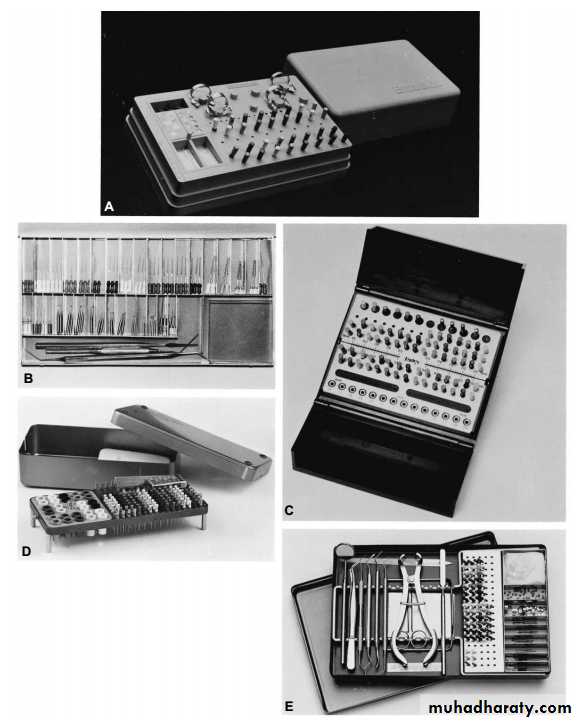
Endodontic Instruments
Dr. Abduladheem R. Sulaiman
Conservative Dentistry1
CLASSIFICATION OF ENDODONTICINSTRUMENTS
ISO - FDI (Federation Dentaire International) :grouped rootcanal instruments according to their method of use:Group I : Hand use only for example, K and H-files, reamers,broaches, etc.Group II : Latch type Engine driven: Same design as groupI but can be attached to handpiece.Group III : Drills or reamers latch type engine driven forexample, Gates-Glidden, Peeso reamers.Group IV : Root canal points like gutta-percha, paper point.2
Alloys Used for Manufacturing Endodontic Instruments
• Carbon steelb. Stainless steelc. Nickle-titanium .a. Carbon steel:
Advantage: They have high hardness
than stainless steel instruments.Disadvantages• Prone to corrosion, so cannot be
re-sterilized• Prone to rust.b. Stainless steel instrumentsAdvantage: Corrosion resistantDisadvantages:• Stiff in nature• Prone to fracture• Prone to distortion
3
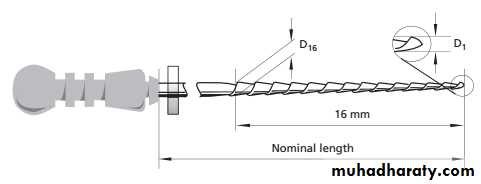
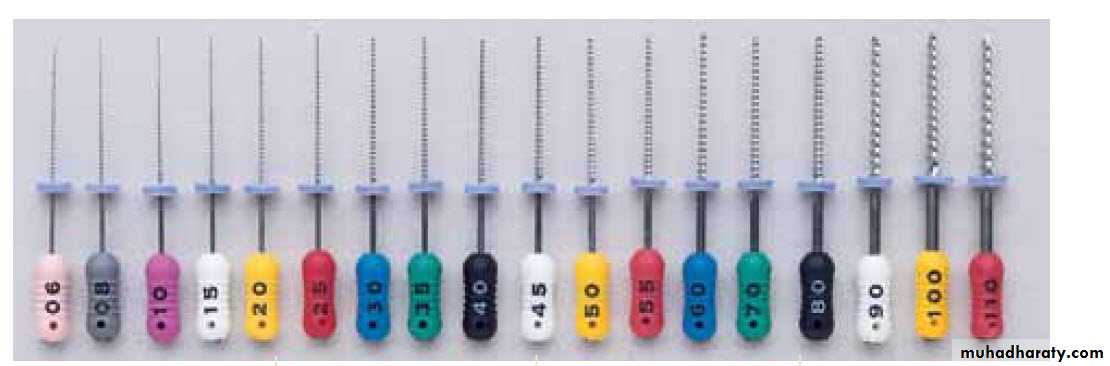
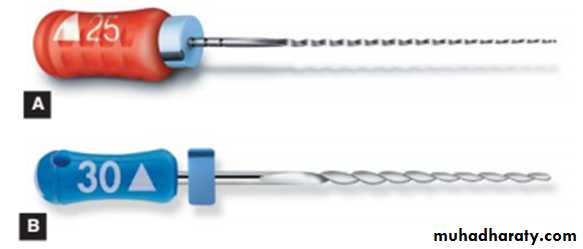
Standardization of Endodontic Instruments• Instruments are numbered from 10-140. There is increase in (5) units up to size 60 and in (10) units till size 140.(Now there is no. 6, 8)• Each number should represent diameter of instrument in 100th of millimeter at the tip.• Working blade shall begin at tip (D1) and extend 16 mm up the shaft (D2). D2 should be 0.32 mm greater than D1, ensuring that there is constant increase in taper, i.e 0.02 mm per mm of instrument. The nickel titanium rotary instruments have other variable tapers of 0.04 and 0.06. For every millimeter of length, the diameter increases by 0.04 or 0.06 mm. These greater tapers make these more aggressive in creating marked flaring preparation.• Instruments are available in following lengths: 21, 25, and 31 mm. Shorter instruments afford improved operator control and easier access to posterior teeth, to which limited opening impairs access. The 25- and 31-mm instruments are used for longer roots.
4
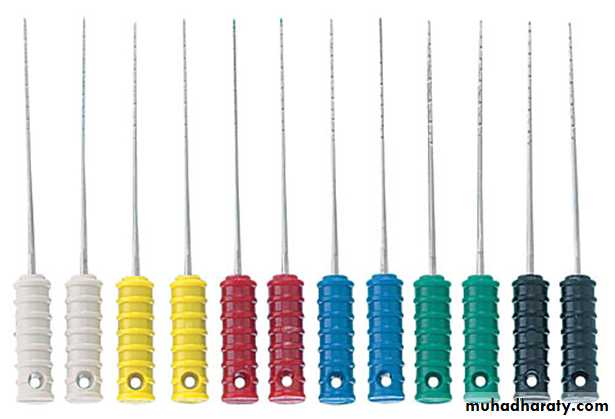
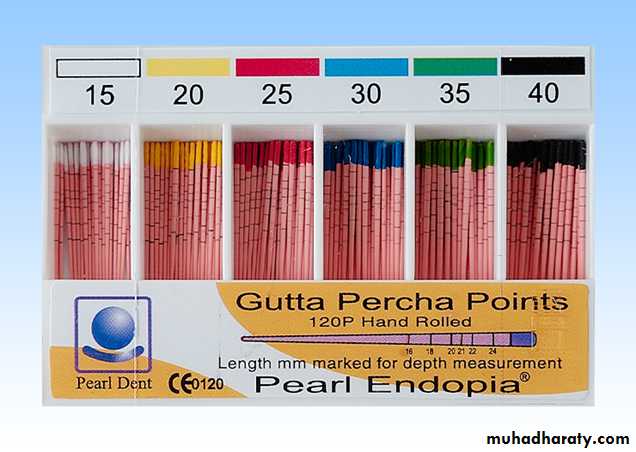
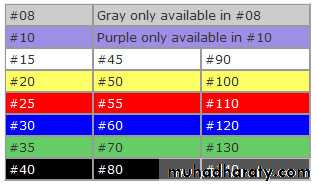
• Instruments handles should be color coded for their easier recognition (Pink, grey, purple, white, yellow, red, blue, green, black………….)
5
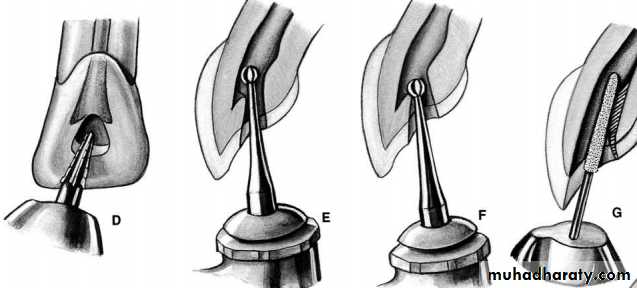
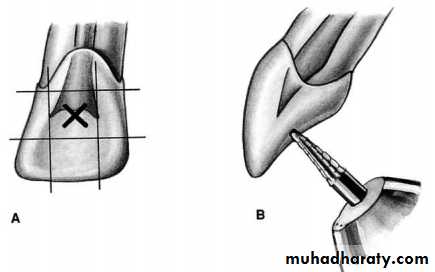
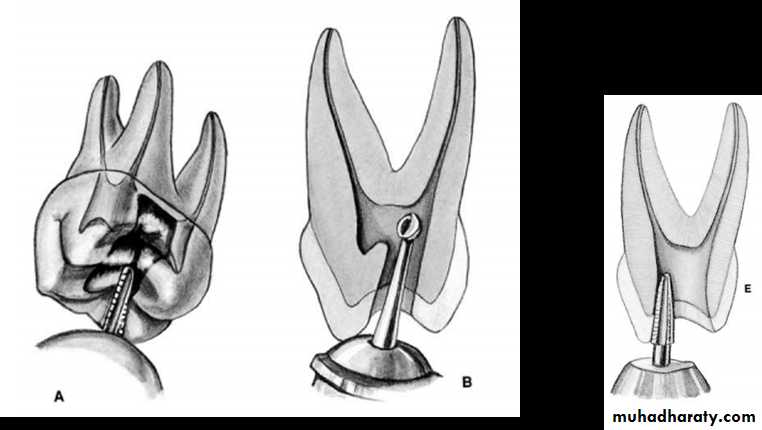
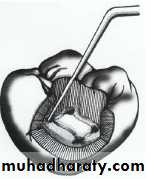
Instrument s for access cavity preparation
Turbine, Handpiece and bursName
BursFunction
several types of burs will be used to accomplish good access preparation. Fissure burs are used in the initial stage of access preparation to establish the correct outline form ,Round burs are used to lift the roof of the pulp chamber and eliminate overhanging dentine ,Tapered Non end-cutting bur is used to 'lift lid' of pulp chamber and refine cavity.
6
7
Root canal explorer
NameProbe/root canal explorer
Function
Used to probe and detect canal orifices within the
pulp chamber
8
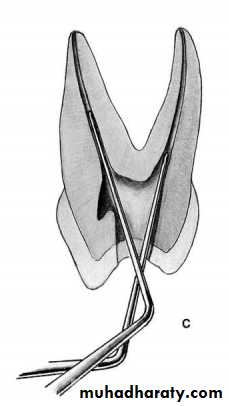
Endodontic plier:
Nonlocking and locking pliers for gutta-percha and absorbent points. The working part has grooves for holding of points.9
endodontic spoon excavator
Function
"larger than conventional excavator" its shape allows curettage of the pulp chamber when conventional one will not reach the floor of the chamber, and used as surgical aid to excavate periapical lesion.10
Instruments for root canal preparation
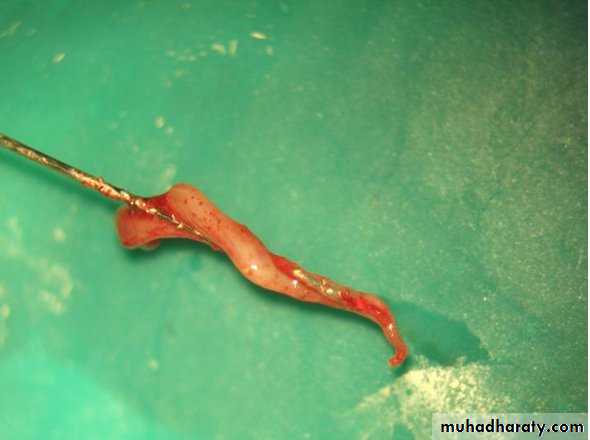
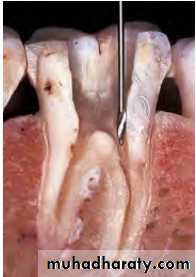
Extirpation Instrument
NameBarbed broaches
:Functions
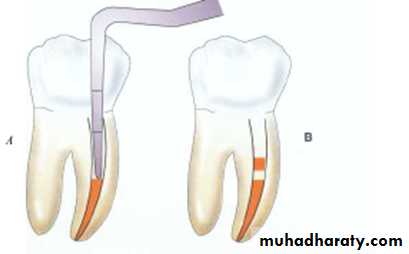
1- Used to remove the intact pulp
2-Retrieve a paper point or cotton pellet trapped in the canal
• ‘Barbs’ on the broach snag the pulp to facilitate removal
• Broach does not cut the dentin
• Broach should not be forced apically into the canal.
11
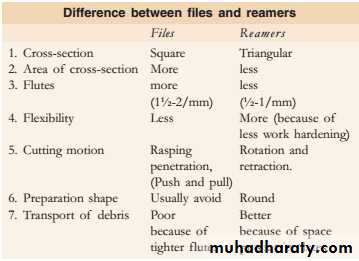
Reamers1. Reamers are K-type instruments (manufactured by Kerr company), which are used to ream the canals. They cut by inserting into the canal, twisting clockwise one quarter to half turn and then withdrawing, i.e.penetration, rotation and retraction.2. Reamers have triangular blank and lesser number of flutes than files
12
• Files
Files are the instruments used during cleaning and shaping of the root canals for machining of the dentin. Since Kerr manufacturing company was first to produce them, the files were also called K-files.Files are predominantly used with filing or rasping action in which there is little or no rotation in the root canals. It is placed in root canal and pressure is exerted against the canal wall and instrument is withdrawn while maintaining the pressure (Push-Pull Motion)
13
14
Though reamer has fewer numbers of flutes than file, cutting efficiency is same as that of files because more space between flutes causes better removal of debris.
15
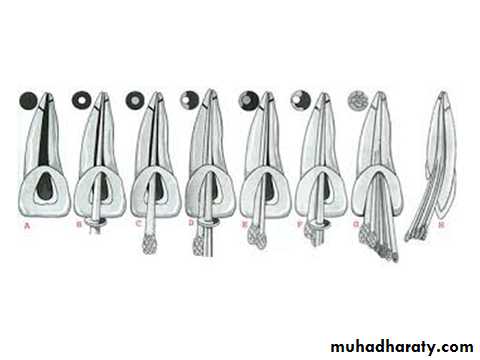
Types of files
1- K-files• They are triangular, square or rhomboidal in cross-section, manufactured from stainless steelwire.• Tighter twisting of the file spirals increases the number of flutes in files (more than reamer).• Triangular cross-sectioned files show superior
cutting and increased flexibility than the file or reamers with square blank
16
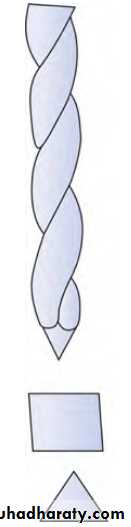
2- K-flex Files
• It was realized that square blank of file results in total decrease in the instrument flexibility. To maintain shape and flexibility of these files, K-flex files were introduced.• K-flex files are rhombus in cross section having two acute angles and two obtuse angles.• Two acute angles increase sharpness and cutting efficiency of the instrument.• Two obtuse angles provide more space for debris removal. • They are used in filing and rasping motion.17
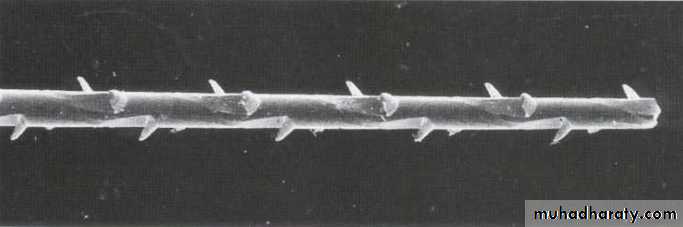
3- Hedstrom Files (H-files)
• Hedstrom files have flutes which resemble successively triangles set one on another.• They are made by cutting the spiral grooves into round, tapered steel wire in the same manner as wood screws are made.
• Hedstrom files cut only when instrument is withdrawn because its edges face the handle of the instrument.• When used in torquing motion, their edges can engage in the dentin of root canal wall and causing H - files to fracture.
• Hedstrom files should be used in straight canals because they are strong and aggressive cutters. Since they lack the flexibility and are fragile in nature, the H-files tend to
fracture when used in torquing action.
18
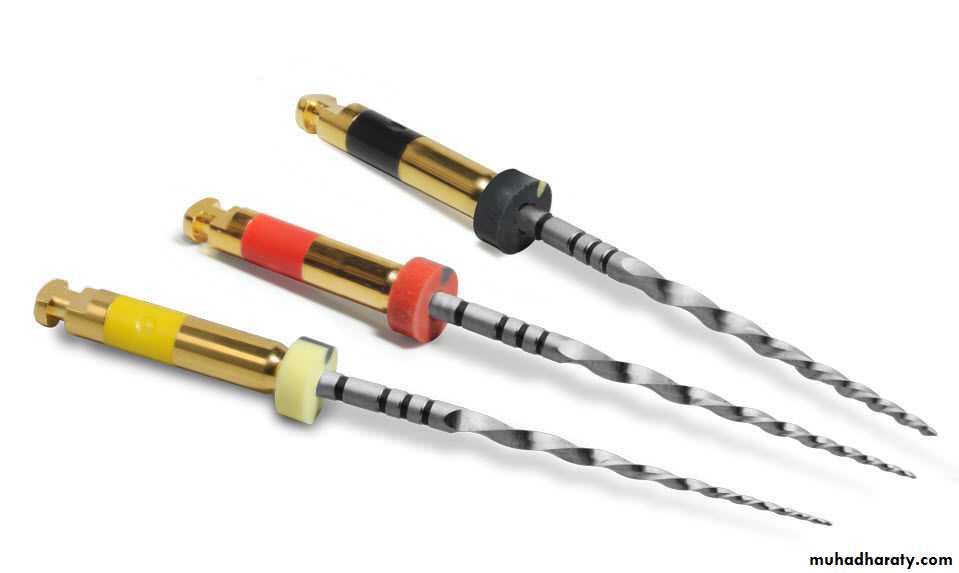
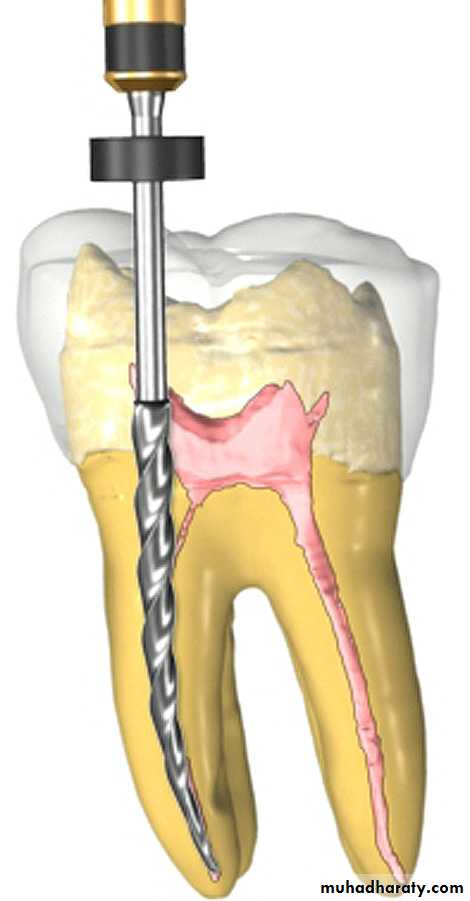
ENGINE DRIVEN INSTRUMENTS1- Gates-Glidden Burs
• Traditional engine driven instruments include Gates-Glidden drills which have flame-shaped cutting point mounted on long thin shaft attached to a latch type shank.• Gates-Gliddens are available in a set from 1 to 6 with thediameters from 0.5 to 1.5 mm.• Due to their design, Gates-Glidden drills are side cuttinginstruments with safety tips.19
Uses of Gates-Glidden Drills1. For coronal flaring during root canal preparation2. During retreatment cases or post space preparation for removal of gutta-percha.3. Widen the canal when an instrument has fractured within it.
If used incorrectly, for example using at high rpm, incorrect angle of insertion, forciful drilling, the use of Gates-Glidden can result in procedural accidents like perforations, instrument separation.
20
2- PEESO REAMERS• They are rotary instruments used mainly for post space preparations.• They have safe ended non-cutting tip.
• Their tip diameter varies from 0.7 to 1.7 mm.• They should be used in brushing motion.
Disadvantages of using peeso reamers are:1. They do not follow the canal curvature and may cause perforation by cutting laterally.2. They are stiff instruments.3. They have to be used very carefully to avoid iatrogenic errors.
21
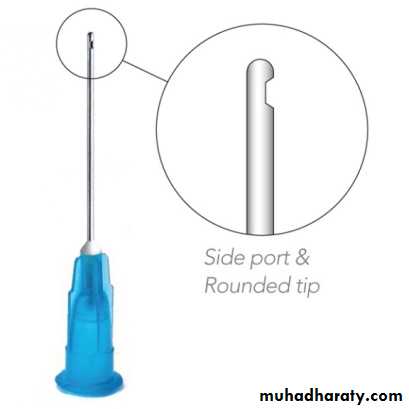
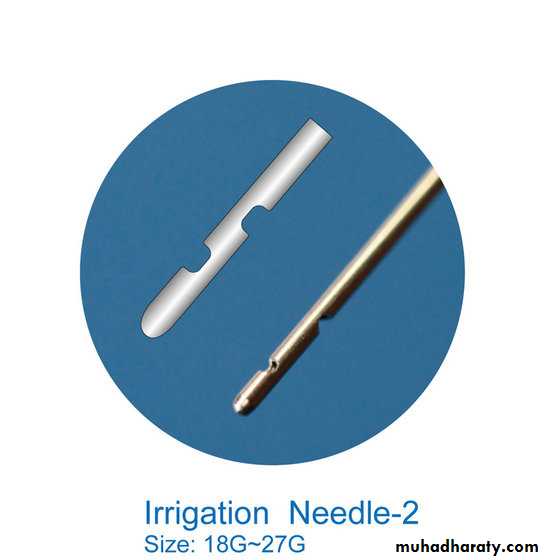
Disposable irrigating syringe and disposable irrigation needle
Paper points: used to dry the canals after irrigationGutta percha: used for obturation of root canal space
22
Instruments used for root canal Filling
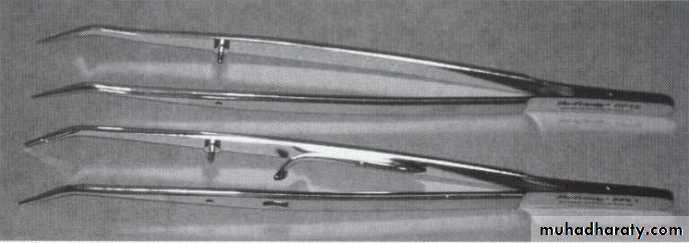
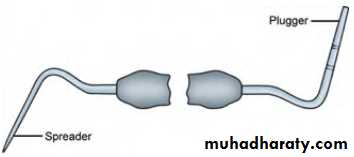
Spreaders and pluggersAre the instruments used to compact the gutta-percha into root canal during obturationA- Hand Spreaders• They are made from stainless steel and are designed to facilitate the placement of accessory gutta-percha points around the master cone during lateral compaction technique• These spreaders do not have standardized size and shape.• They are not used routinely because excessive pressure on the root may cause fracture of root.
23
B- Finger Spreaders
• They are shorter in length which allows them to afford a great degree of tactile sense and allow them to rotate freely around their axis.• They are standardized and color coded to match the size of gutta-percha points.• They can be manufactured from stainless steel or nickel titanium24
Pluggers
A- Hand Pluggers• They consist of diameter larger than spreader and have blunt end .• They are used to compact the warm gutta-percha verticallyand laterally into the root canal.• They may also be used to carry small segments of gutta percha into the canal during sectional filling technique.• Calcium hydroxide or MTA like materials may also be packedinto the canals using pluggers.25
B- Finger Pluggers
• They are used for vertical compaction of gutta-percha. They apply controlled pressure while compaction, and have more tactile sensitivity than hand plugger.
Care should be taken with spreaders and pluggers while compacting the gutta-percha in canals. They should be cleaned prior to their insertion into the canal; otherwise the set sealer from previous insertion may roughen their surface and may pull the cone outside the canal rather than packing it. Also one should discard the instrument when it has become bent or screwed to avoid instrument separation while compaction.
26
Lentulo spiral
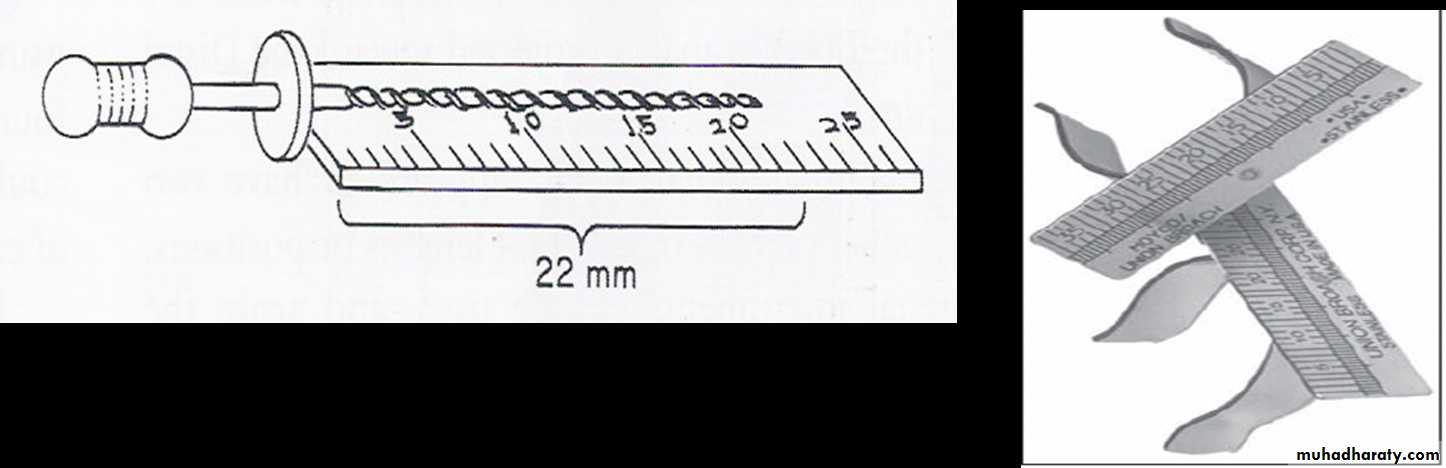
• They are used for applying sealer to the root canal walls before obturation.• They can be used as hand or rotary instruments.Endodontic ruler
Used for measuring the length of instruments27
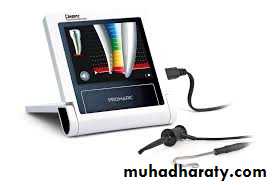
Electronic Apex Locators
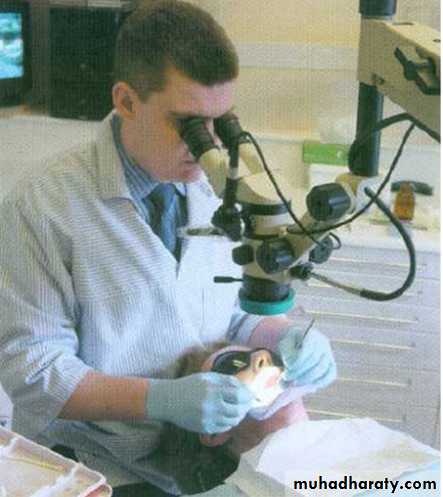
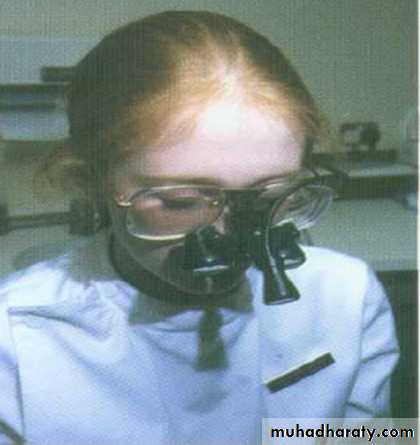
• An electronic instrument used to determine the distance to the apical foramen(Working length)Operating loupes and microscopes:
Illumination and magnification are vital for the location of root canals. The endodontist would use a surgical microscope while a general dental practitioner might have loupes and a headlight that give excellent magnification and illumination.28