
Dr. Ali Kadhim
Examination
Stand on right side
•
Permission
•
Position of patient
•
Supine for abdominal
◦
Siting for breast and thyroid (on chair)
◦
Standing of hernia , also supine
◦
Exposure
•
Abdominal from nipples to mid thigh
◦
Thyroid from nipples upward
◦
Abdominal examination
Parts include
•
Clavicle and supraclavicular in gastric carcinoma
◦
Bile diseases to back
◦
Intestinal may cause fracture vertebra
◦
PR for rectal and colonic carcinoma
◦
Inguinal for intestinal obstruction
◦
Scrotum for any undescended testis and huge hernia of intestines
◦
Steps of examination
•
Inspection
◦
Palpation
◦
Percussion
◦
Auscultation
◦
Inspection
•
End bed from foot
◦
For any asymmetry or bulging
‣
From right side
◦
For respiration
‣
Normally there is thoracic and abdominal
•
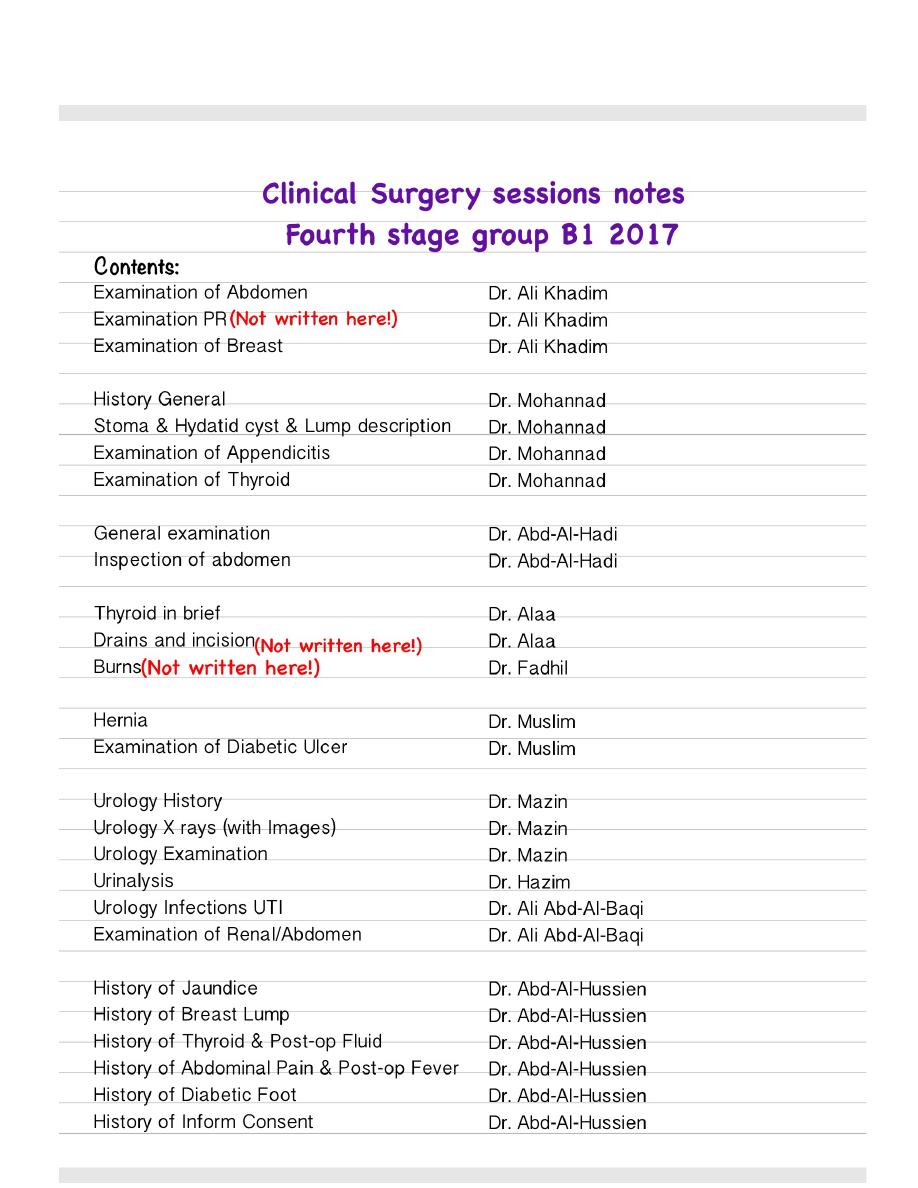
Acute abdomen presents as rigid abdomen
•
Epigastric pulsation in aneurism,
•
For umbilicus
‣
Inverted, normally
•
Flat,
•
Everted
•
In hernia or ascites
◦
Hair distribution
‣
Shape of abdomen
‣
Distended, flat, or scaphoid
•
Can be 4 parts division or 9 parts division
◦
Scars
◦
Longitudinal midline
‣
Laproctomy
•
Para median
•
Oblique
‣
For inguinal hernia
•
Grid iron for appendectomy (can be lance incision for cosmetic)
•
Koch for cystectomy
Pocket handle
‣
Ask him to cough for any herniation
◦
Palpation
•
2 parts
◦
Superficial
‣
For superficial masses and
•
tenderness
Start with part away from pain,
•
either clockwise or anti clockwise
Look for facial impression for any
•
pain
Deep
‣
For deep masses and
•
organomegaly
by palmar surface of hand
◦
Liver span:
◦
Percussion from 2nd rib
Till it become dull
Then by deep palpation from right iliac
fossa
Spleen palpation from right iliac fossa
‣
Renal palpation, left hand below costal margin and right palpation the kidney
‣
Difference between renal and spleen
‣
Splenic notch
Percussion dull in spleen
Pass hand between costal margin to check organomegally
Kidney retroperitonial
Pallout of kidney is present but not for spleen
Percussion
Dull or resonance
•
For ascites
•
Shifting dullness
◦
Transmitted thrill
◦
Auscultation
Iliocecal valve at mc point for bowel sounds
•
Renal bruit (indicate renal artery stenosis)
•

Dr. Ali Khadim
Breast examination
Parts:
•
Inspection
◦
Palpation
◦
Examination of axilla
◦
Examination of upper limb
◦
History
•
Identity
◦
Chief complain
◦
Story
◦
Systemic review
◦
Family and social histor
◦
Examination
•
Permission and right side
◦
Position of patient : sitting
◦
Exposure: both sides, from wrist to all chest, neck and head.
◦
Inspection
•
Symmetry
◦
Shape
◦
Size
◦
Color (like peau d'orange (a sing due to cutaneous lymphatic edema) in Ca and breast)
◦
abscess)
Scars , inflammation and other noticeable irregularities
◦
Breast is divided into four quadrants, common site for Ca is upper lateral (60%), and in
◦
areolonipple region (12%).
If any visible abnormality, Mention position, expected dimensions, description of color, any
◦
material or other things.
Dilated veins in chest and breast in mondor disease, sometimes associated with
◦
thrombophlebitis.
Nipple
◦
Retraction, (mainly due to cancer)
‣
Normally directed upward laterally.
◦
Directed towards tumor.
•
Discharge
‣
Bloody: ductal papilloma
•
Dirty green: breast abscess and ductactasea, ante-fibroadinosis
•
Axilla for any visible masses (Ca disseminate in 85%) or ulcers
◦
52 lymph nodes in axilla
‣
Apical
•
Central
•
Medial
•
Lateral
•
Posterior
•
Also supraclavicular lymph nodes
‣
Breast lymph nodes draining is to axillary and to intra mammary
‣

First lymphnodes drain breas is sentinel lymphnode
•
Aerola
◦
Dark color in pregnancy
‣
Swelling in montgomery cyst (sub areolar swelling)
‣
Neck swellings
◦
Upper sternal notch
◦
Ca breast can disseminate to contralateral lymph nodes
◦
Upper limb check for
◦
Edema
‣
Distended veins
‣
Scars and deformity
‣
Clubbing
‣
Palpation
•
By palmar surface of hand, we can use bimanual examination(2hands, also used in renal,
◦
salivary, thyroid, Cervical lymph nodes)
Start away form the site of lesion
◦
Clock wise or anti clockwise
◦
Measure dimension, regularity, hardness state
◦
Movable or not
◦
Margins (everted in ulcerative epeithelioma or carcinoma), also base of ulcer for rigidity
◦
Also axilla palpation by three positions (either raise patient hands, or put her hand on your
◦
elbow, or from behind of the patient)
Upper limp for pulse, edema (non pitting), clubbing.
◦

Dr. Mohannad
History
Identity
Name,
•
third name for differentiation
age,
•
sex,
•
thyroid related to females more than male
address,
•
Occupation
•
asbestosis in mine workers
urinary tumors in factories
jaundice in health care stuff due to HBV
Nationality
•
ca esophagus is common in Iran
bilharziasis is common in Egypt
ca stomach in Japan
ca breast in western country
Next of kin
•
for communication
Marital state
•
mostly in females
Date of admission
•
Chief complain and duration
History of Present illnes
analysis of chief complain
•
ask about related symptoms according to system or site involved
•
common questions
•
weight lose
fever
jaundice
reaction of patients
•
consulting, managed at home, herbal, investigation, medications
what is he waiting now?
•
investigations, follow up,
current state?
•
Review of systems
Past childhood history and vaccination
Past medical history
Past surgical history
previous operation
•
any complication, like pain, bleeding,

previous admissions
•
previous transfusion ?
•
Drug history
any chronic usage
any allergic for a drug or food
ask about common drugs
aspirin, antihypertensive, b blocker, insulin, antiepileptic drugs, steroids
Family
familial diseases
•
goiter, gall stone
Gynecology history
menstrual cycle, regularity, duration, first time menarche
•
Social
smoking
•
any animals
•
foot zoonotic diseases
alcoholic
•
General examination
Examination of exposed parts of body
(head and neck, both hands, both feet)
Description points:
young patient
•
built
•
position
•
state comfortable or not
•
conscious
•
orientation
•
dyspnea
•
JACOP (jaundice, anemia, cyanosis , odema, lymphadenopathy)
•
(Jaundice checked from upper sclera because it contain collagen fibers and discoloration
◦
appear easily )
(pallor from conjunctive, or lips, or palm and creases)
◦
Cyanosis central or peripheral
◦
oral hygiene
•
clubbing
•
edema
•
over shin of tibia 10 cm above medial malleolus for 30-60 seconds, and looking to face
◦
pitting edema causes( organ failure)
◦
non pitting (lymphatic obstruction, filariasis , lymphadenopathy, lymph adenopathy, DVT,
◦
myxedema)
lymph nodes examination of neck
•
2 groups
◦
circular
◦
sub mental, submandibular, pre auricular, occipital, Supra clavicular
‣

tonsillar, juguloomohyoid, ...
‣
central longitudinal
◦
enlarged in carcinoma of thyroid, meningeal
‣
check vital signs
•
pulse bilaterally, for rate, volume, rhythm, and state of blood vessels,
◦
Temperature, pressure and respiratory rate
◦

Dr. Mohannad
Enterocutaneous fistula: abnormal connection between bowel and skin.
Stoma
In surgery, stoma is artificial connection of viscera to skin.
•
Named according to the part of viscera
•
Uretrostomy
◦
Cystotomy
◦
Gastrostomy
◦
Ileostomy
◦
Indications of bowel stoma
•
Permanent
◦
In case of rectal and anal resection
‣
Temporarily
◦
Colonic resection in non prepared operations
‣
Trauma to colon
‣
Obstruction
‣
Tumor
‣
High fistula in ano
‣
Hirschsprung's disease, congenital intestinal obstruction due to aganglionic segment
‣
(three stages: first colostomy, resection, then anastomoses)
Types
•
End colostomy (2 stoma : proximal and mucous)
◦
Loop colostomy (1 stoma only, stoma in the anterior wall only and the posterior wall is
◦
remain connected)
Double barrel (1 stoma only, resection but then anastomosed and opened to one stoma)
◦
Hartman procedure (1 stoma for proximal, and distal is closed in its place like rectum)
◦
Ileostomy: Ileum differs from colon in that colon form well formed stool, while ileum contents
•
contain digestive enzymes. So in ileum the stoma is raised above the skin, called spout.
Site:
•
Comfortable for patient (not umbilicus)
◦
Not near prominence parts (not in ASIS), neither on rectus sheath.
◦
Best site is: Mid way between umbilicus and ASIS , because avascular (away from rectus
◦
sheath) and not on a prominent part.
Complications
•
Infections (colostomy diarrhea)
◦
Bleeding, usually delayed.
◦
Hernia (Para stomal hernia)
◦
Obstruction
◦
Prolapse
◦
Retraction
◦
Skin necrosis
◦
Psychological upset
◦
Bags
•
Disposable
◦
Types (normal, concentrating, odor absorbing).
◦
Hydatid cyst
Simple cyst is thin lined, homogenous non septa containing. Other wise it is complex.
•

Usual presentation is drugging and heavy weight complain.
•
If ruptured, presented with peritonitis and anaphylactic because fluid is highly antigenic
•
Investigations:
•
Ultrasound
◦
CT is important for surgery
◦
MRCP in jaundiced complaining.
◦
Blood count show eosinophilia
◦
Serological is ELISA
◦
Treatment
•
Medical (albendazole 400 mg daily for 3 months, mebendazole) in case the size is less than
◦
4 cm or in danger place like adjacent to inferior cava.
Praziquantel for preventing of recurrence.
‣
PAIR: for well localized cyst, aspiration then injection of scolicidal like hypertonic saline.
◦
Surgery: in symptomatic or more than 4cm. Deroofing (germinal and laminated layers), with
◦
omentoplasty if needed.
Laparoscopic
◦
Lump
Site
•
Shape
•
Color
•
Surface
•
Edge
•
Consistency
•
Tenderness
•
Temperature
•
Reducibility
•
What make the lump noticed
•
Duration
•
What the patient think about its diagnosis
•
Composition
•
Cells that make it solid
◦
Extravascular fluid (urine, serum, CSF)
◦
Gases
◦
Intravascular fluid (blood)
◦
Consistency
•
Stony hard (like wood)
◦
Rubbery
◦
Spongy
◦
Soft (like ear lobe)
◦
Firm (like nose cartilage)
◦
Fluctuation
•
Fluid thrill
•
Translucency (by torch in dark room) indicate clear fluid like hydrocele.
•
Pulsation (like aneurism)
•
Compressibility (decrease in size but does not disappear) like varicocele. ((Compressibility differs
•
from reducibility in that reducible mean disappear))
Bruit (audible sound of turbulent flow) like partially obstructed vessels
•

Dr.Mohannad
Appendicitis
(Read official lecture of FourtStage/Dr.Mohannad for full information)
Pelvic appendicitis can give diarrhea (pseudous , irritative diarrhea)
•
Peek age are teenagers 16-20
•
Rarely in children because of wide base of appendix
◦
DD in elderly can be Ca cecum
•
Examination
Inspection
•
Distended due to ileus but not always
◦
Pointing sign when asked to say where is the pain
◦
Cough pain positive
◦
Palpation
•
Deep seated tenderness (most important sign)
◦
Rebound tenderness
◦
Rising sign, when pressing on other site, the patient suffer from pain at right iliac fossa
◦
For
retrocecal appendicitis
◦
Psoas sign
‣
Sleep lateral,then make the patient over extend his hip joint
•
Obturator sign
‣
Internal rotation of knee joint
•
Hematurea sometimes due to close position to ureter.
‣
Diagnosis is clinically by:
Alvarado Score:
•
More than 7 acute appendicitis
◦
5-7 equivocal
◦
Less than 5 not acute appendicitis
◦
Symptoms (each is one point)
•
Shifting pain 1
◦
Anorexia 1
◦
Nausea and vomiting 1
◦
Sings
•
Deep tenderness
2
◦
Rebound tenderness 1
◦
Mild pyrexia 1
◦
Investigation
•
WBC
2
◦
Neutrophilia is extra 1
‣
Also check:
Pregnancy even if unmarried
•
Ultrasound:
•
Can determine presence or absent of acute appendicitis by (90%)
◦

CT scan can diagnose it also.
•
Treatment of acute appendicitis by Surgery after preparation of the patient.
Complication of appendicitis (before operation)
Appendicular mass: inflammatory mass
•
Due to good immunity (omentum work)
◦
If operated in this condition can cause
iatrogenic fistula.
◦
Conservative by horshner resheen regime
◦
Management by
Ochsner Sherren regimen:
◦
Addmision
‣
Antibiotic (for E.Coli, anaerobes, bacteroid, klebselia) -->(Cephalosporin 3: cefitaxin
‣
which is
Claforan)
Analgesia
‣
I.V fluid
‣
Null by mouth or fluid diet.
‣
Monitor size of mass with pencil daily.
◦
Failure of conservative
◦
Acute abdomen pain
‣
Hectic type fever
‣
If treated, no need for surgery and no recurrence will occur in 2/3 of patient.
◦
Appendicular abscess
•
Post operative Complication
•
Infection
◦
In accute infection 10-20%
‣
More than 40% in perforated or dirty wound (when you see drain with grid iron incision it
‣
is mostly perforated appendicitis)
Paralytic ileus
◦
Incisional hernia, and direct inguinal hernia
◦
Adheison (most common cause of post operative intestinal obstruction, other common is
◦
gynecological) usually in terminal ileum.
Recurrence (due to not compelete dissection "partial appendectomy", mostly due to
◦
labroscopic operations mostly
Tumor:
Adenocarcinoma of appendix 1-2% of large bowel tumor.
•
Cecum tumor 12%
•
Ca most common in sigmoid and upper rectal junction 38%
•
Ascending, transverse, descending each 5%
•
In appendix most common is
carcinoid
Crypts in appendix secrete serotonin
•
If carcinoid tumor is functional and reached liver it is called
carcinoid syndrome
•
Symptoms : flushing attack, aggravated by alcoholism, loud bowel sounds, diarrhea, with
◦
valvular heart diseases.
Treated by simple appendicectomy (if not done already, otherwise do nothing)
•
If involved cecum or more than 4 cm need right hemilectomy (appendix, cecum, part of ileum
◦
and part of ascending colon)
Anatomy of appendix should be read in lecture

Extra Dr Mohammad (Part of B2)
Parathyroid is small orange similar to nodule , if resected cause severe hypcalcemia
Infection in thyroid surgery is rare because it is clean area and highly blood supplied.
Difference between keloid and hypertrophied scar is,
Keloid extend beyond incision,
•
While hypertrophied scar does not extend and is limited to incision
•
Multinodular goiter should treated by subtotal thyroidectomy
Examination of thyroid
Position: siting position
•
Exposure: head and neck till nipple
•
Inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation
•
Inspection
•
Anterior aspect, is there any swelling ? Its size ? Center of neck ? Shape ?
◦
Ask patient to swallow
◦
If it moved then it is related to tongue and it is not Lymph node, dermoid or other.
‣
Ask patient to protruding the tongue
◦
If not moved, it is goiter, not thyroglossul cyst (should be removed because it is
‣
complicated by malignancy and infection)
Is it tender or not
◦
Position of trachea by index finger in Suprasternal notch, deviated means retrosternal
◦
extension
Ask patient to raise his hands from shoulder, flushing and congestive is positive due to
◦
obstruction of veins
Palpation
•
Stand behind the patient chair, Flex head a little bit
◦
Put your hands on ipsilateral anterior part of neck, then move of one hand at a time (by
◦
fingers)
If movable it is not malignancy (malignant is fixed)
◦
Edge of extension (if not found, maybe retrosternal extension)
◦
Also check lymph nodes of that site,
◦
Carotid pulse (anterior border of the upper two third of sternalcledomastoid), if absent or
◦
decreased, it is sign due to tumor extension
Thril means hypervascularity
◦
Repeat the other side bilateral.
◦
Percussion
•
On clavicle with one finger
◦
Normal resonance, if not means something is under it
◦
Also chest.
◦
Auscultation
•
Bruit in graves
◦
Examination of eye
Due to post oribtial infiltration of fluid and cells
•
Unilateral is found but very rare
•
Mild oxopthoalamous Lower edge of upper sclera is visible , called sign
•

Moderate oxoopthalamous : lost of forehead wrinkling when looking upward
•
Severe exophoalamous: opthalmoplasia diplopia, hyperplasia of extra orbital muscle (superior
•
rectus and inferior oblique, superior lateral position vision)
Congestion of lower conjunctiva, Chemosis
◦
Möbius sign, lose of convergence
◦
Lid retraction due to overactiivty of sympathetic activity
•
Lid lag: Delay in following object upward and downward,
•
Hand and leg examination
Nail changes
•
Hair lose
•
Wasting of muscles
•
Sweaty palm
•
Tremor (fast fine tremor, occur in tension and thyrotoxicosis), (coarse tremor in Parkinson's
•
disease)
Pulse: sinus tachycardia , suprvnetricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation
•
Hyperreflexia of knee jerk, or delay in relaxation phase of reflex in knee.
•

Dr. Abd Al-Hadi
General examination
Examination of exposed part of body
•
Head
◦
Neck
◦
Upper limbs
◦
Lowe limb
◦
1.Permission and introduction
2.First clues (ABCD):
Age (number or term)
•
Built: obese, thin, cachexic, average,
•
Comfortablilty: not in pain, irritable, lethargic, sleepy
•
Disability (Orientation): (time, place, person), conscious
•
3.Surroundings and position
4.General signs (JACCOL):
Jaundice (yellowish discoloration, it is a sign)
•
In upper sclera while the patient looking downward, under natural light.
◦
Also in palm if high level of bilirubin.
◦
If so progressive like in Ca, can be very intensive or nearly green.
◦
Anemia (pallor)
•
HB < 10
◦
In conjunctiva while patient looking upward
◦
Also found palm creases.
◦
Cyanosis (bluish discoloration, due to increased carbon dioxide)
•
Two types:
◦
central(important an pathological) in tongue and lips.
‣
peripheral( can be normal) fingers and nails.
‣
Clubbing
•
Oedma (extravasation in interstitial space)
•
Examined bilaterally by pressure with thumbs on legs 10 cm above medial malleolus and
◦
look to patient face (pain) for one minute, if positive finding then go upward proximally and
repeat test.
Pitting or non pitting.
◦
Lymph nodes
•
Siting position
◦
Classified to vertical and transverse cervical groups. Also classified to superficial and deep.
◦
Submental, submandibular, post auricular, pre auricular (horizontal)
◦
And occipital (indicate rubella)
‣
Superficial and deep cervical (vertical)
◦
Includes: Upper & jugulodigastric lymph nodes
‣
Examined along the sternocledomastoid muscle.
‣
Also Supraclavicular (mostly left node is affected)
◦
Check:
◦
Matted (in TB)
‣
Discrete
‣
Tenderness
‣
Hard or soft
‣
Size
‣
5.Regional (Head&Neck&Hands&Legs)
Head
Hair distribution
•
Forehead
•
Eyebrows
•
Nose deviations
•
Scars
•
Pigmentation or tattoo
•
Mouth: tongue, lips, ulcers
•
Neck
Veins
•
Scars
•
Pigmentation
•
Masses
•
Thyroid
•
Lymph nodes
•
Hands
Skin
•
Pigmentation or erythmia
•
Swellings
•
Deformity
•
Muscles wasting
•
Nails (koleneckia, leukonekia)
•
Clubbing
•
Legs
Movements
•
Color
•
Swellings
•
Tenderness
•
To ease the procedure, divide each part to:
skin(scar, hair, pigments, veins, ulcer, pain...)
•
muscle (wasting, movements, pain...)
•
bone (deformity, disability, pain, swelling...)
•
internal objects (masses, pain, swellings...)
•
6.Vital signs:
Temperature
•
Thermometer in tongue for 1 minute
◦
Axillar (+0.5)
‣
Rectal (-0.5)
‣
NormL 37.2 +- 4
◦
Fever >37.5
‣
Pyrexia > 38.5
‣

Hyperpyrexia >40
‣
Can be caused by infection or metabolic problem
◦
Respiration
•
Normal 16-18
◦
Tachypnea >20
◦
Blood pressure
•
Bilateral on brachial
◦
Hyper 140/100
◦
Pulse rate
•
1 minute
◦
60-100
◦
Check also:
◦
Rhythm
‣
Volume (good, threads)
‣
Character
‣
State of blood vessels
‣
Synchronicity between right and left
‣
Radiofemoral delay (coaractation)
‣
7. Thanks patient, help him dressing if needed and wish him healthiness.
Summarize findings (Positive and negative) to examiner.

Dr. Abd Al Hadi
Inspection of abdomen
End bed assessment for abdomen:
•
Is it flat ? Is it symmetrical ?
◦
Near patient right side be at level of abdomen:
•
Respiratory movement
◦
Pulsation
◦
Peristalsis
◦
Masses
◦
Look for:
•
Hair distribution
◦
Dilated veins
◦
Any pigmentation, tattoos, cautery
◦
Striae
◦
Scars
◦
Incisions
◦
Umbilicus shape
◦
Discharges
◦
Ask patient to cough for locating hernia orifice
•

Dr. Alaa
Thyroid
Exophthalmus
Appearance of lower sclera
1.
Lid retraction, appearance of upper sclera
2.
Opthalmoplagia
3.
Ecchymosis
4.
irrevrisible even if thyroid treated
•
Hand
Sweating
1.
Fine tremor
2.
Pulse (sleeping pulse)
3.
Pemberton's sign by raising hands due to retrosternal goiter, most common in female due to
•
short neck.
Thyroid move with swallowing because it is attached to pretracheal fascia
•
Normal thyroid is impalpable.
•
But even if was impalpable, you have to
exam the regional lymphnodes like cervical in
◦
case of occult tumor.
Q/what is the difference between occult tumor and lateral apparent tumor?
◦
Any
lump check if: not compressible, not reducible, not pulsatile, not attached to skin, not
•
attached to internal structures, move with swallowing? And mention site and dimension and
appearance.
Check trachea position
•
Percussion to clavicle on the medial two third of clavicle to check if retrosternal goiter, normally
•
resonance if no mass underneath.
Auscultation to check if there were bruit.
•
Superior thyroid of artery lied on upper pole of thyroid
◦
Old age, rapidly progressive with hoarseness of voice indicate anaplastic tumor
•
(For complete notes on thyroid, check theoretical lecture Fourth Stage Dr.Alaa)
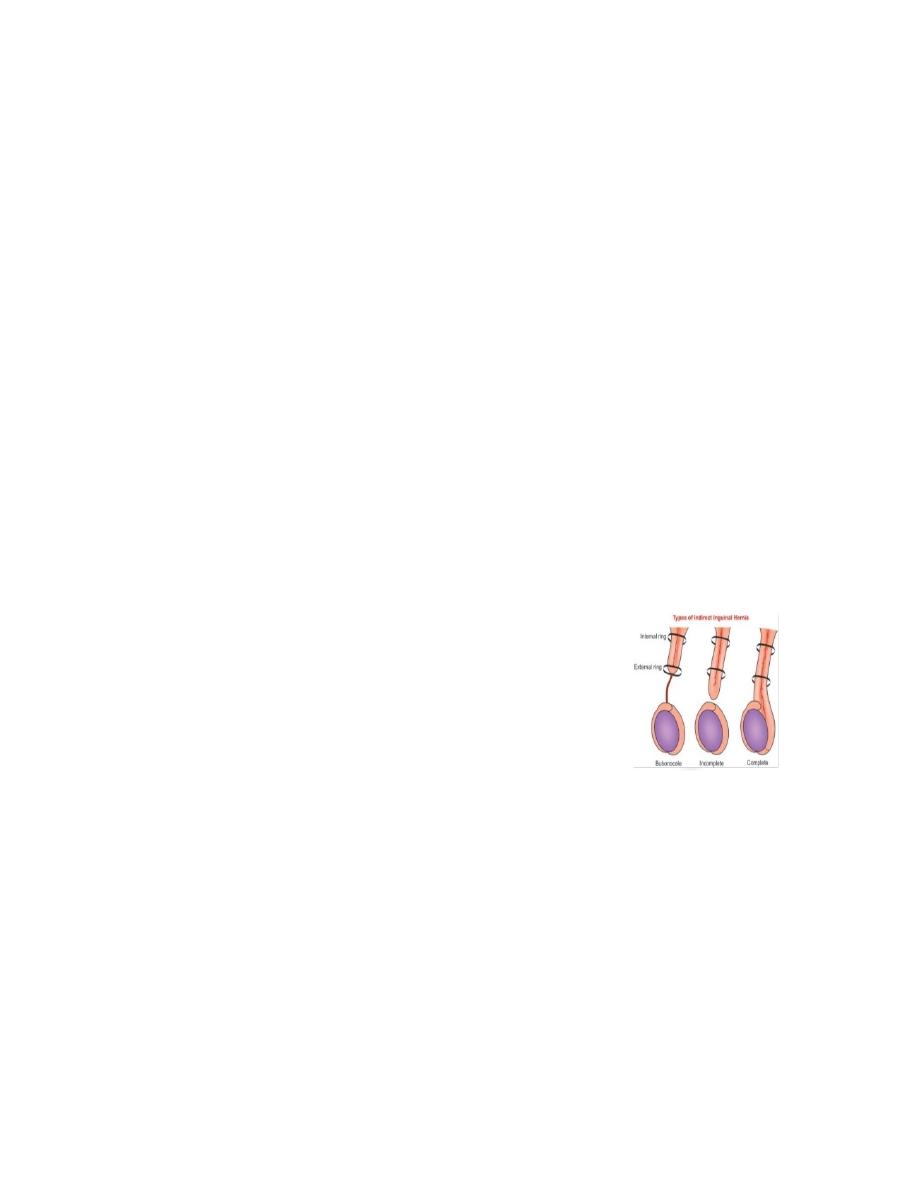
Dr. Muslim
Hernia
(Read hernia official lecture or other source(required), these notes only for few highlighted things)
Causes of hernia:
•
Congenital
◦
Acquired:
◦
Increase pressure
‣
Pregnancy
•
Ascites
•
Weakness in the walls
‣
General feature
•
Sac
◦
Contents
◦
Coverings
◦
Stab wound injury if viscera get out from it, differs from viscera getting out in hernia, in that the
•
(Stab wound) does not have sac.
In inspection part in examination of hernia case, don't forget to ask the patient to cough "
cough
•
impulse".
Also in inspection of hernia there is two positions, laying and standing.
•
Differential diagnosis of cough impulse:
•
Reducible hernia (only this type of hernia)
◦
Psoas abscess, in spinal TB.
◦
Saphenous varices, examined on standing position, differentiated from hernia by finding
◦
dilated tortuous veins in leg, disappear when lifting the leg upward, becoming more clear
when walking.
Inguinal hernia according its
level:
•
Bubonocele (limited to inguinal canal)
◦
Funicular (extend outside inguinal canal above the testis)
◦
Complete or scrotal (extend beside testis, indicate congenital
◦
patent processes vaginalis)
Cardinal 5 features of
intestinal obstruction:
•
Constipation
◦
Vomiting
◦
Colic pain
◦
Distention
◦
Dehydration
◦
Diagnostic test in intestinal obstruction is X-Ray in standing position
•
(fluid levels).
In abdominal examination never forget
Genitallia and PR and Back examination.
•
Mass in groin differential diagnosis:
•
Irreducible hernia
◦
Mass
◦
Lymph node
◦
Sepaceous abscess
◦
Lipoma
◦
Undescended testis
◦
Hydrocele
◦
Tumor
◦
Unobliterated processed vaginalis types according to level:
•
Hernia
◦
Levels of indirect
inguinal hernia
Insisted
◦
Hydrocele
◦
Swellings in scrotum differential: Either hernia or testicular/scrotal problems, differentiate by
•
Cough impulse test
‣
"Can get above it" test
‣
In scrotal, can catch it and letting it being completely below your pressuring fingers,
•
also by palpation it is felt narrow or thin.
In hernia, can not get above it and by palpation felt thickened.
•
In cough impulse positive hernia result, you can differentiate:
•
Either direct, indirect inguinal or femoral.
◦
First reduce it.
◦
By
Three finger test (Zieman's technique): Put your three
◦
middle fingers on :
1-deep ring (midpoint of inguinal ligament),
2-superficial ring (medial to deep ring) and 3- femoral ring
(below and lateral to pubic tubercle).
Ask patient to cough.
◦
Remove one finger at a a time (start from femoral) and repeat
◦
the test to identify the correct site.
Strangulated hernia
•
Signs of obstruction
◦
Non reducible
◦
Local signs of redness, tenderness, pain and swelling maybe.
◦
Emergency
◦
First try reduction methods:
‣
Head down or laying.
•
Elevated legs.
•
Sedation usage to relax
•
Try to reduce it manually, but not forceful (if forcefully might cause reduction-in
•
mass, contusion, rupture, reduction indoculous E):
Small bowel difficult at beginning then easy.
◦
Omentum easy at beginning and difficult later.
◦
Inguinal
ligament
Three finger test
position

Dr.Muslim
Compartments of lower limbs to check:
Vascular
•
Dilated veins, atrophy skin, abnormal distribution of hair, anemic, cyanosed.
◦
Neural
•
Drop foot
◦
Sensation and pain
◦
Skeletal and muscles
•
Atrophy
◦
Wasting
◦
Deformity: club foot, hallux valgus, Genu varum, flat foot, polydectally, hammer toe,
◦
amputation.
Lymphatic
•
Diabetic ulcer examination
Inspection
•
Exposure above the knee
◦
Any Deformity (mentioned above)
◦
Vascular abnormalities (mentioned above)
◦
Ulcer
◦
Ulcer is discontinuuation of epithetial surface
‣
It is chronic wound
‣
In diabetic it is usually
painless (that's why you see multiple scars on leg and foot)
‣
Types of ulcer:
‣
Atrophic (arterial) : due to poor blood supply
•
Venous ulcer: due to varciocele
•
Common sites:
‣
Arterial:
•
Pressure areas (big ball(of toe), lesser ball and heal)
◦
Friction areas (between the toes, prominence under big toe with shoes
◦
especially new shoes, medial mallelous)
Venous: above medial mallelous
•
Describe: site, size, shape,
‣
Coverings, pus
•
Discharge,
•
Margins (
slope which is most common), under man or iceberg, rule out(in Ca and
•
chronicity))
Multiple trauma or previous scars (because of lose of sensation)
◦
Palpation
•
Vascular
◦
Capillary refilling (you can compare with your hand)
‣
Temperature (with dorsum of both your hands moving them on both legs to compare
‣
distal with proximal parts)
Distal pulsation
‣
Femoral,
•
Popliteal,
•
Flex the knee , or on a prone position
◦
Posterior tibial, (between medial mallelous and achilles tendon)
•
◦
Dorsalis pedis (between first and second middle metatarsal)
•
10% have no dorsalis pedis as normal variety
◦
Maneuver is:
•
Three finger
◦
Relax by mildly dorsoflexion of the feet
◦
Check for presence or not, and also:
•
Rate, regularity, volume , any other abnormaliy
◦
Ankle brachial index (blood pressure), normally it should be near one. Abnormal when
‣
=<0.6 (ischemia)
Buerger's test
‣
Elevate the foot and leg
•
Pallor and emptying of veins
•
Then move it back, this cause severe pain due to sudden gushing of blood.
•
Ulcer
‣
Check base of ulcer weather superficial movable or fixed
•
Ankle
edema
‣
Non pitting in lympharic
•
Pitting in interstitial
•
Neurological
◦
Sensory
‣
Superficial Touch with cotton on different parts of both legs
•
Deep touch
•
Pinprick to check pain (ناحتملااب كايو سوبمد)
•
Temperature
•
Joint position
•
Motor
‣
Tone
•
Power
•
Against resistance 5/5
◦
Against (between 5 and 3) 4/5
◦
Against gravity 3/5
◦
With gravity 2/5
◦
Frickles 1/5
◦
No 0
◦
Reflexes
‣
Babinisky sign
•
Ankle jerk
•
Knee jerk
•
Venous
◦
Vneoun ulcer usually above medial mallelous (saphenous vein)
‣
Varicosity
‣
Abnormal valves between superficial and deep
•
Above ankle
‣
Mid way between knee and ankle
‣
Above knee
‣
Mid way between knee and saphenous opening
‣
Above femoral or saphenous opening.
‣
Tested by
tourniquet test
◦
Color the dilated veins at the sites mentioned
‣
above
Varicosity will disappear
‣
Tourniquet test

Then make him move, and remove one by one from below and check
‣
which one varcicosity is related to.
Auscultation
•
For bruit
◦
at site of arteries
‣
Pulsatile mass (aneurism)
‣

Dr.Mazin
Urology History
Ages
-18 childhood
•
19-45 young
•
46-65 middle age
•
66-80 elderly
•
85- geriatric
•
Common in childhood is congenital
•
Common in old is cancers
•
Sex
Ca bladder common in male
•
UTI common in female
•
Congenital common in male
•
Urethritis cystitis common in female
•
Address
Bilharziasis is common in rural
•
UTI and stones in city
•
Marital state
STI
•
Chief complain
The symptom brought the patient to seek medical care
•
In patient language
•
Systems review
Start with system involved then most related system
•
Family
Familial diseases
•
Social
Smoking
•
Drugs
•
Present illness: theses main stories:
Loin pain
Position
•
Character
•
Onset gradual or sudden
•
Severity
•
Mild which does not interfere with life
◦
Moderate interfere with life
◦
Severe is that prevent patient form engagement in daily activity
◦
Continuous or colicky
•

Continuous: in disease in renal system: distended kidney that hit capsule or inflamed
◦
mucosa.
Colic , wax and wine but does not relief (يفتخي ام سب مللاا لزنيو دعصي), occur in obstruction in
◦
hollow viscous like ureter stone due to peristalsis.
Site and Radiation
•
Loin pain radiate to abdominal area indicate kidney (if continuous pain) and upper ureter (if
◦
colicky) (upper ureter is from PUJ to upper border of sacral promontory)
In flank, radiate to umbilicus T10 feature of middle ureter (upper of sacral promontory to its
◦
lower border)
In Supra public radiate to testis or labia features of lower ureter (lower border of Sacral
◦
promentray to vesicouretral junction) , mostly cystitis
Relieving and aggravating factor
•
Rest, drugs, actiivty
◦
Association
•
Frequency (more than 2 times in 3 hours)
◦
Urgency (urgent desire for micturation)
◦
Incontenince
◦
Dysurea : painful difficult, feature of infection
◦
Nocturea: urination preceded by sleep and followed by sleep, brothersome symptom.
◦
Straining رحطي and delay in initiation, hesitency
◦
Week stream, and intermittency , post void dribling, feeling of incomplete empty.
◦
Vomiting , associated with loin pain and stones
◦
Fever, if with rigor called high grade fever. Fever associated with infection.
◦
Any previous attack or recurrence
•
Hematurea
Passing of red color urine (normal urine is colorless to deep yellow, due to prescience of
•
urochrom that came from liver)
Age is important
•
Over 65 indicate ca or BPH
◦
Child maybe bleeding tendency
◦
Sex
•
Male BPH
◦
Female mostly UTI
◦
Differential
•
Diet like shwanther and sbenach
◦
Drugs, refampicin, warfarin, (flagile make dark yellow)
◦
Stones
◦
UTI
◦
Trauma
◦
Tumor
◦
Intermittent of continuous
•
Intermittent in CA (the mechanism is that tumor increase in size then shed and shrink
◦
causing bloody urine, then grow again in a silence until next shed occurs)
Continuous in stone, bleeding tendency, drugs.
◦
Painful or painless
•
Painless feature of CA
◦
Painful in UTI and stone
◦
Severity of hemature "redness" (Macroscopical or microscopical )
•
Mild, light red or pinkish (It is more serious)
◦
Moderate, red profuse
◦

Advanced, with clot
◦
Aggrevating
•
Movements and daily activity due to stone movement inside ureter.
◦
Relieving
•
By rest and reduce activity, mostly in clothing in bladder
◦
Associated features
•
Pain
◦
Umbilicus -> ureter stones
‣
Urine retention
◦
features of prostrate
‣
Features of anemia
◦
Anorexia
‣
Dyspnea on excercise
‣
Previous episodes
•
Investigation
•
Urine
◦
More than 3 cells is abnormal.
‣
Blood
◦
Imaging
◦
System involved like cardio and anemia features
•
Family
•
Diet and other members
◦
Social and drugs
•
Smoking and drug history (warfarin, ampiclin, refampicin)
◦
Urine retention
Inability to pass urine with full bladder (anurea is with empty bladder).
•
Age
•
Congenital --> vesicourethral valve
◦
Severe urine retention should relieve immediately
•
Sudden
•
Stone
◦
Gradual
•
BPH
◦
Differential diagnosis:
•
Meatal stenosis
◦
Urethral stricture
◦
Bladder neck contracture
◦
BPH or CA
◦
Vesical stone
◦
Neurological
◦
In female
•
UTI
◦
Cystocele
◦
Aggrevating
•
In stones, sitting agrevate it but can be relieved with movement.
◦
In BPH, associated with drugs like cholinergic drugs.
◦
Intermittency
•
Association
•
Drugs history
•
Antidepressant, anticholinergic
◦
Dr. Mazin
X ray of urology
This a
KUB film (Kidney-ureter-bladder)
•
Pubis symphysis, and xiphoid of sternum
◦
If these two not shown, it is
plain
‣
abdominal film
KUB is taken while the patient is standing.
•
Named: name of patient
•
Labeled for known direction
•
Dated
•
Showing (any findings)
•
Plain X ray means without contrast
•
Look for any
radio opaque opacity
•
Osteoporosis shows black area in bone
•
Radioopaqe opacity means white spot
•
Diffrential diagnosis
•
Foreign body in clothes
◦
Scars in skin
◦
Calcified lymph node
◦
Calcified hematoma
◦
Calcified tumor
◦
Stones
◦
◦
Double J catheter, a stent
•
J shape end for staying in position , form both
◦
ends
Indications
◦
Prophylaxis
‣
Prevent obstruction after or within surgey
•
For gynecological purpose to avoided
•
uretric injury During hysterectomy "Water
under bridge)
Treatment
‣
Bypass stone or obstruciton
•
Uretric trauma
•
Uretric surgery
•
Common side effect
◦
Irritative voiding system
‣
Hematurea
‣
Slipping and migration inside the body
‣
Don't say stone, but say most likely stone
•
Don't the the opacity in ureter or bladder, but say it in
•
pelvic region, then say most likely stone in the ureter
for example
Radio opaque in right kidney misleading with gall
•
bladder (gall bladder stones mostly radio lucent,
confirmed by lateral x ray (if anterior to mid axillary line
most likely gall bladder, if posterior to it most likely
renal) or ultra sound )
KUB film named, labeled, dated.
Showing radio opaque opacity in
pelvic lesion, most likely a vesicle
stone (secondary to upper system)
KUB, named, dated, labeled (label
should be on right not left). Showing
radio opaque opacity in pelvic
lesion, most likely uretric stone
(because lateral position, if vesical it
should be with gravity)
IVU film (intra venous urography, contrast excreted
•
exclusively by kidney) ةنولم ةعشأ
Always say I need KUB film
‣
Indications
◦
Recurrent hematurea
‣
Trauma
‣
Tumor
‣
Congenital anomaly
‣
Gynecological
‣
Recurrent UTI
‣
At night fasting, no eat in morning, take rectul
◦
suppository to reduce gasses, ask for allergy to
penciline and asthma and pregnancy
(contraindication)
Also contraindicated in DM patients who taking
◦
metformin (cause lactic acidosis), should stop it
2 days before and after, and use insulin during
this period.
Always
must be KUB before IVU
◦
First image in one minture of injection called
◦
nephrogram.
Delay means impairment in kidney, like
‣
renal artery stenosis
Second image in fifteen minutes called
◦
pyelogram (calyx and pelvis and upper ureter)
Dilated uretric means hydrouretronephrosis
‣
due to stone for example.
Third image in 30-60 min called cystogram
◦
Nephronstomy catheter (
Nephrostogram)
•
Indications
◦
Diagnostic
‣
To know level of obstruction
•
Taking biopsy
•
Therapeutic
‣
Destruction of renal stone
•
Bypass obstruction
•
Evacuation of pu
•
Pelvic kidney , 1/400000-600000
•
Liable for stasis, stones, TB, and carcinoma,
◦
Problematic in pregnancy
◦
Most common cause of bilateral hydronephrosis in
•
children is posterior valve obstruction (congenital)
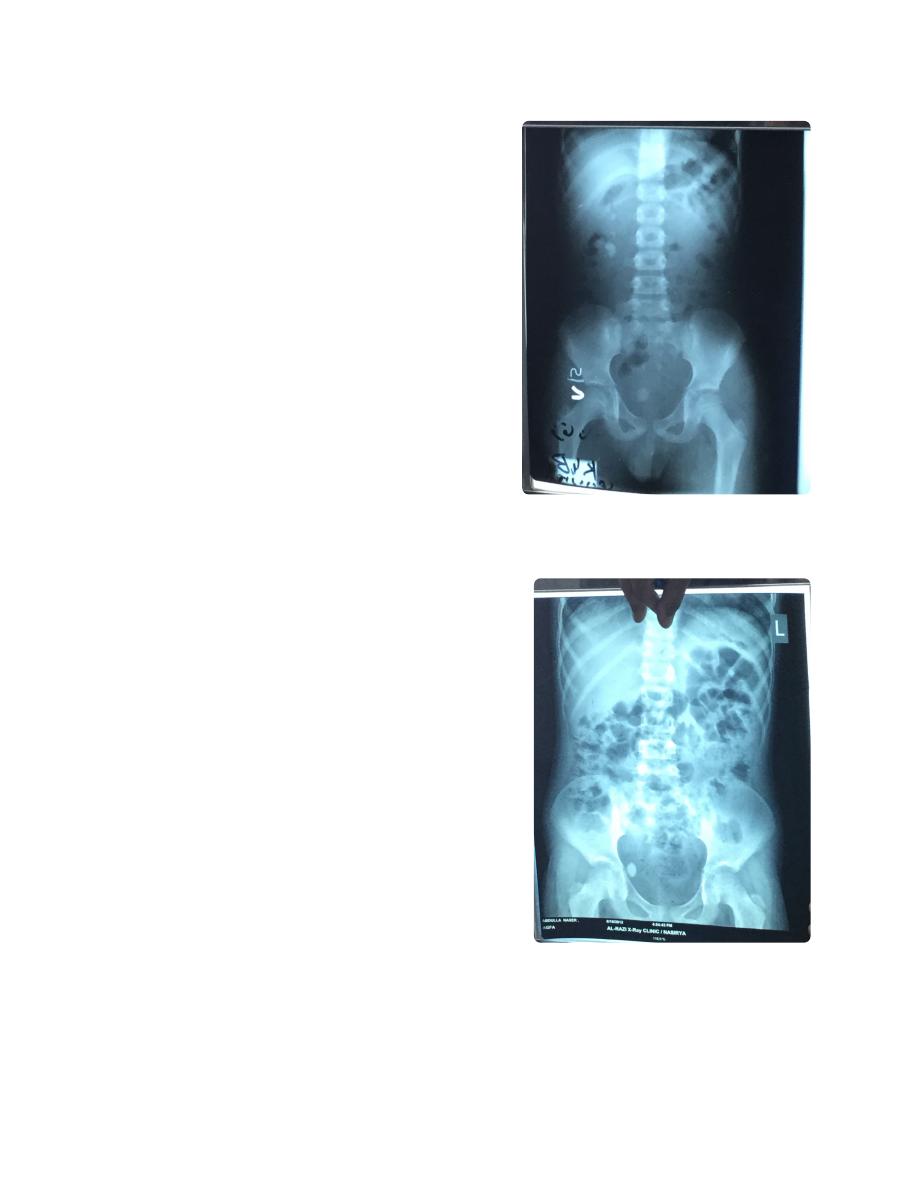
KUB film, not named, labeled, dated.
Showing multiple radio opaque
opacity in right renal area, most likely
multiple renal stones.
KUB ... etc
Showing Double J tube
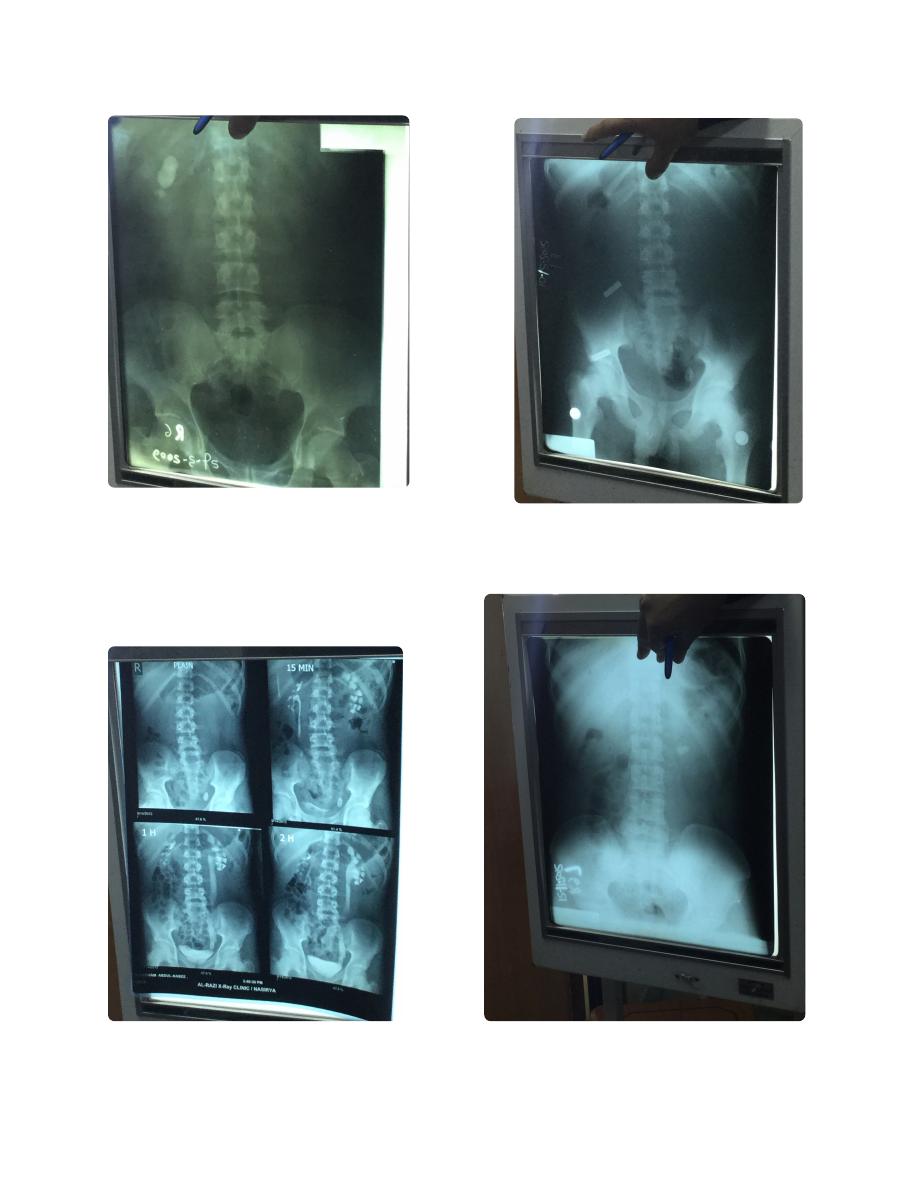
KUB ... etc. Showing radioopaque
opacity in right renal area.
(misleading with gall bladder (gall
bladder stones mostly radio lucent,
confirmed by lateral x ray (if anterior to
mid axillary line most likely gall bladder,
if posterior to it most likely renal) or
ultra sound ))
IVU, I need KUB
It is named, labeled, dated.
6KUB ... etc
Showing radio opaque opacity in
pelvic region, most likely uretric
stone.
8Plain abdominal X ray! (Symphysis pubis
not shown)
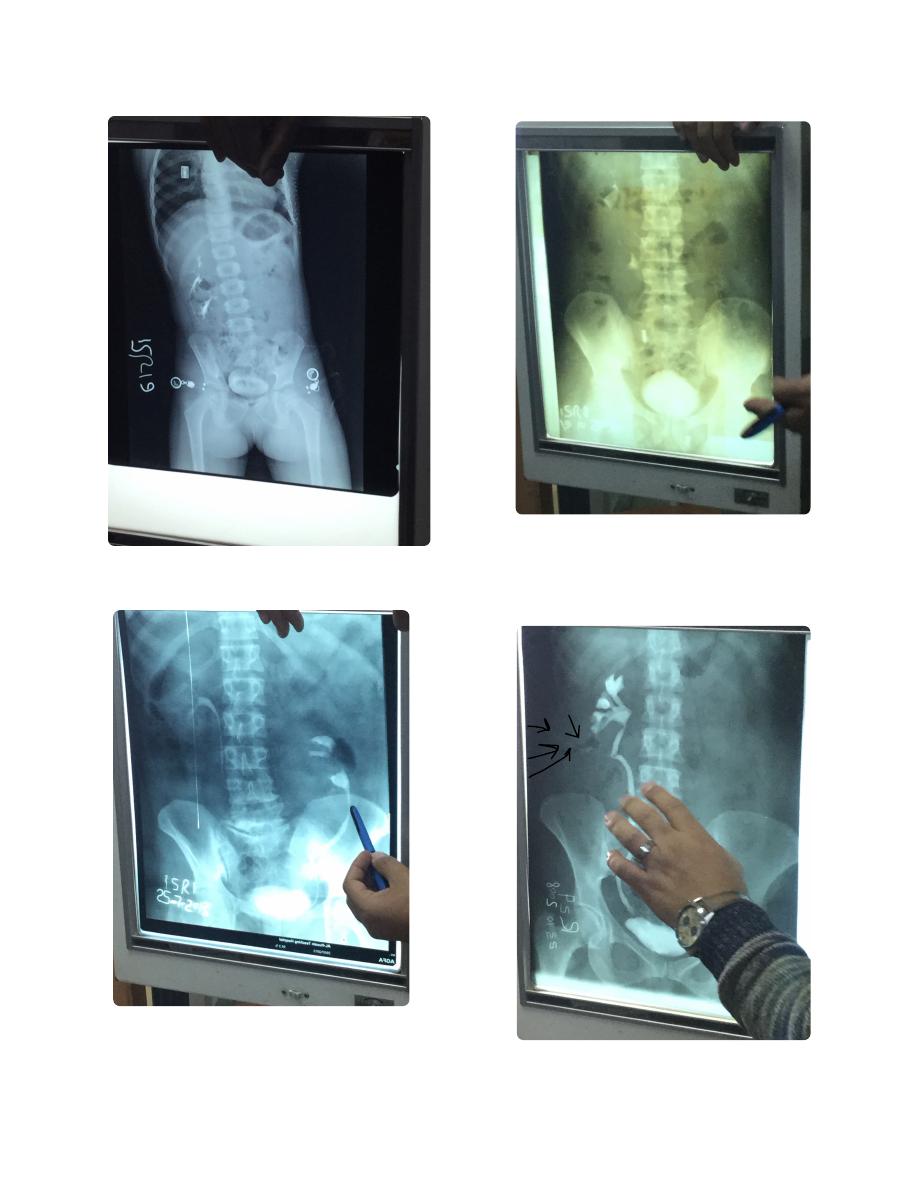
IVU , I need KUB ...etc
Ectopia
Nephrostogram (not IVU)
IVU...
Cross-renal ectopia, congenital
anomaly (But ureter does not cross
because of different origin)
IVU ...
Malrotated kidney زعالنه
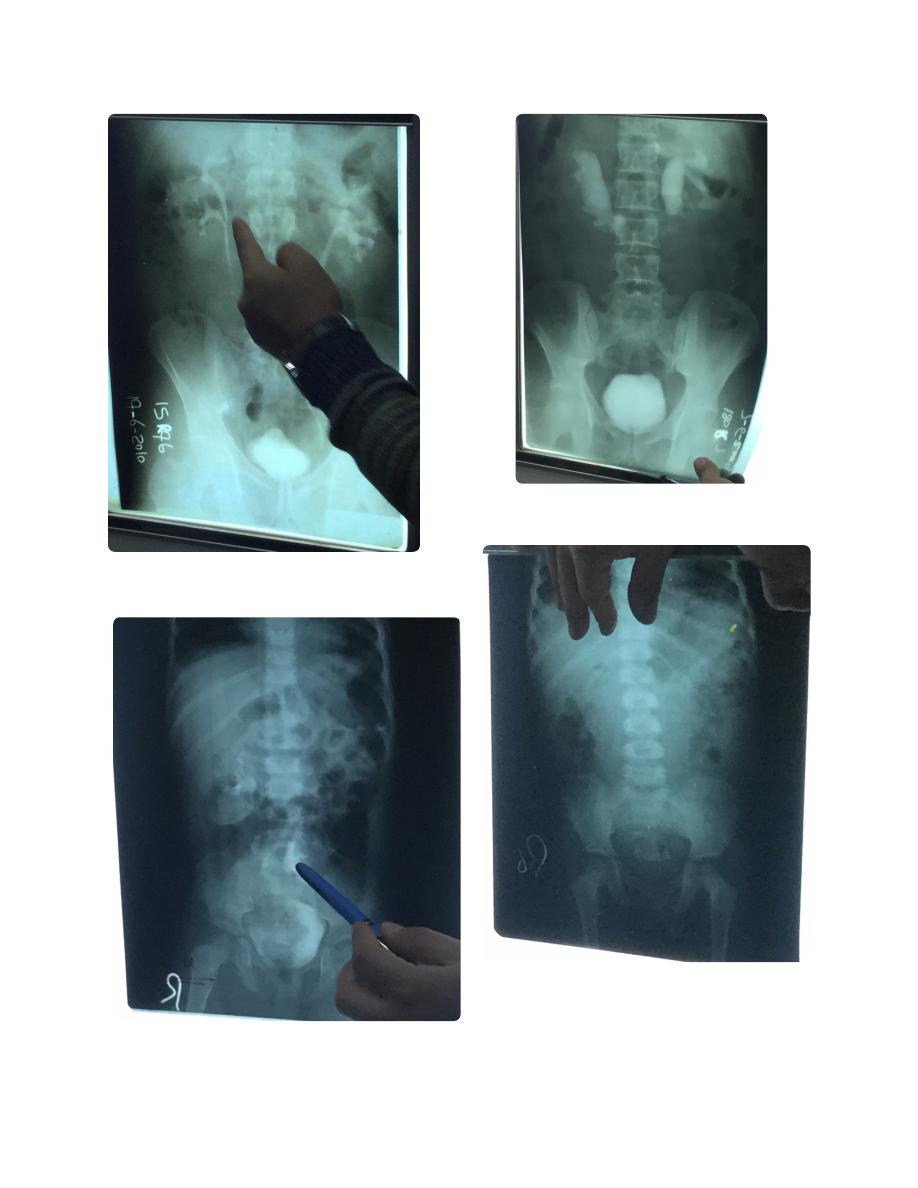
IVU...
Hydronephrosis
IVU... etc
Pelvic kidney
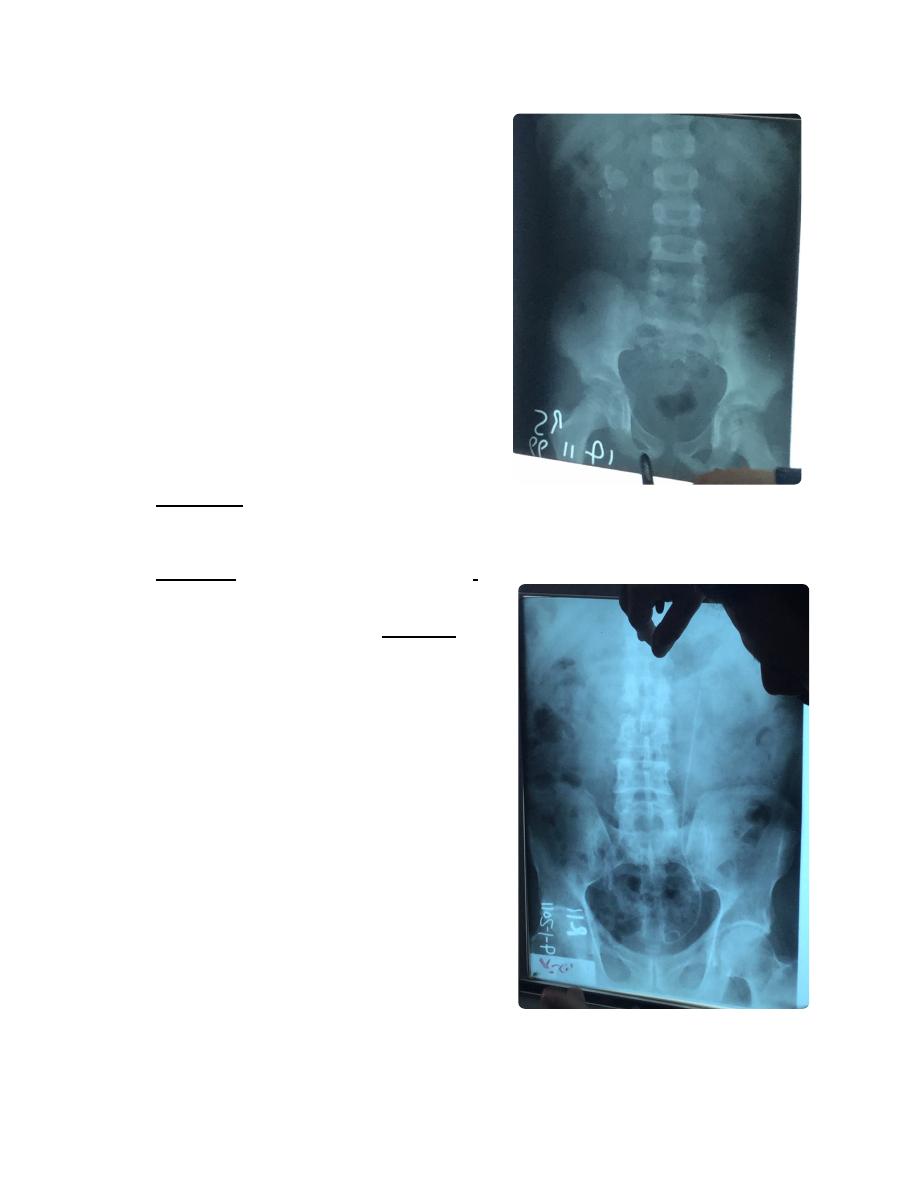
KUB film not named not dated not labeled.
Multiple vesicular stone. (This presents as
unanimity to urinate while sitting, but able
when stand and move around)
(This is a child, epi-phiseal plates un united)
IVU ... etc
Bivid pelvis of right kidney
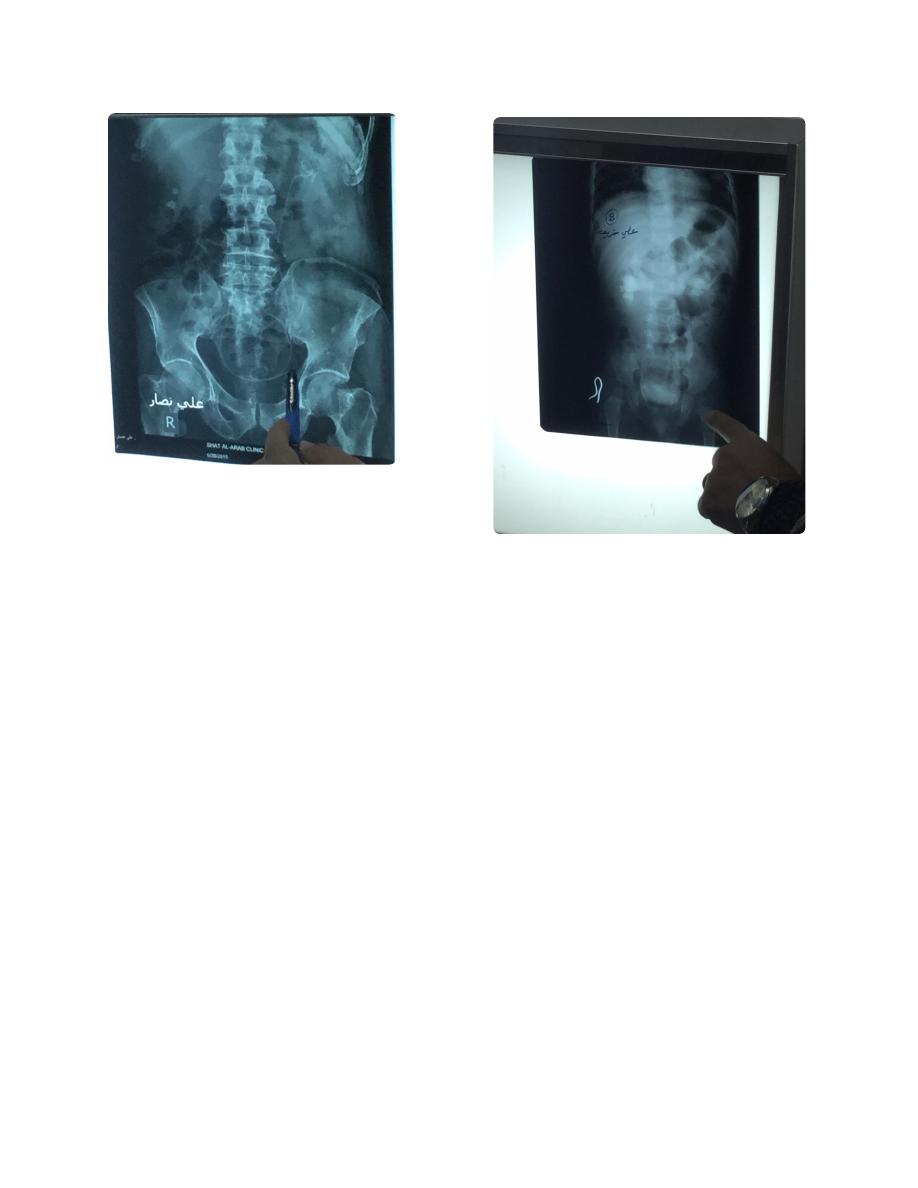
Ectopic note from Dr. Alaa
Stoma closed 8-12 weeks
Not earlier due to inflammation
Not after due to distal part atrophy
Complication of double J tube
(perforation)
IVU, I need a KUB
Named, not dated, labeled.
Child (un united epi phiseal plates) with
bilateral hydronephrosis, most common
cause is posterior valve obstruction
(congenital)
Dr. Mazin
Urology examination
Face:
Palar
Anemia of chronic disease: chronic renal failure
•
Sometimes related to pain
•
Jaundice
Most of renal drugs metabolized by liver
•
Ca can metastasize to liver
•
Cyanosis
Peripheral related to cardiac function
•
Central related to respiratory
•
Hands:
Capillary refilling
Clubbing:
due to ischemia of nails
•
In chronic disease like chronic renal failure
•
Palar
By comparing hands
•
Wasting muscles
Thinner and hypothinner muscles
•
May relate to type of job of patient and occupational diseases
•
Farmer hand looks hard, his work is risky for bilhariziasis
◦
Pulse
Each one degree in temperature increase pulse by 10
•
Temperature
Blood pressure
More than 30% of cases due to urologic like BPH
•
Legs:
Edema
10 cm above medial malleolus
•
Local due to lymphatic and venous obstruction
•
In case of masses in pelvis, or pregnancy
◦
Bilateral pitting
•
Protein problems due to renal causes, or liver, or heart
‣
Abdomin:
Exposure: from nipples to mid thigh
Inspection
Position of umbilicus:
•
normally central
◦
Eccentric due to mass
‣
Pulled due to fibrosis
‣
Normal Everted
◦
Inverted in obese
‣
Hair distribution:
•
Hirsutism in polycystic ovarian disease
◦
Scars:
•
Pfannenstiel incision indicate pelvic surgery
◦
Gibson incision (hook shape) for uretric surgery
◦
Loin incision
◦
Stria or dilated blood vessels
•
Palpation
Types
•
Superficial
◦
Deep
◦
Ask patient about site of pain
•
Either clockwise to or anti clockwise
•
You eyes on the face of patient
•
Kidney:
Either bimanual ballottement or fist
•
Bimanual ballottement
•
One hand anterior to kidney, other hand on back
◦
Index finger edge of one hand at edge of costal margin
◦
Fix one hand and move the other each time
◦
Normally impalpable except in children and thin female
◦
Fist
•
In the area between
◦
Twelve rib
‣
Paraspinalis muslcle
‣
Iliac Christ
‣
Hit By your fist on little finger side slightly on that area
◦
Bladder
Don't forget to ask about voiding state of bladder, must be voided.
•
Look first for scars and bulging
•
By lateral edge of little finger from above the umbilicus
•
Then move your hand step by step downward till touching the bladder
•
Note: Testicular tumor cause gynecomastia

Dr. Hazim
Hypospidous urethral opening (meatus) is below to normal (or proximal)
Epispidous urethral opening is more dorsal than normal
Varicocele more common in left because vein is attached to renal vein (longer course), the right is
•
directly to IVC.
Bilateral varicocele is 15%
•
If right side only , there must be other cause.
•
Exclude serious disease:
Hematuria in Ca is
intermittent
•
Obstructive jaundice in elderly due to
Ca pancrease
•
Neonatal fever and reluctant to feeding due to
meningitis
•
Delaying cause Handicap
◦
Hemoptysis and cough is mostly
bronchogenic carcinoma,
•
Fever, splenomegaly, murmur is mainly due to
infective endocarditis
•
Epigastric pain and retrosternal chest pain is mainly
myocardial infarction
•
Loin pain, fever and rigor is mostly
pyelonephritis , diagnosed clinically , not needed
•
radiological or laboratory , no need for admission , drugs used is Methibrime 2*2 or sulfodar 1*2
for 2 weeks
Admission if there is anatomical ( single kidney, bilateral pyelonephritis, obstructed, reflux),
◦
physiological (uremic, pregnant, elderly, DM,
sepsis (most clinical sign between UTI and
sepsis is decreased
blood pressure due to venous dilatation, but earlier sign is tachpnea) )
If admitted, give (Ampicillin + garamycin ) or third generation cephalosporin,
for 3 days
‣
(not less than 72 hours) after fever subside, then discharge with previous anti biotic for
14 days. If fever persist more than 3 days then
do CT if any renal abscess
Urinalysis
Appearance
•
Normal color is straw (light yellow)
◦
White like water , well hydrated
◦
Dark yellow, concentrated , urobilinogen (tea color, indicate jaundice mostly obstructive)
◦
Red (can be hematurea or other like food,drugs), confirming by
◦
History
‣
Microscopic examination for RBC
‣
Biochemical
•
Sugar ( if positive then BG more than 180)
◦
Protein ( less than 200 per 24 hour is not significant)
◦
Urine for bile pigment (bilirubin)
◦
Microscopical
•

RBC
◦
WBC (pus)
◦
Any WBC is abnormal
‣
3-5 in male
‣
5-8 in female
‣
So generally 5
‣
RBC
◦
2-3
‣
Casts
◦
Crystals
◦
Cystine crystals stones : metabolic error of aminoacids
‣
Strovate stone
‣
Culture and sensitive
•
Urine sample should be taken 3 days after free previous antibiotics
◦
At least 3 days in culture
◦
UTI is E.Coli in 80%
◦
Drugs
◦
Not allergic.
‣
High concentration in urine, and less concentration in blood.
‣
Chosen drugs should not be used as emergency drugs (like penicillins and
‣
cefaolsporom) to spare it for vital conditions and avoid getting resistance for it.
Not affecting bowel flora and vitamin K.
‣
Example for used drug is methoprim.
‣
Hematurea causes
Medical
•
Either
◦
Pre renal (bleeding tendency, drugs)
‣
Renal (glomerular)
‣
Features:
◦
Dismorphic RBC
‣
Significant prominent urea
‣
Granular cast (WBC or RBC within tubules)
‣
Surgical
•
Post renal
◦

Dr. Ali Abd al Baqi
UTI types:
Upper U S : kidney and ureter
•
Pyelonephritis
◦
Inflammation of renal parenchyma
‣
Most likely bacterial infection
‣
Loin pain, fever, rigor
‣
Antibiotic, anlegesia, anti pyretic for 14 days (in home if hemodynamic stable)
‣
If symptoms persisted, then admit to hospital
‣
Pylonephrosis
◦
Accumulation of pus writhin pelvicalyceal system
‣
High Fever, rigor, loin pain
‣
Should be drained
‣
Emphysematoua pyelonephritis
◦
Gas collection within pelvicalyceal system, on an existing pyelonephritis due to
‣
obstruction
Emergent syndrome
‣
Treatment by antibiotic and Should be drained either percutaneously nephrostomy or
‣
double J.
Peri nephric abscess
◦
Collection of pus around kidney under Gerota's fascia.
‣
Should be drained
‣
Xanthogranulomatous kidney
◦
When patient has DM and obstruction and multiple organ infections
‣
Destructed kidney, looks like a mass
‣
Can not be distinguished from renal tumor
‣
Treated by nephroctomy
‣
Ureter:
◦
Uretritis
‣
Symptoms like pyelonephritis
•
Associated with obstruction
•
Lower U S : urethra and bladder
•
Cystitis and urethritis Symptoms (LUTS):
◦
Urgency
•
Frequency
•
Dysurea
•
Intermittency
•
Nocturnal
•
Rarely cause fever
•
Most common organism is E. Coli
‣
Urethritis
◦
Gonococcal
‣
Disharge and symptoms
•
Non gonococcal (Non specific or non bacterial)
‣
Inflammatory to different materials
•
UTI basics
Inflammatory response of urothelium to the bacterial invasion (or other microorganism)
•

Recurrent UTI: it is either 2 attacks per 6 months or 3 per 1 year
•
Due to improper antibiotic use
◦
Improper dose
◦
Uncontrlling patient
◦
Reinfection can happen
•
Female always more susceptible to UTI except in first year of life which male is more, and after
•
elderly the chance is equal.
Simple UTI
•
Occur in patient with normal physiological and anatomical state
◦
Complicated UTI
•
Occur in patient with abnormal physiological or anatomical state
◦
This abnormality should be resolved in order to resolve the infection
‣
Defense mechanisms
Jet of urine
•
Acidic pH of urine
•
Tamm–Horsfall glycoprotein (THP)
•
GAG (glucose amino glycan)
•
Antibiotic
If First time 14 day
•
If Recurrent
•
When symptom occur, start for 3 days then stop. And so on
◦
Ampicillin
•
Mainly on gram positive
◦
Combined with clavuranic acid
◦
Cephalosporin
•
Third and fourth is important
◦
Aminoglycoside
•
Affect RNA and protein synthesis
◦
Quinolone
•
Works on DNA gyrase
◦
On gram negative
◦
Metronidazole
•
Elaborate free radicals
◦
Drains
Open
•
Corrigate, gauze, Wick
◦
Closed
•
Tube drain, radivag drain
◦
Internal
•
Double J (length of ureter 25m)
◦
T tube
◦

Dr. Ali Abd Al Baqi
Uretric colic/Abdominal examination
Differentiated for appendicitis by:
Not relieved by lying (appendicitis can be relieved by lying by decreasing peritonium irritation by
•
inflamed appendix)
Pain from nerve ending and musculature of ureter.
•
Inborn error of metabolism
COLA (cystine, ornithine, Lucien, arginine)
•
Inability to metabolize certain amino acids, can cause stone forming (cystine stones)
•
Family history is imoortnant here
•
Inspection
Type of abdomin
•
Flat
◦
Scaphoid
◦
Bully
◦
Distended
◦
Umbilicus
•
Everted in increase intra abdominal pressure
◦
Inverted normal
◦
Scars
•
Spider nevi
•
Dilated veins
•
Drain or blaster
•
Hernia check orifice
•
Palpation
Superficial
•
Warm hands, permission
◦
Ask about site of tenderness, begin away of this site
◦
Either clockwise or vice
◦
Exam for masses and tenderness
◦
Deep for organs and masss
•
Liver
•
Start from right iliac fossa, looking to patient eyes
◦
Using fingers and pressure
◦
Tell patient to make inspiration
◦
Remember lower edge of liver, in order to do liver span
◦
Spleen
•
From right iliac fossa to sleep site.
◦
Petient can help by inspiration, bending to lateral
◦
Normally impalpable
◦
Kidney
•
By two hands
◦
Put left in costophrenic angle under patient (12 rib and vertebra) and push upward
◦
By right hand palpate from anterior and feel
◦
Normally impalpable
◦
Bladder
•

By lateral margin of hand, from umbilicus downward in male , or fundal downward in female
◦
Herniation
•
Put tip of of fingers on orifices and ask patient to cough
◦
Auscultation
Iliocecal valve at MC berny point, for bowel sound
•
Bilateral renal artery briuit, for renal artery stenosis
•
Percussion
Liver span
•
Shifting dullness
•
Transmitted thrill, ask patient to put his hand in middle
•
Investigations
Available, non invasive, not expensive and informative
•
Urinalysis
•
Anatomy of renal system
(Read it in text book or lecture, can be asked in exam!)

Dr Abd Al Hussien Aljabiry
Jaundice
Questions to ask:
Permission and introduction
1.
Onset
2.
Pain
3.
Fluctuation (حوريو يجي)
4.
Progression
5.
Duration
6.
Fever & rigor (cholangitis)
7.
Lose of weight (Malignant)
8.
Loss of appetite (Malignant)
9.
Itching (precipitation of salts under skin)
10.
Color of urine (tea color on obstructive jaundice)
11.
Color of stoop (clay color in obstructive jaundice)
12.
Past medical
13.
Past surgical
14.
Drugs and blood transfusion
15.
Family history
16.
Social history (smocking, alcohol)
17.
Foreign travel (risk of HIV, HBV)
18.
There are 5 types of Collagen in general, in sclera it is type 1 collagen.
•
Clinical appearance of jaundice at a level of 2-2.5 mg/dL, below it any raise is called subclinical or
•
pre-icterus.
Causes of post operative jaundice:
•
Much blood transfusion
◦
Massive bleeding
◦
Hematoma
◦
DIC (Septicemia)
◦
Anesthetic drugs (Halothane)
◦
Obstruction or ligation to CBD.
◦
Post operative obstructive jaundice management:
•
Fluid
◦
Antibiotic
◦
Vitamin K (
given I.M, because oral is unabsorbable (obstruction to bile, fatty vitamin), and I.V
◦
can cause hemolysis)
Some methods for obstructive jaundice surgery:
•
Stones -> removal of stones
◦
Ca pancreas -> bypass
◦
Obstructive jaundice disappears post operation after:
•
50% at 1.5-2 days.
◦
After that 8% each day.
◦
So in general in 6-7 days totally disappear
◦
If delayed beyond this, that's due to presence of gamma-bilirubin that bind to albumin which
◦
its half life is 18 days till disappear.
Obstructive jaundice bilirubin level nearly 15-30 mg/dL, does not extend beyond. But if > 30 then:
•
Hemolysis.
◦

Renal problems.
◦
Hepatocellular diseases.
◦
Bile duct-Hepatic vein fistula.
◦
Sudden onset jaundice in stone in the biliary ducts.
•
Gradual onset jaundice in Ca pancreas and hepatitis also.
•
Functions of gall bladder:
•
Storage of bile.
◦
Secretion of mucous.
◦
Concentrating bile 5-20 folds.
◦
Antidote for warfarin:
Factor 7a (half life is 8 hours, used in
emergency)
•
Frozen plasma (half life nearly 32 hours)
•
Vitamin K (half life nearly 32 hours)
•
Antidote for heparin:
Heparin half life is 1.5 hours, usually 5000 unit dose
•
Protamine sulfate is the antidote, 1g for each 100 unit.
•
If patient came after half hour'of heparin dose:
◦
Give full dose (50g)
‣
Repeat half dose after half hour (25g)
‣
There is no third dose because Half life of heparin (1.5 hours) is already finished
‣
Rate of transmission of viruses to others:
HBV 30%
•
HCV 3%
•
HIV 0.3%
•
Breast lump
Questions to ask:
Permission
1.
Age
2.
Lump site, single or multiple
3.
Onset, growth rate (progression), variation with menstrual cycle
4.
Pain or painless
5.
Change in breast size and shape
6.
Skin and nipple changes
7.
Discharge (and type of discharge)
8.
Fever (abscess, inflammatory Ca)
9.
Weight lose
10.
Bone and abdominal pain(for secondary)
11.
Arm swellings non pitting type (secondary metastasis to lymph nodes and obstruction)
12.
Previous radiation and radiology
13.
Menstrual cycle
14.
Obstetric history (breast feeding, previous mammogram)
15.
Family history (breast, bowel, or ovarian CA)
16.
Site of possible metastasis (lungs, back, headache, jaundice, weight lose)
17.
(Also ask about trauma (fat necrosis) and axillary masses)

All Ca of breast are painless, except lobular carcinoma (painful and bad prognosis)
•
Triple assessment
•
History
◦
Examination
◦
Investigations
◦
Radiology (x ray, ultrasound, mammogram)
‣
FNAC
‣
Core biopsy (True cut biopsy)
‣
Incision biopsy
‣
Excision biopsy
‣
Risks of Ca
•
Early menarche
◦
Late menopause
◦
Not lactating
◦
Obesity
◦
All females are at risk.
◦
Fibroadenoma is called breast mouse, painless.
•

Dr. Abd Alhussien Al-Jabiry
Thyroid
Questions of thyroid swelling
Permission
1.
Location (centre, left, rift, or all)
2.
Duration
3.
Change in size (does it increase or decrease or Sam)
4.
Pain
5.
Intolerance to hot or cold weather
6.
Anxiety and sleep disturbance
7.
Palpitation
8.
Airheads and constipation
9.
Menstrual disturbance
10.
Abortions and infertility
11.
Fever
12.
Sweaty or dry skin
13.
Change of voice and speech pattern
14.
Respiratory E obstruction
15.
Drugs
16.
Radiation exposure
17.
Past medical history especially cardiac problems
18.
Family history of goiter.
19.
Differential diagnosis of neck swelling or mass:
Goiter
•
Thyroid
•
Pretracheal lymphomde
•
Thyroglossal cyst
•
Extrinsic Ca of larynx
•
Subhyoid bursa
•
Other notes:
Retrosternal extension (Cause respiratory obstruction): tested by raising hand for 1 minute called
•
pampirtone test:
Dyspnea
◦
Flushing
◦
Stridor
◦
Cyanosis
◦
Engorgement of neck veins.
◦
Incision of goiter called: collar incision
•
Nerve at risk are recurrent laryngeal nerve and external branch of superior laryngeal nerve (can't
•
raise his voice) also other nerves rarely (supraclavicular, transverse cervical).
Dyspnea after surgery If such occurs in emergency just evacuate hematoma and send for
•
operation
Post operative fluid
Types
•

Crystiloid: normal saline, ringer, glucose saline, glucose water...
◦
Colloid: albumin, starch, palmsin, blood...
◦
First day: 2 L glucose water (i.e. 4 bottles, each 500 ml)
•
Second day: 2 L glucose water + 1 L normal saline.
•
Third day: same as second day + 60 mmol/day of K+ (20 mmol for each 1 L)
•
Burns
In first day
•
Parkland formula=4 ml*weight*percentage of burn
◦
Crystiloids
◦
In a 24 hours
◦
Half amount in 8 hours
‣
Second half in 16 hours
‣
In second day
•
Colloid (0.3*weight*percentage) +
!
◦
Glucose water (daily requirement=35ml/kg)
◦

Dr. Abd Al Hussien Al Jabiry
Abdominal pain
Permission
1.
Present illness Onset and duration
2.
Location and severity
3.
Radiation
4.
Time related to food (duodenal ulcer)
5.
Aggrevating and relieving factor
6.
Associated factor rigor and fever (cholangitis, intrabdominal abcess)
7.
Nausea and vomiting
8.
Change in bowel motion and stool
9.
Weight lose
10.
Past history of previous episodes
11.
Past surgical and medical history
12.
Drugs history
13.
Jaundice
14.
Social history (shocking, alcohol)
15.
Differentiation between intra and extra abdominal pain
Carnett sign
•
Patient sit against resistance (like flexion of neck) and hand on site of abdomin, if pain increased it
is extra abdominal.
Fothergill's sign
•
Similar to Carnett with your hand on the mass, if mass disappeared it is intra abdominal.
Post operative fever causes
First day
•
Reactionary or atelectasis (chest infection)
◦
2-3 day
•
UTI or atelectasis
◦
4-5 day
•
Wound infection, that's why we don't remove patient dressing till fourth day
◦
5-6 day
•
Thrombophlebitis, check patient cannula
◦
6-7 day
•
Residual abscess
◦
7 to 8 day
•
DVT (so check Calf muscle)
◦
Diabetic foot
Questions to ask
Permission
1.
Does he have DM or not
2.
When was the DM diagnosed
3.
How it was diagnosed (routine examination or symptoms)
4.

What is the treatment he was on
5.
What treatment is he is now (in diabetic food treatment should changed to insulin)
6.
Any incidence of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia
7.
Is there a regular follow up
8.
Foot problem, how it started (wound, trauma, pain)
9.
Does he feel his foot? Any numbness ?
10.
What treatment did he received
11.
Treatment
Control of blood sugar
•
Antibiotic
•
Surgical (debridement)
•
Grading of diabetic foot
Grade 0 : just erythema
•
Grade 1 : skin and sub-cutaneous tissue ulcer
•
Grade 2 : Involve the muscle
•
Grade 3 : involve the bone
•
Grade 4 : pre gangrene dusky
•
Grade 5 : gangrene
•

Dr. Ali Abd al Hussien
Inform consent
Mnemonic "
Consents"
Permission
1.
Condition: explain the condition of the patient to him
2.
Option: either surgery or other medical option
3.
Name of procedure: like grid iron for appendectomy in male, or explorative
4.
Side effect and complications: General complication anesthesia and operation (thyroid for
5.
example)
Extra procedures: like folley or Drain
6.
Name of operative surgeon and his assistance
7.
Trial: tell the patient if this is the first time you do this operation
8.
S: sign by family
9.
Zylocain usage
3-5 mg per kg
•
Works after 2 min
•
Effect remain 1.5 hours to 2 hours
•
Sings of toxicity
Metallic taste
•
Chivering
•
Tinnitus
•
Confusion
•
Tremor
•
Vasovagal attack
•
Respiratory arrest
•
