
Antihypertensive(objectives
)
1
-
Know classification of Antihypertensive drugs & at least two
drug examples for each class or subclass
2
-
Describe treatment strategies & goal of Antihypertersives
therapy.
3
-
Know the mechanism of action ,Kinetics, theraputic
indications, contraindication & side effects of commonly used
Antihypertensive drugs.
Hypertension is defined as a persistant elevation of systolic
&/or diastolic B.P to above 140/90 mmHg in person aged 18
years or olden.
Aetiolog
:
-
Primary, essential, multifactorial, age, genetics,
environmental, weight, race.
Secondaryhypertension:
Mechanisms for controlling B.P :-
1
.
Baroreceptors & the sympathetic N.S (moment to
moment regulation of B.P – short term(
2
.
Rennin-angiotensin-aldosterone (long term
regulation of B.P - RAAS(
Cl
assification of antihypertensive drugs
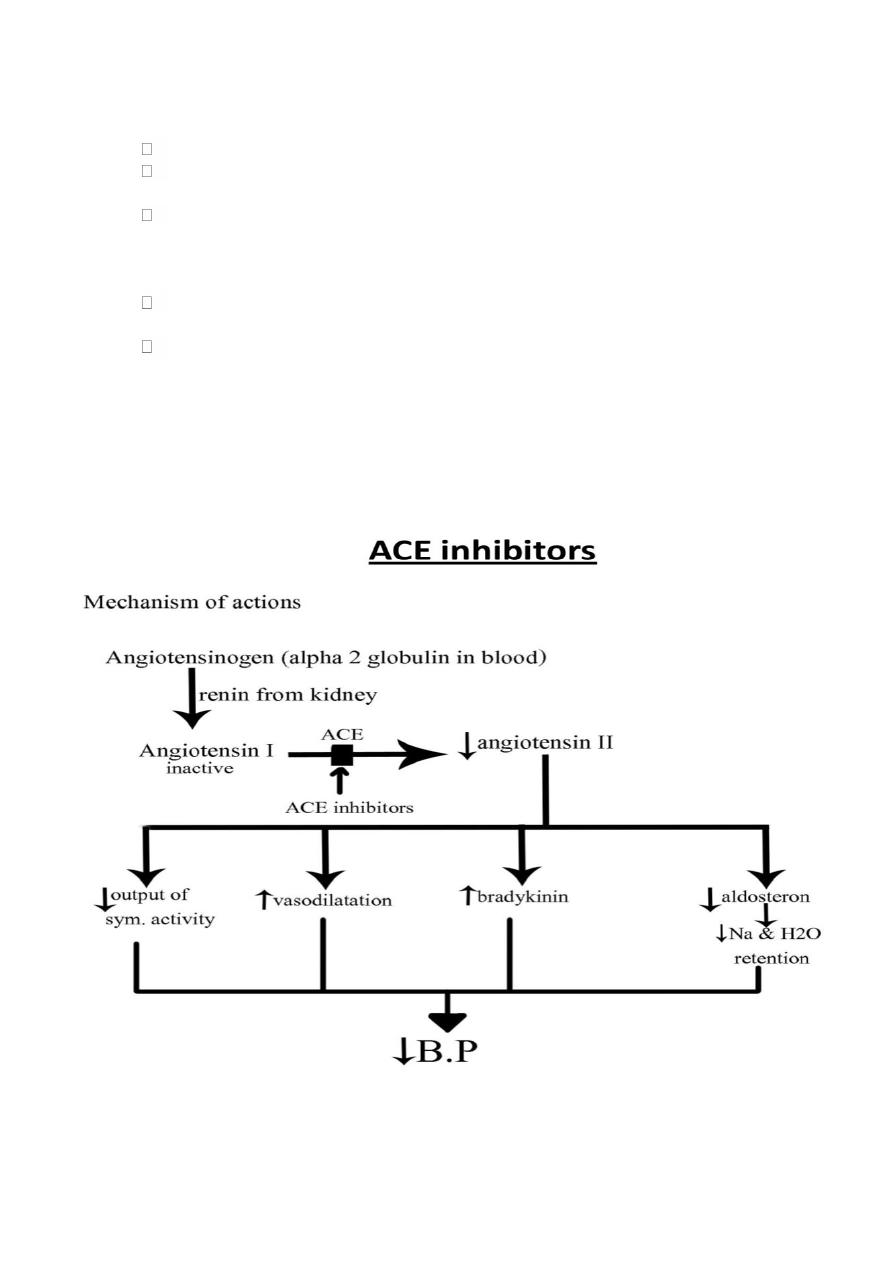
1. ACE inhibitors
2
.
3
.
4
.
5
.
Captopril, Enalpril, Lisinopril
Angiotensin II – receptor antagonists (ARBs)
Losartan, valsartan, telmisartan
Rennin inhibitors
Aliskiren
calcium channel blockers (CCBs)
nifidipine, verapamil, deltiazem, amlodipine, nicardipine,
nimodipine.
Diuretics
Thiazides:H.ch.thiazide,chlorthalidone,indapamide
Highceiling:furosemide
6
.
Badrenergicblockers
Proprandol, atendol, metoprolol
7
.
Alphaadrenergicblockers
Prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin
8
.
Beta&alphaadrenergicblockers
Labetalol, carvedilol
9
.
Centralsympathetics
Clonidine, methyldopa
10
.
Vasodilators:
Arteriolar(hydralazine,minoxidil,dinzoxide) Arteriolar +
venous (Na nitroprusside)
Chemical strategies
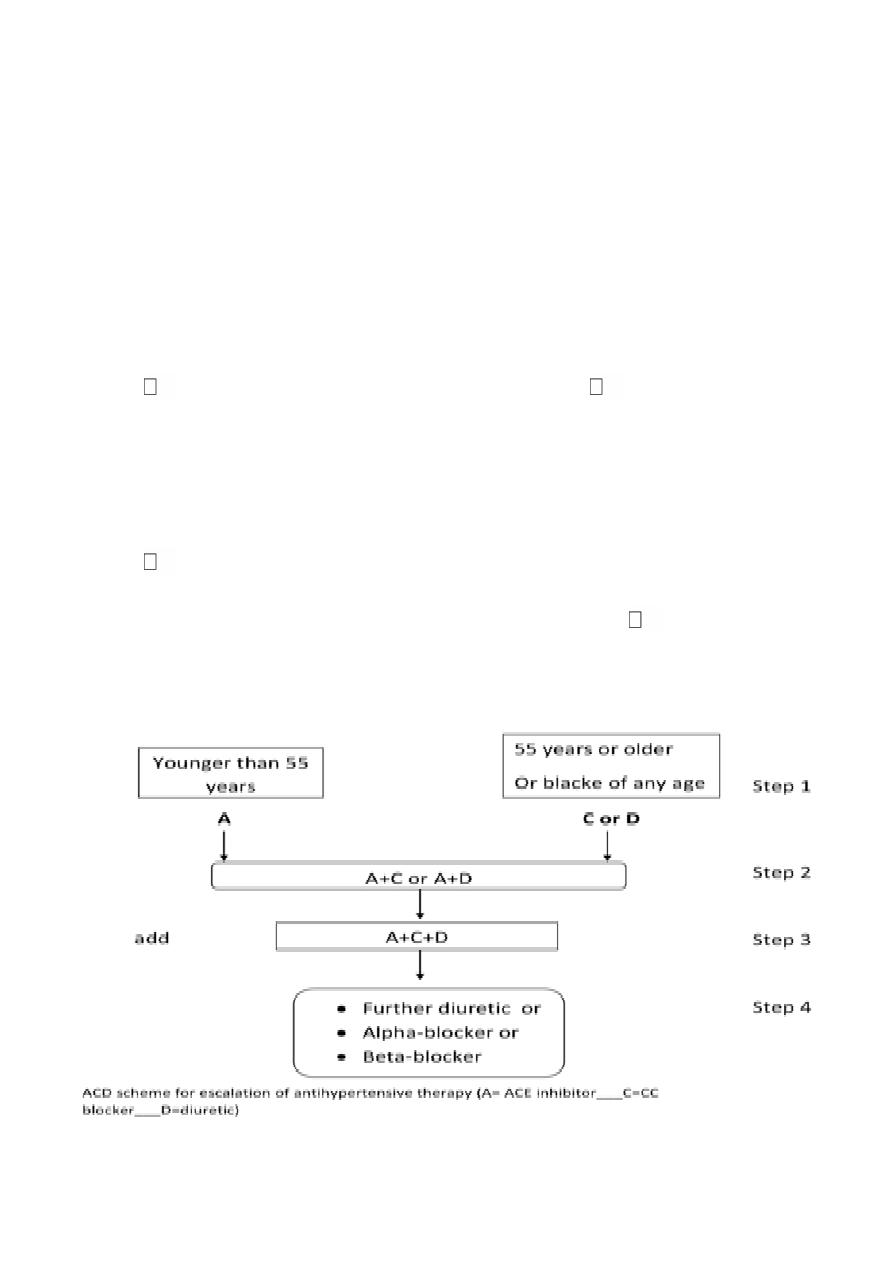
Drug therapy : ACD scheme for antihypertensive
therapy
the treatment target blood pressure of <140/<85
suggested by British hypertension society (BHS)
will increase the patient needing 2 or more drugs a simple
stepped regemen is the (ACD) scheme in
the following (2006-NICE & BHS)
Diuretics
-
Low dose is safe & effective in preventing stroke, MI & CHF ( decrease mortality)
-
Superior to B-blockers for treatment of HPT in older adult
I- thiazide diuretics
Mechanism of action of thiazide in treatment of HPT
Loop diuretics
act even in patients with poor renal function
cause decreased renal vascular resistance&
increase renal blood flow
loop diuretics increase the calcium content of
urine
III-Potassium-sparing diuretics (reduced K+
loss in urine(
Amilorid & triametrine (inhibitors of sodium transport & late distal & collecting
ducts)
Spirinolactone (cardiac remodeling in heart failure) & eplerenone (aldosterone-
receptor antagonist)
Alpha-beta- adrenoreceptor blocking agents
labetalol & carvedilol block α1, β1 & β2 receptors. carvedilol: 1- an effective
hyperantitensive
2
-
mainly used in treatment of heart
failure (reduce mortality)

Therapeutic uses
:
1
.
Hypertensive patients (white & young)
2
.
CHF (congestive heart failure)
3
.
Myocardial infarction (MI)
4
.
Prophylaxis in high cardiovascular risk subjects 5. Diabetic nephropathy
6
.
Scleroaderma crisis
Adverse effects
:
1
.
Common side effects
Dry cough (10%) due to increase level of bradykinin Rash, fever, altered taste
Hyperkalemia & hypotension
2
.
Angioedema : is rare but potentially threatening due to increase level of
bradykinin
3
.
1 st dose syncope
4
.
Reversible renal failure in patient with severe bilateral renal artery stenosis
5
.
Fetotoxic & should not be used during pregnancy
Angiotensin II-receptor antagonists
The angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs).
Losartan, valsantan, candesartan, ebrosantan, ibresantan, olmesantan &
telmisantan.
Pharmacological effects:
1
.
They produce arteriolar & venous dilation
2
.
They block aldosteron secretion & decrease Na & H2O retention
3
.
ARBs don't increase bradykinin level.
Uses
:
In hypertensive diabetics (ARBs decrease nephrotoxicity of diabetes) Side effects : -
similar to those of ACEIs
-
The risks of cough & angioedema are significantly decreased
-
ABRs are also fetotoxic
Renin inhibitors (Aliskiren
)
Effects:
-
Aliskiren directly inhibits rinin & thus acts earlier in
the RA.AS than ACEIs or ARBs.
-
It lower B.P & effective as ARBs, ACEIs, thiazides
-
It can be combined with diuretics , ACEIs, ARBs or
CCB... etc S/E:
-
Diarrhea at high dose
-
Cough & angioedema < ACEIs - Fetotoxic

Centrally acting adrenergic drugs
Alpha2 adrenoreceptor agonists
1
.
Clonidine
Therapeutic uses:
HPT that not respond to 2 or more drugs HPTcomplicatedbyrenaldisease.
)
Clonidine does not decrease renal blood flow or GFR
with diuretics : Clonidine (⇧ or ⇩ ) produce H2O & Na retention
Migraineprophylaxis,menopausalflashing,chorea with low dose & mimorale
Adverse effects
: - Sedation
-
Dry nose
-
Rebound HPT following abrupt withdrawal of the drug. So the drug should be
withdrawal slowly.
Methyldopa
Therapeutic uses:
1
.
Hypertensive patients with renal insufficiency 2. Hypertensive pregnant patients
(safety profile) Adverse effects:
Sedation (frequent) lead to failure of male sexual
function
Nightmares,depression,involuntarymovements
Scoreorblacktongue
Nausea, flatulence, constipation
Positivecoomb'stestwithoccasionallyhemolytic
anaemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia
Hepatitis
Gynaccomastia&lactationduetointerferencewith
dopaminergic suprresion of prolactin secretion
Vasodilators
(Direct acting smooth muscle relaxant) Pharmacological actions:
1
.
Relaxant of vascular smooth muscle ⟶ VD ⟶ ⇩PR ⟶⇩BP
2
.
Reflex stimulation of heart ⟶⇧heart rate & O2 consumption ⟶ +or - angina
pectoris, MI or heart failure ( in predisposes individuals )
3
.
⇧ Plasma rennin ⟶ Na+ & H2O retention
Hydralazine
Direct vasodilator acting primary on arteries & arterioles ⟶ ⇩ PR ⟶⇩BP
Reflex ⟶ ⇧ HR & CO
Therapeutic uses:
1
.
Hypertension in pregnancy (lack of teratogenecity)
2
.
Moderately severe hypertension(always with B-blocker&
diuretics) Adverse effects:
-
Headache, tachycardia
-
Nausea, sweeting
-
Arrhythmia & precipitation of angina
-
A lupus-like syndrome can occur with ( huge dose or slow
acetylators(

But it is reversible on discontinuation of the drug.
Minoxidil
This drug causes dilatation of resistance vessels. Arterioles but not venules
Therapeutic uses:
1
.
Orally : for treatment of severe to malignant HPT that
is refractory to other drugs.
Reflex tachycardia & fluid retention may be severe & require the concomitant use of
loop diuretics & β blockers
2
.
Topically to treat man pattern baldness
S/E:
1
.
Serious Na & H2O retention ⟶ volume overload
)
edema & congestive heart failure(
2
.
Hypertrichosis (the growth of body hair)
Diazoxide
Its emergency use is obsolete because of excessive hypotension outweigh the
benefit.
Three other vasodilator find a role outside hypertension:
1
.
Nicorandil : in angina
2
.
Papaverine : in male erectile dysfunction
3
.
Alprostadil :I.V for patency of ductus arteriosus
Hypertensive Emergency
The therapeutic goal to rapidly reduce B.P
a. Na nitroprusside
-
It is administered intravenously, it is poisonous if given orally because of its
hydrolysis to cyanide
-
It is light sensitive & should be protected from light Pharmacological actions:
1
.
Reduce B.P in all patients regardless of the cause of HPT
2
.
Has little effect outside the vascular system
3
.
Actsequallyonarterial(⇩P.R)&venous(preload)smoothmuscle
-
It is metabolized rapidly (t1/2 = minutes) & requires continuous infusion to
maintain its hypotensive action
A
dverse effects
:
1
.
Hypotension caused by overdose
2
.
Cyanide toxicity (rare) & treated by infusion of Nathiosulfate
Cyanide + Nathiosulfate ⟶ thiocyanate (less toxic & eliminated by kidneys)
a. Other drugs:
1
.
Labetolol (IV) α & β blockers
2
.
Nicardipine (IV) Ca channel blockers 3. Fenoldopam (IV) D1 agonist
