نسائية دكتورة مروة المحاضرة الثانية
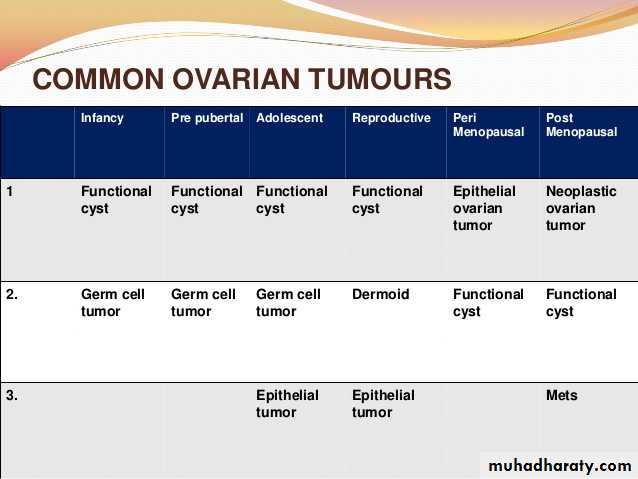
NORMAL OVARIES
Normal size 5 x 3 x 3cm Variation in dimensions can result from Endogenous hormonal production(varies with age and menstrual cycle) Exogenous substances, including OCs, GnRH agonists, or ovulation-inducing medication, may affect size
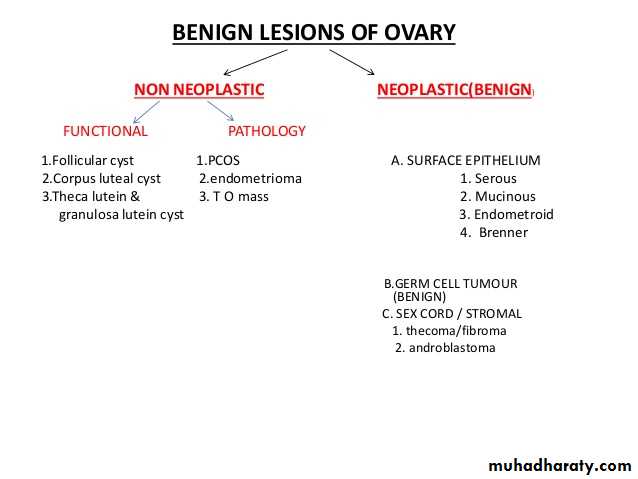
Lifetime Risk of ovarian neoplasm
A woman has 5–10% lifetime risk of undergoing surgery for a suspected ovarian neoplasm and 13–21% of these will be found to be have an ovarian malignancyDIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF THE PATIENT WITH AN ADNEXAL MASS Complete physical examination Pelvic ultrasound examination Computed tomography scan with contrast enhancement or intravenous pyelography Colonoscopy or barium enema study, if symptomatic Laparoscopy, laparotomy
SEROUS CYSTADENOMA
Generally benign Bilateral – 10% Risk of malignancy : 5 – 10 % borderline malignant 20 -25% malignant GROSS : multilocular with papillary components. MICRO : low columnar epithelium with cilia. Characteristic psammoma bodies (end products of degeneration of papillary implants)are found. Associated fibrosis may lead to “cystadenofibroma”MUCINOUS CYSTADENOMA
Have tendency to become huge masses Round to ovoid masses with smooth capsules that are usually translucent or bluish to whitish gray. Interior divided by discrete septa into loculi containing clear , viscid fluid. Epithelium – tall, pale staining, secretary with basal nuclei and goblet cells 5 – 10% are malignantDERMOID CYST
Often bilateral (15 -25%) GROSS: thick, opaque , whitish wall. CONTENTS: hair, bone, cartilage, and a large amount of greasy sebaceous material. MICROSCOPICALLY : all the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) Malignant change occurs in 1-3%. Usually of a squamous type. Risk of torsion is 15% An ovarian cystectomy is almost always possible, even if it appears that only a small amount of ovarian tissue remainsFIBROMA
Most common benign, solid neoplasms of the ovary. Compose approx 5% of benign ovarian neoplasms and 20% of all solid tumors of the ovary. Frequently seen in middle-aged women. Characterized by their firmness and resemblance to myomas Misdiagnosed as exophytic fibroids or primary ovarian malignancy Not hormonally active Fibromas may be associated with ascites or hydrothorax as a result of increased capillary permeability thought to be a result of VEGF Mieg’s syndrome (ovarian fibromas, ascites and hydrothorax) is uncommon and usually resolves after surgical excision.
THECOMA
Solid fibromatous lesions that show varying degrees of yellow or orange discoloration Almost always confined to one ovary Usually >40 years, 65% after menopause May be hormonally active and hence associated with estrogenic or occasionally androgenic effects. Luetinised thecoma – younger, sclerosing peritonitis and ascites Leydeig cell thecoma – ass. with Reinke crystals Rarely malignantCOMPLICATIONS
Torsion Intracystic hemorrhage Infection Rupture Pseudomyxoma peritonei MalignancyTVS
Pattern recognition is superior to all other scores. Subjective evaluation of ovarian masses based on pattern recognition can achieve sensitivity of 88% to 100% and specificity of 62% to 96%. Adding doppler does not seem to yield much improvement in the diagnostic precision, but increases the confidence with which a correct diagnosis of benignity or malignancy is made
DOPPLER EVALUATION
Hypoxic tissue in tumors recruit low-resistance, high-flow blood vessels Role in evaluating ovarian mass is controversial – as the ranges of values of RI,PI,MSV between benign and malignant masses overlap. PIOTHER IMAGING MODALITIES CT, MRI, PET
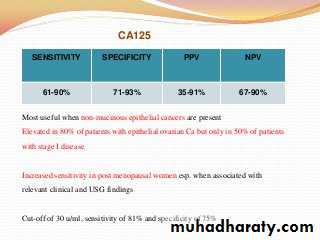
not recommended in the initial evaluation CT scan: evaluating LN involvement, Omental mets, peritoneal deposits, hepatic mets, obstructive uropathy or a probable alternate primary site when cancer is suspected based upon TVS MRI : differentiating non adnexal pelvic masses (like leiomyomata), expensive and inconvenient.Most useful when non-mucinous epithelial cancers are present Elevated in 80% of patients with epithelial ovarian Ca but only in 50% of patients with stage I disease Increased sensitivity in post menopausal women esp. when associated with relevant clinical and USG findings Cut-off of 30 u/ml, sensitivity of 81% and specificity of 75%
INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY
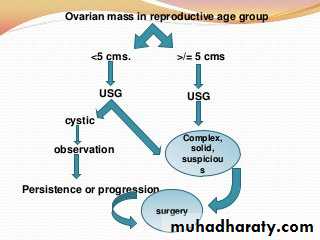
Any solid ovarian lesion Any ovarian lesion with papillary vegetation on the cyst wall Any adnexal mass >10cm in diameter Palpable adnexal mass in a premenarchal or postmenopausal women Torsion or rupture suspected
CYST ASPIRATION
Diagnostic cytology has poor sensitivity to detect malignancy, ranging from 25% to 82% Not therapeutic, even when a benign mass is aspirated Approx. 25% of cysts will recur within 1 year Aspiration of a malignant mass may induce spillage and seeding of cancer cells into the peritoneal cavityOPERATIVE MODALITIES
Laparoscopy vs laparotomy – decision based on suspicion of malignancy and technical expertise No RCTs comparing recurrence rates following laparoscopy or laparotomy. The objective is to try cystectomy if possible. Laparoscopic surgery for benign ovarian tumours is associated with less pain, shorter hospital stay, and fewer adverse events than with laparotomy.The standards for laparoscopy in benign tumours 1. careful examination of the external surface of the tumour and sampling of the peritoneal cavity 2. avoidance of any tumoral rupture 3. protection of the ovarian tumour with an endoscopic bag before removal
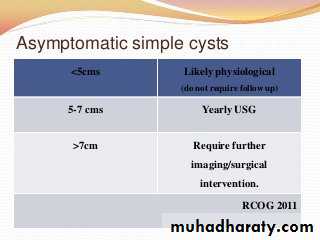
Ovarian cysts in post menopausal women
Post menopausal gonad atrophies to a size of 1.5 X 1 X 0.5cm on average Shouldn‟t be palpable on pelvic examination. Presence of palpable ovary must alert the physician to the possibility of an underlying malignancyASSESSMENT
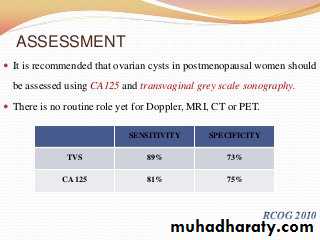
It is recommended that ovarian cysts in postmenopausal women should be assessed using CA125 and transvaginal grey scale sonography. There is no routine role yet for Doppler, MRI, CT or PET