Non plaque induced gingival lesions
Non plaque induced gingival lesions
Different origins of inflammation from that of routine plaque associated gingivitis that present with characteristic clinical features.Such gingivitis does not disappear after plaque removal but its severity depend on interaction with present plaque.
Infectious gingivitis
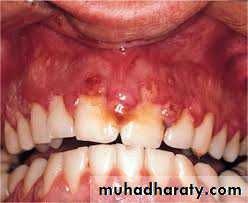
Gingival lesions of specific bacterial origin rarely occur by non-plaque related pathogens like in sexually transmitted diseases as Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Treponema pallidum .Oral lesion may be secondary to systemic infection or may occur through direct infection .
It may or may not associated with lesion in other sites of body.
Fiery red,edematous,painful ulceration, as asymptomatic mucous patches or as a typical non-ulcerated highly inflamed gingiva.
Infectious gingivitis
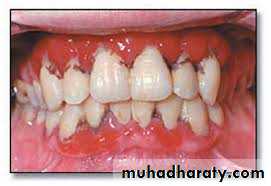
Streptococcal gingivitis or gingivostomatitisIt is a rare condition present as fever, malaise & pain associated with acutely inflamed ,diffuse red & swollen gingiva with increase bleeding .
Gingiva infection preceded by tonsillitis.
Viral infection
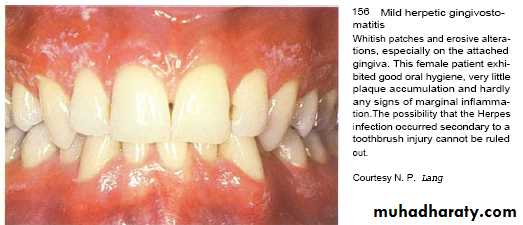
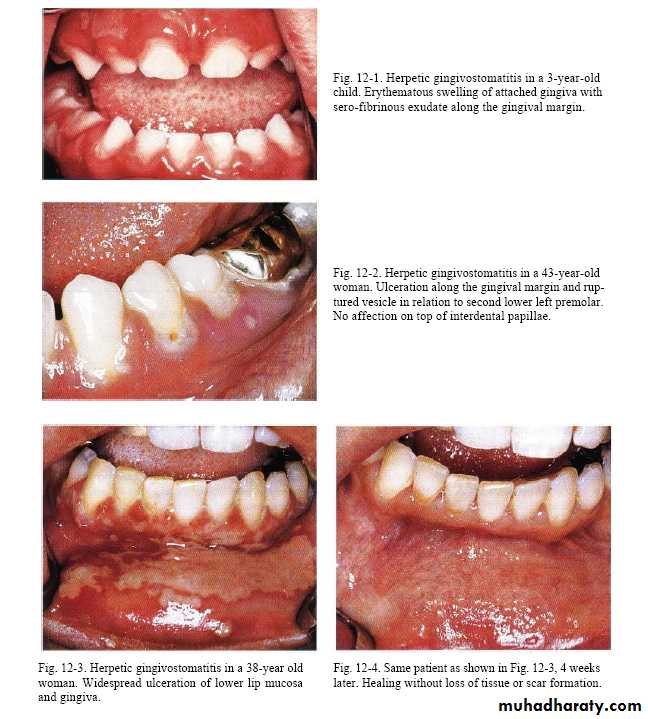
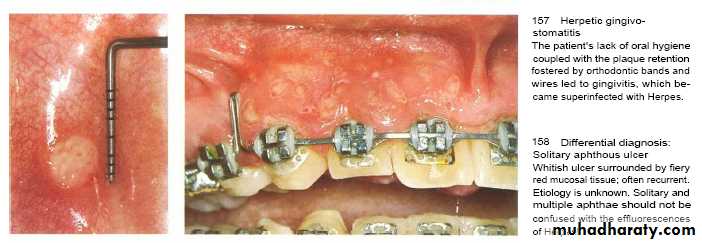
Herpes simplex virus type 1 & 2 & Varicella-zoster virus that inter body in childhood & induce lesion followed by period of recurrent infections occur in 20-40 % in form of herpes labialis.Factors triggering reactivation of latent virus are; Trauma , ultra violet light and fever .
Varicella-zoster virus
chicken pox as primary self limiting infection mainly in children & later reactivation of virus in adult causes herpes zoster ( shingles).Fever, malaise & skin rash ,intraoral lesions are small ulcers on tongue , palate & gingiva.
Virus remain latent in dorsal root ganglion.
Reactivation of virus induce unilateral lesions that followed infected nerve , can occur intraorally with manifestation of severe pain & paraesthesia.
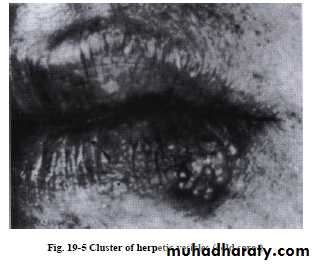
Gingival lesion
Vesicles that rapture to leave fibrin-coated ulcers with irregular form.
In AIDS patient, V.zoster virus infection result in severe tissue destruction with tooth exfoliation & necrosis of bone .
Diagnoses is obvious due to unilateral occurrence of lesion.
Viral infection
Varicella zoster virus
Fungal infectionsBlastomycosis,candidosis,cryptococcosis,histoplasmosis &
other infection
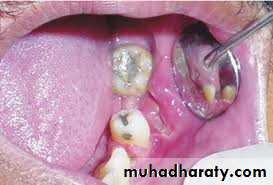
Candidosis ; infections by:-
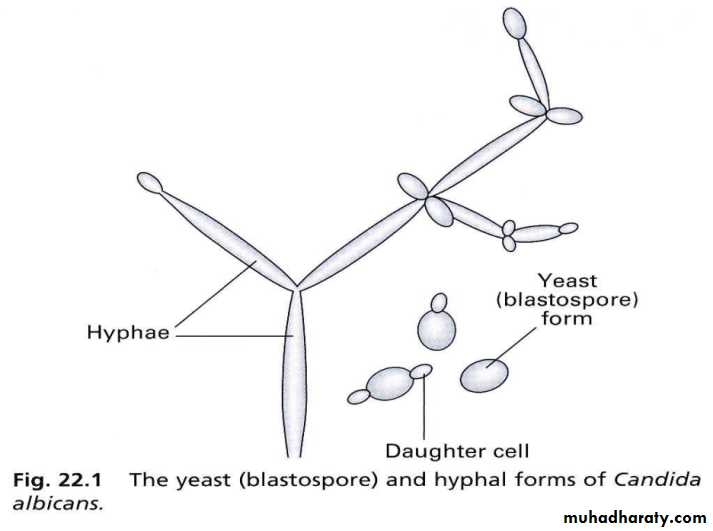
C.albicans, C.glabrata, C.krusei, C.tropicalisCandida albicans is opportunistic infection & occur as a consequence of reduced host defense in:
1- immunocompromised pt.
2- disturbed oral flora by long term use of broad spectrum AB3- under prosthetic devices
4- topical steroid uses
5- decrease salivary flow,increased salivary glucose or
decrease salivary pH.
Candidosis
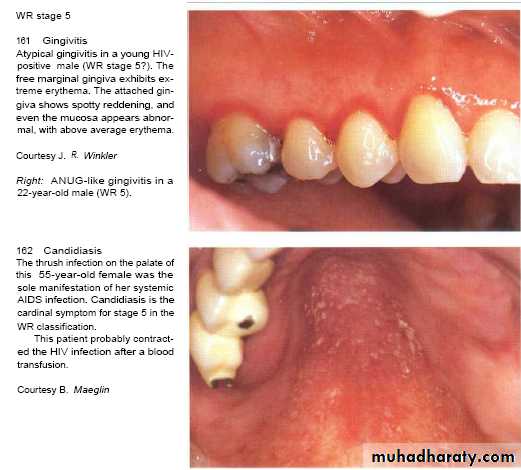
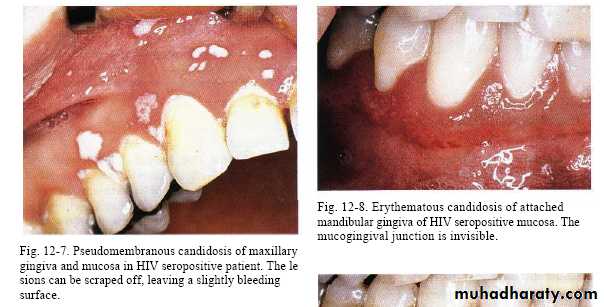
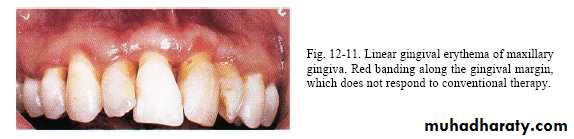
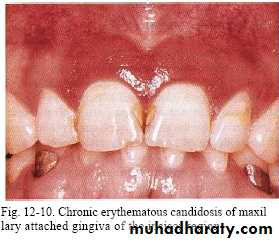
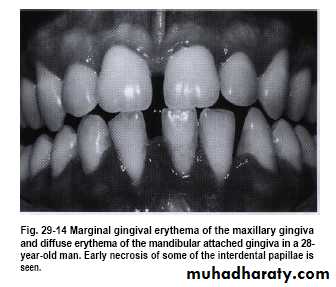
Rarely seen in gingiva of healthy persons but in HIV-seropositive & others immuno compromised patients seen in attached gingiva with manifestation of erythema.( HIV-associated gingivitis or linear gingival erythema )
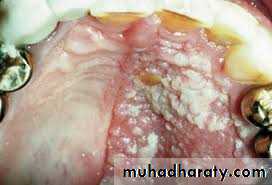
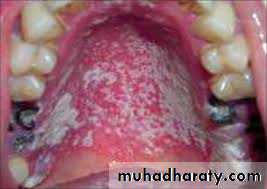
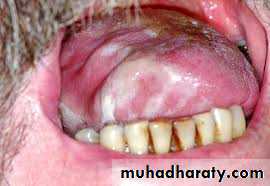
Pseudo membranous candidiasis.
( also named thrush in neonates) ,
whitish patches that cab be wiped off the mucosa with instrument or gauze leaving bleeding surface .
Candida albicans
•Acute•Pseudomembranous
• Erythematous
Chronic
•Erythematous
•Pseudomembranous
• Hyperplastic
• Nodular
• Plaque-like
• Candida‑associated lesions
•Angular cheilitis
• Denture stomatitis
• Median rhomboid glossitis
• Keratinized primary lesions superinfected with Candida
• Leukoplakia
• Lichen planus
• Lupus erythema
Candidosis
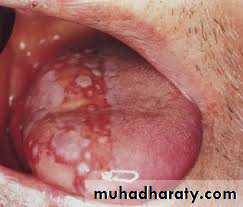
Erythematous lesionsfound anywhere in oarl mucosa ;intensely red lesion with severe pain.
Plaque type ;
whitish plaque that cant removed with no symptoms.
Nodular type;
slightly elevated nodules of white or reddish color.
Culture, smear & biopsy needed to confirm the diagnosis
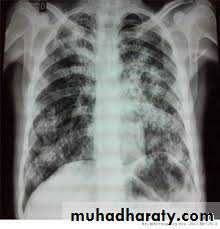
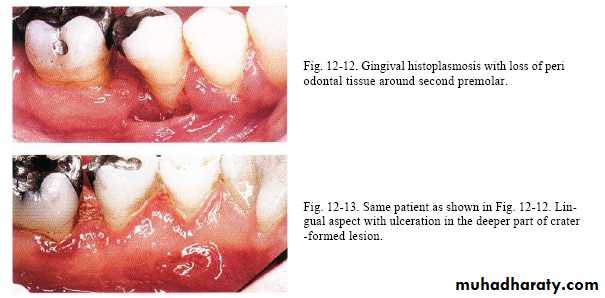
Histoplasmosis
It is a type of lung infection.It is caused by inhaling Histoplasma capsulatum fungal spores.
These spores are found in soil and in the droppings of bats and bird
It is disseminated form that occur in immunocompromised patient.
Oral lesions in 30% of cases & can effect any area ,
initiate as nodular or papillary & later become ulcerative & painful.