Detrusor Instability
Definition: is presence of spontaneous or provoked detrusor contractions during the filling phase when the patient is attempting to inhibit micturitionA etiology:
. idiopathic is most cases. neurogenic is found in the presence of condition such as multiple sclerosis, spina bifida, and upper motor neuron lesion
. secondary to pelvic or incontinence surgery
. recurrent UTI
Clinical presentation
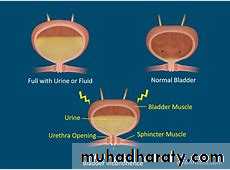
. frequency, urgency, urge incontinence, nocturia, nocturnal enuresis. provocative factors often trigger it such as cold weather, hearing running water
. bladder contraction may also be provoked by increase intra-abdominal pressure leading to complaint of stress incontinence which may be misleading
. quality of life may be effected
Investigations
.GUE and urine culture.frequency\volume chart
Typically increase diurnal frequency associated with urgency and episodes of urge incontinence , nocturia is common
.urodynamic
Characterized by involuntary detrusor contraction during the filling phase of micturition cycle, which may be spontaneous or provoked
. exclude metabolic causes like diabetes or physical causes like prolapse or faecal impaction and urinary pathology like UTI
Treatment
1.conservative measures
Reduce fluid intake ,stop caffeine and alcohol
2.bladder retraining
Based on the ability to suppress urinary urge and to extend the interval between voiding3.Drugs :
.inhibit bladder contractilityAnticholinergic agent
.increase outlet resistance
Alpha adrenergic agonist
.decrease urine production
Antidiuretic hormone
.improve local tissue
Estrogen
4.surgery if all measure fail
Urinary diversion or bladder augmentationURINARY FISTULAE
Definition :is an abnormal opening between the urinary tract and outside
Types :vesicovaginal
UretrovaginalUrethrovaginal
Vesicocervical
Causes
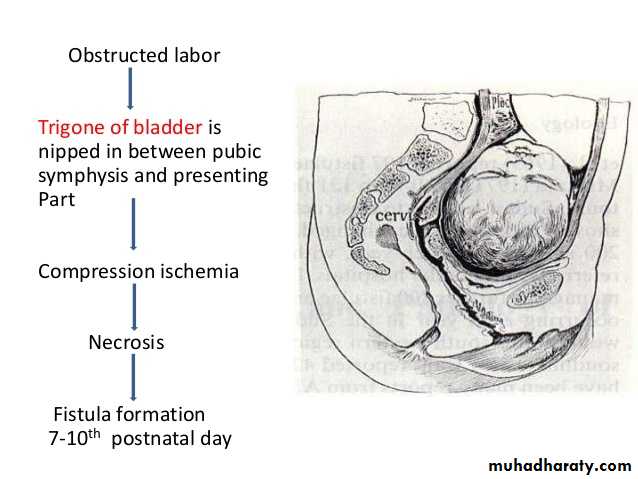
1.obstetrics causesProlonged obstructed labor which leads to ischemic vascular injury from the compression of the soft tissue between the fetal head and maternal pelvis .ischemic tissue necrosis leads to development of genitourinary fistula in the puerperium usually after 7 – 10 days
.instrumental delivery
.during caesarean section
Most obstetrics fistulae are vesicovaginal
2.operative injury
Abdominal or vaginal hysterectomyRepair of prolapse
Pelvic tumor
Most gynecological fistulae is ureterovaginal
3.accidents
4.malignancy
5.radiotherapy
Clinical features and diagnosis
.continuous leakage of urine both day and night .if the patient never needs to void ,it signifies that the fistula communicates with the bladder .if ,however the bladder fills and empties as well, it suggests afistula into one ureter is most probable cause .. discomfort and excoriation in the genital region as the urine irritates the skin
.if the fistula is relatively small then a woman may just complain of increase vaginal discharge .
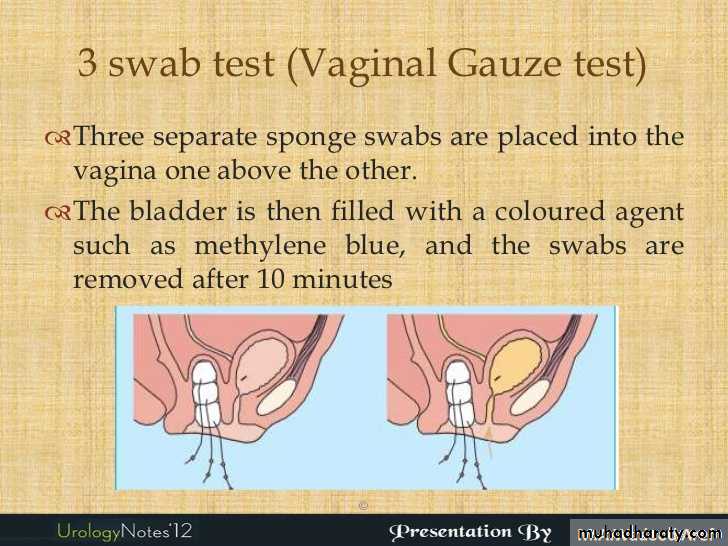
.three swab test (methylene blue test )
Inject the methylene blue dye into the bladder by using foleys catheter after putting three cotton swab into the vagina
If lower one stain blue –urethrovaginal
If middle one stain blue –vesicovaginal
If non but upper one is wet –uretric fistula
.every case needs investigation to determine the exact position of the fistula ,and the
anatomy and function of the rest of the urinary tract ..the minimum requirement are examination of the urine ,pyelography ,cystoscopy and renal function tests
.menouria occur in uterovasical fistula ,presented with haematura at time of menstruation ,the patient remaining free from urinary incontinence .the fistula can be demonstrated by hystrography but not by cystography .
Treatment
Conservative :bladder rest by catheterization for one month
Surgery
After three months to give time for tissue oedema and inflammation to subside
.vesicovaginal fistula: dissect the region and separate the bladder from the vagina and then suture the opening in the bladder and vagina with placing intervening tissue like omentum in between to avoid recurrence
.ureteric fistula :anastomosis
Re implantationDiversion