
1
Reaction to Physical
&
Chemical Agents

2
Lecture objectives
:
To understanding of different physical and chemical
factors affected viruses such as:1-Heat & Cold, 2-
Stabilization of Viruses by Salts, 3-pH, 4-Radiation, 5-
Photodynamic inactivation, 6-Ether Susceptibility, 7-
Detergents, Formaldehyde, Antibiotics & Other
Antibacterial Agents
.
Assessment:
Homework, quizzes, examination, poster
and mini-research discussion.
References:
Main textbook:
Medical Microbiology
,
Jawetz,
Melnick
26th ed.,
2013

3
Heat & Cold
There is great variability in the heat stability of different
viruses
.
-
Icosahedral viruses tend to be stable, losing infectivity after
several hours at 37°C
. Enveloped viruses are much more
heat-labile, rapidly dropping in titer at 37°C
.
-
Viral infectivity is generally destroyed by heating at 50–60°C
for 30 minutes, exceptions (eg, hepatitis B virus,
polyomaviruses)
.
Viruses can be preserved by storage at deep-freezing
temperatures, and some may withstand lyophilization and can
thus be preserved in the dry situation at 4°C or even at room
temperature. Enveloped viruses tend to lose infectivity after
prolonged storage even at -90°C and are particularly sensitive
to repeated freezing and thawing
.

4
Stabilization of Viruses by Salts
Many viruses can be stabilized by salts in concentrations
of 1 mol/L. The mechanism by which the salts stabilize
viral preparations is not known. Viruses are preferentially
stabilized by certain salts
.
MgCl
2
, 1 mol/L, stabilizes
picornaviruses
and
reoviruses
;
MgSO
4
, 1 mol/L, stabilizes
orthomyxoviruses
and
paramyxoviruses
;
Na
2
SO
4
, 1 mol/L, stabilizes
herpesviruses
.
pH
Viruses are usually stable between pH values of 5.0 and
9.0. Some viruses (eg, enteroviruses) are resistant to
acidic conditions. All viruses are destroyed by alkaline
conditions
.

5
Radiation
Ultraviolet, x-ray, and high-energy particles inactivate
viruses. The dose varies for different viruses. Infectivity is
the most radiosensitive property because replication
requires expression of the entire genetic contents
.
Photodynamic Inactivation
Viruses are penetrable to a varying degree by vital dyes
such as toluidine blue, neutral red, and proflavine. These
dyes bind to the viral nucleic acid, and the virus then
becomes susceptible to inactivation by visible light
.

6
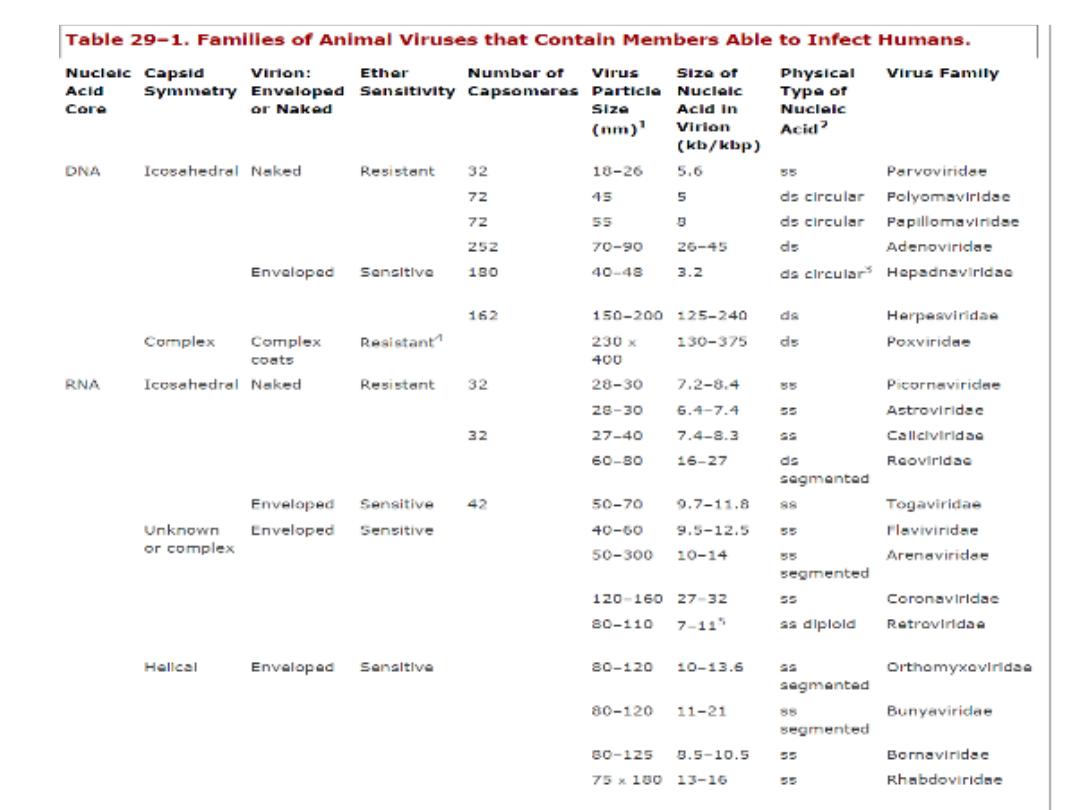
Ether Susceptibility
Ether susceptibility can be used to distinguish viruses that
possess an envelope from those that do not
29-1
As shown in table
Detergents
Nonionic detergents—eg, Nonidet P40 and Triton
X-100—solubilize lipid constituents of viral membranes. The
viral proteins in the envelope are released (denatured)
.
Anionic detergents, eg, sodium dodecyl sulfate, also solubilize
viral envelopes; in addition, they disrupt capsids into
separated polypeptides
.
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde destroys viral infectivity by reacting with
nucleic acid. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are
inactivated much more rapidly than those with double-
stranded genomes. Formaldehyde has minimal adverse
effects on the antigenicity of proteins therefore it has been
used frequently in production of inactivated viral vaccines
.
7

8
Antibiotics & Other Antibacterial Agents
1
-
Antibacterial antibiotics and sulfonamides have no effect on
viruses. Some antiviral drugs are available
.
2
-
Larger concentrations of chlorine are required to destroy
viruses than to kill bacteria, especially in the presence of
extraneous proteins. For example, the chlorine treatment of
stools adequate to inactivate typhoid bacilli is inadequate to
destroy poliomyelitis virus present in feces
.
3
-
Alcohols, such as isopropanol and ethanol, are relatively
ineffective against certain viruses, especially Picornaviruses
.
