ORAL HYGIENE MEASUREMENT
Dr.KHAWLA MOHAMMEDP.O.P DEPAREMAMT
Good oral hygiene results in a mouth that
looks and smells healthy. It includes all the process to keep mouth clean and healthy.Good oral hygiene is necessary for prevention of dental caries, periodontal diseases, bad breath and other dental problems.
Dental plaque:
It is the non – mineralized, bacterial aggregation on the teeth and other solid structures in the mouthadherent to the surface that is resists removal by salivary flow or a gentle spray of water across its surface.
or Structured , resilient , yellowgrayish
substance that adheres tenaciously tointraoral surfaces including
removable and fixed
restorations.
Did you know ?
Bacteria[plaque] forms in 2-3 hours afterbrushing and flossing.
Flossing can increase your span to 6.4 years.
Flossing delays the effect of aging.
Smoking may lead to more than half of all cases
of gum disease.
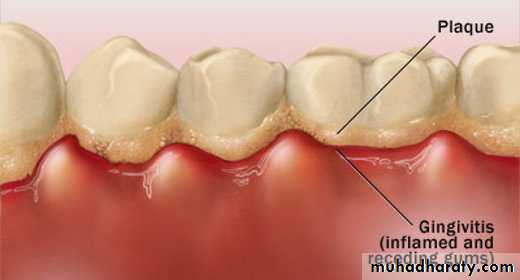
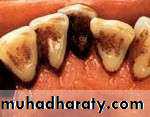
Plaque become mineralized to form calculus.
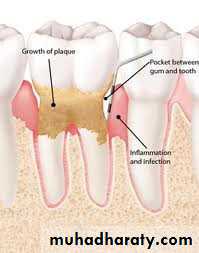
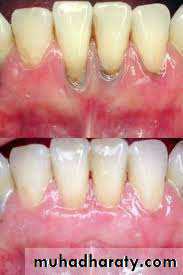
Bacteria in the plaque release acids from sugar rich foods → erode enamel surface→dental cariesPlaque build-up beneath the gumline cause gingivitis (gingival erythema, edema, bleeding, changes in contour, loss of tissue adaptation to the teeth.
Dental calculus:
Mineralization with in plaque result in calculus formation.The inorganic content of calculus (70 – 90 %) is mostly crystalline amorphous calcium phosphate. The organic component includes protein, carbohydrates, lipid, and various non – vital microorganisms.
Stain:
It is caused by food substances such as tea, coffee and , by tobacco, by the products of chromogenic bacteria or by metallic particles. The pigments become absorbed by plaque or pellicles.Factors predisposing to plaque accumulation:
A. Anatomical factors as:
Tooth malalignment.
Crowding.Tipped or rotated teeth.
B. Dental (Iatrogenic) factors are often result of poor quality dental treatment or treatment planning as:
Rough surfaces of restoration which accumulate plaque more readily than a well – finished or highly polished restoration.
Overhanging or defective cervical margins of restoration act as retention site for dental plaque.
Subgingival restoration margins which lead to greater plaque accumulation.
Removable partial denture.
Fixed orthodontic appliance.
Factors modifying the inflammatory response:
Smoking.Diabetes.
Oral hygiene measure
1. Periodontal health education:The objective of oral hygiene education is to produce a change in behavior, which will result in a reduction of plaque accumulation:
Dental hygiene advice.
Dietary advice.
Smoking cessation advice.
2.plaque removal 2.plaque removal
2.plaque removalWe have different ways and methods to remove dental plaque :
1.mechanical method.
2.natural method.
3.chemical method.
4.professional method.
Mechanical method:
1.Tooth brushing (manual):Design variation in tooth brushes include:
The length, diameter and moduls of elasticity of the filaments.
Dimensions of the head.
Number, distribution and angulation of the filaments.
V SHAPED BRISTLECRISS
CROSS BRISTLEPOLISHING CUP BRISTLE
PARTS OF TOOTHBRUSH
• Bristles• Head
• Handle
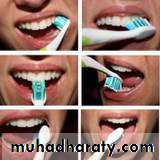
Tooth brushing methods:
They are categorized according to the direction of the brushing storke:• Vertical.
• Horizontal.
• Roll technique.
• Vibrating technique.
• Circular technique.
• Physiological technique.
• Scub brush method.
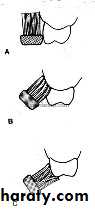
Roll (sweep) technique:
The brush is placed on the attached gingiva close to the gingival margin of the teeth with bristles pointing apically in 30-40 degree angle to the long axis of the teeth then with a rolling or sweeping stroke,the brush is moved in a coronal direction until the bristles make 90 degree angle with the tooth surface at the occlusal edge of the teeth,
only moderate pressure is applied
and the movement are repeated five to six times for each segment covered by the brush,
from the lingual and palatal side only few teeth can be covered by each movement of he brush
occlusal clean with horizontal stroke, the brush is used hard or medium.
Brushing Your Teeth
Advantages:• Easy to learn.
• Require moderate skill.
Disadvantages:
Dose not clean sulcus area.
If hard brush is used carelessly may produce damage to gingiva.
TOOTH BRUSHINGOUTCOME DEPENDS ON
• 1.The design of the tooth brush• •2. The frequency of brushing
• •3. Duration of brushing
• • 4.The skill of the individual.
TOOTH BRUSHREPLACEMENT
• Tooth brush should bereplaced when first sign of
filament is worn.
• Average life 2-3 months
• Newer brush are more
effective in removing
plaque
2.Powered tooth brushes:
Used in specific patient groups:With fixed orthodontic appliances.
Children and adolescents with a physical or learning disability.
Institutionalized patients.
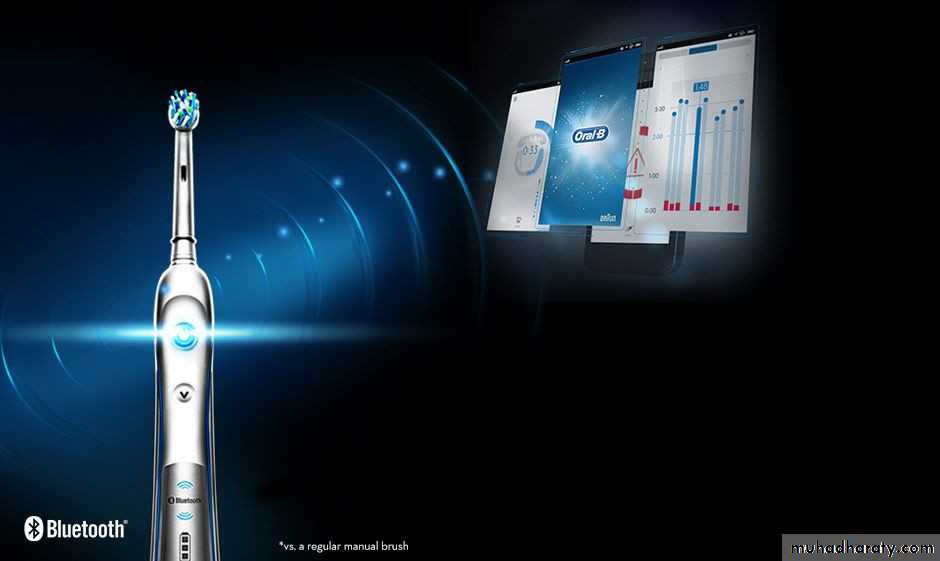
NEWER ADVANCEMENTS
Tooth brush with
BLUETOOTH CONNECTIVITY
ULTRASOUND TOOTHBRUSH
3. Cleaning between the teeth:
1. Wood points (tooth picks):Is effective only where sufficient inter – dental space is available to accommodate it. it used in case of bone resorption when there is spaces between teeth.
types:
Triangular (best one).
Round.
Rectangular.
Dental floss:
Need digital skill, time consuming than wood point. Take 30 cm and use it between the teeth toward the proximal surfaces of teeth and not downward, when there is no space between teeth. Best done before brushing.Types:
• Unwaxed dental floss
recommended for patients with
normal tooth contacts
• Waxed dental floss - tight tooth
Contact(CL2 RESTORATION)
• Powered floss - with special
handle - No significant
difference in plauqe removal
but preferred by patients due to
ease of use.
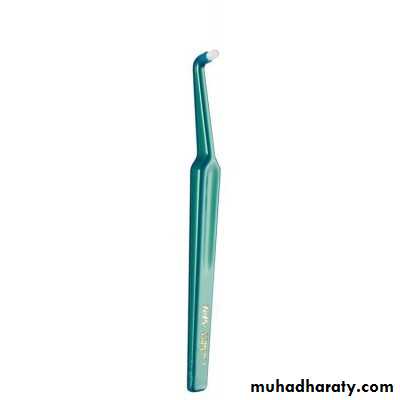
3.Inter space brush (Single – tufted tooth brush):
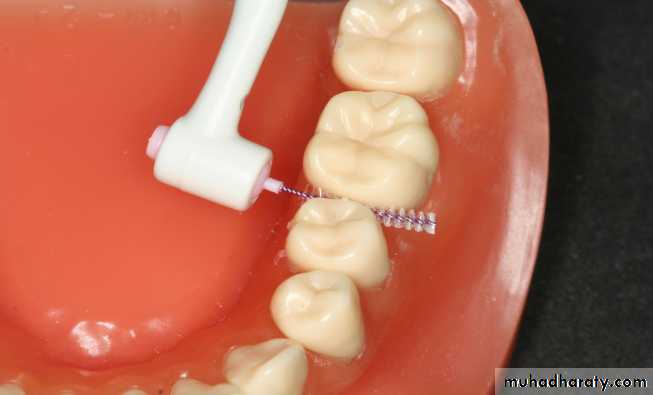
This device was introduced to improve access to tipped, rotated or displaced teeth and teeth affected by gingival recession.4. The inter dental brush (bottle brush):
Used for cleaning of open interdental space.
Types:
Larger type: held by its wire handle.
Smaller type: with metal or plastic handle.
5. Irrigation devices:
These provide a steady or pulsating stream of water escaping through a nuzzle under pressure. Oral irrigation should not be use as a substitute for tooth brushing, and are time consuming and messy to use.• Employed in supragingival irrigation
• Can be power or non power driven
• Available with interchangeble tips
• Easy to use
• Performed by any individual
. No clinical setup required
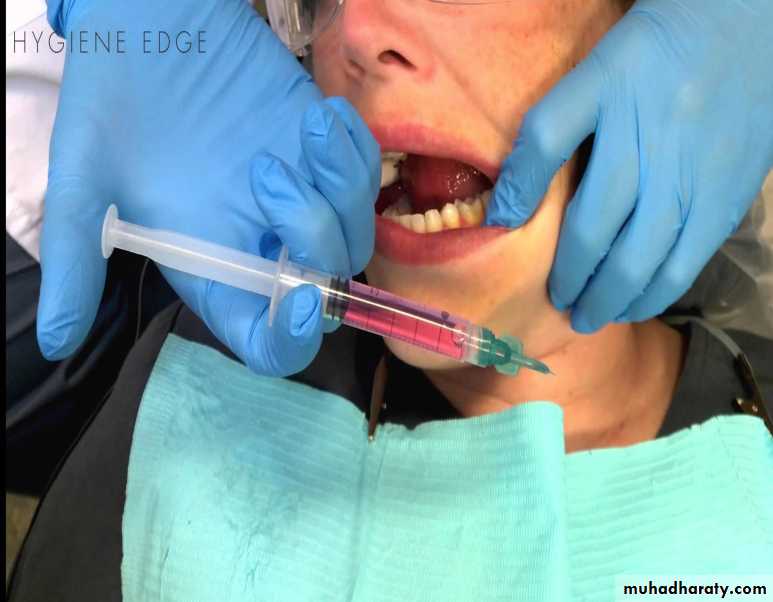
PROFESIONALLY APPLIED
• iNDICATED IN SUBGINGIVAL IRRIGATIONaided by
Syringe
Jet irrigator with a cannula
Ultrasonic unit
Natural method
1.fibrous foods: like apple, carrot, because these foods contain fibrous filaments and malic acid which stimulate the flushing of saliva.2. sugar free chewing gum: that stimulate the flow rate of saliva.
Avoid eating sweets & sticky foods, aerated drinks
Eats foods rich in fibre
Fruits & vegetables (natural cleansers)
Drinking plenty of water
Sip some water after eating that will help dilute the
acids
Rinse your mouth after meals
Chemical method (as Chlorhexidine):
is a chemical anti-septic material that can be bacteriocidal in high concentration and bacteriostatic in low concentration.Dose of mouth rinse:
10 ml of 0.2% twice daily.
15 ml of 0.12% twice daily
5-7 days and duration of rinsing is 2-3 minutes.
Mouth Rinsing should be used in this manner
1. Regular Rinsing with a good mouthwash helps to
keep your mouth germs free, clean and fresh.
2.Daily rinses must be alcohol free (They cause
• dryness of oral )
• 3.Fluoride rinses helps to boost the strength of newly
• erupted teeth.
• 4 It is important to follow manufacturer’s instructions.
Side effects:
• Taste disturbance:• Staining: the development of a yellow brown stain on teeth and tongue and margins of anterior restoration.
• Desquamative lesions of the oral mucosa.
• Parotid gland swelling.
• 5.Supragingival calculus formation.
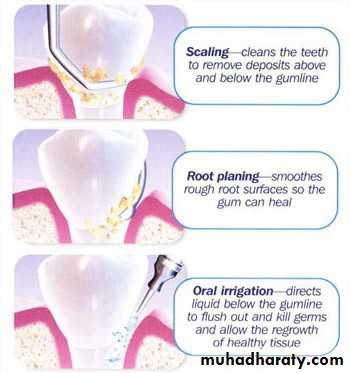
Professional Cleaning:
Scaling and polishingroot planning.
Scaling alone is sufficient to completely remove plaque and calculus from enamel leaving a smooth clean surface which will facilitate plaque removal for the patient.
Thank you
A healthy mouth and healthy body go hand in hand.Good oral hygiene and oral health can improve your
overall health, reducing the risk of serious disease
and perhaps even preserving your memory in your
golden years.