
Arthrology
•
Field of study concerned with the
study of joints.

Definition of joint
Is the articulation between boney
surfaces wich allow free or limited
movement.
The classification is according to the
type of material by wich the
articulating bones are united.
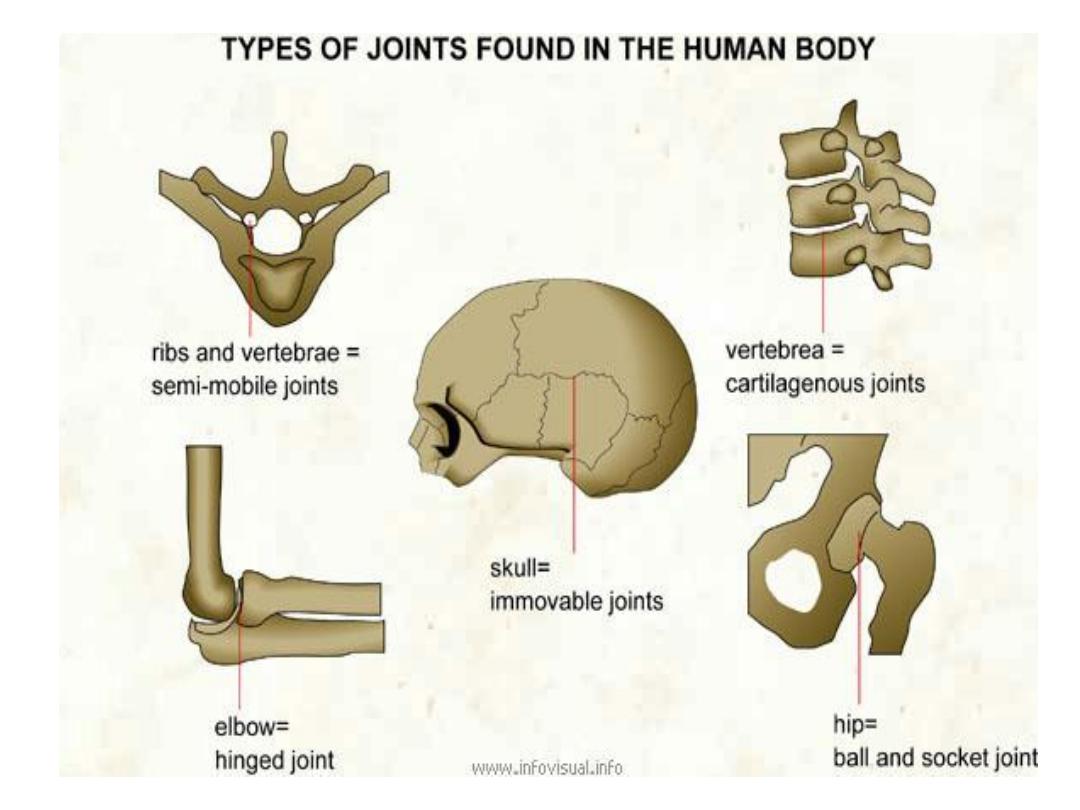

classification
•
1-fibrous joints
*
syndesmosis
•
*
sutural joints
•
*
gomphosis
(teeth)
•
2-Cartilagenous
*
symphesis
•
*
synchondrosis
•
3-Synovial joints (6)

2. Solid joints:
of two types fibrous and cartilaginous
1. Fibrous : The articulating surfaces of the
bones are
joined by fibrous tissue. thus there is very
little
movement
a.
Sutures
of the vault of the skull, where
adjacent
bones are lined by thin layer of connective
tissue
termed a sutural ligament.
.

b.
Syndesmoses
: The two adjacent bones are
linked
by a ligament or by an interosseous membrane ,
eg.
Ligamentum flavum which connects adjacent
vertebral
lamina and interosseous membrane which links
the
radius and ulna.
c.
Gomphosis
: occur only between teeth and
adjacent bone , short collagen tissue fibres in the
periodontal ligament run between the root of the
teeth
and the bony socket
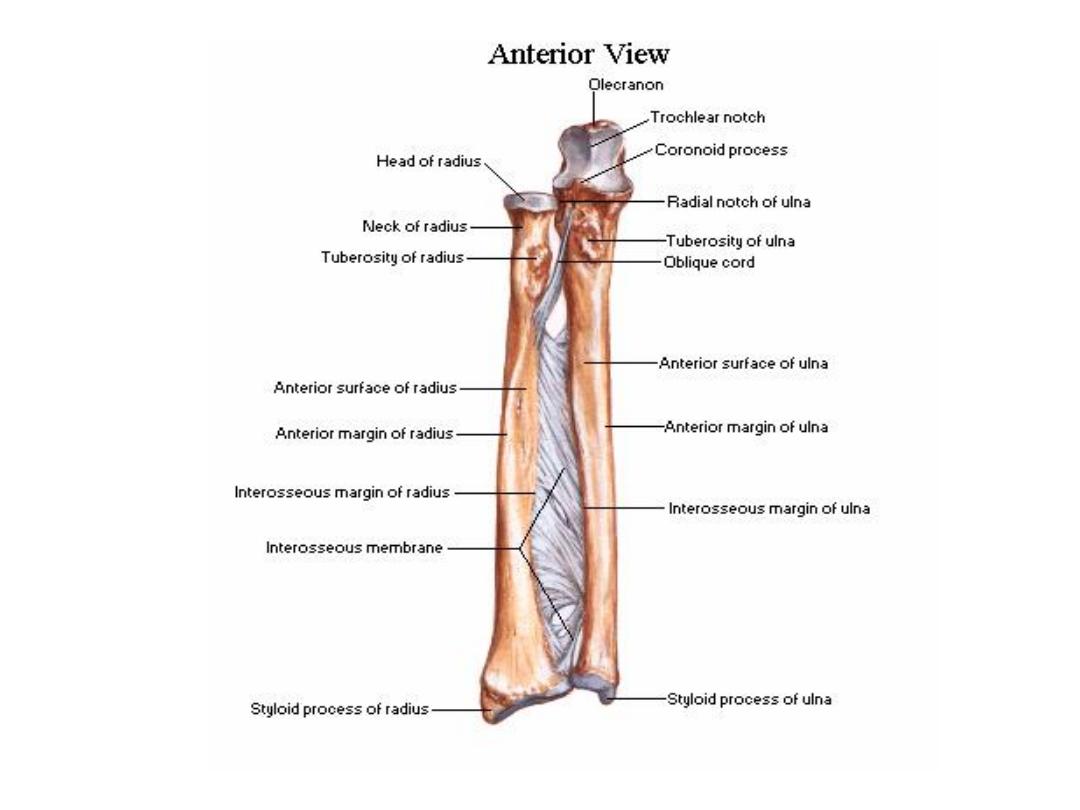

FIGURE The side-to-side
articulation of the ulna and
radius
forms a syndesmotic joint. An
interosseous ligament tightly
binds
these bones and permits only
slight movement between
them.

2 . Cartilaginous Joints : of two types
a.
Synchondrosis
or Primary cartilaginous
j.
Bones are united by plate of hyaline
cartilage
eg. Union between the epiphysis and the
diaphysis of a growing bone, eg.2
between first
rib and manubrium sterni, no movement
is
possible.

A fracture of a long bone in a child may be
extremely serious if it
involves the mitotically active epiphyseal
plate of a synchondrotic
joint. If such an injury is left untreated,
bone growth is usually
retarded or arrested, so that the
appendage will be shorter
than normal.

b.
Symphyses
or Secondary Cartilaginous J .
Bones are united by a plate of
fibrocartilage,
and the articular surfaces are covered by
thin
plate of hyaline cartilage eg. Joints between
vertebral bodies, eg . symphysis pubis, small
amount of movement is possible.


Types of Joint
A joint is the point where two or
more bones meet. There are three
main types of joints; Fibrous
(immoveable), Cartilaginous (partially
moveable) and the Synovial (freely
moveable) joint
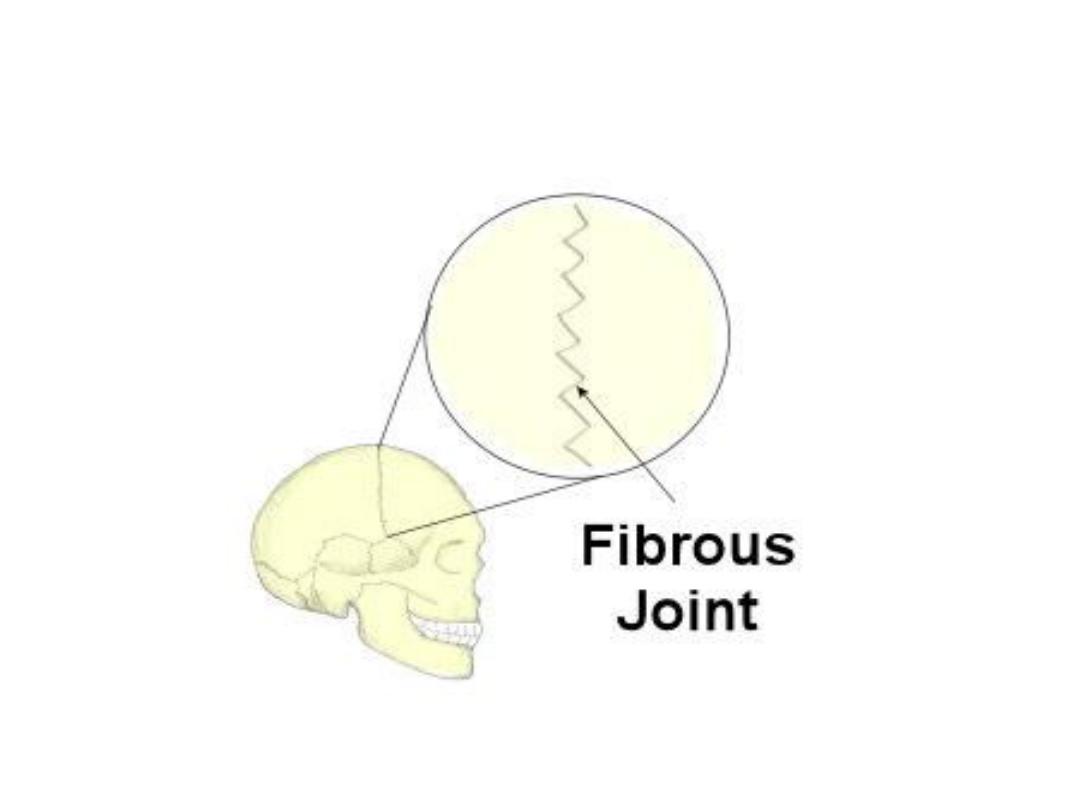

Fibrous joints
Fibrous (synarthrodial): This type of joint is
held together by only a ligament. Examples
are where the teeth are held to their bony
sockets and at both the radioulnar and
tibiofibular joints.sutural joints.
Cartilaginous
Cartilaginous (synchondroses and
sympheses): These joints occur where the
connection between the articulating bones
is made up of cartilage for example
between vertebrae in the spine.
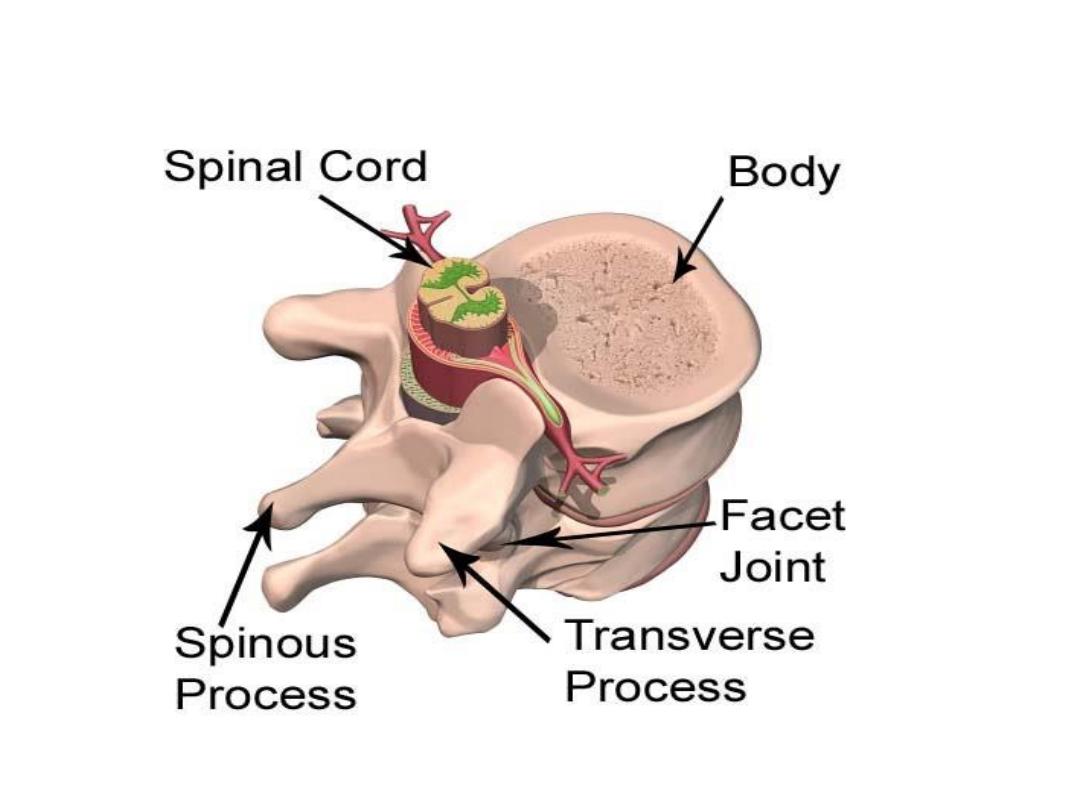
A cartilagenous joint between two vertebrae

Synchondroses
are temporary
joints which are only present in
children, up until the end of
puberty. For example the
in long bones.
Symphesis joints are permanant
cartilagenous joints, for example
the pubic symphesis.

Synovial Joints
Synovial (diarthrosis): Synovial joints are by far
the most common classification of joint within
the human body. They are highly moveable
and all have a synovial capsule (collagenous
structure) surrounding the entire joint, a
synovial membrane (the inner layer of the
capsule) which secretes synovial fluid (a
lubricating liquid) and cartilage known as
hyaline cartilage which pads the ends of the
articulating bones. There are 6 types of
synovial joints which are classified by the
shape of the joint and the movement
available.

Types of Synovial Joint
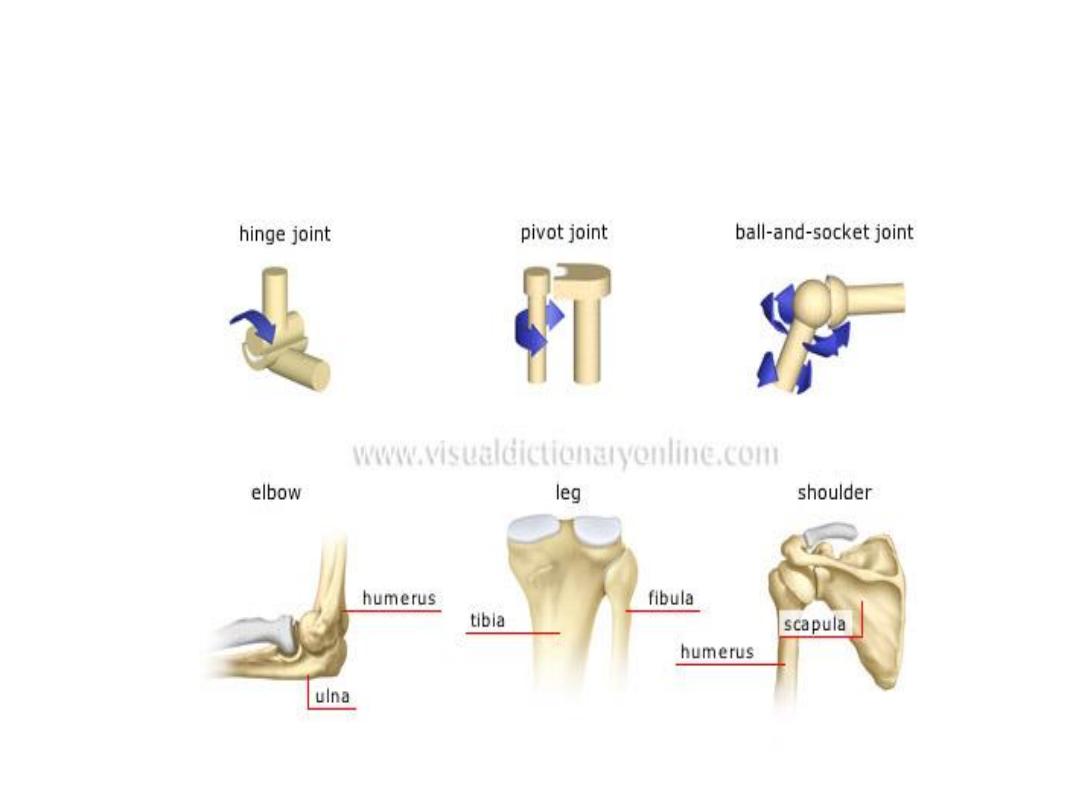
Hinge
Flexion/Extension
e.g tibiofemoral joint
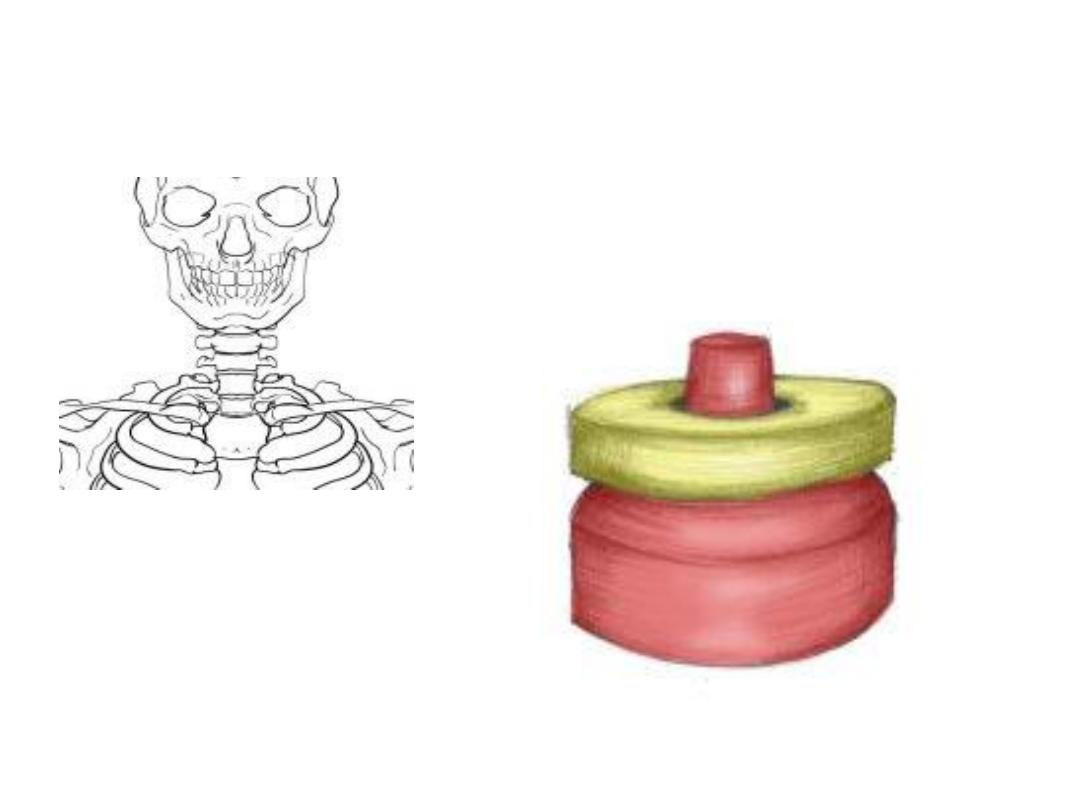
Pivot
Rotation of one bone
around another
Top of the neck
(atlas and axis bones)
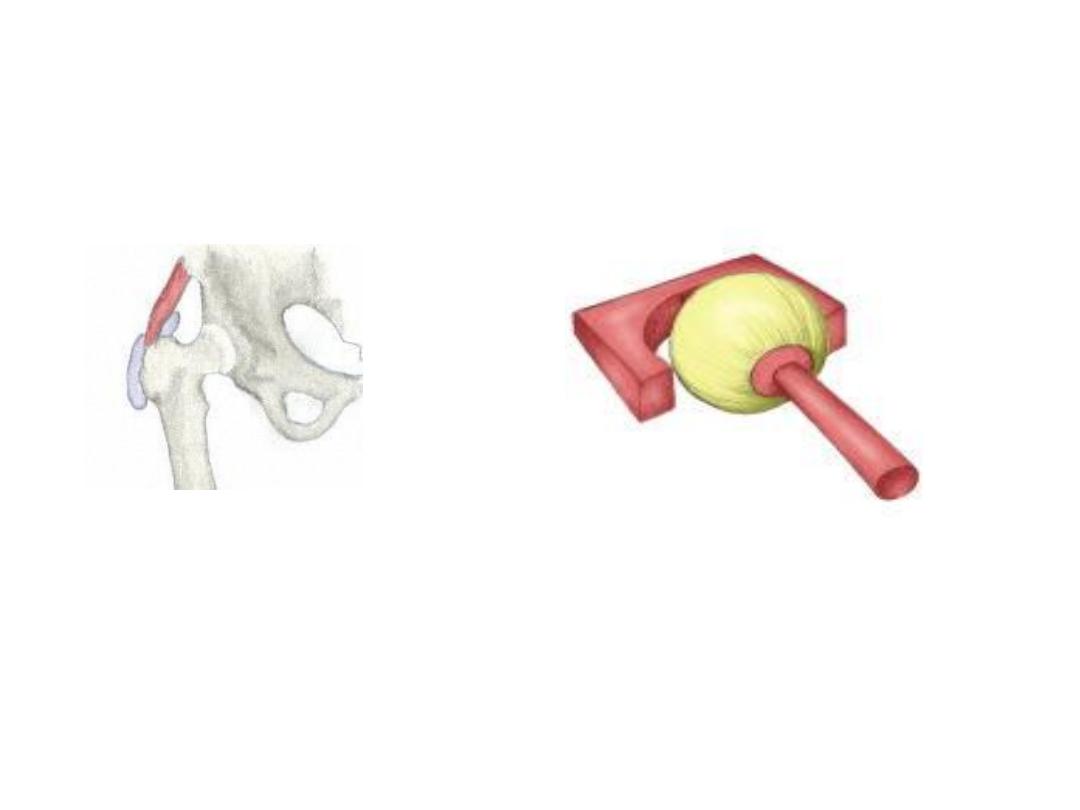
Ball and Socket
Flexion/Extension/Adduction/
Abduction/Internal & External Rotation
Shoulder/Hip
Ball and socket joint
Saddle
Flexion/Extension/Adduction/
Abduction/Circumduction
CMC joint of the thumb and
sternoclavicular joint
Saddle joint
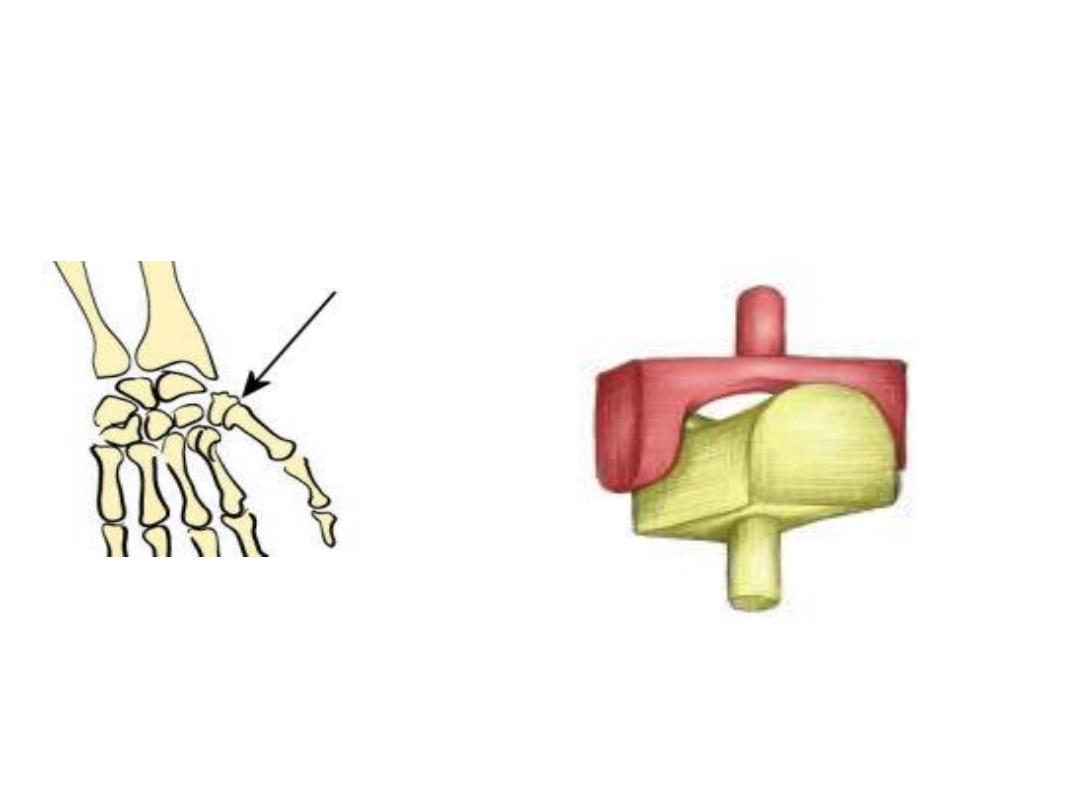
Condyloid
Flexion/Extension/Adduction/
Abduction/Circumduction
Wrist/MCP & MTP joints
Condyloid joint
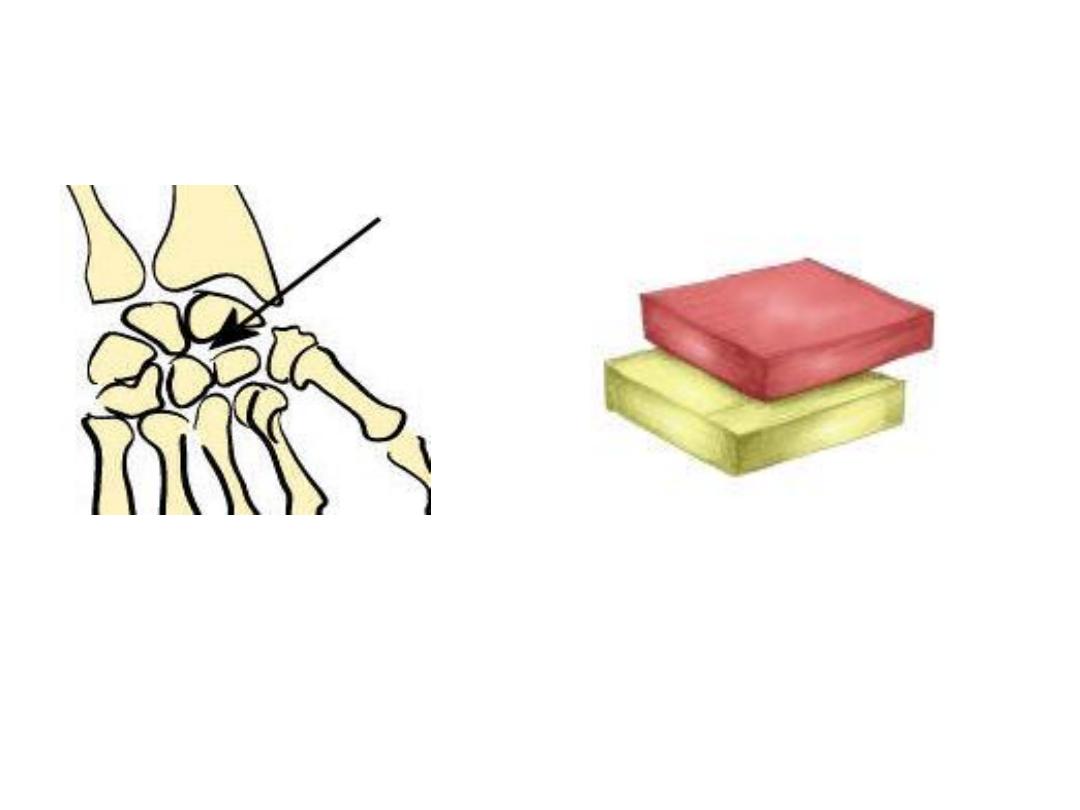
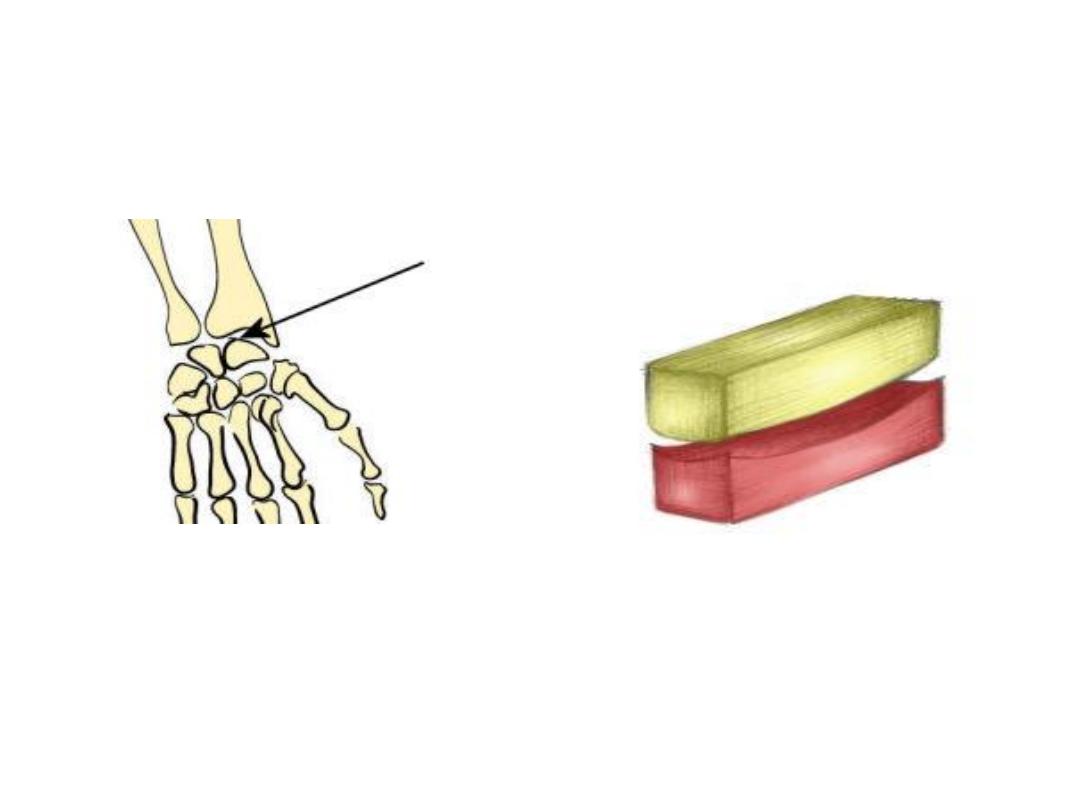
Gliding(simple plane joints)
Gliding movements e.g
intertarsal and acromioclavicular J.
Intercarpal joints
Gliding joint

Gomphoses
(socket joints) are
immovable joints found between the
teeth and jaws. They are held
together by a periodontal ligament
that acts as a shock absorber.

Saddle Joints
Saddle joints are so named because the ends of each
bone resemble a saddle, with concave and convex
portions that fit together. Saddle joints allow angular
movements similar to condyloid joints but with a greater
range of motion. An example of a saddle joint is the
thumb joint, which can move back and forth and up and
down, but more freely than the wrist or fingers

