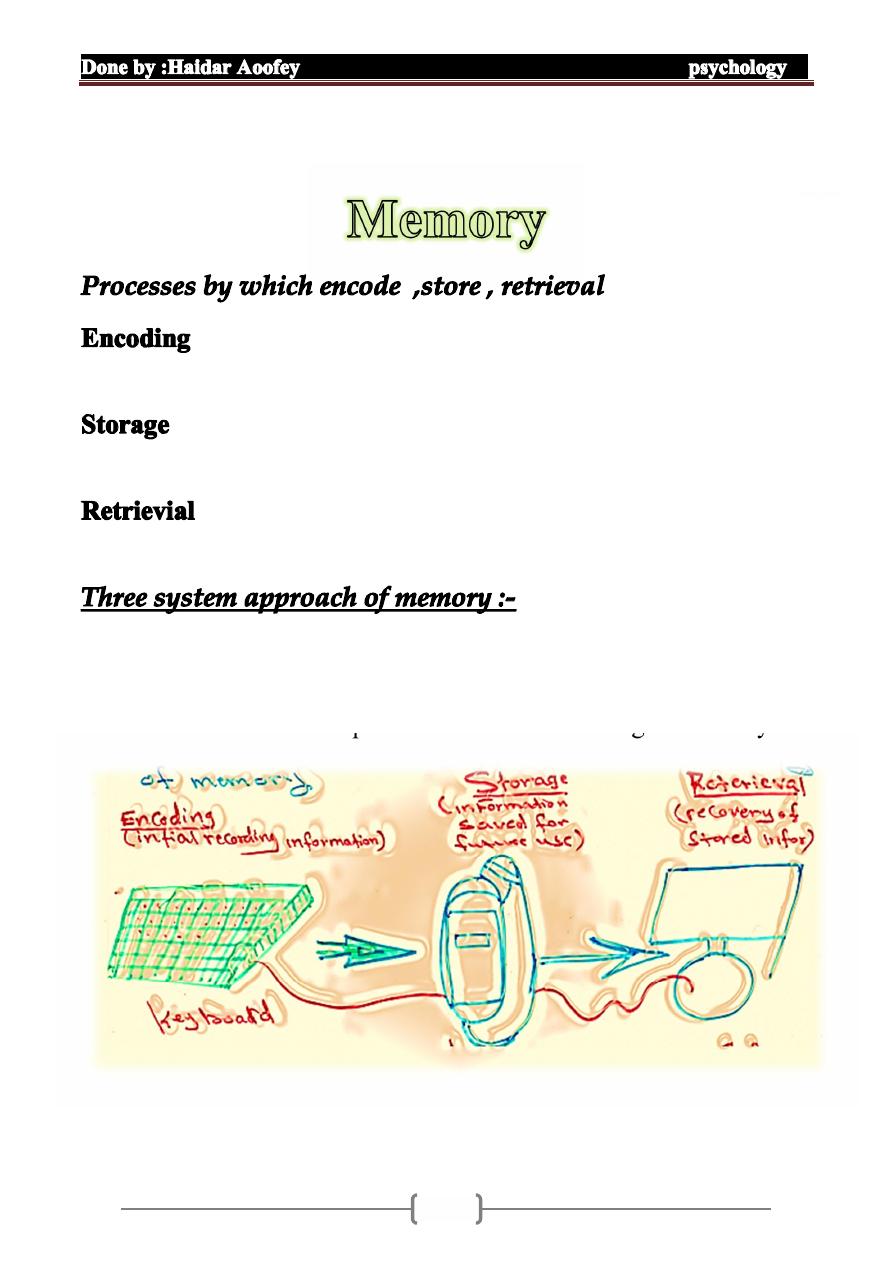
: the intial process recording information in form
usable to memory
: maintenance of material saved I n memory if
memory not stored well it cannot be remembered
:allocation of stored information & bought it to
awareness to be useful
stage through which information must travel if it is to be
remembered ( Atkinson& shiffrin)
influential in development ofour understanding of memory
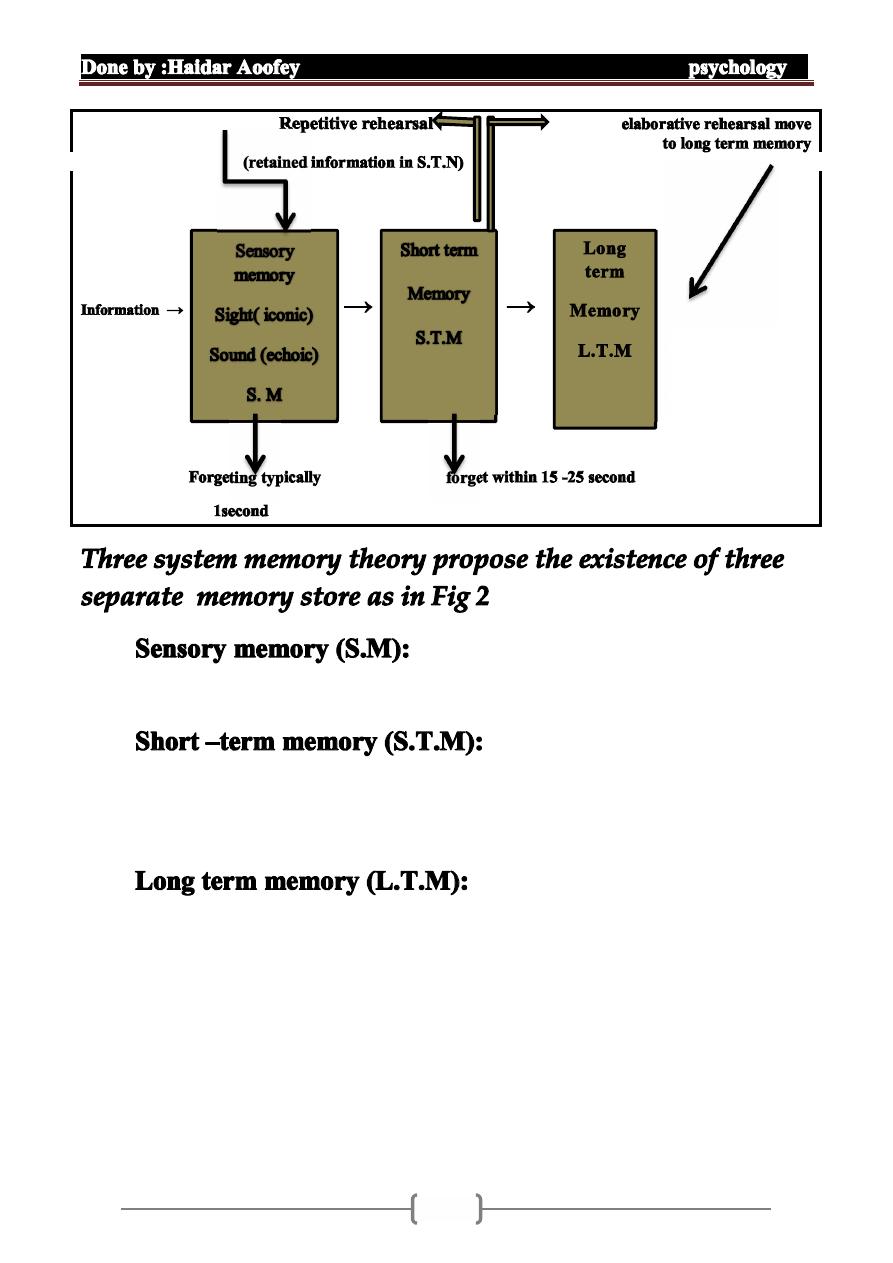
1.
refers to the intial , momentary
storage of information that last only an instant .
2.
hold information from 5-25
second and stored it according to its meaning rather than a
mere sensory stimulation
3.
information is stored in long –
term memory on a relation relatively permanent basis ,
although it may difficult to retrieve .

Stimuli that are initially & fleetingly stored. Actually there are
several type of sensory memory . example:-
:reflect information from visual
system like light flash .last less than 1 second .
:auditory information coming from
the ear .
fade within 2-3second .
S.M store information for short time , however its precision is
high
George-sperling (1960) : demonstrate S.M in series in
When exposed to this pattern of letter for just 1/2 of second ,
most people could call four- five letter accurately

Although they remember as they see more but the memory of
those letter had faded by time except the first 3-4 letter can be
verbalize.
The result show people had storing the complete pattern on
memory
They accurately recalled the letters in the line that had
indicated by tone regardless of whether it was top , middle or
bottom
Obviously all line they had been stored in sensory memory ,
despite rapid loss , then the information in sensory memory
was an accurate representation of what people had seen.
The decline to recall aparticular raw of pattern when tone was
sounded decline progressively as period between visual
exposure & the tone increased
Sensory memory operate as snapshot
that store
information which may be of visual , auditory , of the sensory
.
Because information that is stored in S.M is briefly
stored , so it is not meaningful to us
To make its meaningful this is carried out by retaining
Information should transfer to next stage of memory
which (S.T.M)

Is memory store in which
information first has meaning , although the maximum
length of retention is relatively short
The specific process by which sensory memory are
transformed in to S.T.M
The information transfer into graphical representation or
image
Other hypothesized that signs transferred to word
S.T.M has incomplete representation
Specific amount of information can held in . S.T.M has
identified as 7 item or ( chunk) of information up to
-+
5.
is meaningful group of stimuli that can be stored as unit in S.T.M
According to George ililler (1965)
Chunk can be individualized into letter or number permitting
as hold seven digit phone number (226 -4610 )in short
memory .
But chunk also composed of large categorized such as words
There are still 21 letter you would beable to be store in short
memory , since they represent only seven chunk .
Chunk can vary from single letter to number to categorized to
that form complicated .
The specific nature of chunk varies according to one s past
experience.
Although it is possible to remember 7 or so, relatively
complicated set of information can be held for long period ,
just how brief S.T. M
Transfer of material from short to long term memory .
By repetition as in short term memory
1. To maintain information
2. Transfer to long term memory :
a) From short term memory ..repetition to long T.M
b) In S.T.M ..no repetition ..replaced by other data
c) Elaborated rehearsal
Occur in information
Considered
organized in some fashion expand
information

1. Expand information to make it in logic form
2. Linking to each other
3. Turning to image
Organization called memonomic
memonomic
formal technique to organize in formation in
way make it more likely to be easily remembered .
It is short term memory that actively manipulate &
rehearse information .
Sensory information
new information
Pull old material from long term storage
1. Central executive that involve ( reasoning & decision
marker )
2. Visual store visual & spatial information
3. Verbal stone hand & manipulate material relating to
speech ,word ,numbers.
4. Episodic buffer : connection between deferent data
W.M : keep our information active &brief so that we can do
something with information we use w.m
when we are doing multistep arthematic problem in our head
,storing the result of one calculation . whole move to next step
although W.M aid to recall information

1. it is use significant amount of cognitive resource during
operation.
2. if phonic conversation require it well be burden memory
Information take its way from short term memory to long
term memory through stored use of almost unlimited capacity
(like new hard drive )
In long term memory in formation already file & codded , so
that can retrieve when needed .
Brain damage some patient have no, lasting recall of new
information received after damage occurred . although people
& events stored in memory before the injury remain intact .
Laboratory experiment are also consistent with separation of
short term memory ,long term memory .
Example :
In one study people were asked a relatives small amount of
information ( such as set of three letter)
Some externous material aloud , such as counting 3 back
ground by varying the amount of time between presentation of
initial material & the need for investigation found that recall was
quite good , when the interval was very short , but decline rapidly

Therefore, often 15 second had gone by recall hovered around 16%
of material initially present .
Recent research now regard long-term memory as having several
different component or (memory modules)
Each represent separate memory system in the brain .
Memory of factual information , ..like name , face , date & fact
Like bicycle has 2 wheel .
Refers to memory for skill & habit such as how to ride a bicycle
, football , information about how to do the things .
for general knowledge & fact about world rule spell logic
that used to deduce the fact
Memory for event that occur in special time & place ,
context , for example recall learning how to ride a
bicycle
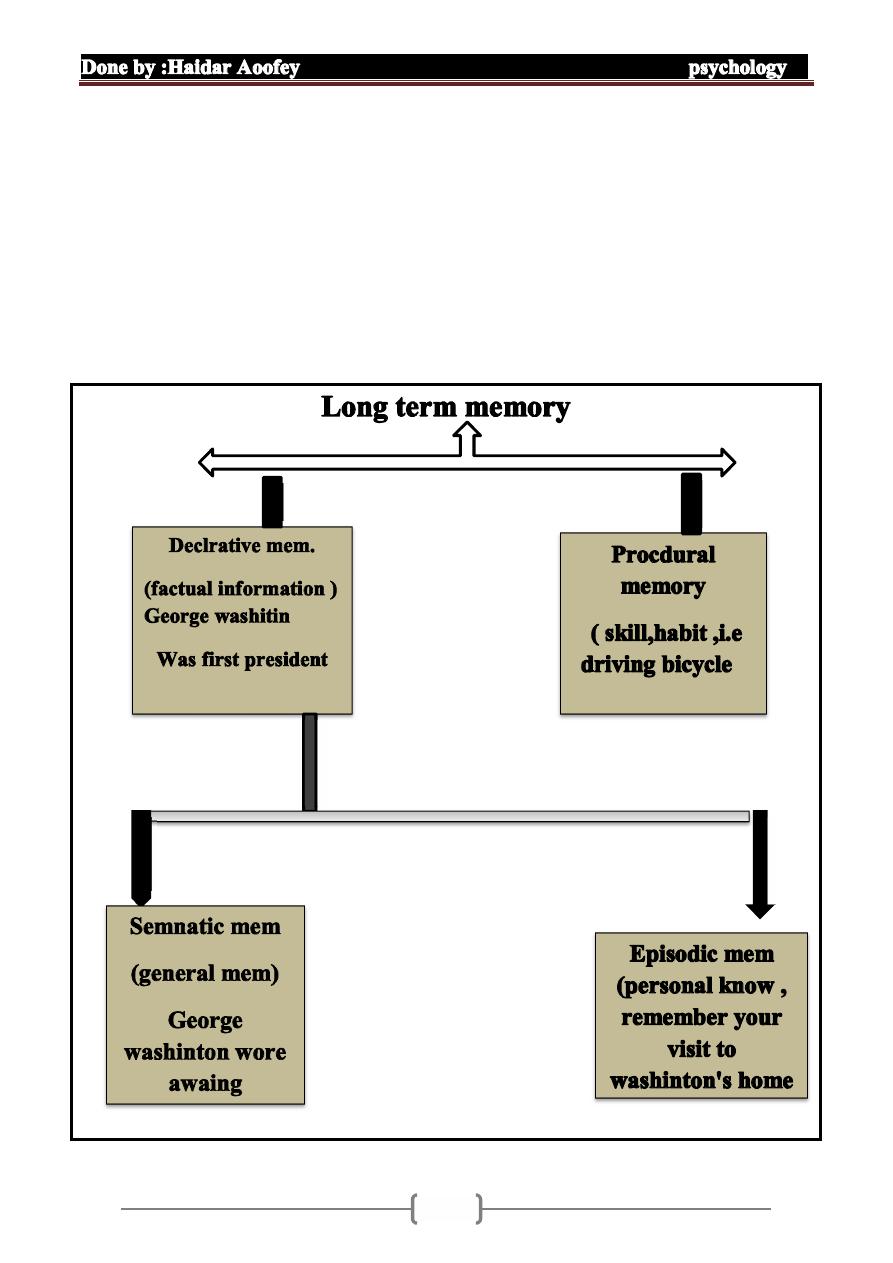
First kiss , episodic memory relative to special context,
also learning of the result of 7 9 =63
Episodic memory can provide information about event
that happened long in the post .
But semantic less than 5 substrate calculation
)
To recall thing we correlated related feature like
remembering fruit with red colour ( apple will come to
mind )
We are able to retrieve specific material from the vast
store of information in long term memory
Sematic network .. is mental representation of cluster
of interconnected information .
Thinking about special concept lead to recall of related
concept for e.g: seeing fire remind as for vehicle
the think of vehicle street bus ambulant
Is there is sigle site for L.T .M on any other memory ?
Is memory distributed in different place & brain ?
The search for the engram
& using a brain
scaning.
Certain area & structure in deferent type – memory
related .
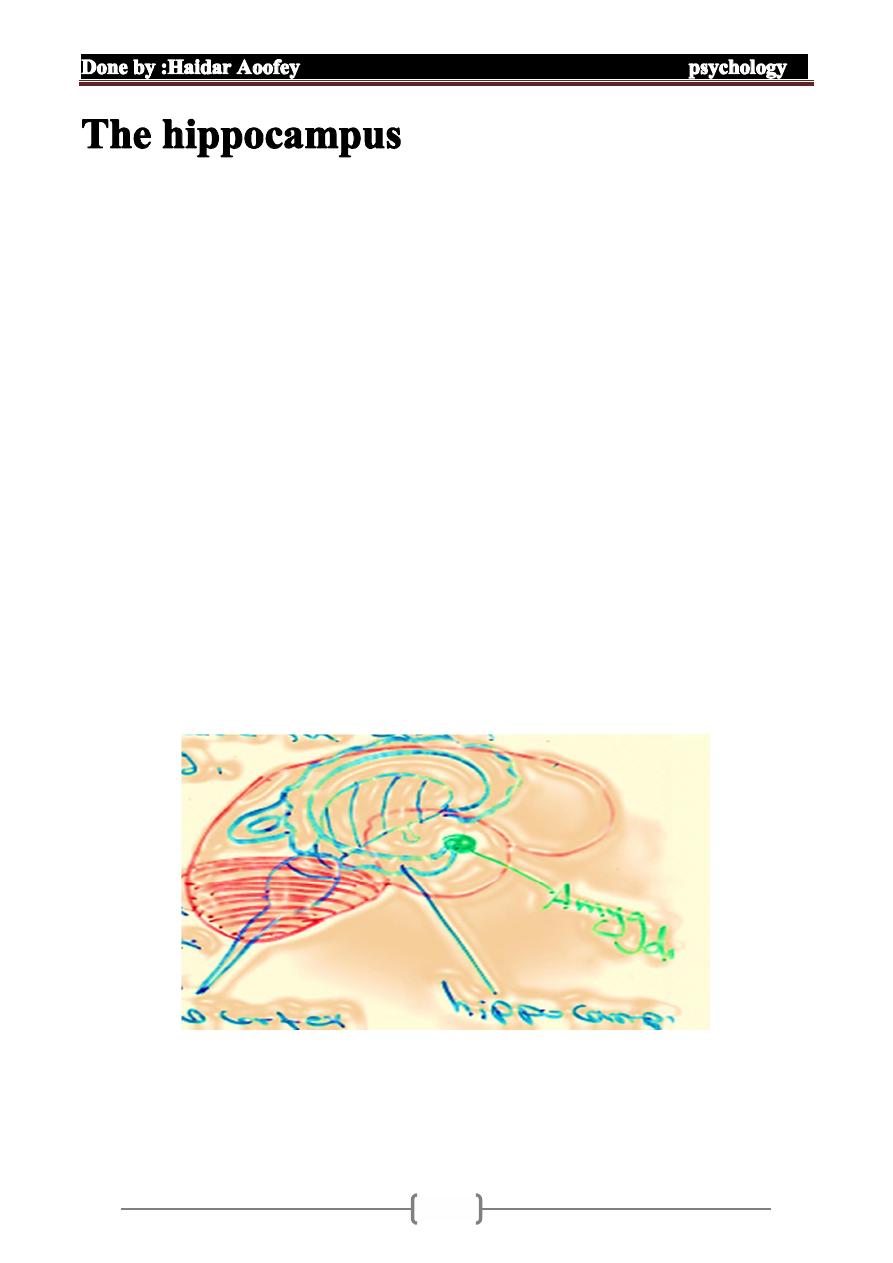
1. part of limbic system
2. play role in consolidation of memory
3. locate with medial temprol lobe
4. it initiate encoding of information
5. act as neurological – E:mail
6. information pass to central cortex where it is stored
taxi-driven in England must have accurate recall of
location of maze street
MRI study shows aback part of hippocampus is
larger than in taxi driven who spetial
&
navigational
memory were highly develop
Although hippocampus & amygdala play role in memory
but how data is transformed
1. Long term memory potentiation : certain neuron
Pathway become easlly excited while new response
been learned & synapse between these neuron start to
increase this in called consolidation
2. Visual stimulation visual center
-----------------------------------------
memory trace in brain
3.
Auditory center
rise song



