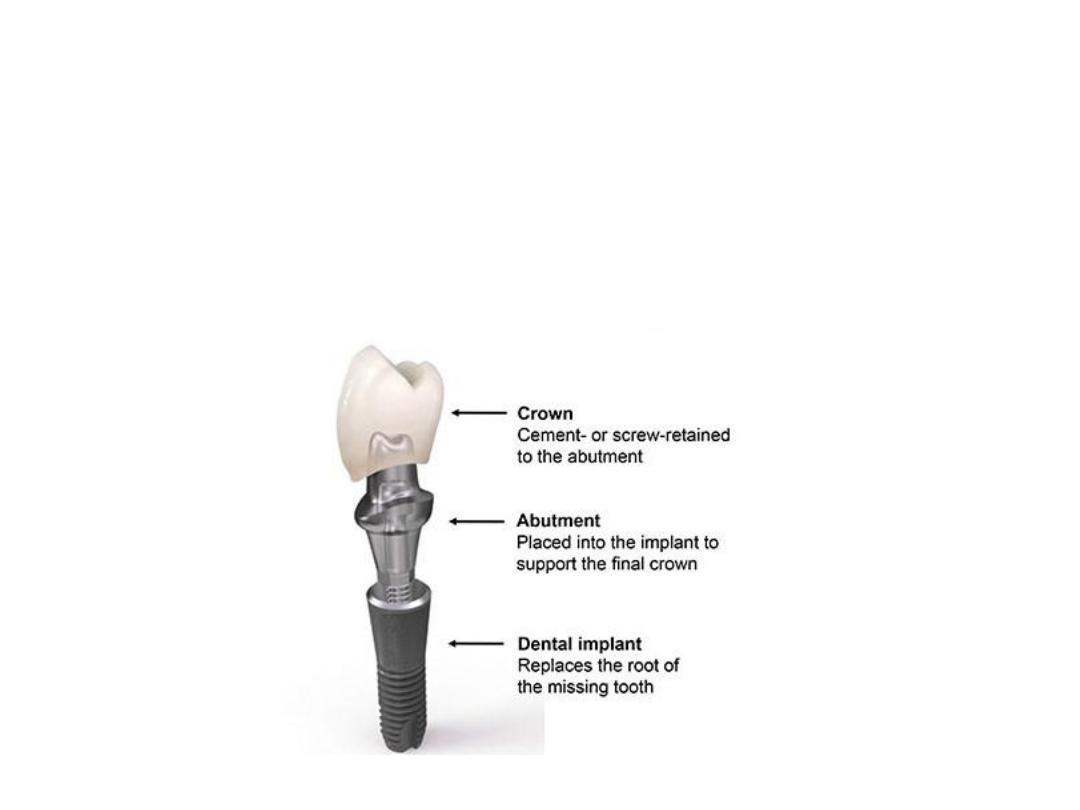
Components of Dental Implants
Although each implant system varies, the parts are
basically consistent:
1.Fixture (endosteal root form) or Dental Implant Body
2. Implant Abutment (transmucosal abutment)
3. Prosthesis (Crown)
(Fixture)

8
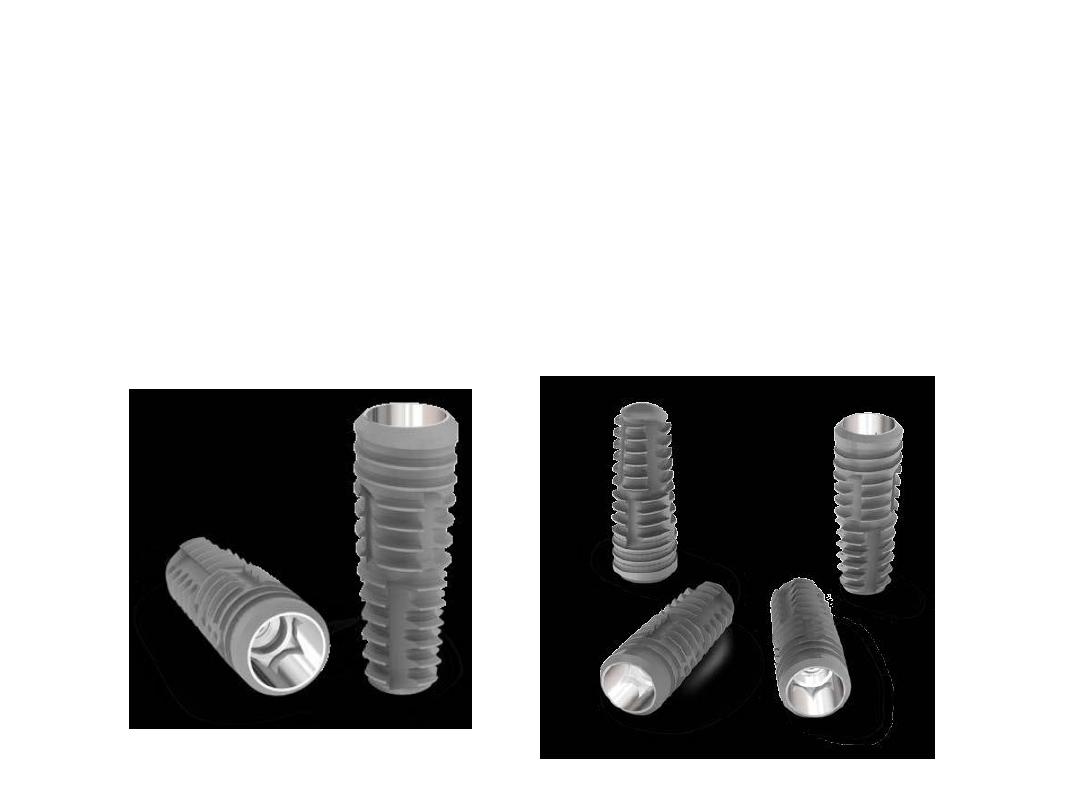
1.Fixture (endosteal root form) or Dental Implant Body: It is the first
component of dental implant. It actually engages bone. Depending on
the implant system, the fixture can have different surfaces (threaded,
grooved, perforated, plasma sprayed or coated).

9
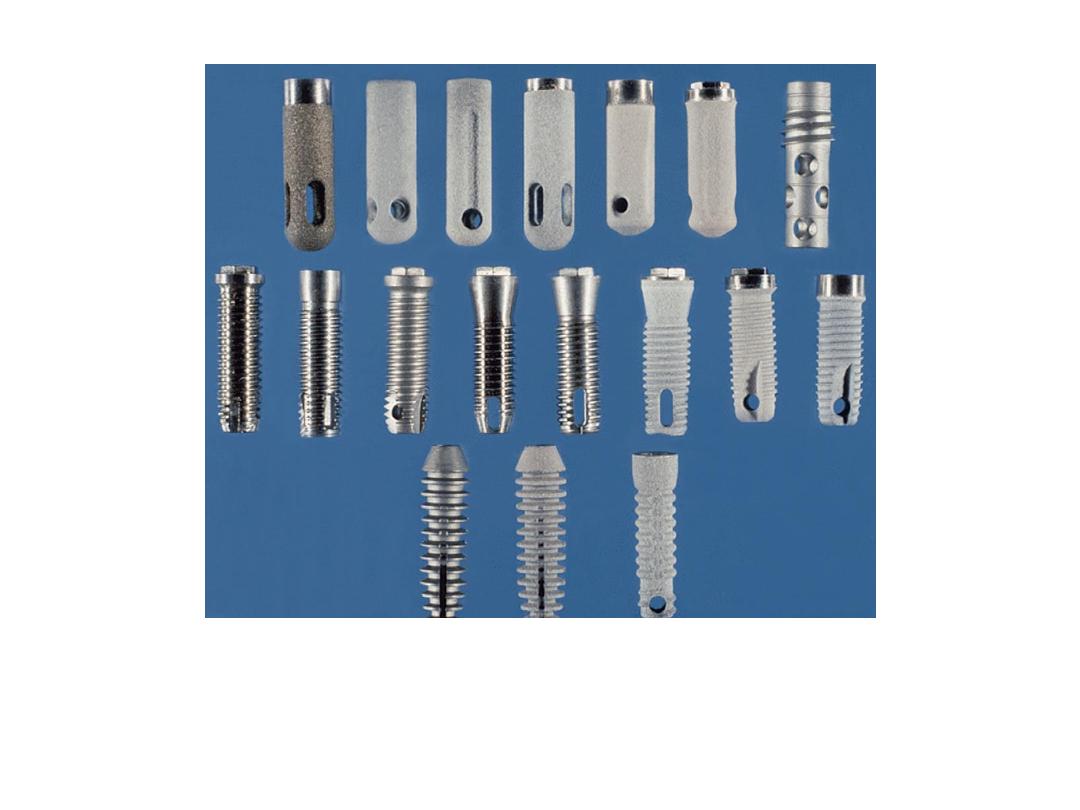
Implant body designs generally relate to three different categories:
cylinder implants (top row), screw design implants (middle row), or a
combination (bottom row).
10
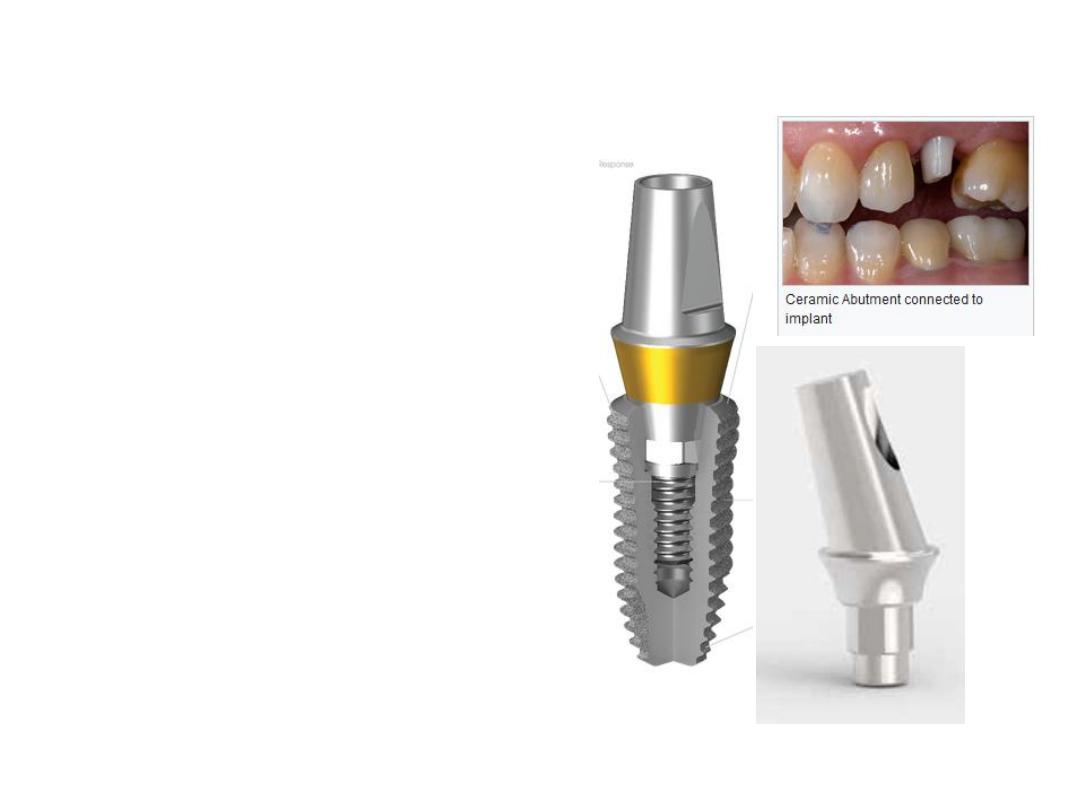
2. Implant Abutment (transmucosal
abutment): It is the second component
which
provides
the
connection
between the implant fixture and
prosthesis that will be fabricated. It is
either screwed or cemented to the
fixture.
It
can
be
cylindrical,
shouldered, or some times angulated in
design.
11
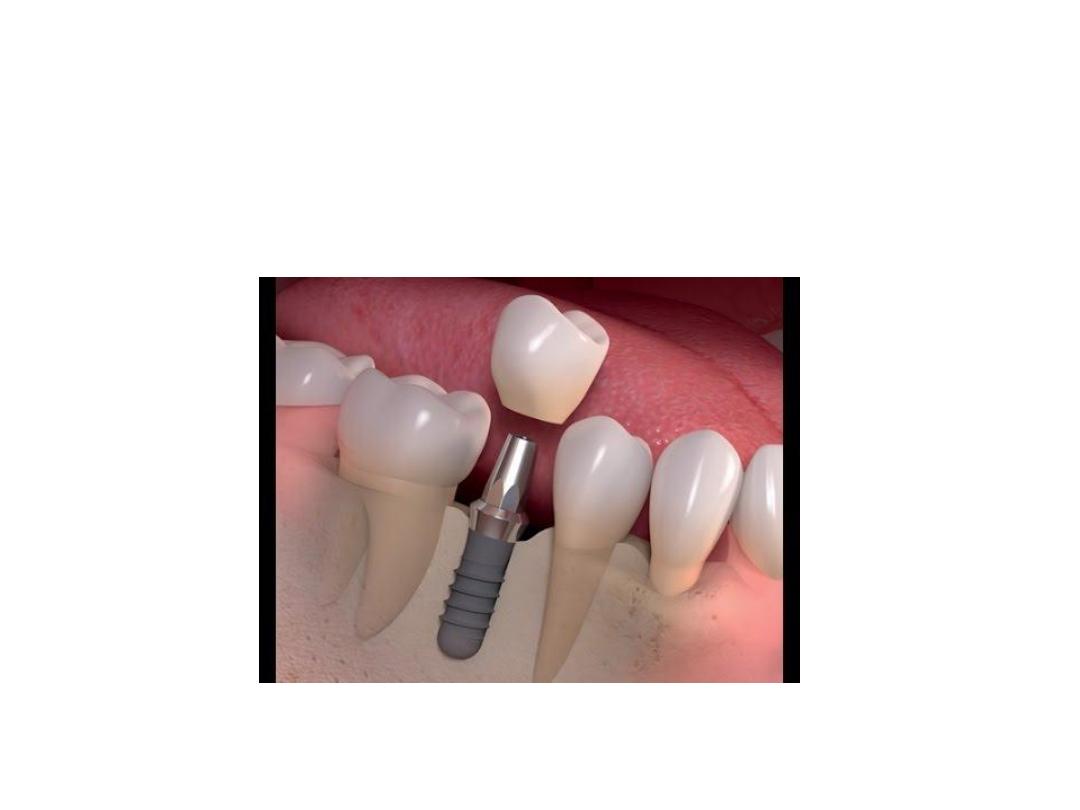
3. Prosthesis: It is the last part of dental implant that is attached to the
abutment through the use of screws, cement, or precision attachments.

12
The accessories of dental implant
1.Cover Screw (dental implant obturator): It is placed at the time of first
surgery and removed when loading the abutment.
2.Healing Abutment (Gingival former): It is a temporary implant connecting
part placed on the implant body to create a channel through the mucosa while
the adjacent soft tissue heal.
3. Transfer Copping: It is used to transfer the position of the implant body or
the abutment to the working cast.
4.Laboatory analogue: An analog is defined as something that is analogous or
similar to something else. An implant analog is used in the fabrication of the
master cast to replicate the implant body or abutment.
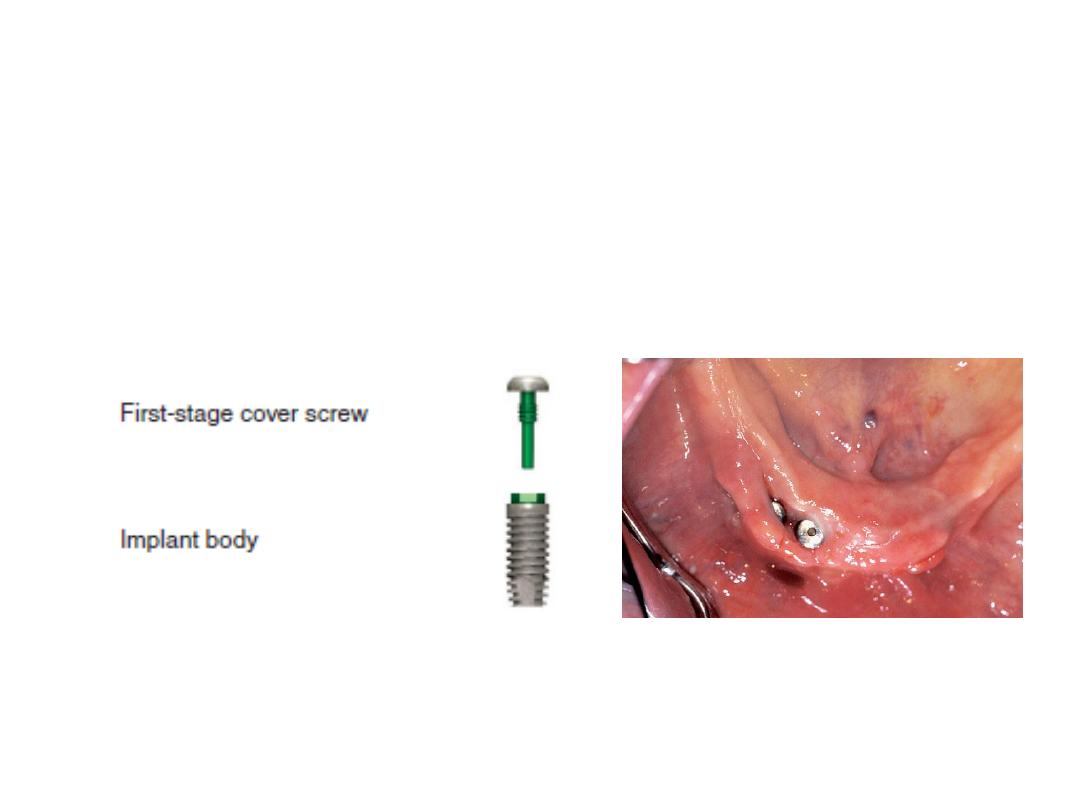
13
1.Cover Screw (dental implant obturator): It is placed at the time of
first surgery and removed when loading the abutment.
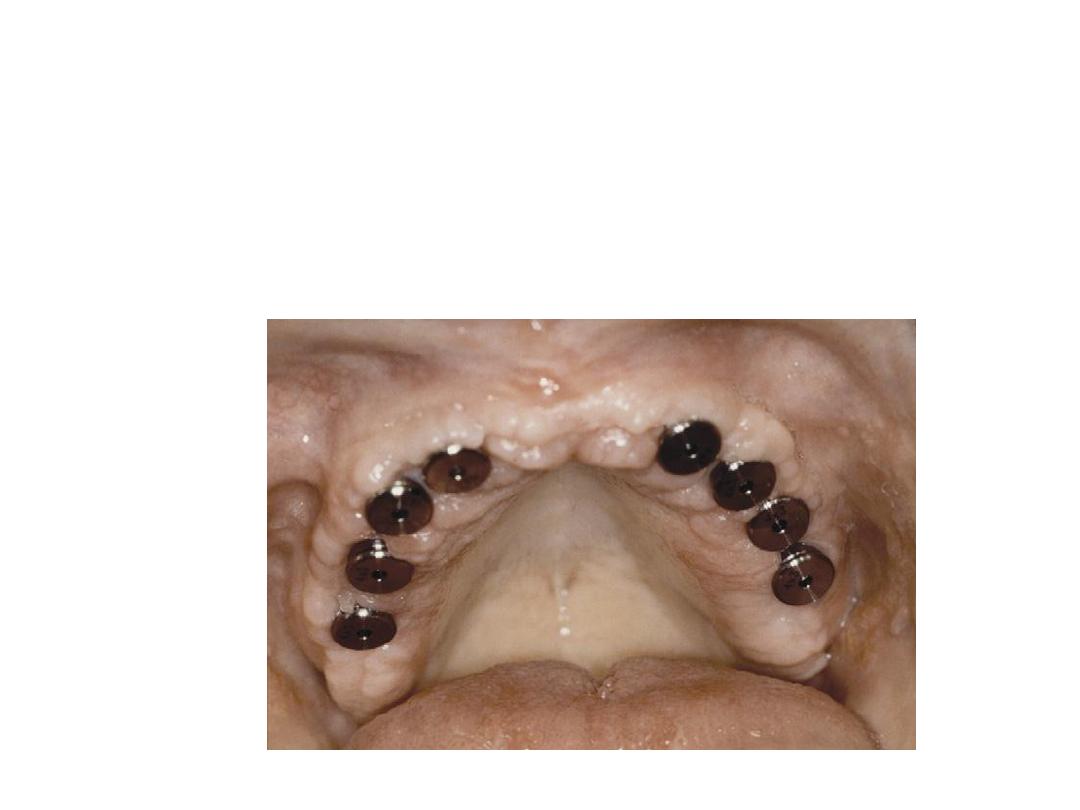
14
2.Healing Abutment (Gingival former): It is a temporary implant
connecting part placed on the implant body to create a channel through
the mucosa while the adjacent soft tissue heal.
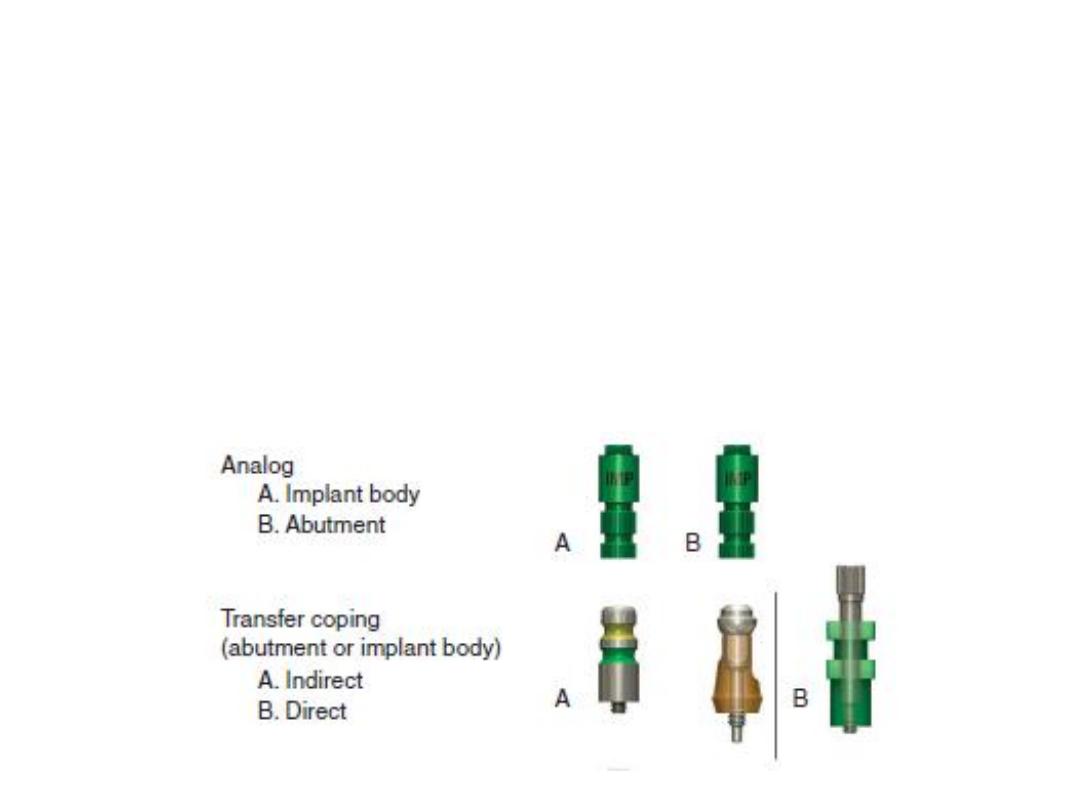
15
3.Transfer Copping: It is used to transfer the position of the implant
body or the abutment to the working cast.
4.Laboatory analogue. An analog is defined as something that is
analogous or similar to something else. An implant analog is used in the
fabrication of the master cast to replicate the implant body or abutment.



