Done by :Ban Basil
Asawer Abd-aljalilSupervised by: dr. Muhanad Al-sherify
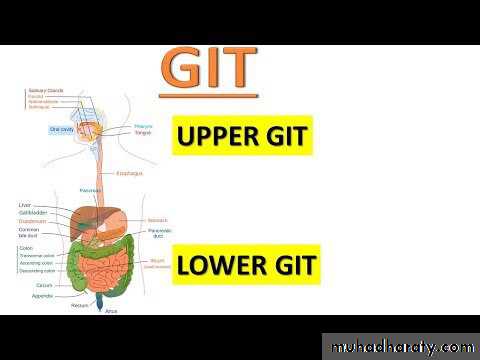
Lower GIT bleeding
ALLPPT.com _ Free PowerPoint Templates, Diagrams and Charts
Introduction:
A lower gastrointestinal bleed is defined as bleeding originating distal to the ileoceacal valve which includes the colon, rectum, and anus . LGIB also defined as any bleed that occurs distal to the ligament of Treitz, which included the aforementioned parts of the intestine and also included the last 1/4 of the duodenum and the entire area of the jejunum and ileum . So lower gastrointestinal bleeding which involves a bleed anywhere from the ileoceacal valve to the anusIncidence :
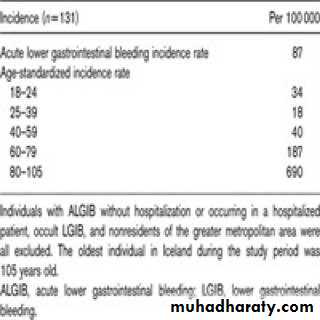
•20-33% of GIT bleeding•the incidence increase with advanced age
•80% resolved spontaneously
25% will be re-bleed.
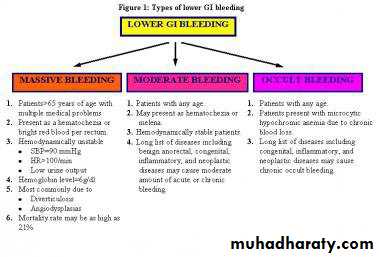
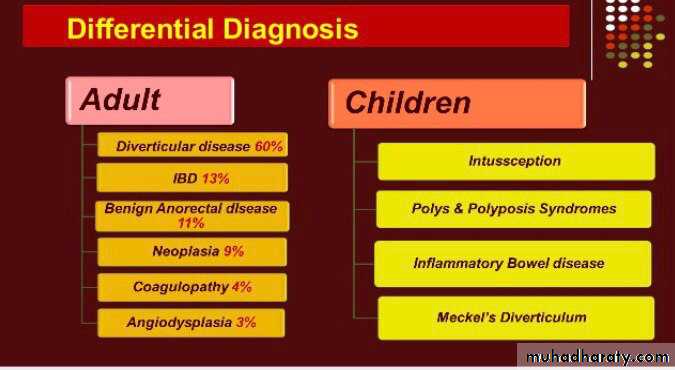
Causes :
The following are possible causes of a LGIB:* Diverticular disease — diverticulosis, diverticulitis
* Colitis
* Ischaemic colitis
* Radiation colitis
* Infectious colitis
* Pseudomembranous colitis
* E. coli O157:H7
* Shigella
* Salmonella
* Campylobacter jejuni
* Hemorrhoids
* Neoplasm — such as colorectal cancer
* Angiodysplasia* Bleeding from a site where a colonic polyp was removed
* Inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
* Rectal varices
* Coagulopathy — specifically a bleeding diathesis
* Anal fissures
* Rectal foreign bodies
* Mesenteric ischemia
* NSAIDs
* Entamoeba histolytica
Presentation:
1- Hematochezia (passage offresh
blood through the anus)
2-pallor as a sign of anemia due to loss blood
3-tachycardia
4-hypotension
5-fatigue,weakness,shortness of breath and abdomen .
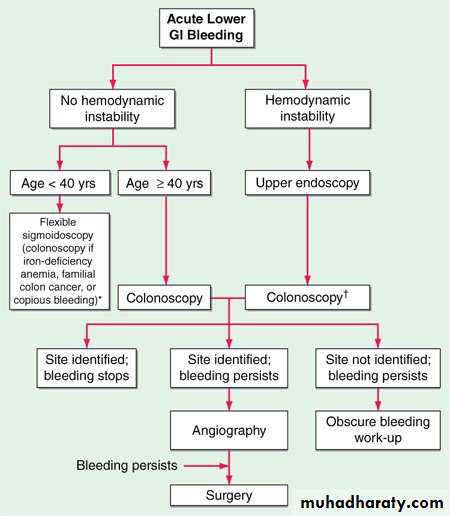
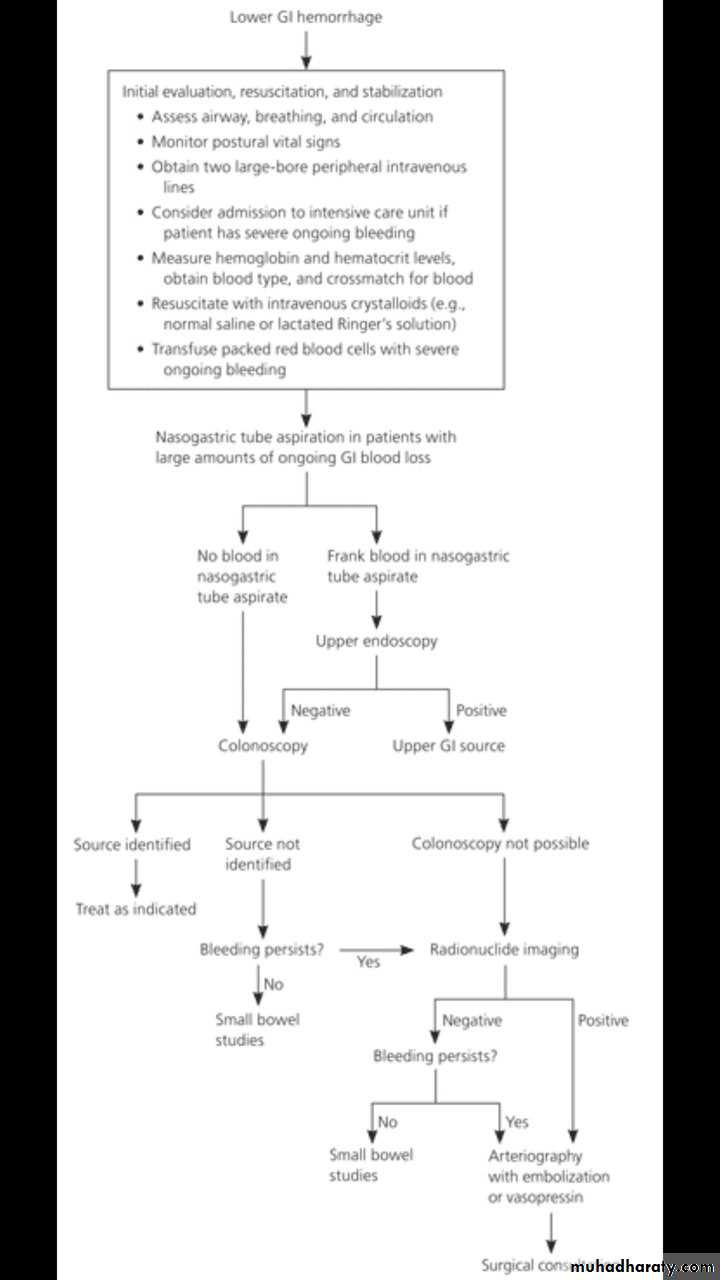
Diagnosis:
1-colonoscopy: full length colonoscopy is the most important investigation (gold standard) ,it help in visualizing from rectum to the 10-15cm from terminal ileum .Therapeutic uses of colonoscopy:
•Electro-cauterization of bleeding points
•polypectomy
Diagnostic uses
•imaging
•biopsy of the lesion.
2-Radionuclide scanning
Advantages is that can be detected very small amounts of bleeding (0.05-0.1ml/min)
3-mesentric angiography :under fluoroscopic guidance
4-capsule endoscopy
•non invasive procedure
•done in stable patient
•only diagnostic value
•the imaging cannot be controlled outside, this pathological site may be missed .
5-blood test
(Hb , pcv , LFT)
(Coagulation profile, RFT)
6-stool examination
(Ova, cyst and worm) for occult blood
Complications:
A gastrointestinal bleed can cause:* Shock
* Anemia
* Death
Treatment
Treated of underlying cause:
•polypectomy of polyp
•massive resection of small bowel in mesenteric
ischemia
•surgical resection in colonic carcinoma
•sigmoid colectomy in sigmoid diverticula
•drug , total prctocolectomuly and anastomoses for UC
•Excision &ligation for piles