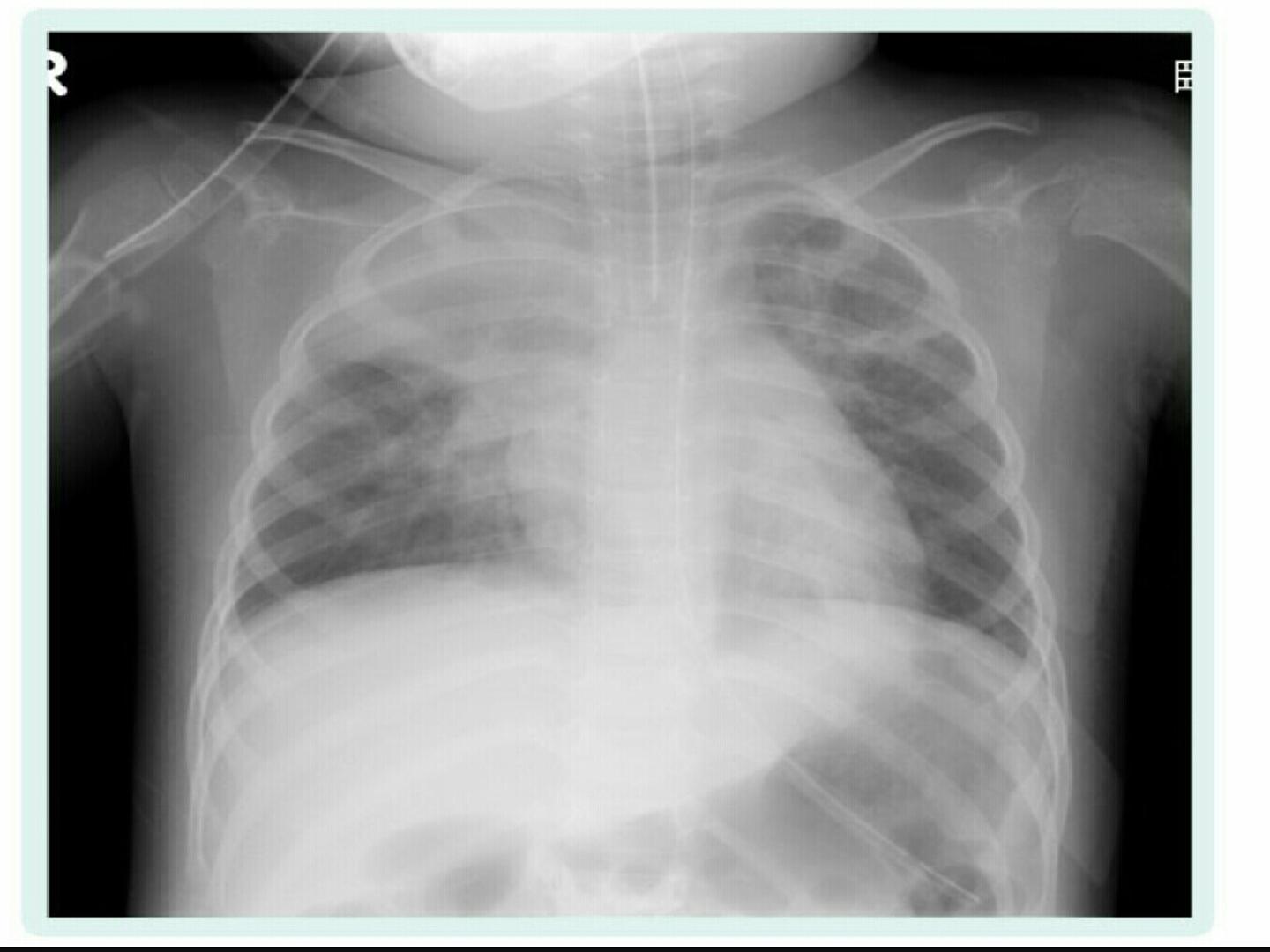
NEONATAL ASPIRATION PNEUMONIAS
1. MECONIUM ASPIRATION:
Meconium-stained amniotic fluid is found in
10-15% of births (usually term or post-
term),following fetal distress & hypoxia.
5% of such infants develop meconium-aspiration
pneumonia when thick meconium is aspirated into
the lungs in utero or with the first breath.
Meconium inactivates surfactant, and can cause
severe respiratory distress by the following
mechanisms:

1. Plugging of small airways with hyperinflation &
atelactasis causing ventilation/perfusion mismatch.
2. Meconium pneumonitis(chemical).
3. Secondary bacterial infection.
CXR:
1. Patchy infiltration & hyperinflation of lungs.
2. Pneumothorax.
PREVENTION:
1.Prevent fetal distress.
2.Aspirate the mouth & oropharynx after delivery of the
head.
3.Endotracheal intubation & suctioning of lungs (in
severely depressed hypotonic neonates).
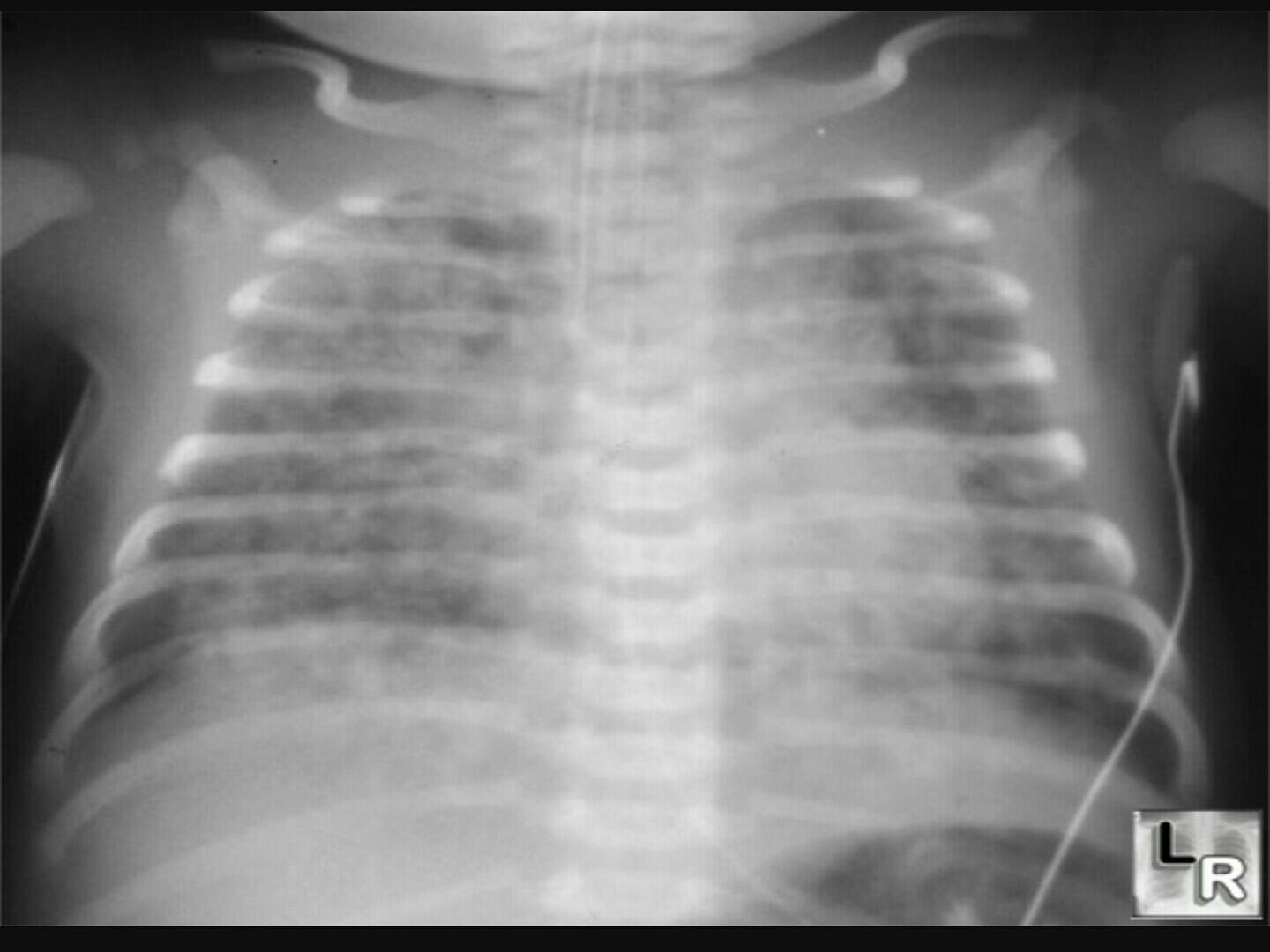

TREATMENT:
1. Supportive care and physiotherapy.
2. I.P.P.V.
3. Surfactant therapy.
4. Inhaled nitrous oxide (iNO).
5. E.C.M.O.(extracorporeal membrane oxygenation).
6. Pulmonary hypertension may follow, and a non selective
pulmonary vessel alpha blocker tolazoline is used.
7. Antibiotics.
8. Pneumothorax occurs in 15%, it should be treated
accordingly.

2. MILK ASPIRATION:
Commonly occurs in preterm infants or in full
term infants with improper feeding technique.
It is characterized by sudden deterioration in
clinical condition (apnea or severe distress).
CXR shows pneumonic patch or collapse usually
involving the right upper lobe.
TREATMENT:
1. Supportive care.
2. Antibiotics.