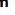PHAGOCYTES:THE EVER-PRESENT
BUSYBODIES OF INFLAMMATION ANDSPECIFIC IMMUNITY
Dr. Dhafer A. Alghezi
Ph. D. cancer research
The general activities of phagocytes
• To survey the tissue compartments and discover microbes, particulate matter (dust, carbon particles, antigen-antibody complexes, and injured or dead cells).
• To ingest and eliminate these materials.
• To extract immunogenic information (antigens) from foreign matter.
The three main types of phagocytes are neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages.
Neutrophils and Eosinophils
A common sign of bacterial infection is a high neutrophil count in the blood (neutrophilia), and neutrophils are also a primary component
of pus.
Eosinophils are attracted to sites of parasitic infections and antigen-antibody reactions, though they play only a minor phagocytic
role.
The developmental stages of monocytes and macrophages. The cells progress through maturational stages in the bone marrow and peripheral blood.
Migrated monocytes are transformed by various inflammatory mediators into macrophages.
This process is marked by an increase in size and by enhanced development of lysosomes and other organelles.
Macrophage: King of the Phagocytes
Macrophages were classified as either fixed (adherent to tissue) or wandering (all macrophages retain the capacity to move about).
Whether they reside in a specific organ or wander depends upon their stage of development and the immune stimuli they receive.
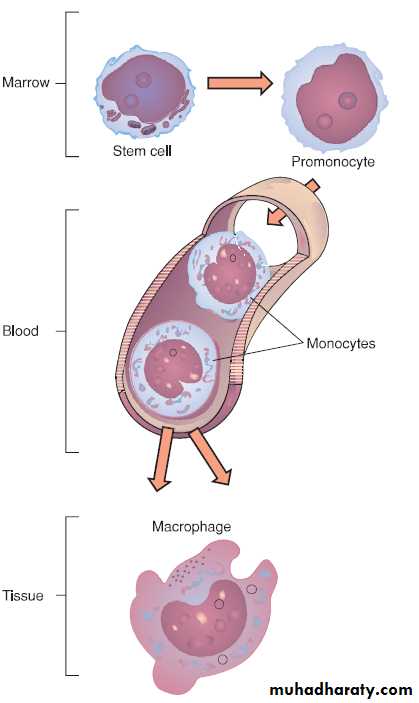
Specialized macrophages called histiocytes migrate to a certain tissue and remain there during their lifespan.
Examples are alveolar macrophages (lung) , the Kupffer cells in the liver, Langerhans cells in the skin and macrophages in the spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, kidney, and brain.
Other macrophages do not reside permanently in a particular tissue and drift nomadically throughout the RES.
Not only are macrophages dynamic scavengers, but they also process foreign substances and prepare them for reactions with B and T lymphocytes .
Liver tissue with Kupffer cells.
micrograph view of a lung with an alveolar macrophage.Langerhans cells deep in the epidermis
Mechanisms of Phagocytic Discovery, Engulfment, and Killing
Although the term phagocytosis literally means the engulfment of particles by cells,phagocytes actually endocytose both particulate and liquid substances..
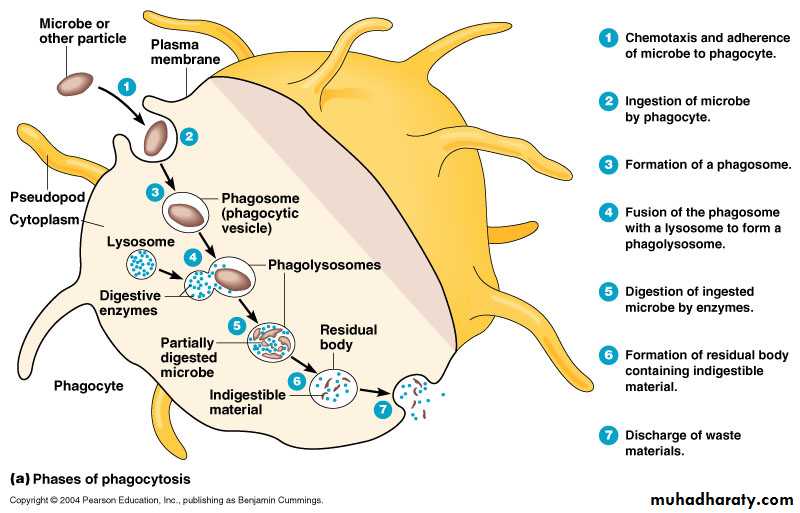
The events in phagocytosis include:
Chemotaxis, ingestion,
Phagolysosome formation,
Destruction,
Excretion
Why phagocytosis concedered not just the physical process of engulfment? because phagocytes also actively attack and eliminate foreign cells with a wide array of antimicrobial substances
Chemotaxis, ingestion,
Phagocytes migrate into a region of inflammation attracted by a gradient of stimulant products from the parasite and host tissue at the site of injury.Phagocytosis is often accompanied by opsonization
Opsonization: is a process that coats the surface of microorganisms with antibodies or complement, thereby facilitating recognition and engulfment.
Once the phagocyte has made contact with its prey, it extends pseudopods that enclose the cells or particles in a pocket and internalize them in a vacuole called a phagosome.
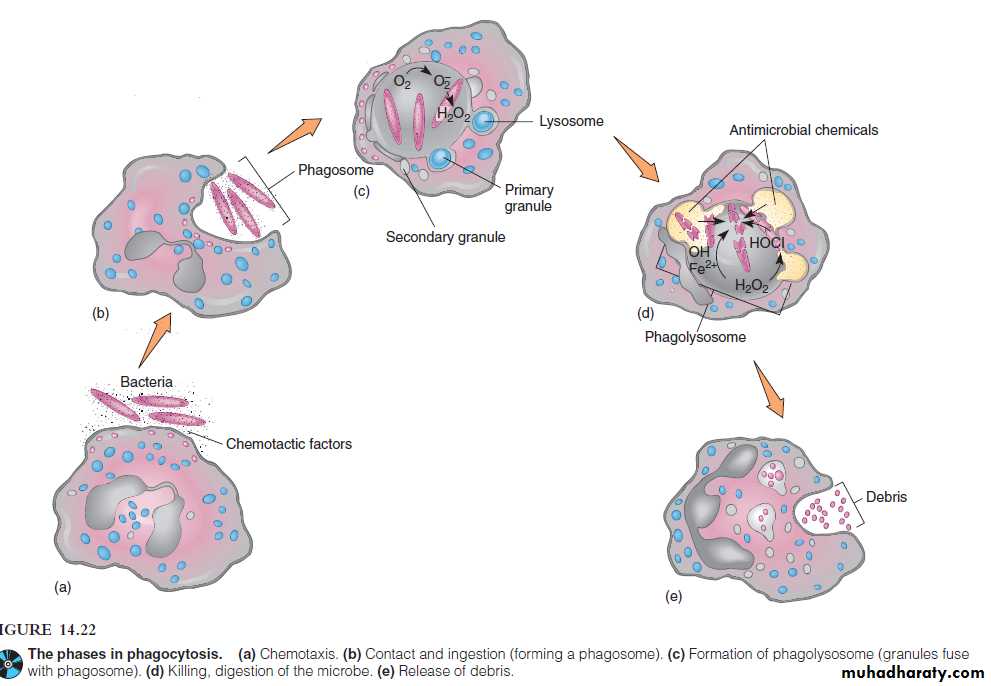
Phagolysosome Formation and Killing
Lysosomes migrate to the scene of the phagosome and fuse with it to form a phagolysosome.Other granules containing antimicrobial chemicals are released into the phagolysosome, forming a potent brew designed to poison and then analyse the ingested material.
The destructiveness of phagocytosis is evident by the death of bacteria within 30 minutes after contacting this battery of antimicrobial substances
Phagocytosis
Destruction and Elimination Systems
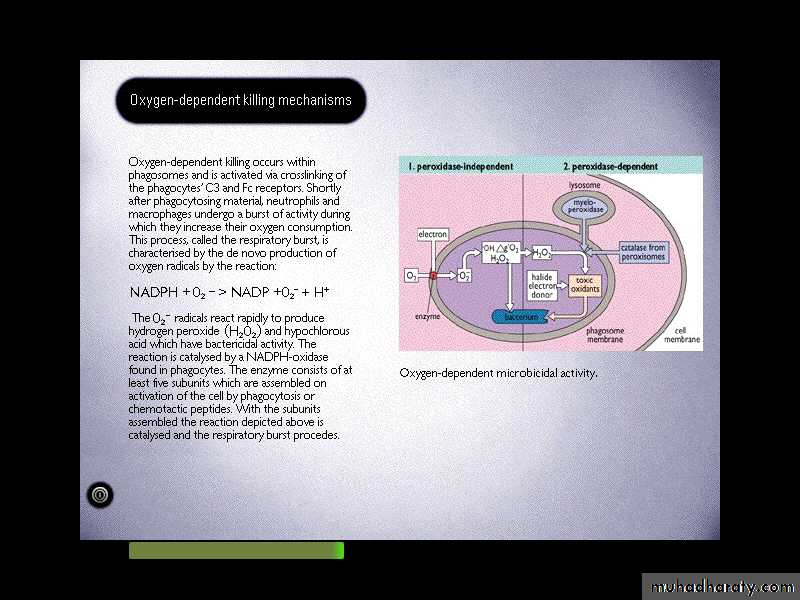
several substances that separately and together have great killing power.Myeloperoxidase, an enzyme found in granulocytes, forms halogen ions (OCl-) that are strong oxidizing agents.
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2),
The superoxide anion (O2 -),
Activated oxygen (1O2),
The hydroxyl free radical (.OH)
the liberation of lactic acid,
Lysozyme,
Nitric oxide (NO), a powerful mediator that kills bacteria and inhibits viral replication.
Cationic proteins that injure bacterial cell membranes
A number of proteolytic hydrolytic enzymes complete the job.
CONTRIBUTORS TO THE BODY’S CHEMICAL IMMUNITY
Interferon: Antiviral Cytokines and Immune StimulantsInterferon (IFN) a small protein produced naturally by certain WBCs and tissue cells that is used in therapy against certain viral infections and cancer.
Although the interferon system was originally thought to be directed exclusively against viruses, it is now known to be involved also in defenses against other microbes and in immune regulation and intercommunication.
Three major types are
Alpha interferon, a product of lymphocytes and macrophages;
Beta interferon, a product of fibroblasts and epithelial cells;
Gamma interferon, a product of T cells.
All are produced in response to viruses, RNA, immune products, and various antigens.
In addition to antiviral effects, all three IFNs can inhibit the expression of cancer genes and have tumor suppressor effects.
Other Roles of Interferon
Interferons act as important immune regulatory cytokines that activate the development of WBCsAlpha interferon produced by T cells activates a subset of cells called natural killer (NK) cells.
beta interferon plays a role in the maturation of B and T lymphocytes and in inflammation.
Gamma interferon inhibits cancer cells, stimulates B lymphocytes, activates macrophages, and enhances the effectiveness of phagocytosis