
OSCE-Surgery

•
•
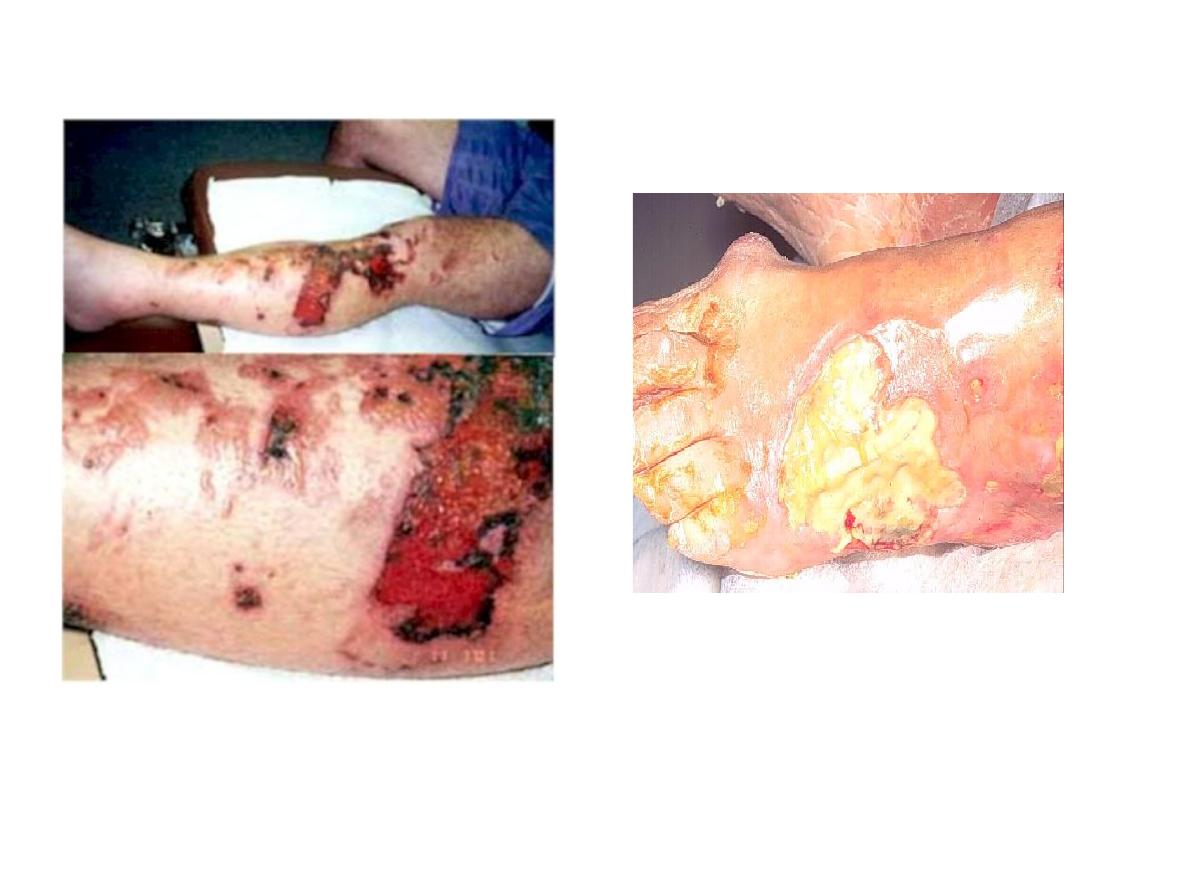
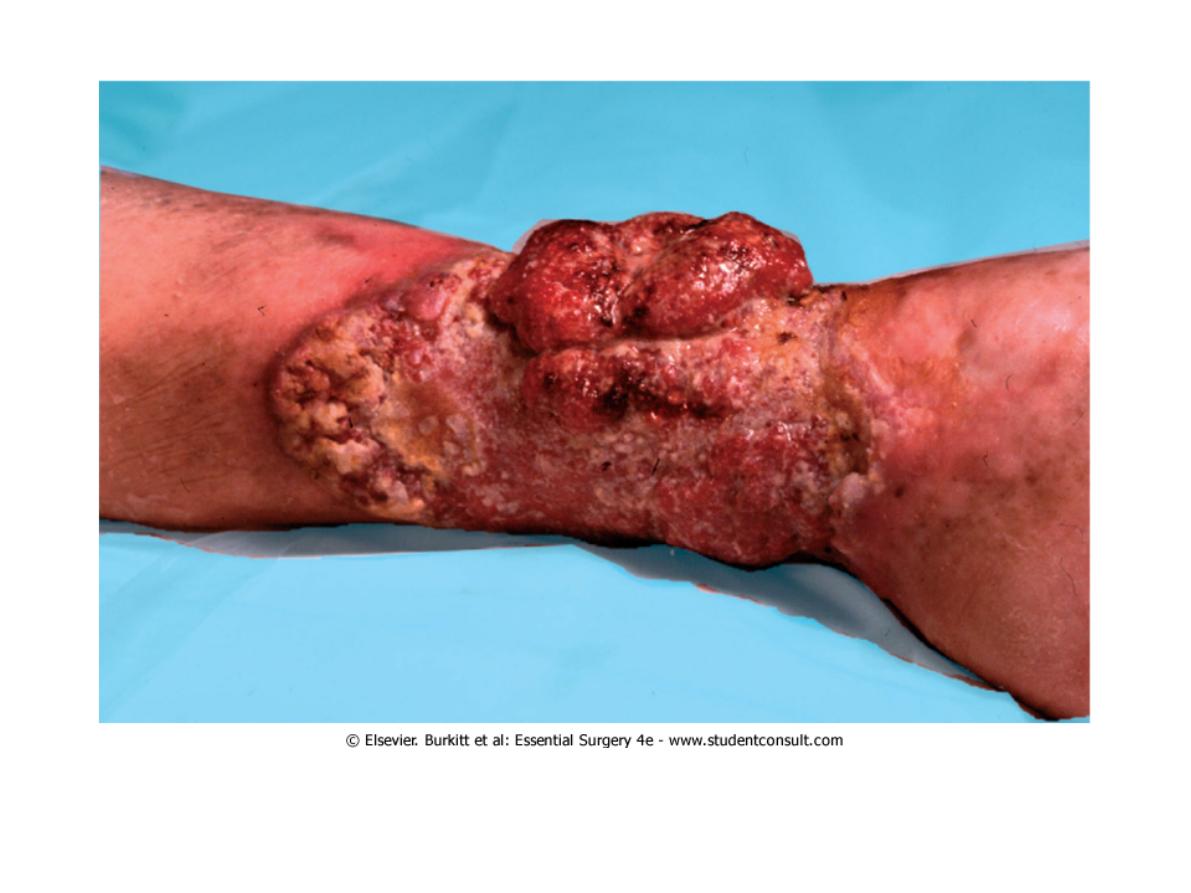
Burns on legs
4 complications
local
-wound contractures
-scarring (full thickness)
general
-infection
-shock
-renal failure from initial hypovolemia d2
plasma loss
-psychological disturbance

•
•
•
•
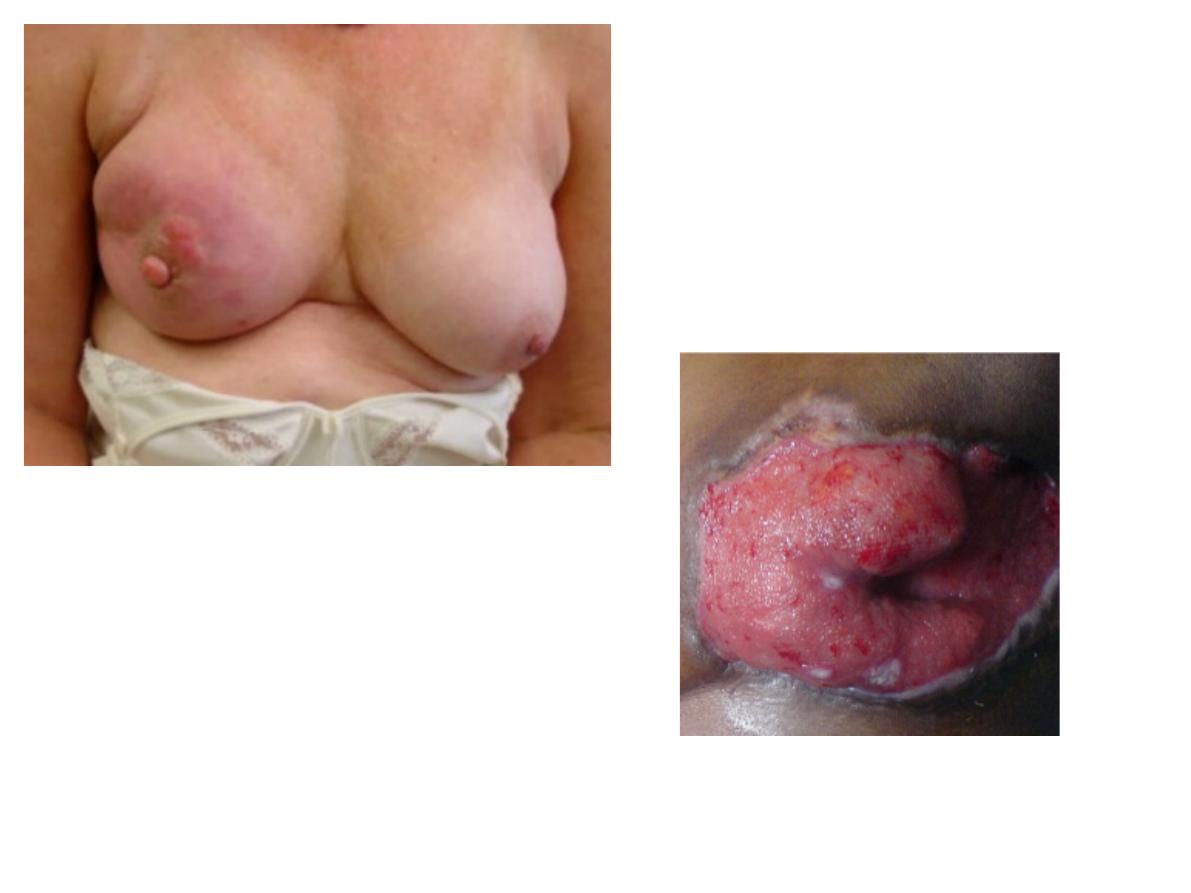
Breast Ca with ulcer
Describe
T staging of TNM
-T1:<2
-T2:2-5
-T3:>5
-T4:skin invasion/chest wall/ both
Clinical type of breast Ca (4 marks)
-Phylloides tumour
-Invasive ductal Ca
-ductal Ca in situ
-medullary Ca

•
•
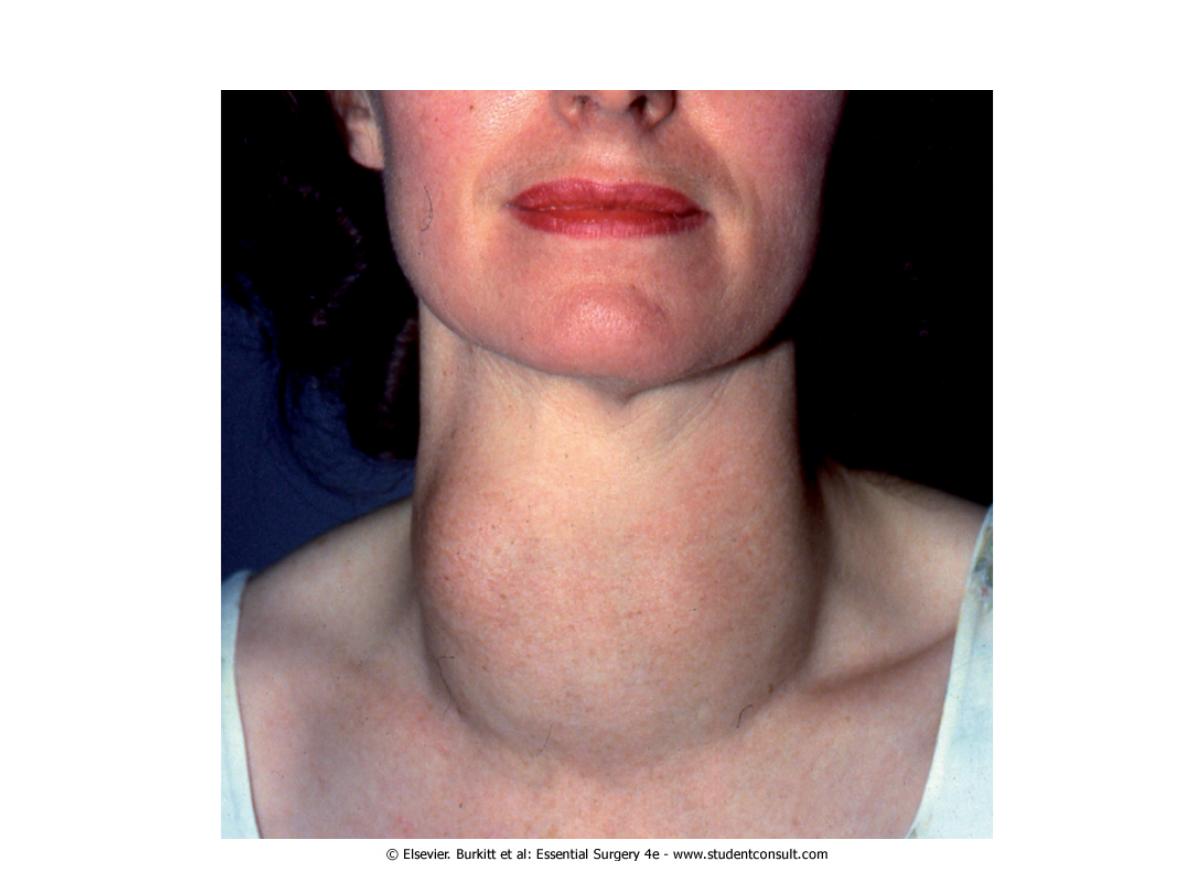
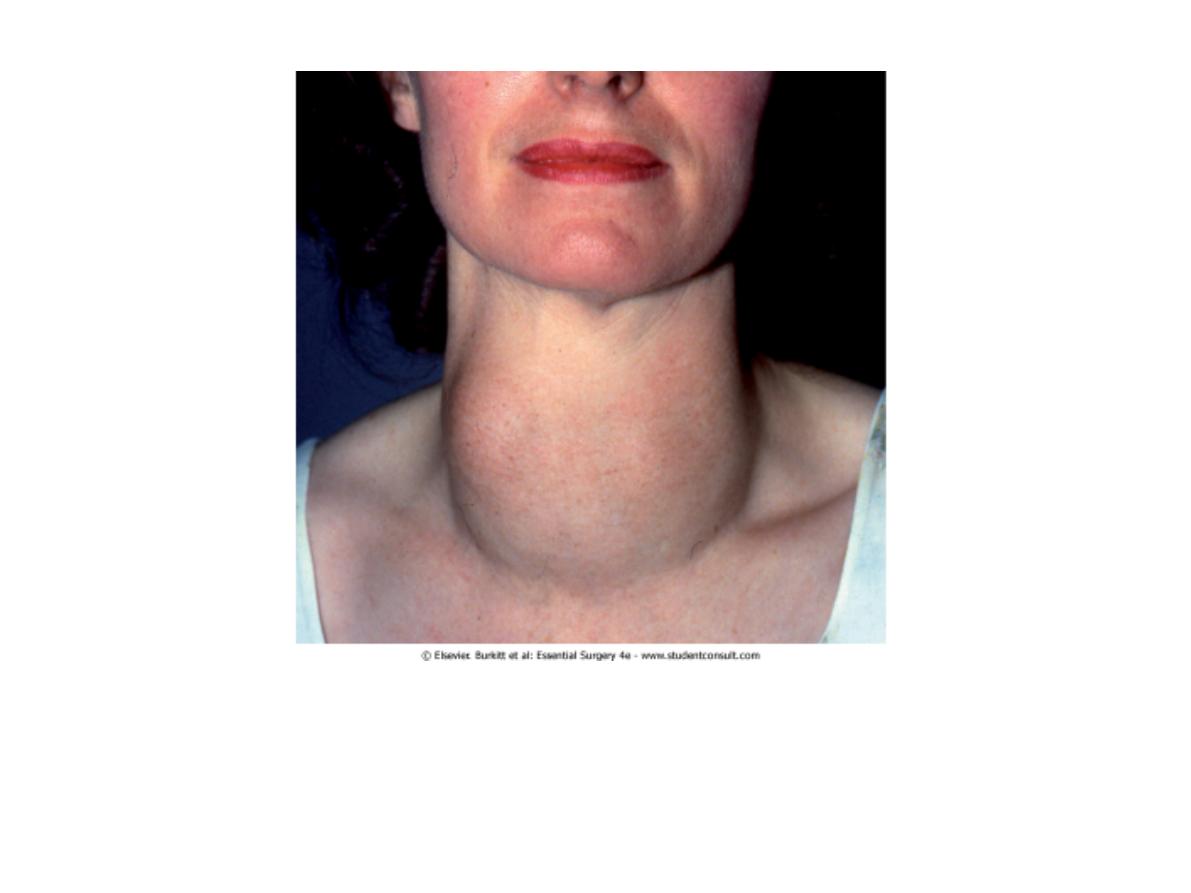
Thyroid lump-multinodular goiter
Ix before operation
-TFT
-ultrasound
-thyroid isotope scan
-FNAC
2 presenting features
Local mass efffects:
-stridor
-dyspnoea
-dysphagic
-SVC obstruciton

•
•
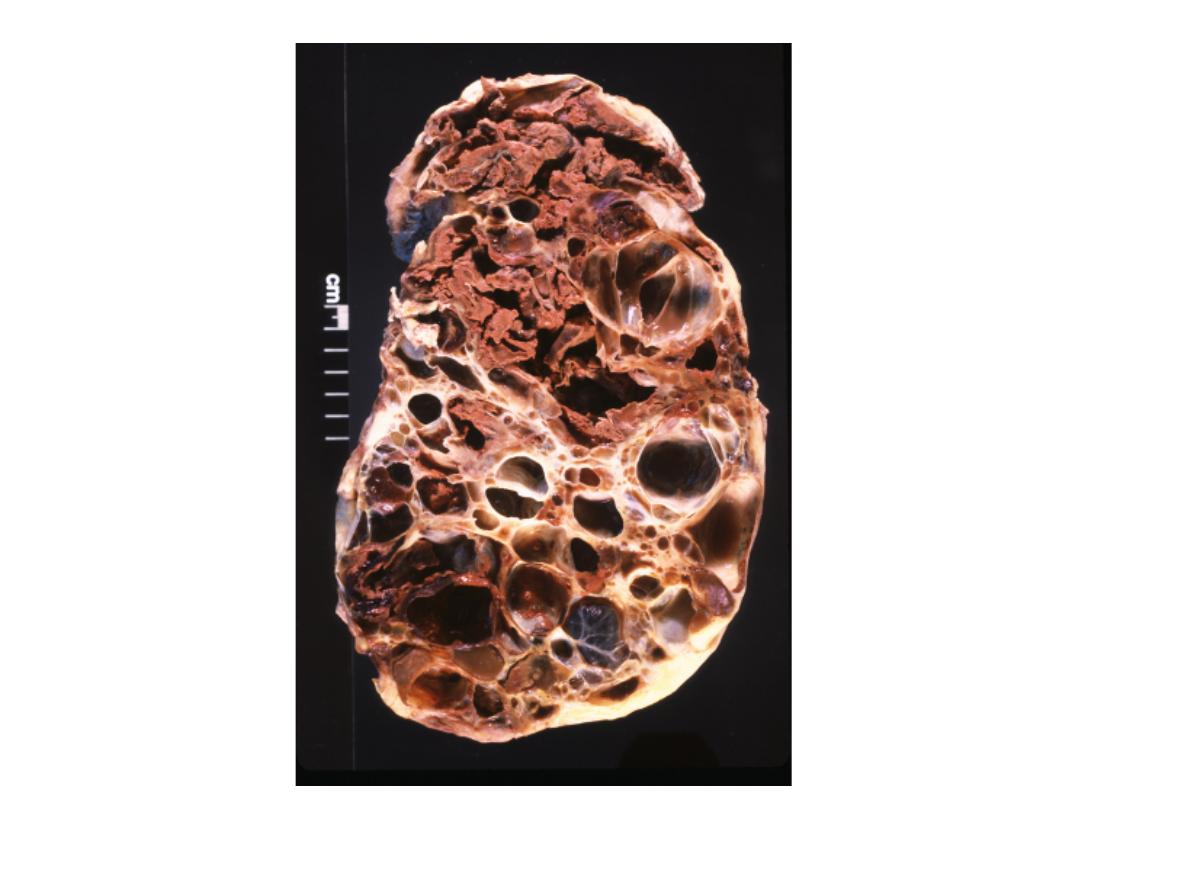
Polycystic kidney
2 symptoms:
-haematuria
-loin discomfort
-hypertension
2 associated symptoms:
-berry aneurysm
-liver cyst

•
Marjolin ulcer
Long standing venous ulcer- squamous cell carcinoma

•
•
•
•
Neck Swelling
Describe (6 marks)
2 differentials (2 marks)
-goitre
-throglossal cyst
-lipoma
What would you ask patient to do (2 marks)
-swallow saliva-goitre
-protrude tounge-thyroglossal cyst
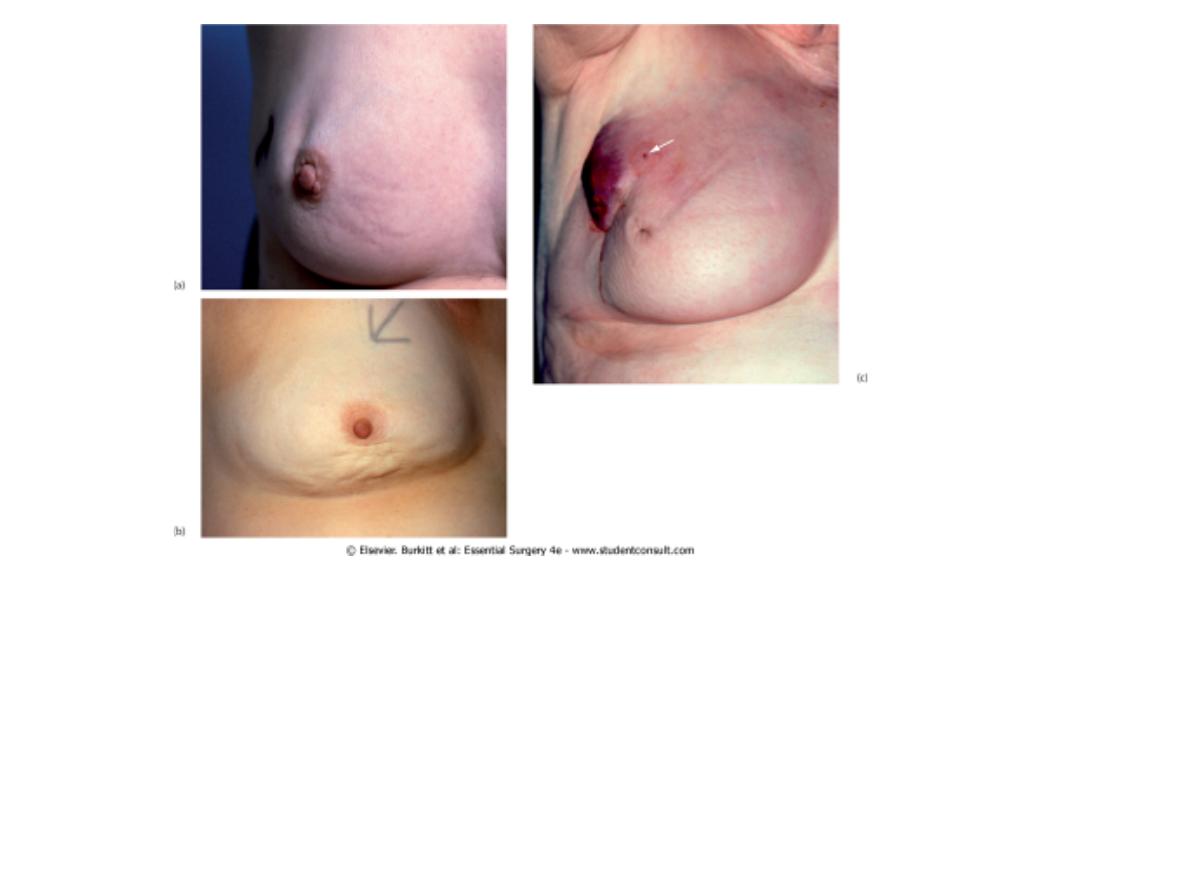
– Carcinoma of the breast
(a) and (b) Characteristic skin dimpling over breast carcinomas. This may be a subtle sign and
only be visible in tangential light. (c) Nipple retraction and widespread 'peau d'orange' resulting
from a large central breast carcinoma. Peau d'orange is caused by a combination of
cutaneous infiltration by tumour and skin oedema (and occasionally by infection). Locally
advanced breast cancer may cause distortion of the breast. The colour change and ulceration
are uncommonly seen and only occur in neglected cases. Note also the puncture wound of a
core biopsy (arrowed). There was no obvious axillary node enlargement.

•
•
•
•
Pic of pt with left breast Ca
Describe (5 marks)
Diagnosis (2 marks)
-breast ca
3 investigations for this patient (3 marks)
-clinical
-radiological-u/s (<35 yrs old) ,mammography(>35 yrs old)
-cytopathology- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
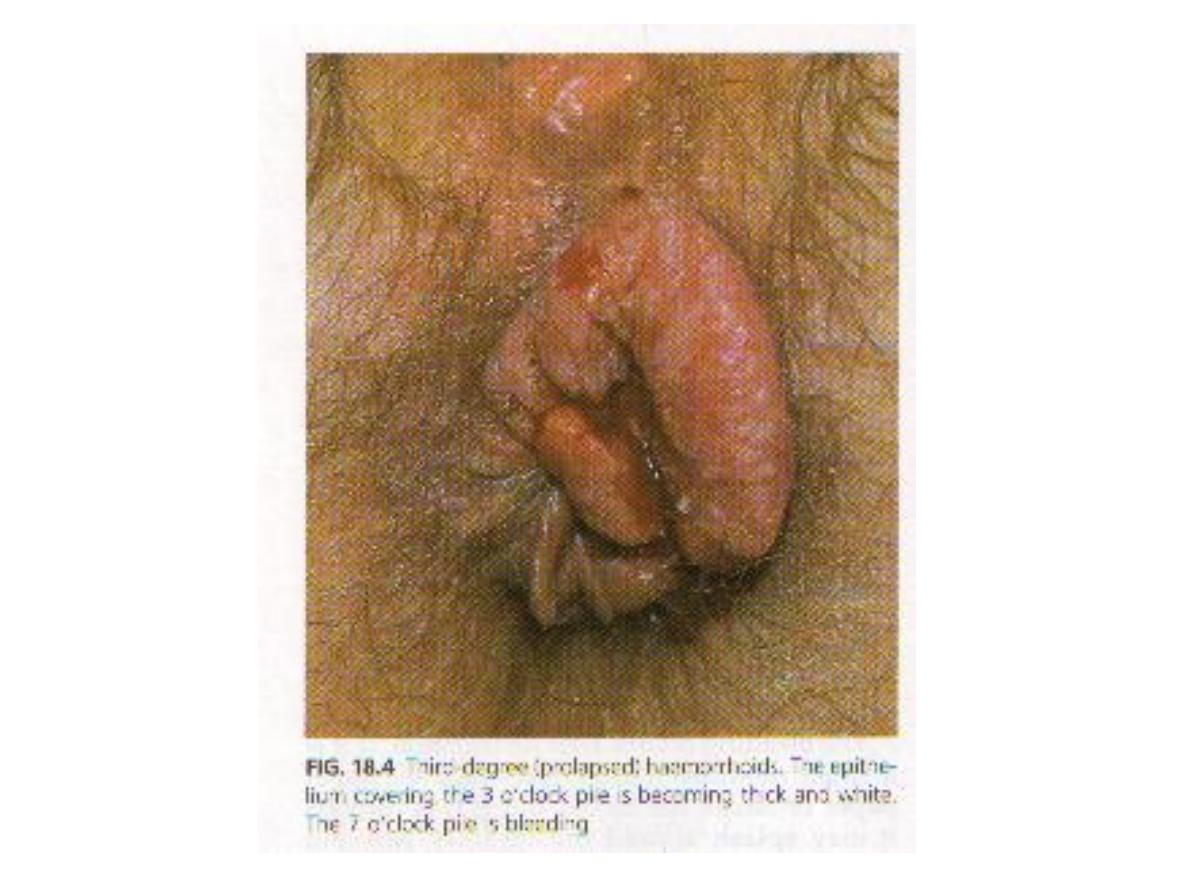
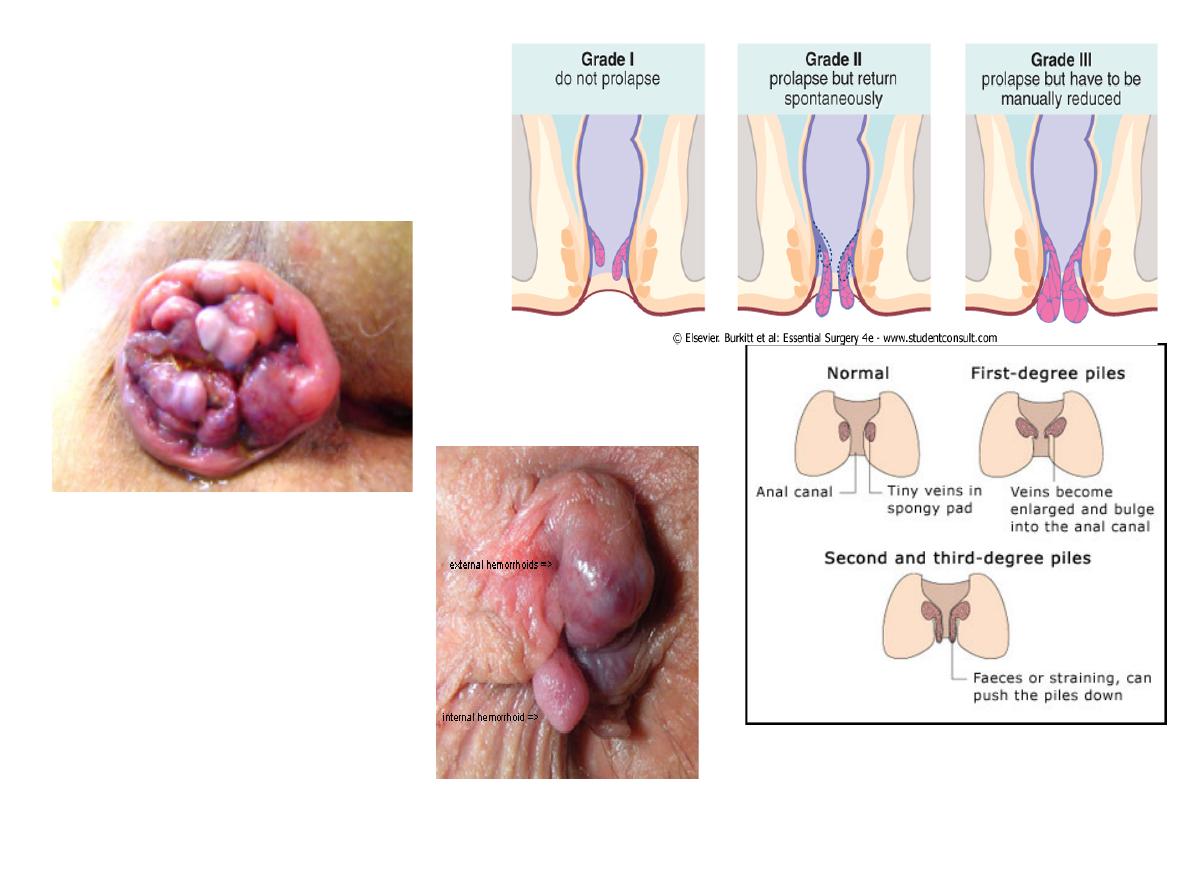
4th degree
haemorrhoids

•
•
•
40 yrs old, male with anal pain
Diagnosis: hemorrhoid 3
◦
4 causes:
-constipation with prolonged straining
-congestion from a pelvic tumour
-pregnancy
-portal hypertension
-CCF
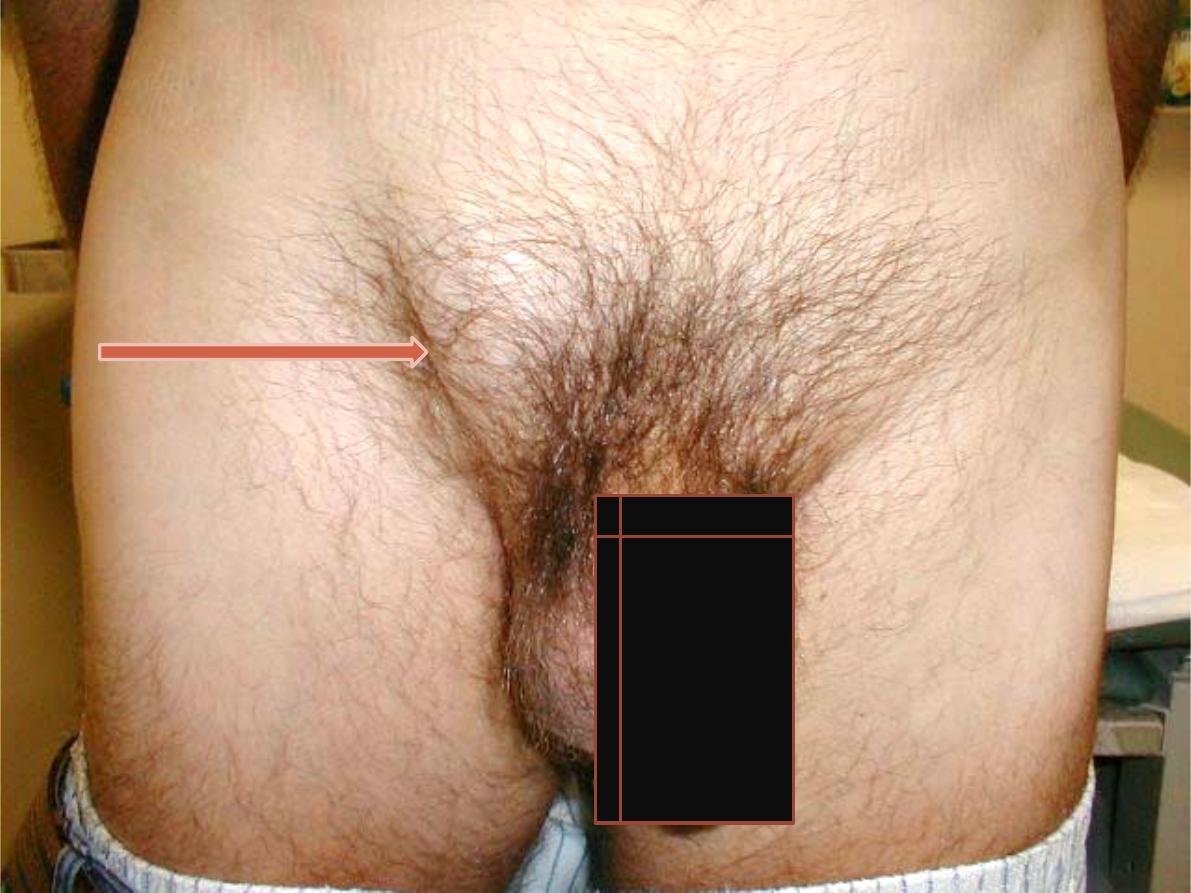
Station: 1
A. Inguinal
swelling
Inguinal hernia.
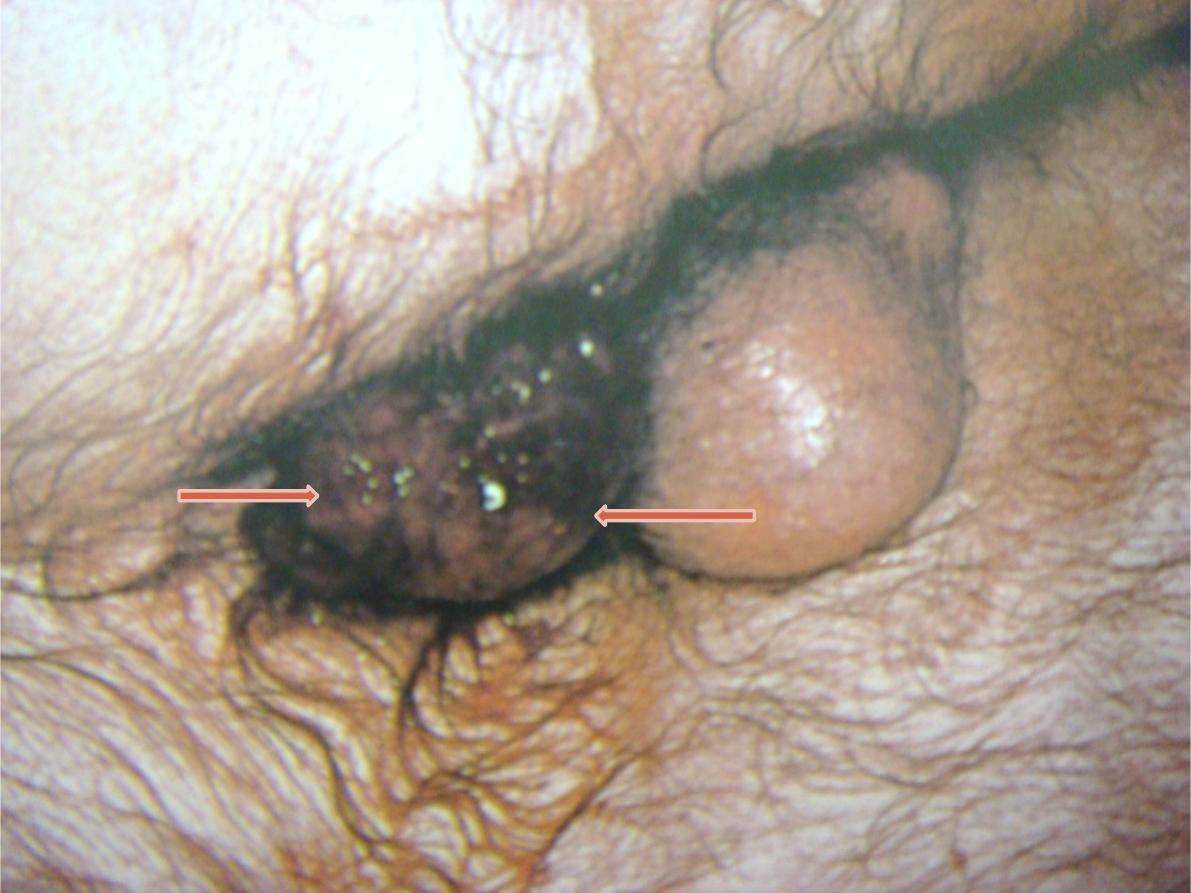
Station: 1
B. Anal lesion
Strangulated 4
th
degree hemorrhoid
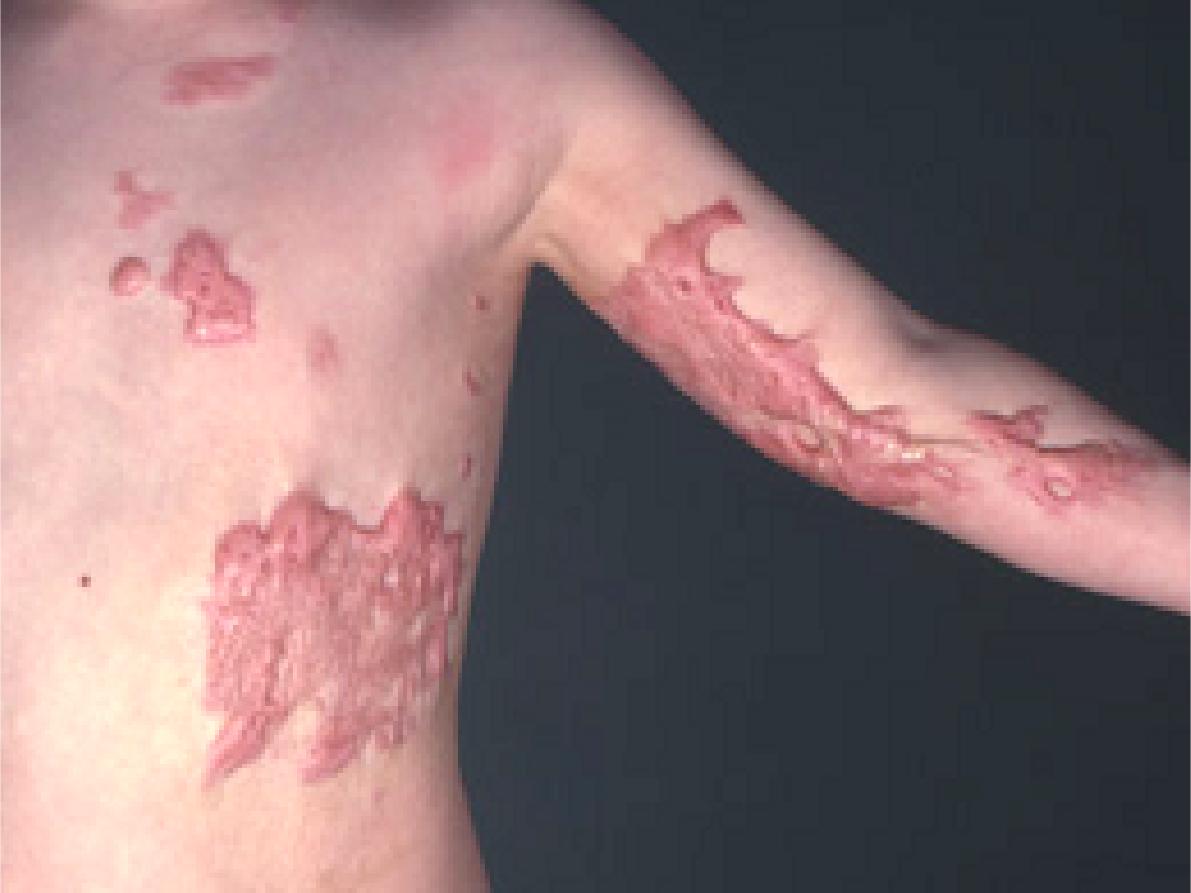
Station: II
A. Skin lesion in the trunk
and left upper limb
Keloid scar.
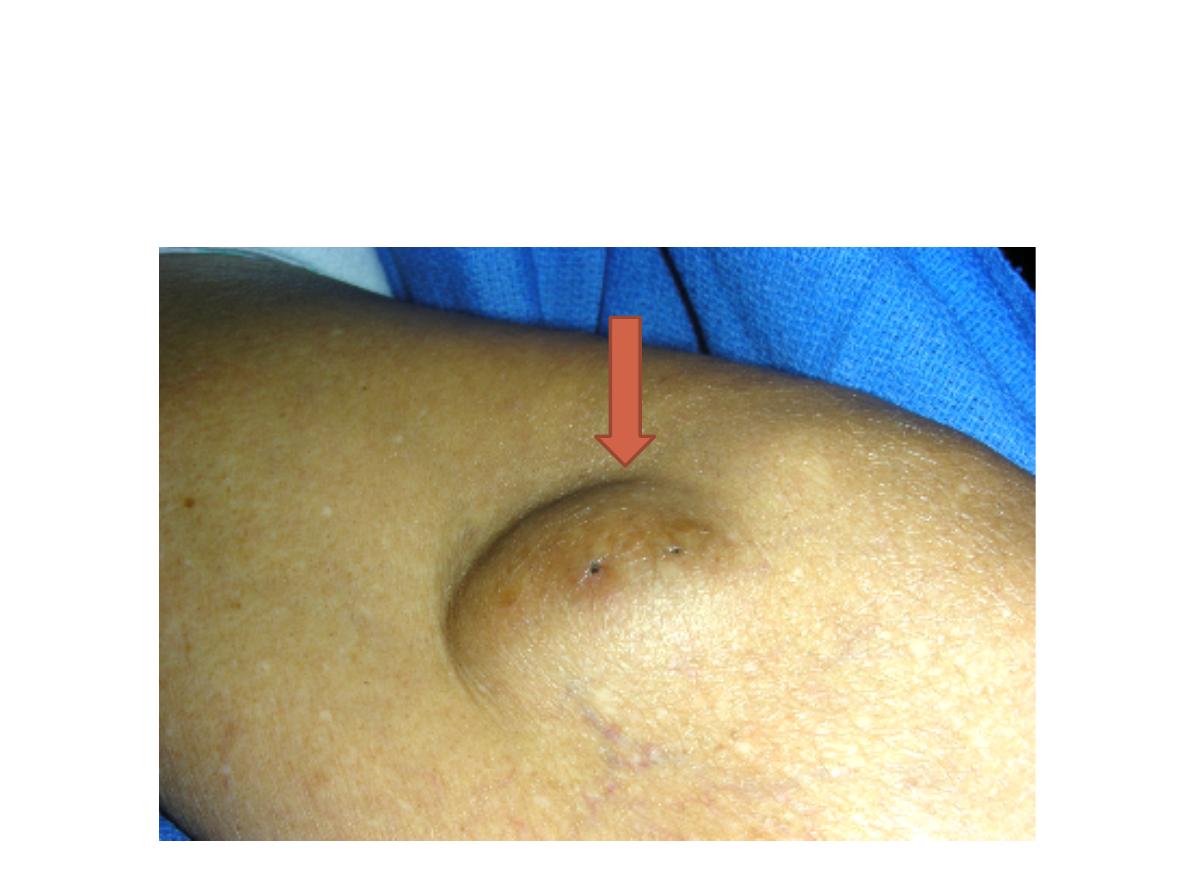
Station: II
B. Skin swelling
Sebaceous cyst (punctum)

Station no. : III
Case management
Time: 5 min.
A fourty eight old multipara female patient
presented to the emergency department
with severe right upper abdominal pain of
48 hours duration. The pain referred to the
right shoulder. On examination she was
febrile; the abdomen was tender in the
right hypochondrium.
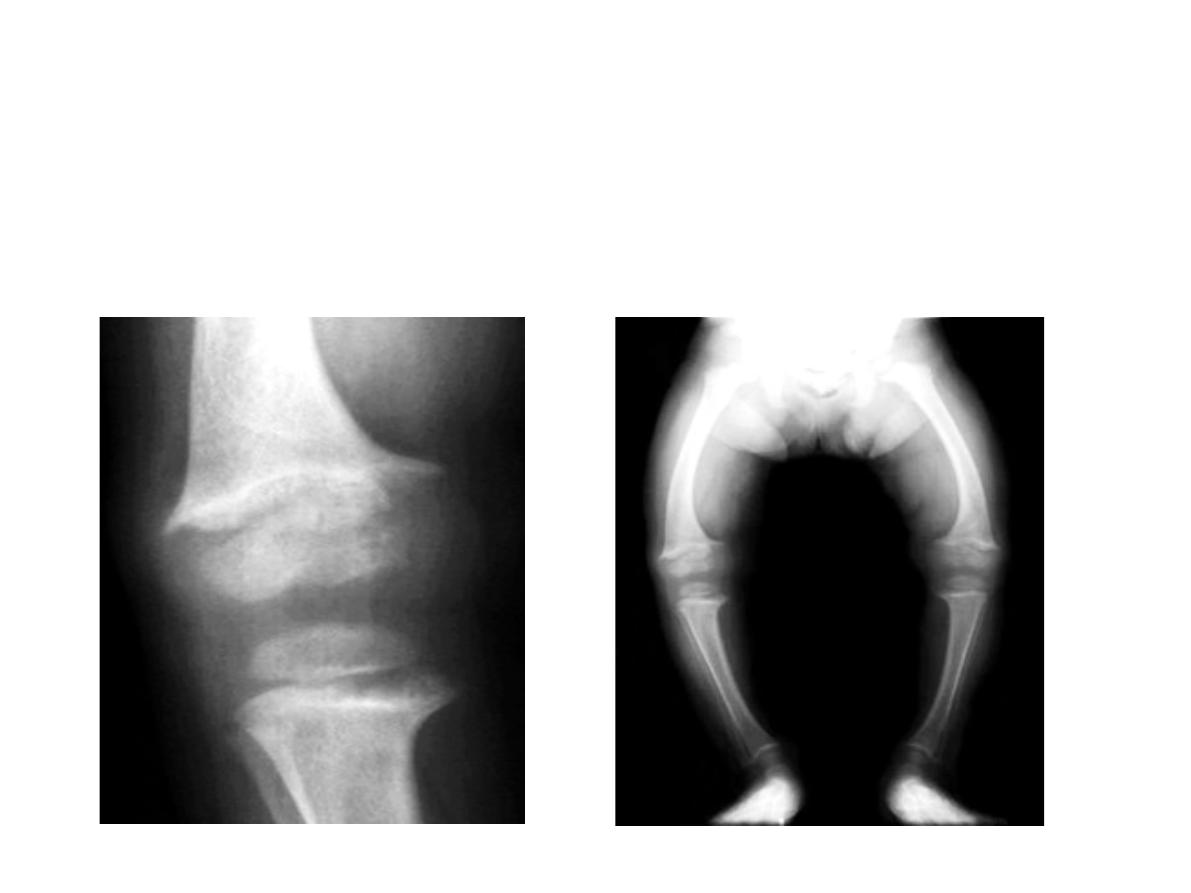
Station no. : IV
Orthopedics slides
Rickets ( legs bowing), widening of growth
plates
A. An 18 months old child with bilateral limb deformity
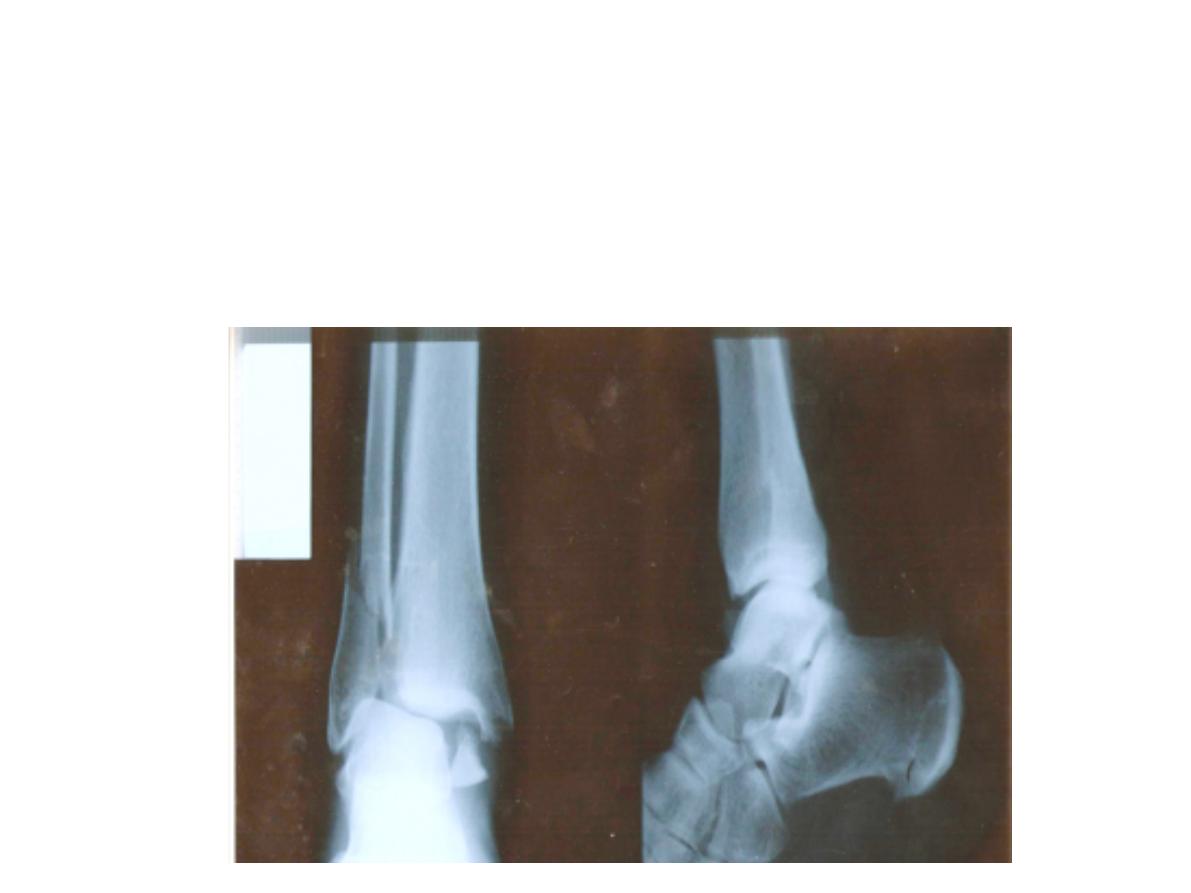
Station no. : IV
Orthopedics slides
Fracture lower end of fibula
B. Ankle trauma:
Station no. : V
Urology
Transillumination
positive
Station no. : VI
X-ray slide:
Time: 5 min.
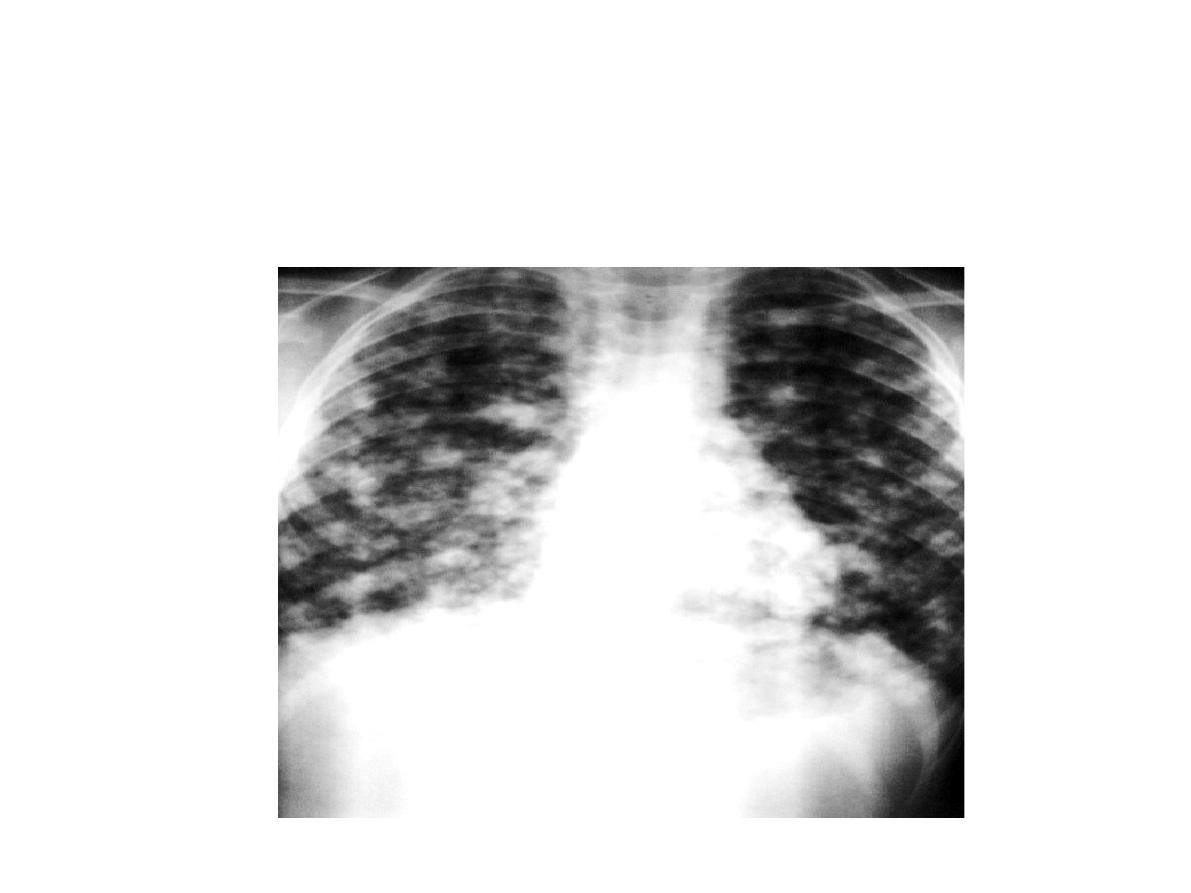
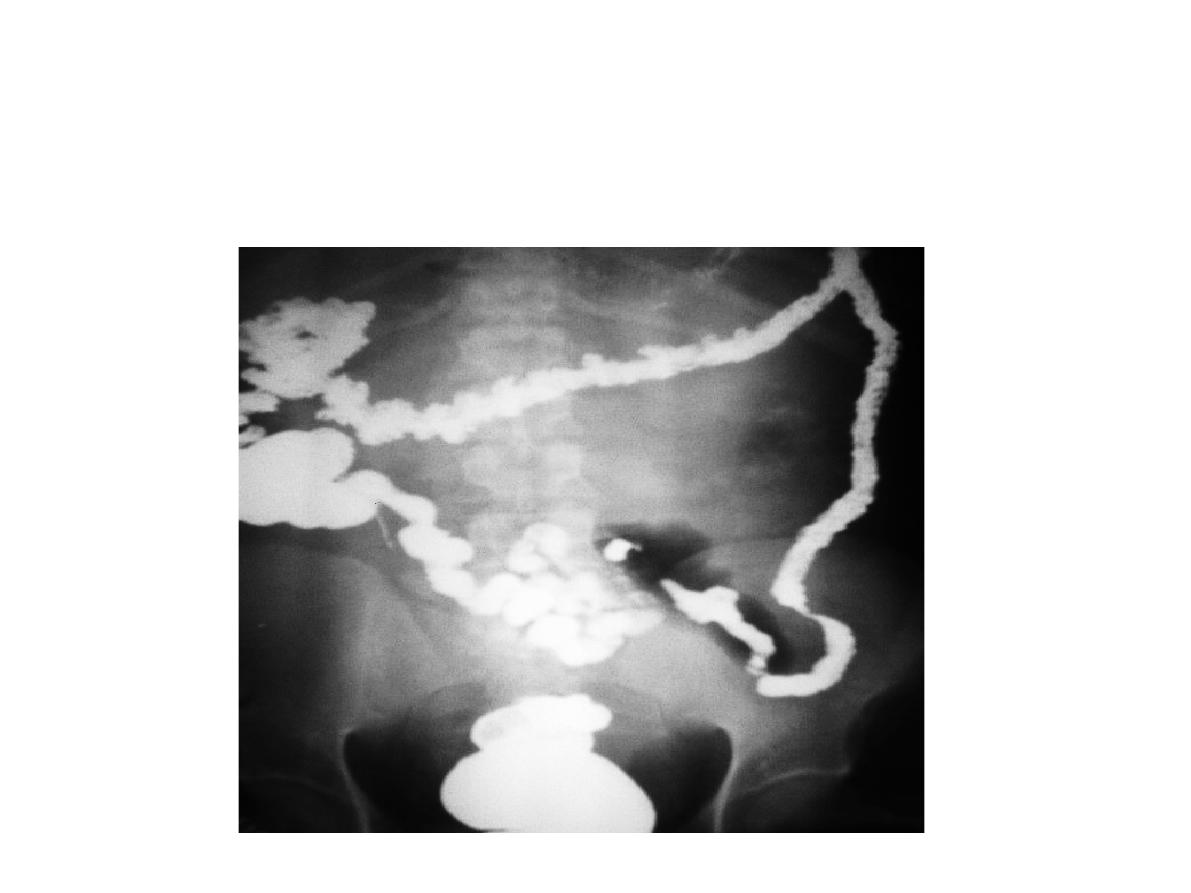
Station no. : VII
Station: X-ray slide
Canonball appearance ( metastasis)
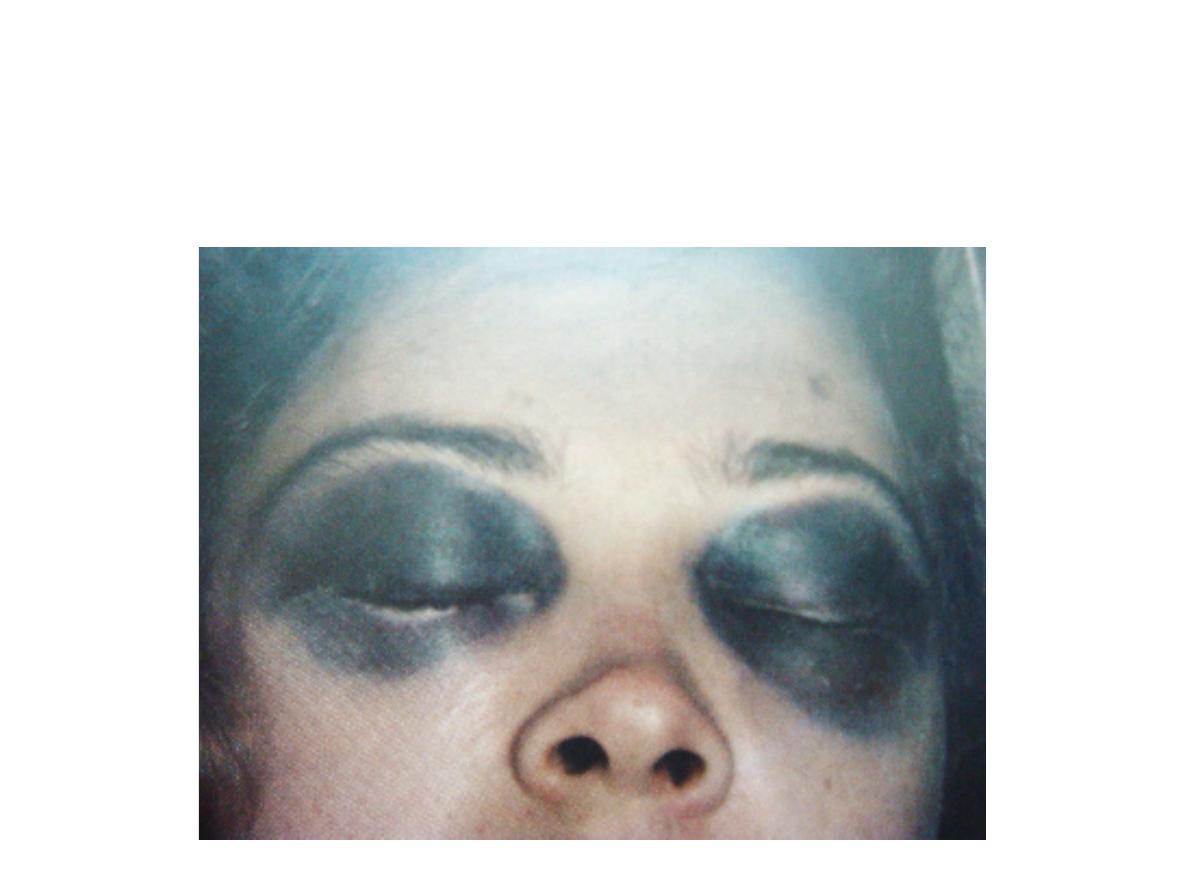

Station no. : VIII
Station: Head injury
Raccon eye ( skill base #)
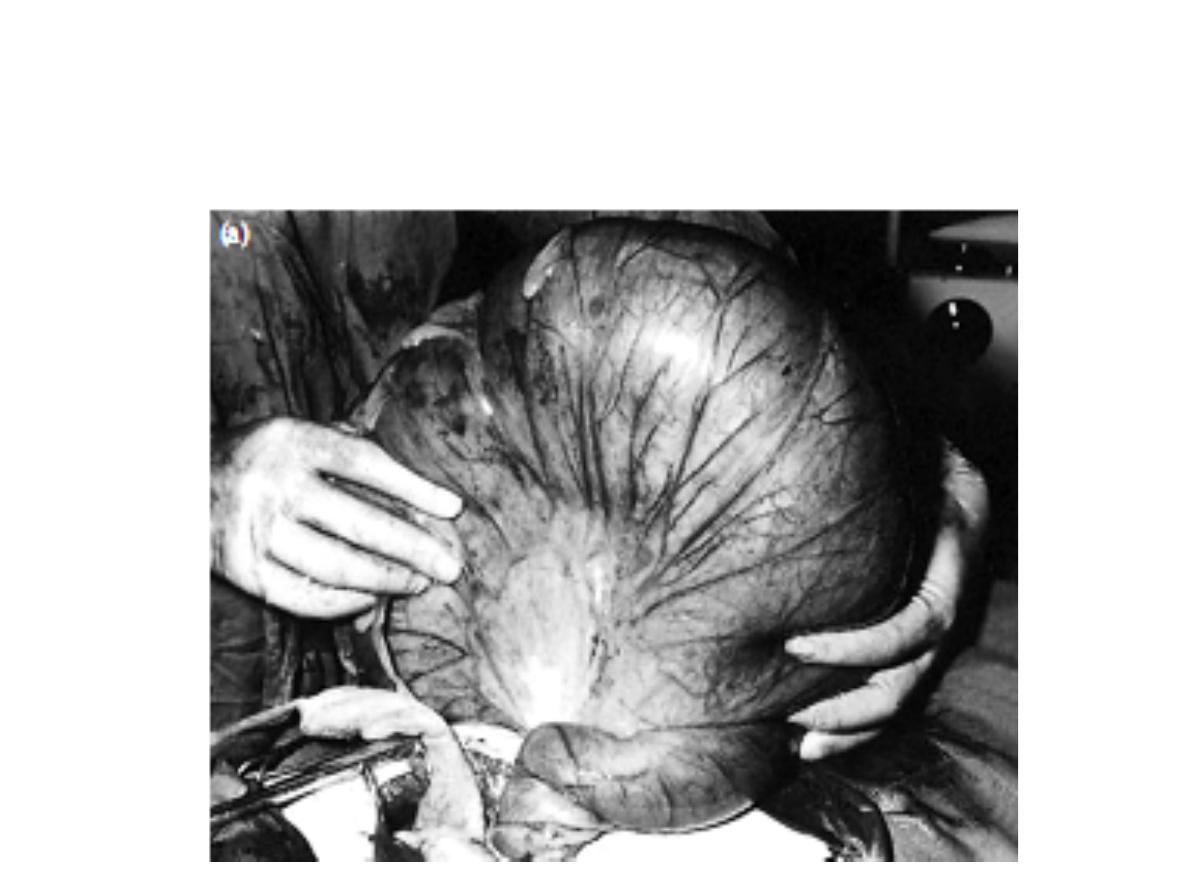
Station no. : IX
Station: Colon lesion
toxic megacolon
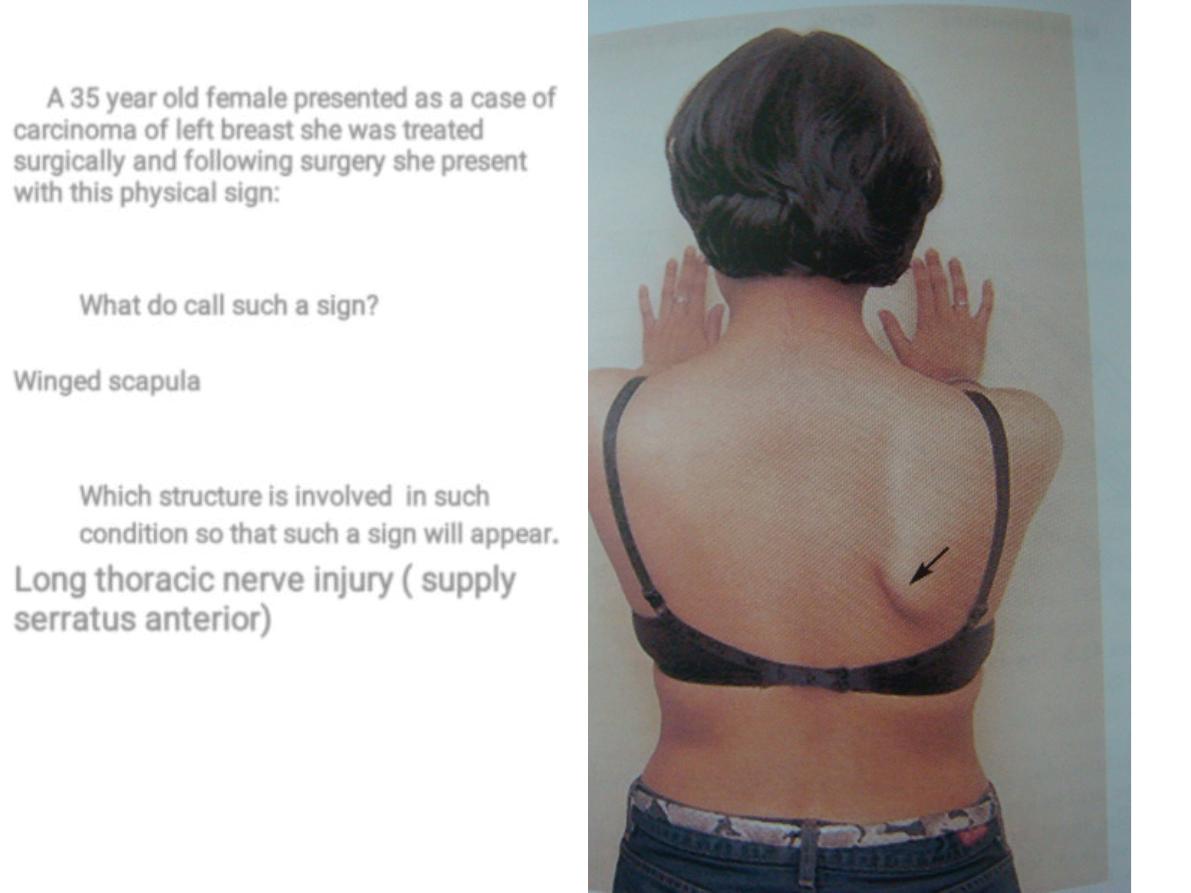
1.
1.
A 35 year old female presented as a case of
carcinoma of left breast she was treated
surgically and following surgery she present
with this physical sign:
What do call such a sign?
Winged scapula
Which structure is involved in such
condition so that such a sign will appear
.
Long thoracic nerve injury ( supply
serratus anterior)
1
a.
a.
a.
A
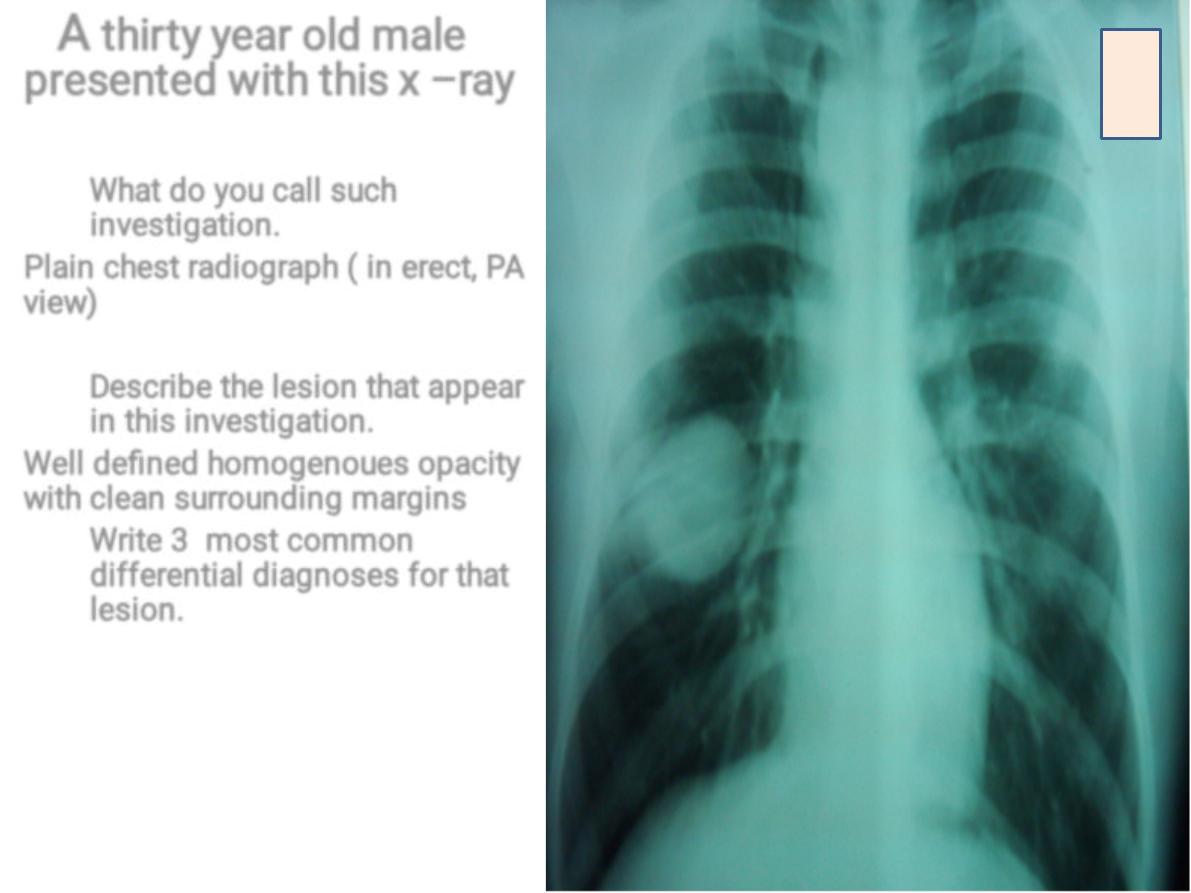
thirty year old male
presented with this x –ray
What do you call such
investigation.
Plain chest radiograph ( in erect, PA
view
)
Describe the lesion that appear
in this investigation.
Well defined homogenoues opacity
with clean surrounding margins
Write 3 most common
differential diagnoses for that
lesion.
1. Hydatid cyst
2. Benign tumor
3. Tuberculoma
2
a.
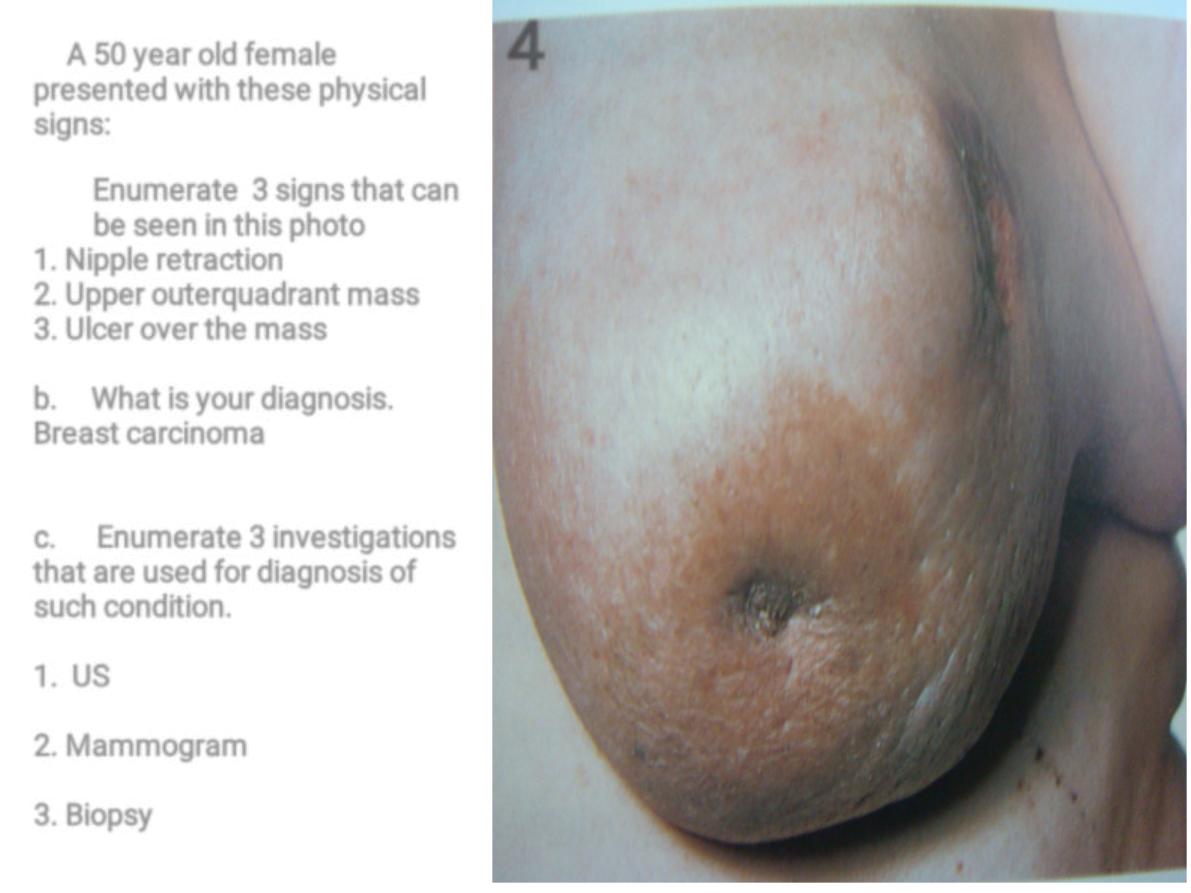
A 50 year old female
presented with these physical
signs:
Enumerate 3 signs that can
be seen in this photo
1. Nipple retraction
2. Upper outerquadrant mass
3. Ulcer over the mass
b. What is your diagnosis.
Breast carcinoma
c. Enumerate 3 investigations
that are used for diagnosis of
such condition.
1. US
2. Mammogram
3. Biopsy
4
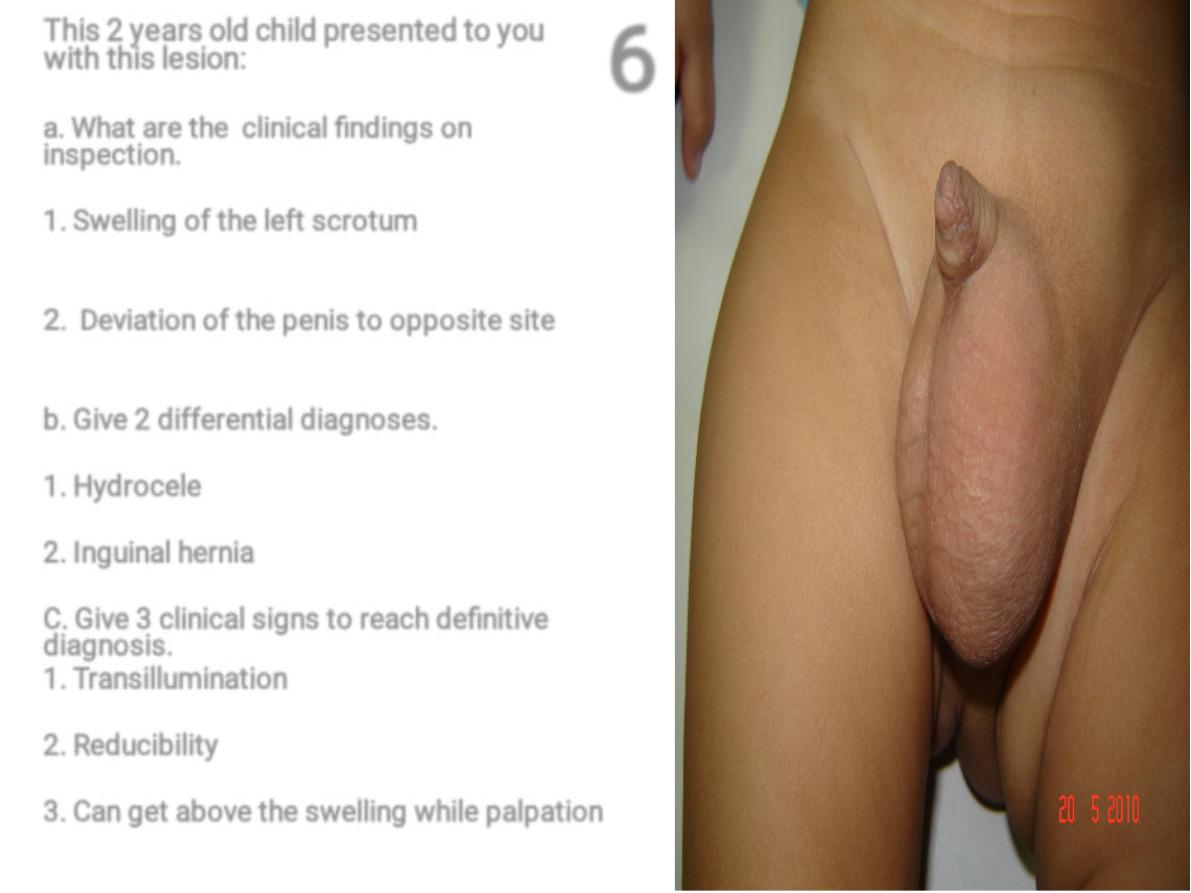
This 2 years old child presented to you
with this lesion:
a. What are the clinical findings on
inspection.
1. Swelling of the left scrotum
2
. Deviation of the penis to opposite site
b. Give 2 differential diagnoses.
1. Hydrocele
2. Inguinal hernia
C. Give 3 clinical signs to reach definitive
diagnosis.
1. Transillumination
2. Reducibility
3. Can get above the swelling while palpation
6

8
8
a.
a.
a.
What do you call such
lines
Langer lines
What do they represent.
Natural orientation of
collagen lines
What is the benefit of
these lines in surgical
practice.
In incisions, to produce
minimal scar
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
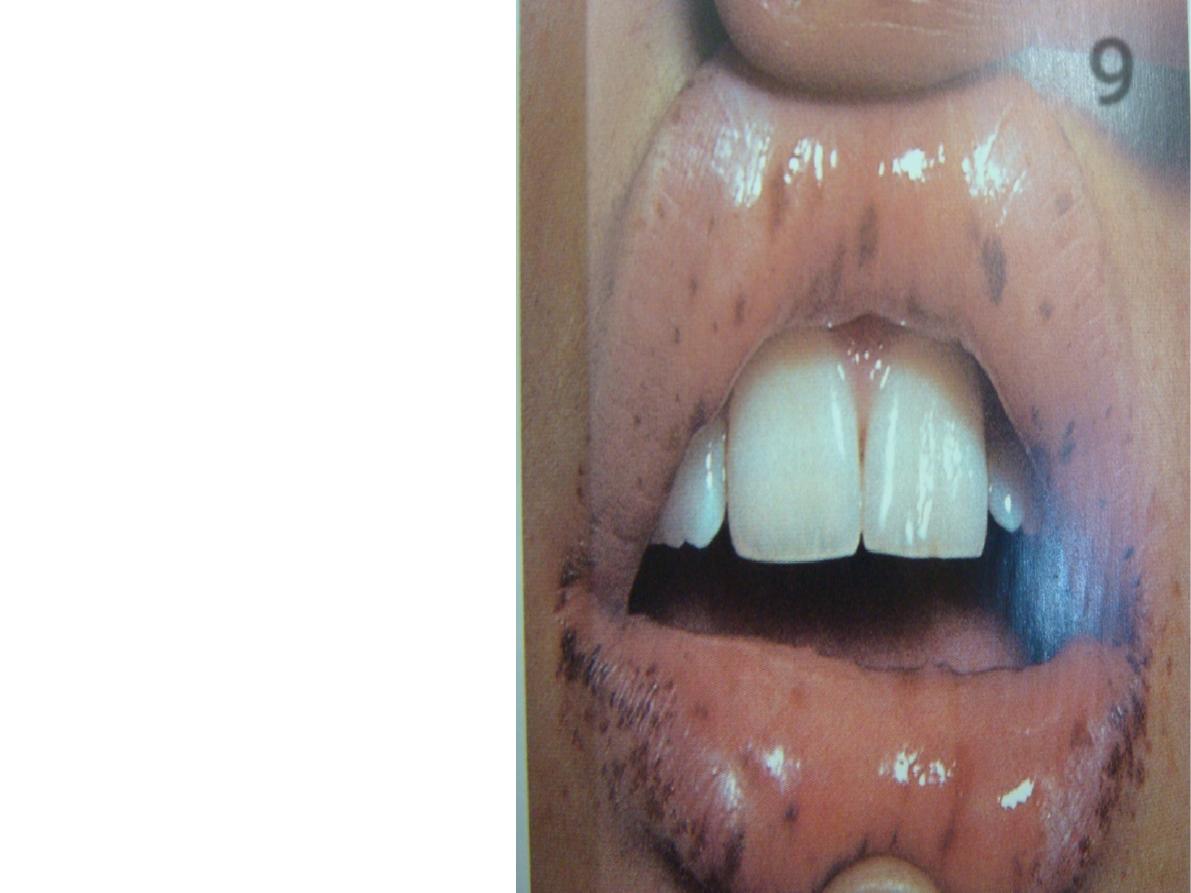
What are the abnormalities
that could be seen in this
photo.
Black or brownish spots over
the lips and oral mucosa
(melanosis)
Nominate the underlying
disease that could result in
such abnormalities.
1.Peutz jegher syndrome
2.Addison diseases
3.smoking
what are the associated
lesions that could be detected
in such patient.
Melanosis on palms and soles
Hamaromatous polyps in GIT
9
1
1
A.
A.
A.
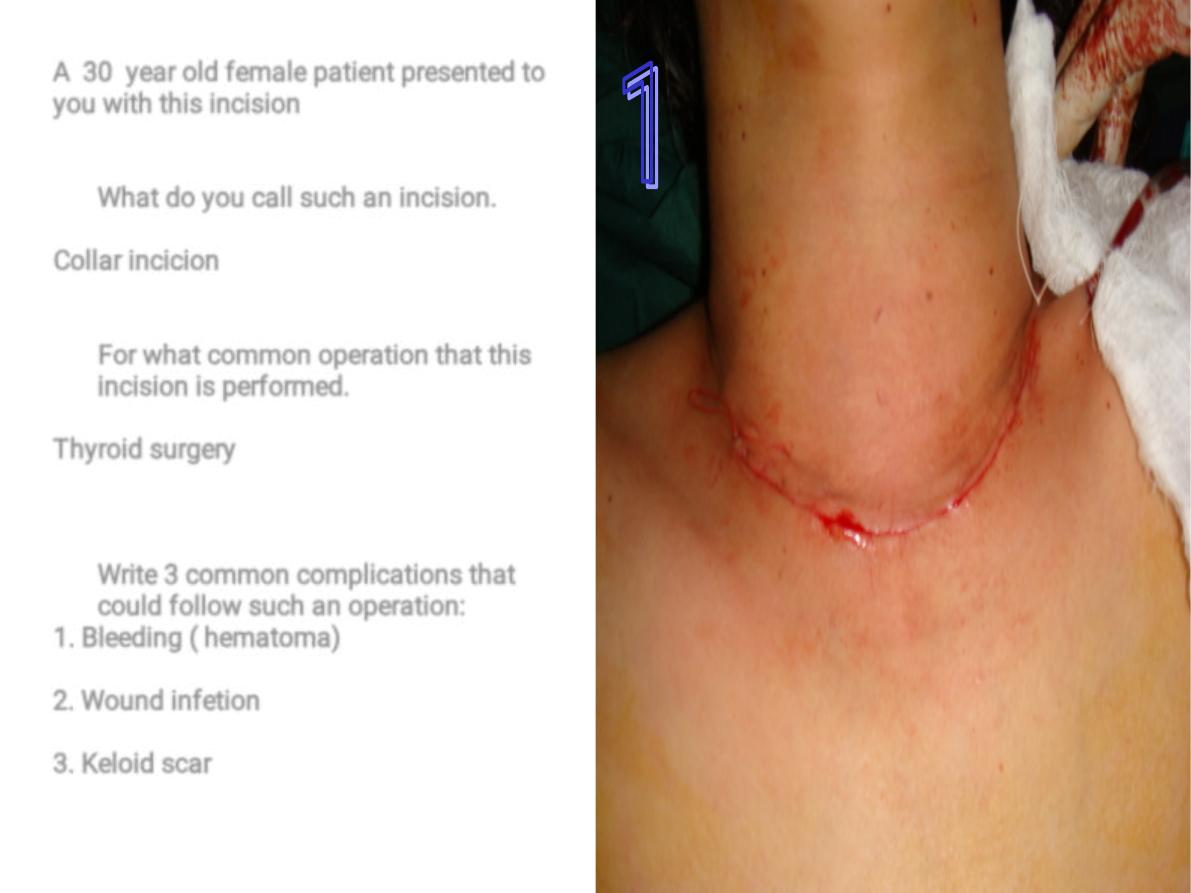
A 30 year old female patient presented to
you with this incision
What do you call such an incision.
Collar incicion
For what common operation that this
incision is performed.
Thyroid surgery
Write 3 common complications that
could follow such an operation:
1. Bleeding ( hematoma)
2. Wound infetion
3. Keloid scar
