Passive ways
How molecules cross the plasma membrane:The plasma membrane is semipermeable.
A permeable membrane allows all molecules to pass through it;
impermeable membrane no molecules can be pass through this membrane ;
a semipermeable membrane allows some molecules to pass through it and the other molecules cannot be pass.
The structure of the plasma membrane effect which types of molecules can freely pass through it :
Small; Non charged; lipid soluble molecules have no difficulty crossing the membrane.
Macromolecules cannot freely cross a plasma membrane , and charged ions have difficulty to pass through plasma membrane.
Certain small molecules can cross a plasma membrane , while large molecules cannot .
some small molecules pass through the plasma membrane quickly , while other have difficulty in passing through or fail to pass through at all , therefore a plasma membrane is often regarded as differentially permeable (or selectively permeable ) as well . ??????
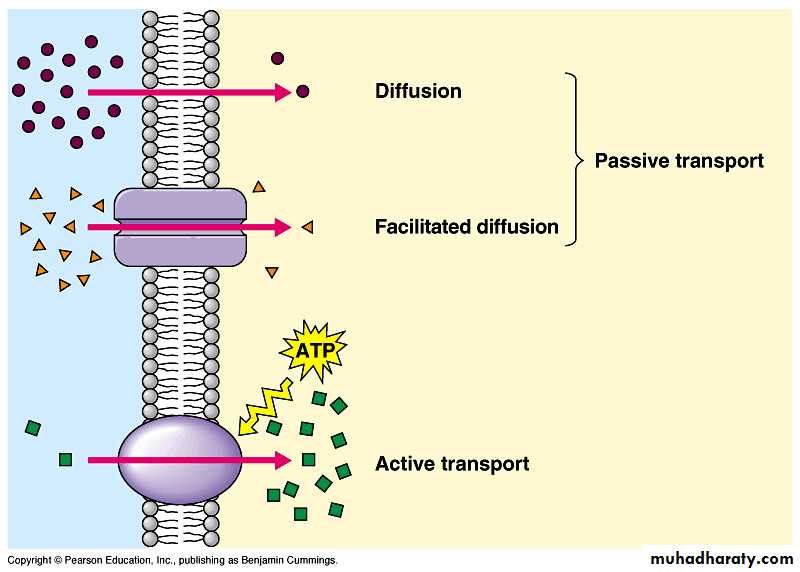
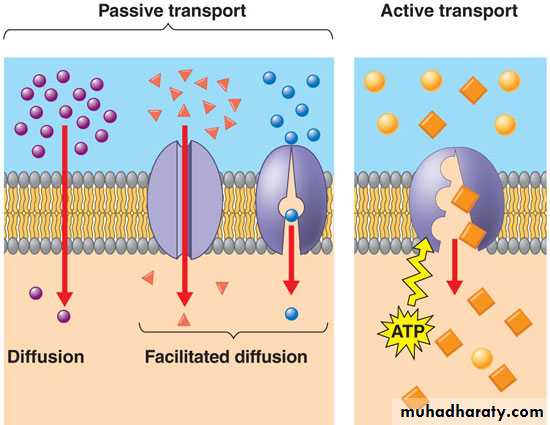
1-Diffusion:
Is the a physical process that can be observed with any type of molecules. During diffusion, molecules move from higher to lower concentration, That is down their concentration gradient until they are distributed equally, for example , when a few crystal of dye (solute ) are placed in water.The chemical and physical properties of the plasma membrane allows just a few types of molecules to inter and exist by diffusion .
Lipid soluble molecules , such as alcohol can diffuse through the membrane because lipids are the membranes main structural component.
Gases can also diffuse through the lipid Bilayer this is the mechanism by which oxygen enters cell and carbon dioxide exit the cell as an example, consider the movement of oxygen from the air sacs (Alveoli) of the lung to blood in the lung capillaries .
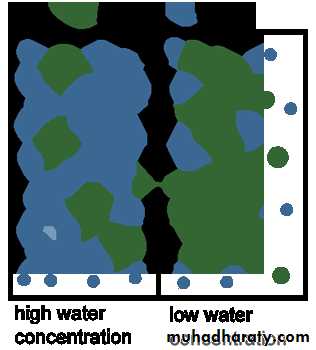
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a differentially permeable membrane has been given a special name, it is called osmosis , osmotic pressure develops on the side of the membrane that has the higher solute concentration.Tonicity
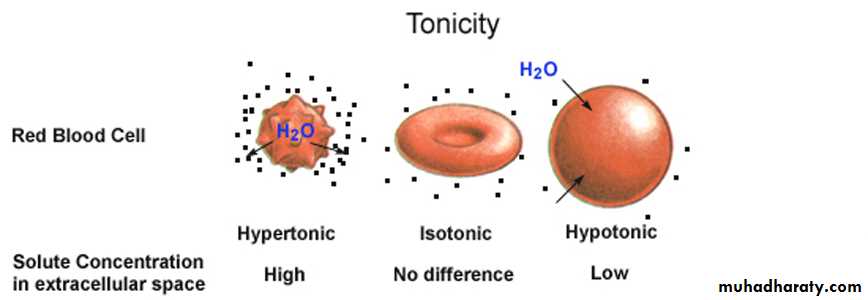
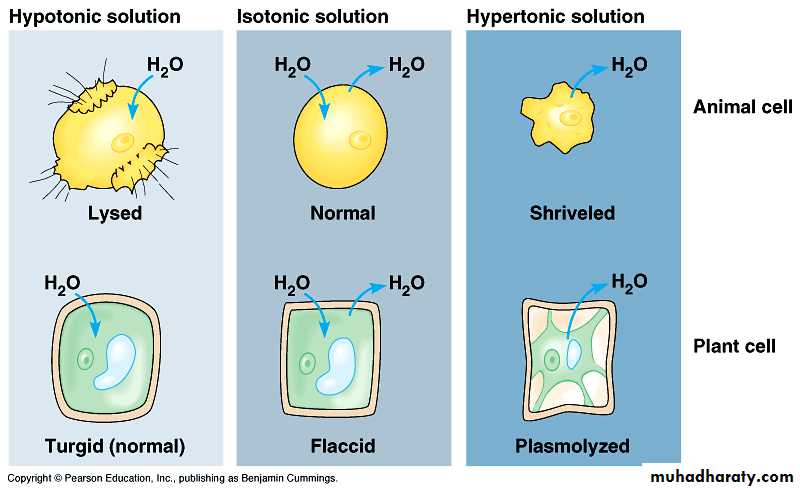
Tonicity refers to the strength of solution in relationship to osmosis. cell can be placed in solution that have the same percentage of solution (isotonic solution) 'a higher percentage of solution (hypertonic solution) or a lower percentage of solute (hypotonic solution) than the cell.In the laboratory, cells are normally placed in solution that cause them neither to gain nor to loss water ,such a solution is said to be an isotonic solution; that is the solute concentration is the same on both sides of the membrane and therefore there is no net gain or loss of water .
the prefix Iso means the same as.
A 0.9% solution of the salt sodium chloride Nacl (is known to be isotonic solution to red blood cells) because the cells neither swell , nor shrink when placed in the solution .
Any concentration of salt solution lower then 0.9 % is hypotonic to red blood cells.
The prefix hypo means less than and refers to a solution with a lower percentage of solute (more water ) than the cell .red blood cell placed in such a solution expand and sometimes burst due to the build up of pressure caused by inward movement of water .
The term lysis is used to refers to destruction cells , hemolysis , then is the process of destructing red blood cell . solution that cause cells to shrink or to shrivel due to a loss of water are said to be hypertonic solution .
The prefix hyper means more than and refer to a solution with a higher percentage of solute (less water ) than the cell . A 1% solution of Nacl is hypertonic to red blood cell . if red blood cells are placed in this solution , they shrink . The term crenation refer to red blood cells in this solution .
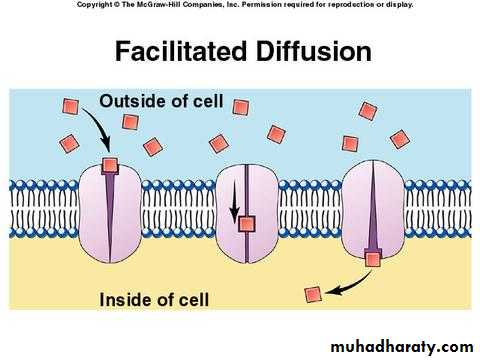
2- Facilitated transport:
Facilitated transport explain the passage of such molecules as glucose and aminoacids across the plasma membrane even though they are not lipid soluble.The passage of glucose and aminoacids is facilitated by their reversible combination with carrier proteins which in some manner transport them through the plasma membrane, these carrier proteins are specific , for example , various sugar molecules of identical size might be present inside or outside the cell, but glucose can cross the membrane hundreds of time faster then the other sugars , as stated earlier , this is the reason that the membrane can be called differentially permeable .
Active ways:
1- Active transport:during active transport , molecules or ions pass through the plasma membrane , accumulating either inside or outside the cell , for example iodine collects in the cells of the thyroid gland , glucose is completely absorbed from the gut by the cell lining the digestive tract; and sodium can be almost completely , with drawn from urine by cells lining the kidney tubules , in these instances, molecules have moved to the region of higher concentration , exactly opposite to the process of diffusion
. in this case , (ATP molecules ) usually is required for the carrier to combine with the substance to be transported .
Proteins involved in example sodium- potassium pump .
A change in carrier shape after the attachment and again after detachment of a phosphate group allows it to combine alternately with sodium ions and potassium ions.
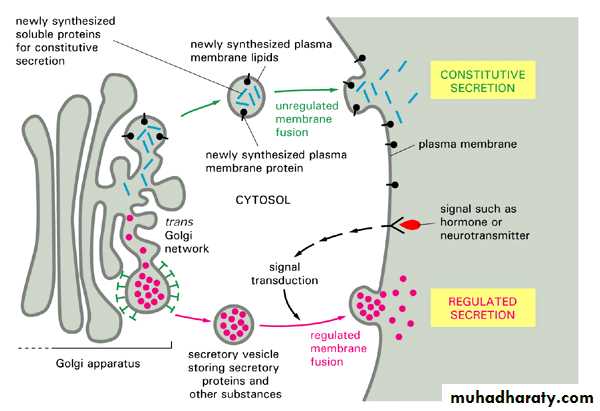
2- Exocytosis:
during exocytosis , vesicle often formed by the Golgi apparatus and carrying a specific molecules , fuse with a plasma membrane as secretion occurs , this is the way that in saline leaves insulin secreting cells . the membrane of the vesicle because a part of the plasma membrane .3- Endocytosis:
During endocytosis , cells take on substances by vesicle formation . a protein of plasma membrane invaginates to envelope the substances and then the membrane pinches off to form on intercellular vesicle .when the material taken by endocytosis is large such as a food particles , the process is called phagocytosis .
A- phagocytosis:
Is common in unicellular organisms like Amoebas and in amoeboid type cell like macrophages which are large cell in mammalsWhen the endocytic vesicle fuses with Lysosomes, digestion occur.
B-Pinocytosis:
Occurs when vesicle form around a liquid or very small particles . blood cells that line the kidney tubules or intestinal wall.