Epithelial
tissuesHistology: is the study of the tissues of the body and of how tissue are arranged to constitute organs.
Human body is made up of units called cells. Aggregation of cells of a common type constitute tissues. Tissues are made of cells and extracellular matrix, two components that were formerly considered separate entities.
The human body is composed of four tissues are organized:
• Epithelial tissue• Connective tissue
• Muscular tissue
• Nervous tissue.
The main functions of extracellular matrix :
1-To furnish mechanical support for the cells.2-To transport nutrients to the cells.
3-To carry away catabolites and secretory products.
The epithelia are a diverse group of tissues, with rare exception line all body surface, cavities and tubes, epithelia thus function as interface between biological compartments.
Epithelial Tissues
• Protection• Transcellular transport
• Secretion
• Absorption
• Control of movement of materials
• Detection of sensations .
Epithelial tissues have numerous functions:
Surface epithelia consist of one or more layers of cells separated by a minute quantity of intercellular material and closely bound to one another by a variety of specialization of the cell membrane.
All epithelia are supported by a basement membrane (basal lamina) of variable thickness.
Basement membrane separate epithelia from underlying connective tissues and are never penetrated by blood vessel, epithelia are thus dependent on the diffusion of oxygen and metabolites from underlying tissues.
Basement membranes consist of a condensation of glycoprotein ground substance reinforced by reticular fibers which merge with those of the underlying connective tissue.
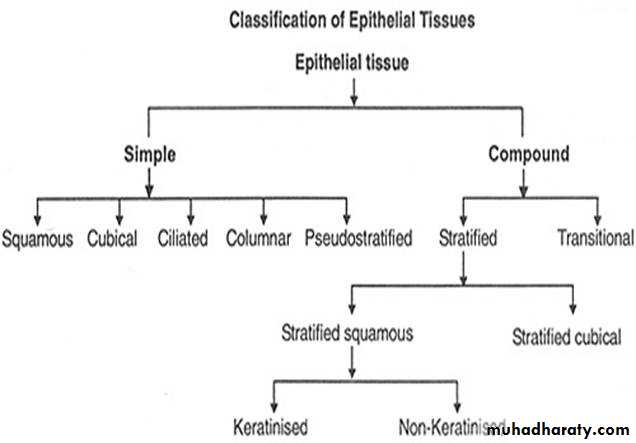
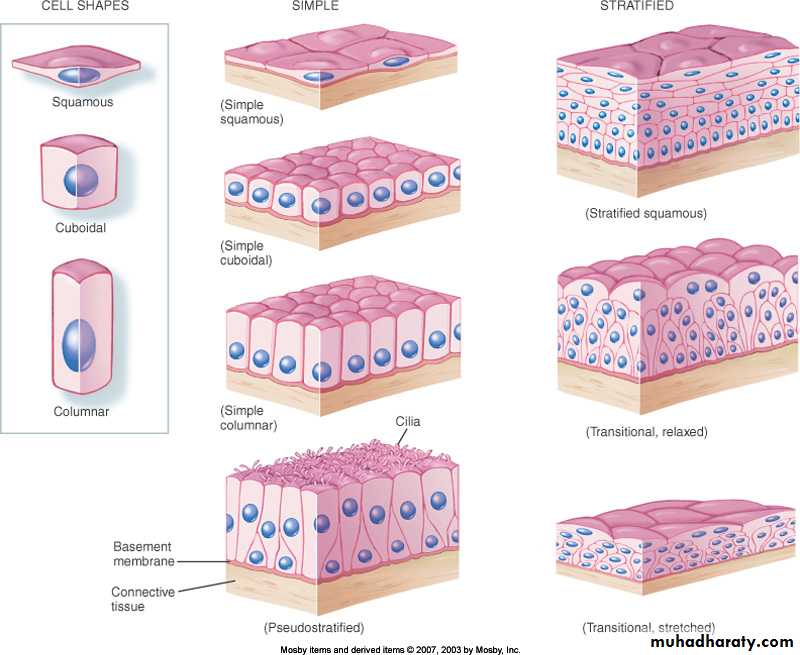
Epithelia are classified according to three morphological characteristics:
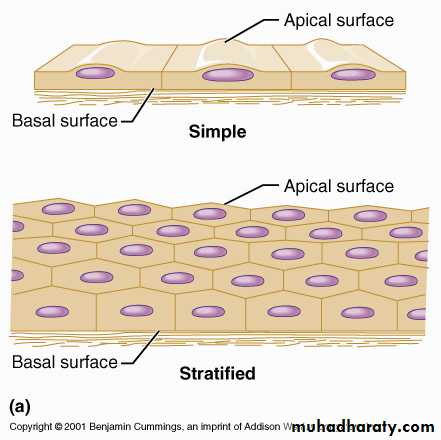
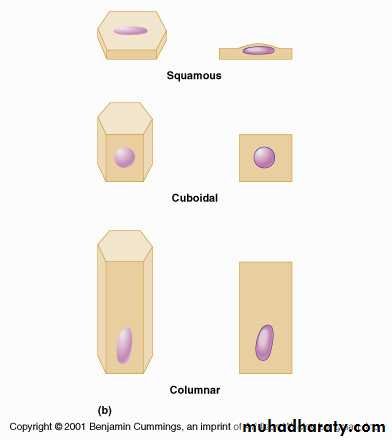
1-The number of the cell layer a single layer of epithelial cell is termed simple epithelia, whereas epithelia composed of more than one layer are termed stratified epithelia .2- The shape of the component cell.
3- The presence of surface specializations such as cilia and keratin.• A. Simple E.T.
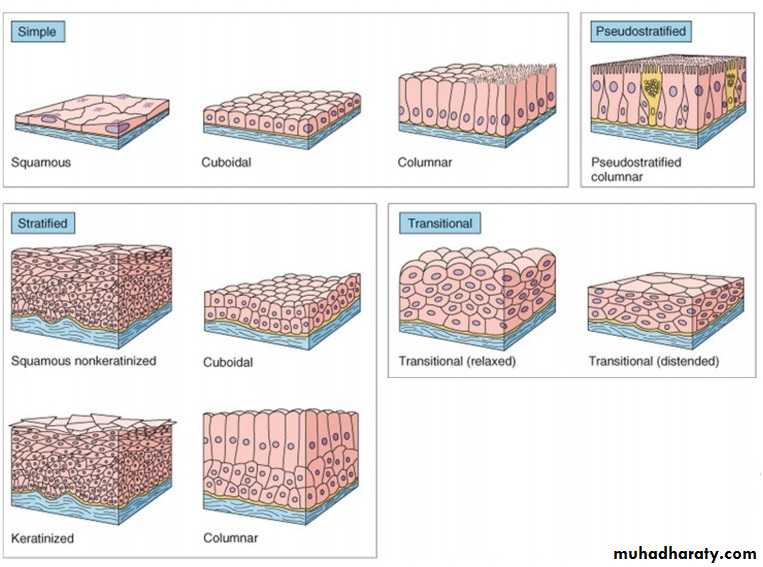
• B. Stratified E.T.1- simple sequemous
2- simple cuboidal3-simple columnar
4- psedostratified
1- S. sequmous
2- S.cuboidal3- S. columnar
4- S. transitional
Classification of epithelial tissue
Membranous (covering or lining) epithelium
Glandular Epithelia
Endocrine G: ductless glands, secrete directly into the bloodstream and their secretions are known as hormones.Exocrine G: discharge their secretion product into duct.
Mixed G: have both characters of exocrine and endocrine gland ex: pancreas.
Simple
Epithelium TissuesSimple epithelia
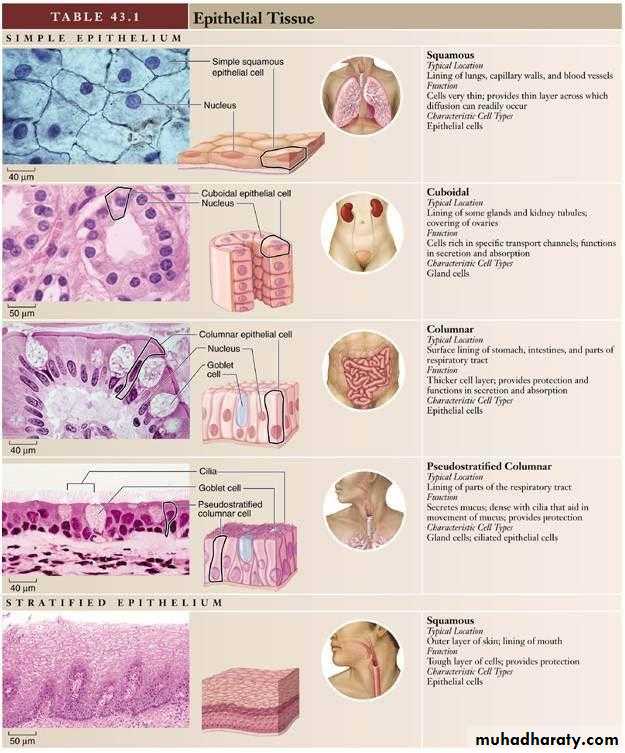
Simple epithelia are defined as surface epithelia consisting of single layer of cells. Simple epithelia are almost found on absorptive surfaces, they provide little protection against mechanical abrasion and thus are almost never found on surface subject to such stresses.The cell comprising Simple epithelia range in shape from extremely flattened to tall columnar depending on their function.
For example flattened Simple epithelia present in little barrier to passive diffusion and therefore found in sites such as the lung alveoli and the lining of blood vessels.
In contrast, highly active epithelia cell, such as the cells lining the small intestine, are generally tall since the must accommodate the appropriate organelles.
Simple epithelia may exhibit a variety of surface specialization, such as microvilli and cilia, which facilitate their specific surface functions.
Simple
squamousepithelium
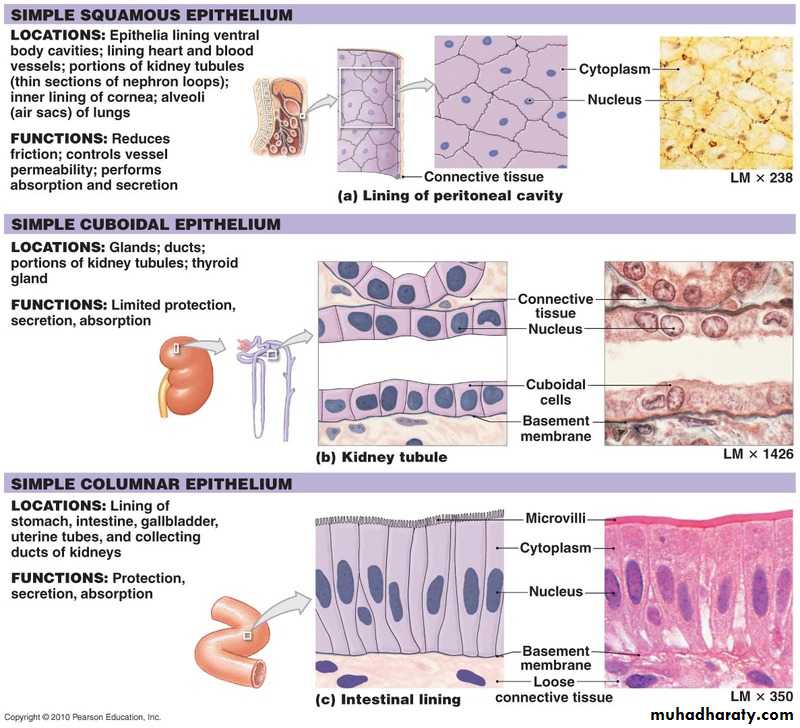
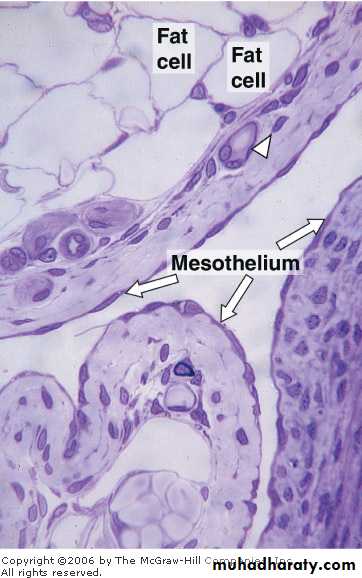
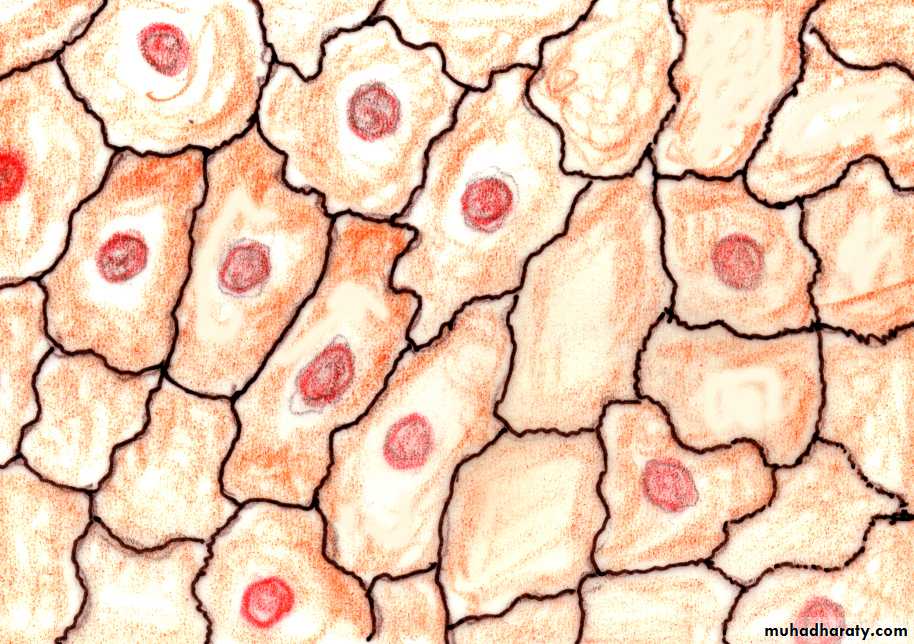
Simple squamous E. is composed of flattened irregularly shaped cells forming a continuous surface this may be referred to as pavement epithelium :
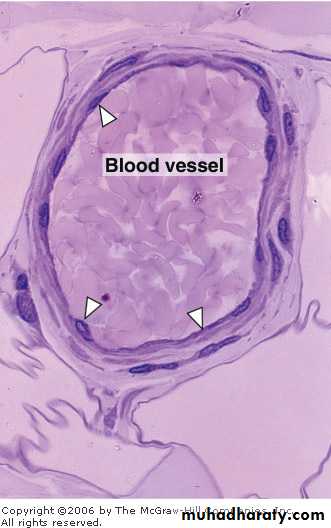
*walls of blood capillaries.
*loop of Henle.
*parietal layer of Bowman.
blood vessels are lined with a simple squamous epithelium
simple squamous epithelium that covers the body cavities (the abdominal cavity in this case) is called mesothelium
Fig (1) Simple squamous epithelium
Simplecuboidal
epithelium
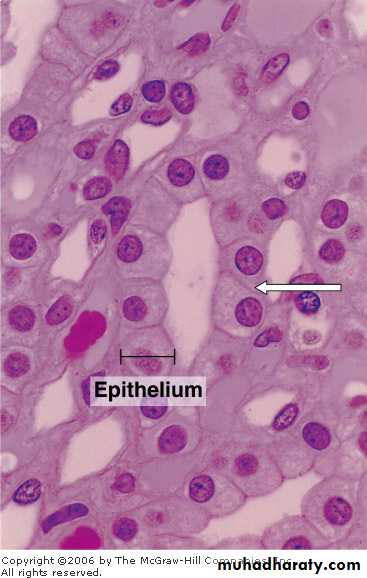
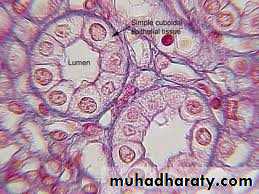
Simple cuboidal epithelium : is intermediate form between simple squamous and Simple columnar, the epithelial cells appear square, leading to its traditional description as cuboidal epithelium .
The nucleus is usually rounded and located in the centre of the cells.
lines small ducts and tubules which may have excretory, secretory or absorptive function Fig:
• small collection ducts of the kidney.
• salivary gland.• pancreas.
• ovary.
kidney collecting tubules
Fig (2) simple cuboidal epithelium
Simplecolumnar
epithelium
Simple columnar is similar to simple cuboidal epithelium except that the cells are taller and appear columnar in section at right angles to the basement membrane. The nuclei are elongated and may be located towards the base, the centre or occasionally the apex of the cytoplasm, this is known as polarity.
Simple columnar epithelium is most often found on
• highly absorptive surfaces ex: small intestine, highly secretory surfaces ex: stomach
• in transportation organs ex: oviducts, ductuli efferentes of testis
• found large ducts of some glands Fig(3).
Fig (3) Simple columnar epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium formed by long cells with elliptical nuclei.
SimplePseudo stratified
epithelium
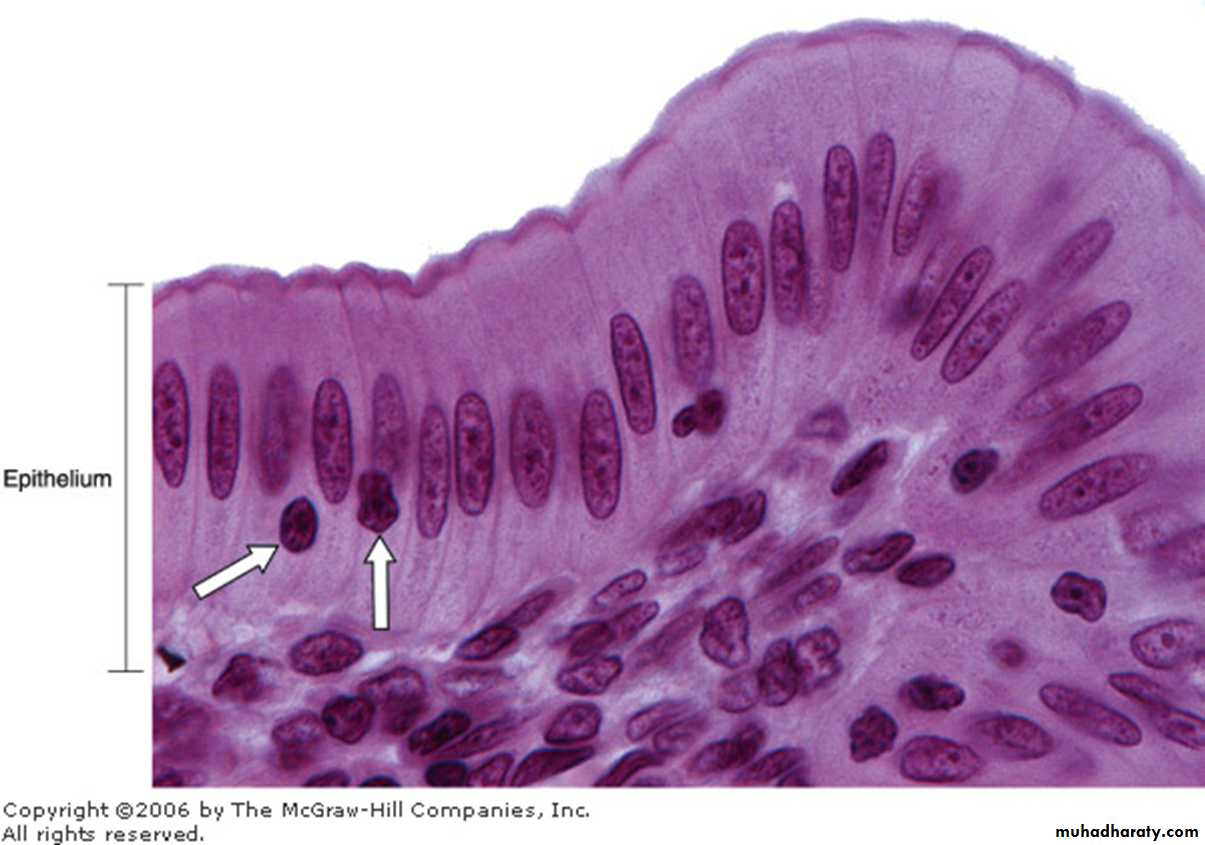
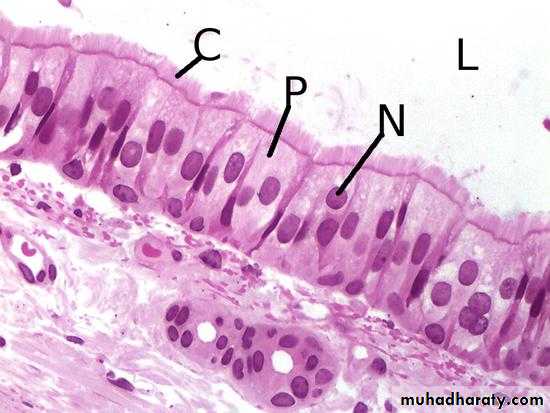
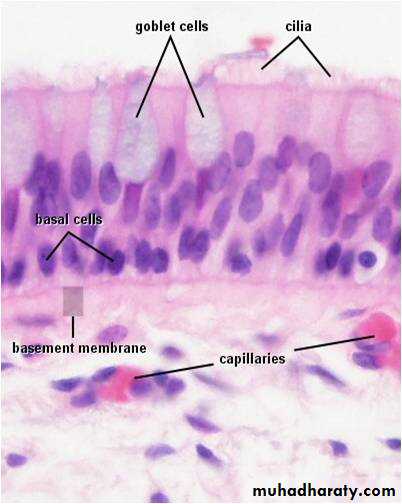
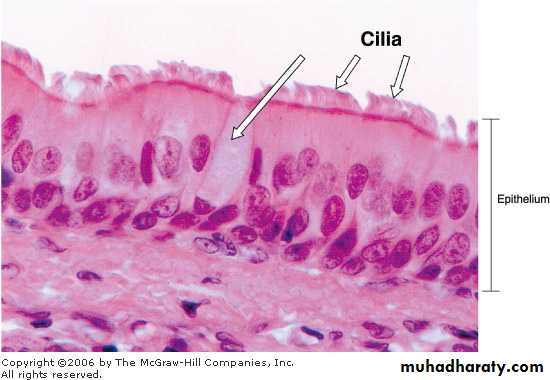
The term pseudo stratified is derived from the appearance of this epithelium in section which convoys the erroneous impression that there is more than one layer of cells. In fact, this is a true simple epithelium since all the cells rest on the basement membrane.
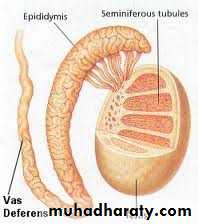
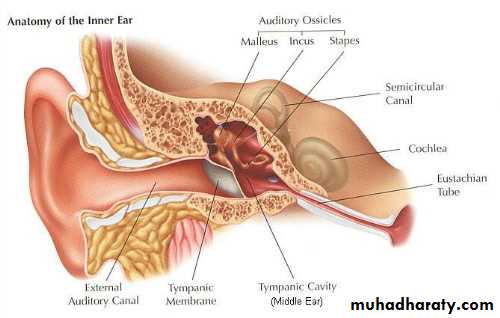
The nuclei of these cells, however, are disposed at different levels, thus creating the illusion of cellular stratification. Pseudo stratified epithelium were Lining primary bronchi, epididymis and vas deferens, auditory tube, part of tympanic cavity, nasal cavity, male urethra, large excretory ducts Fig (4).