
Acne Vulgaris
Dr. Ahmed Abdulhussein AL-Huchami
2020 covid19

Acne Vulgaris
Definition:
It is a
self-limited
disorder of the
pilosebaceous unit
that is seen primarily in
adolescents
, and appears on skin areas with
numerous sebaceous glands
.
Epidemiology:
Nearly all teenagers have acne (acne
vulgaris
).
Only about
15-20%
of affected patients need the help of physician.
Natural History and Course:
12-14
to mid twenty.
Tending to be
earlier
in
females
(earlier onset of puberty) and
more
persistent
.
The
severest
forms occurs more in
males
.

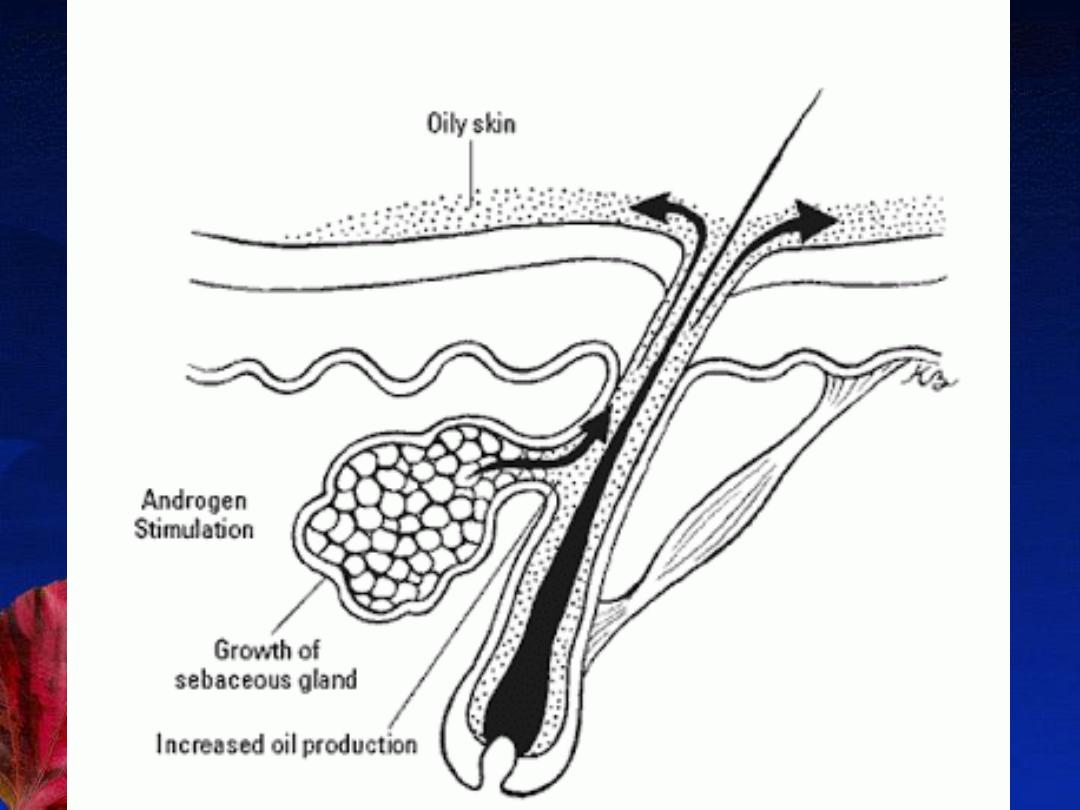
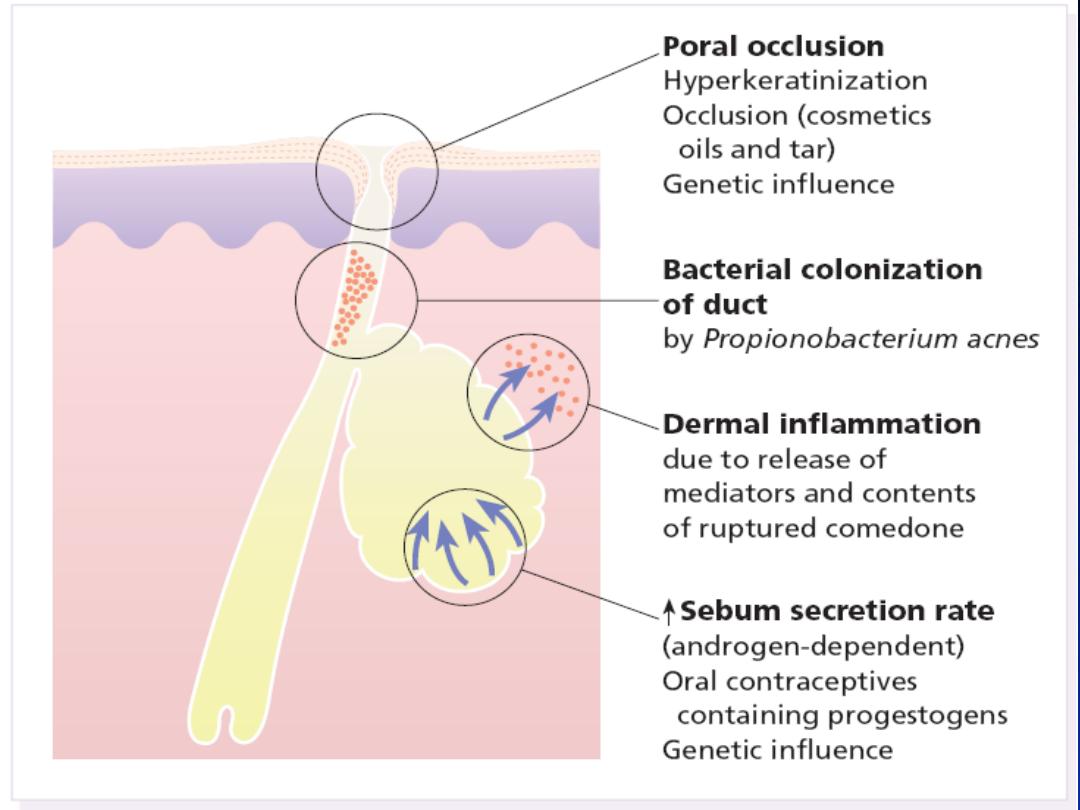
Etiology and Pathogenesis:
Many factors combine to cause acne , included:
1-Poral occlusion
2-Sebum
3-Bacterial:
Cutibacterium acne(C. acne)
4-Hormonal
5-Genetic
6- Diet
7- Emotional stress
Cutibacterium

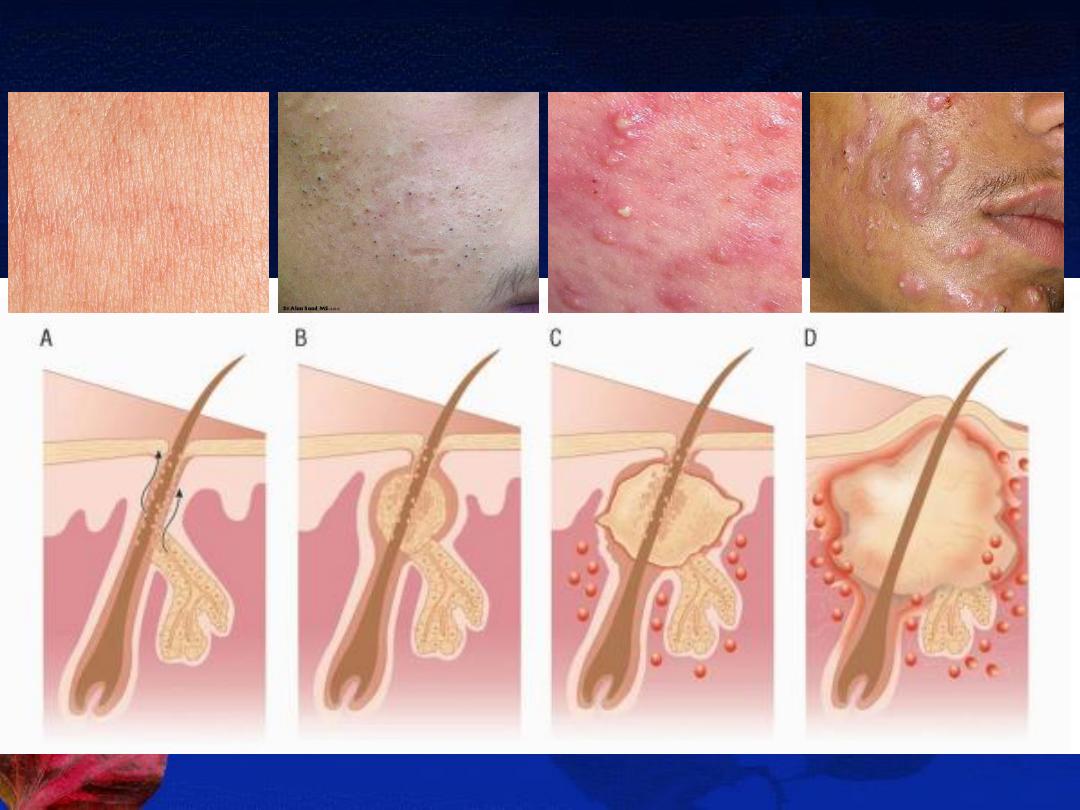
A-Poral occlusion. B-Comedons. C-Papules & pustules. D-Nodules & cysts
.
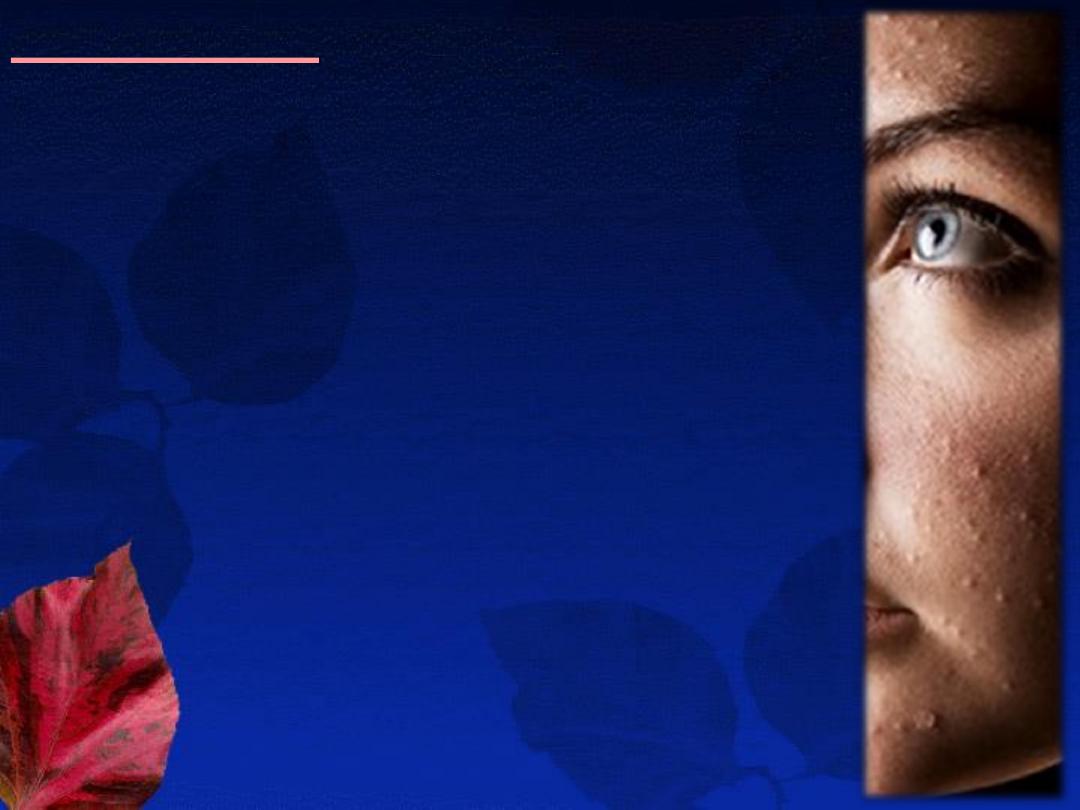
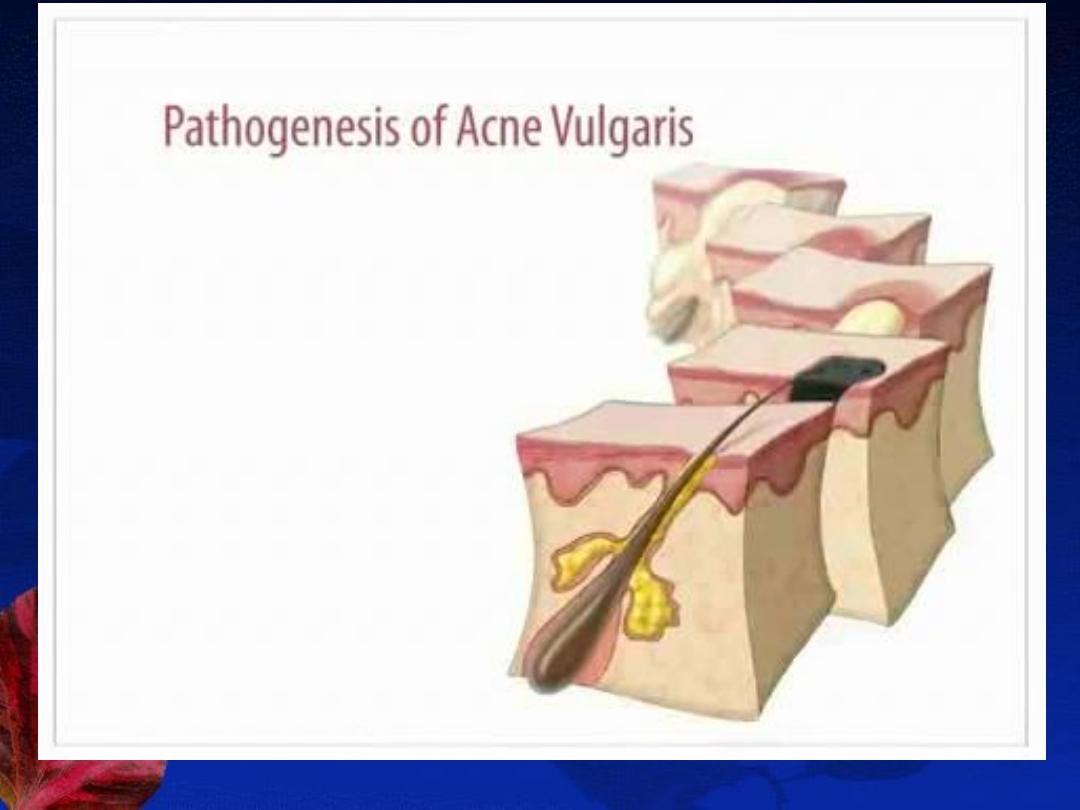

Presentation:
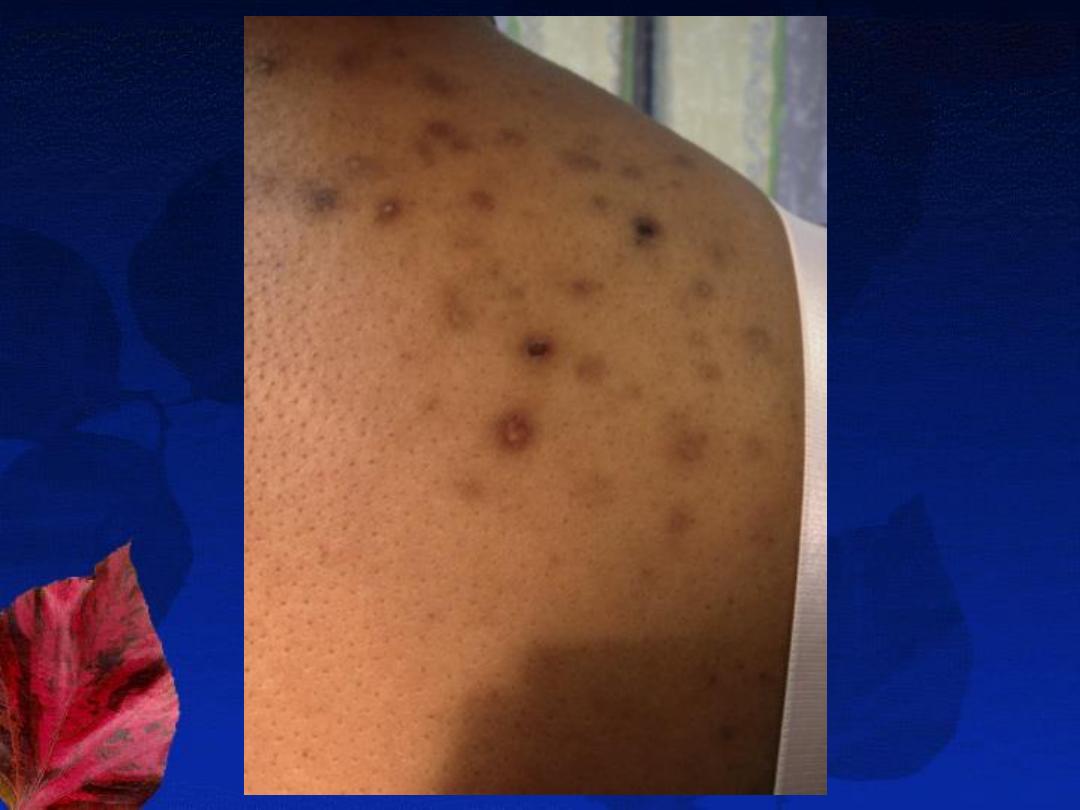
Site:
face, followed by the shoulders, upper chest
and back.
Lesions:
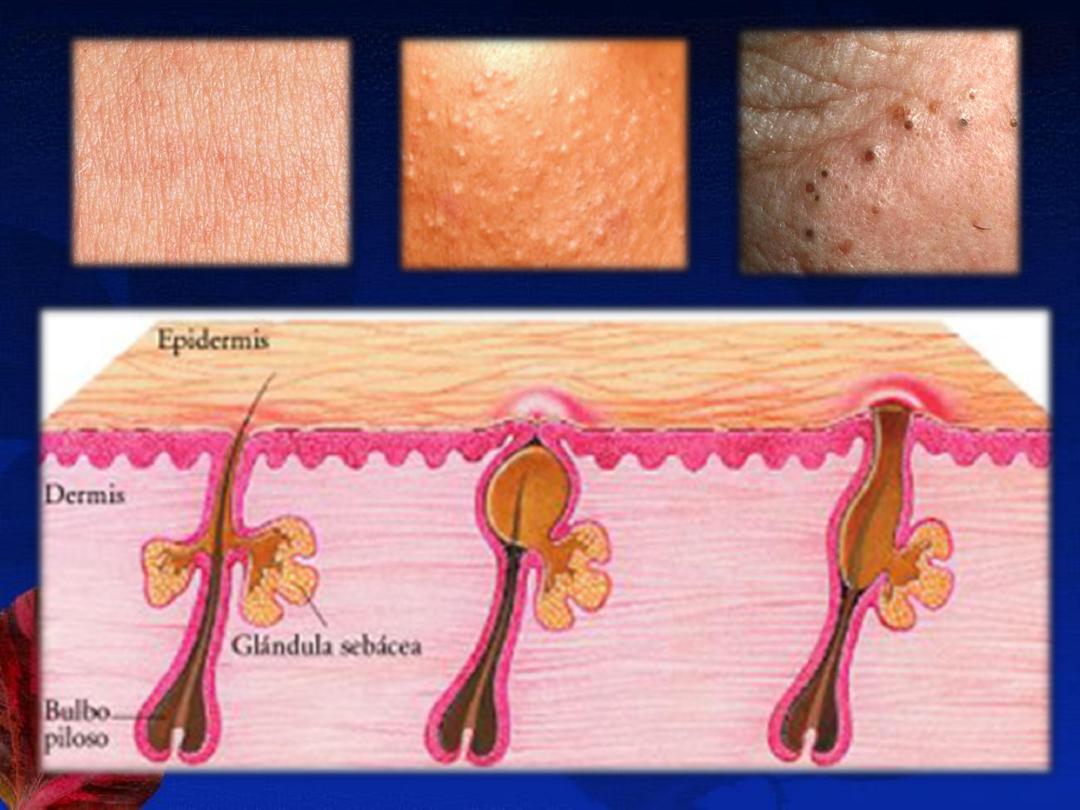
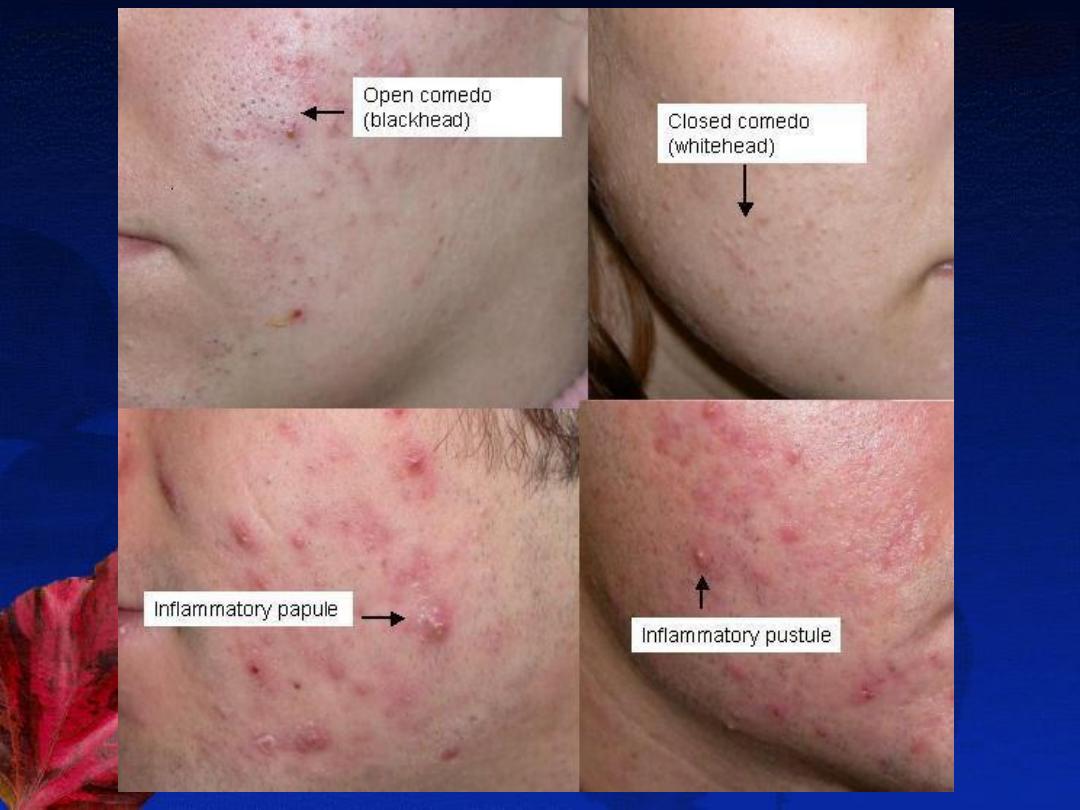
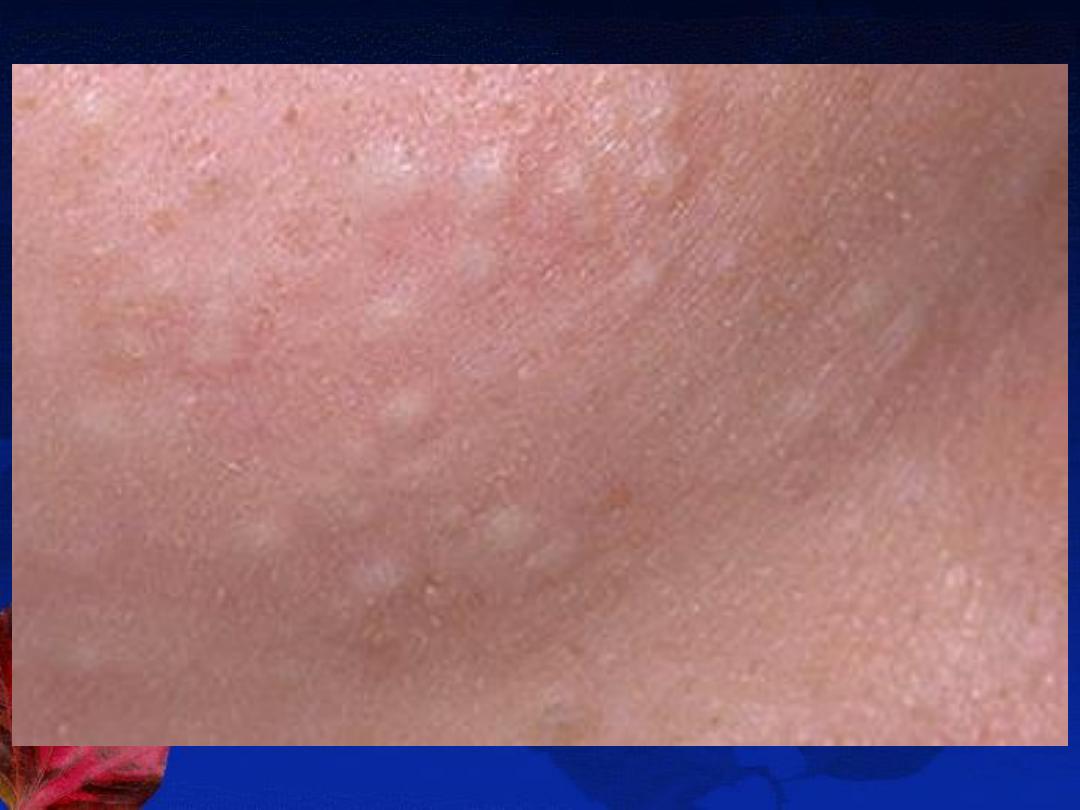
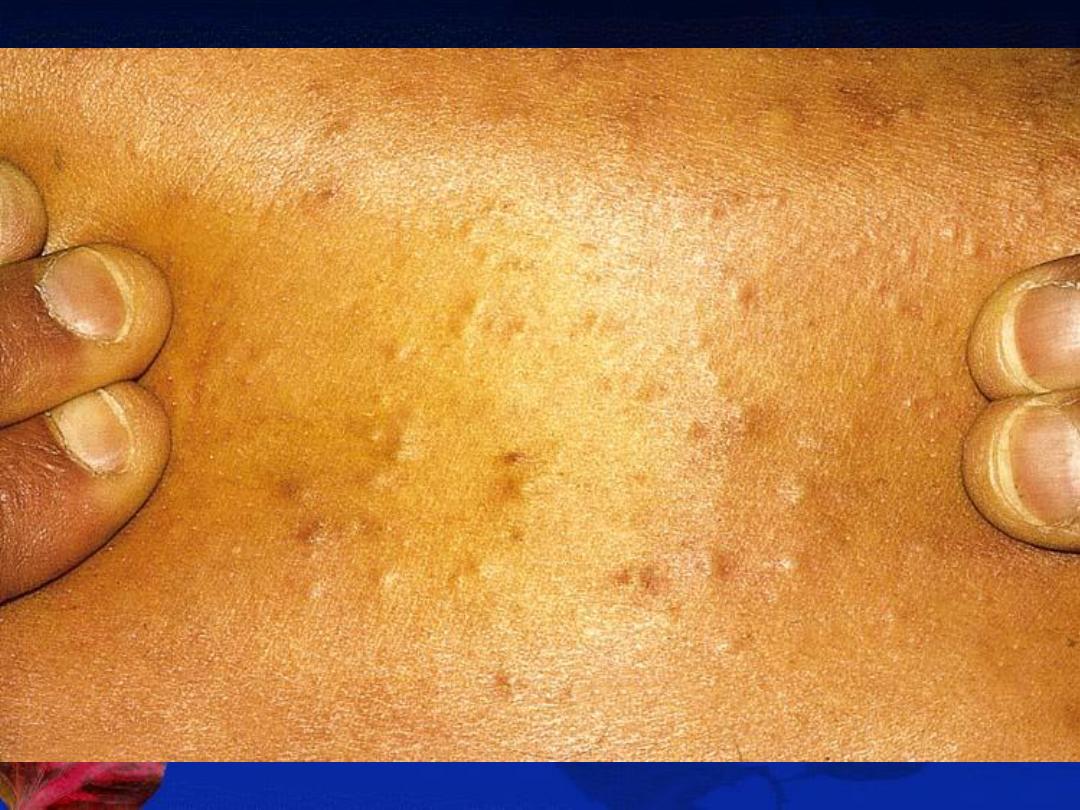
A-The non-inflammatory lesions (Comedones):
open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads).
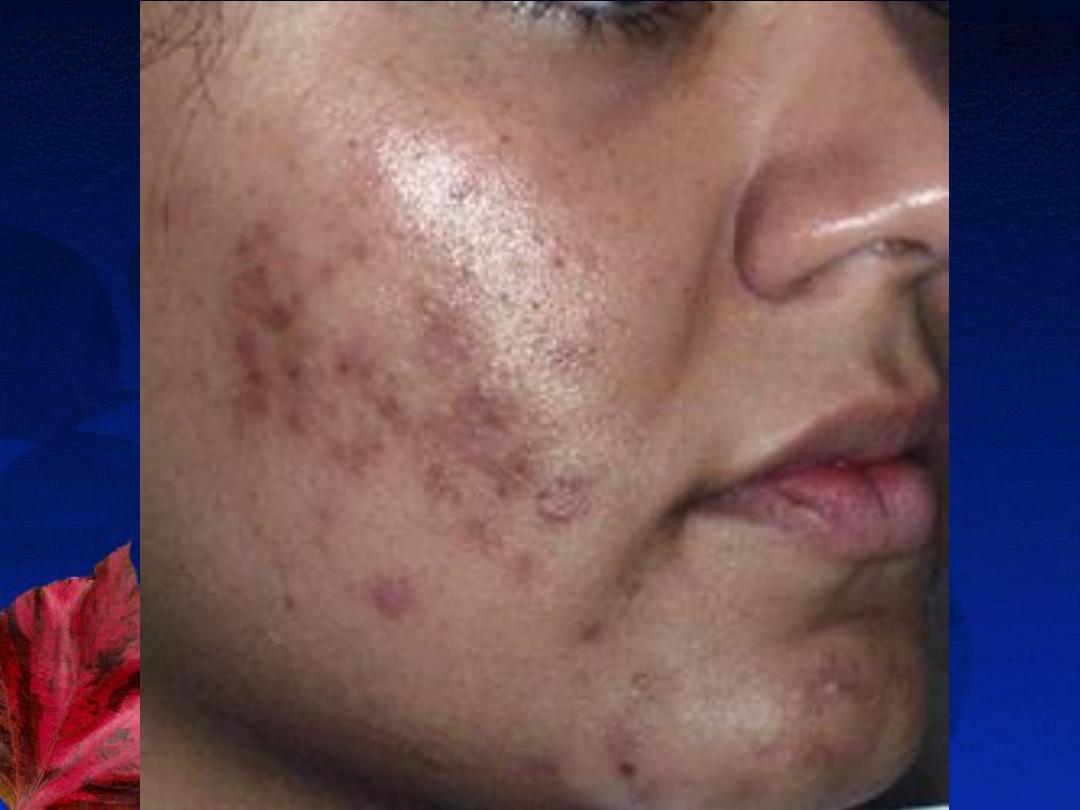
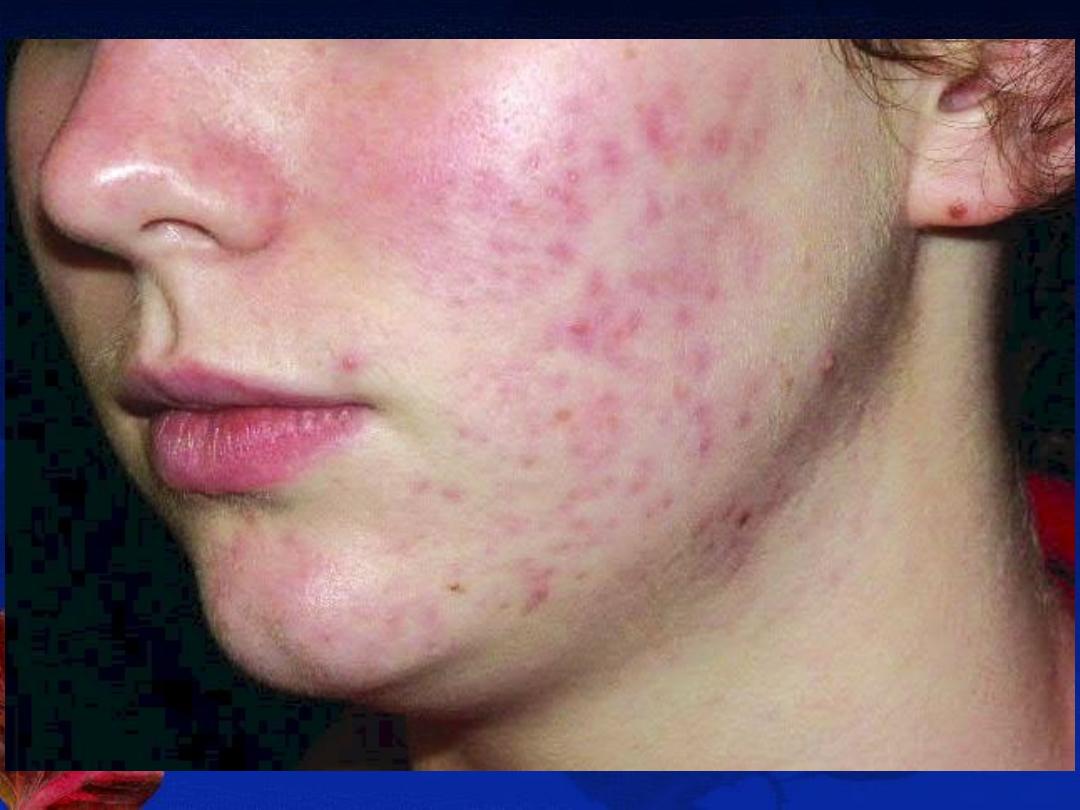
B-The inflammatory lesions:
red papules, pustules, nodules or cysts.
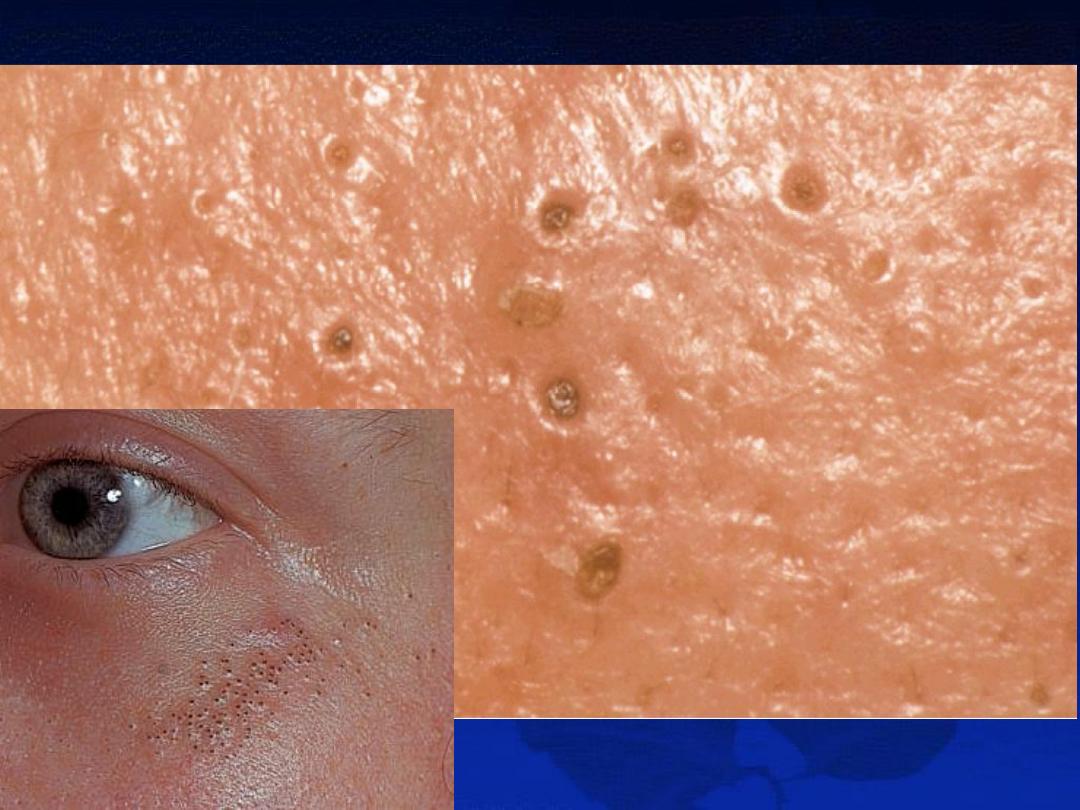
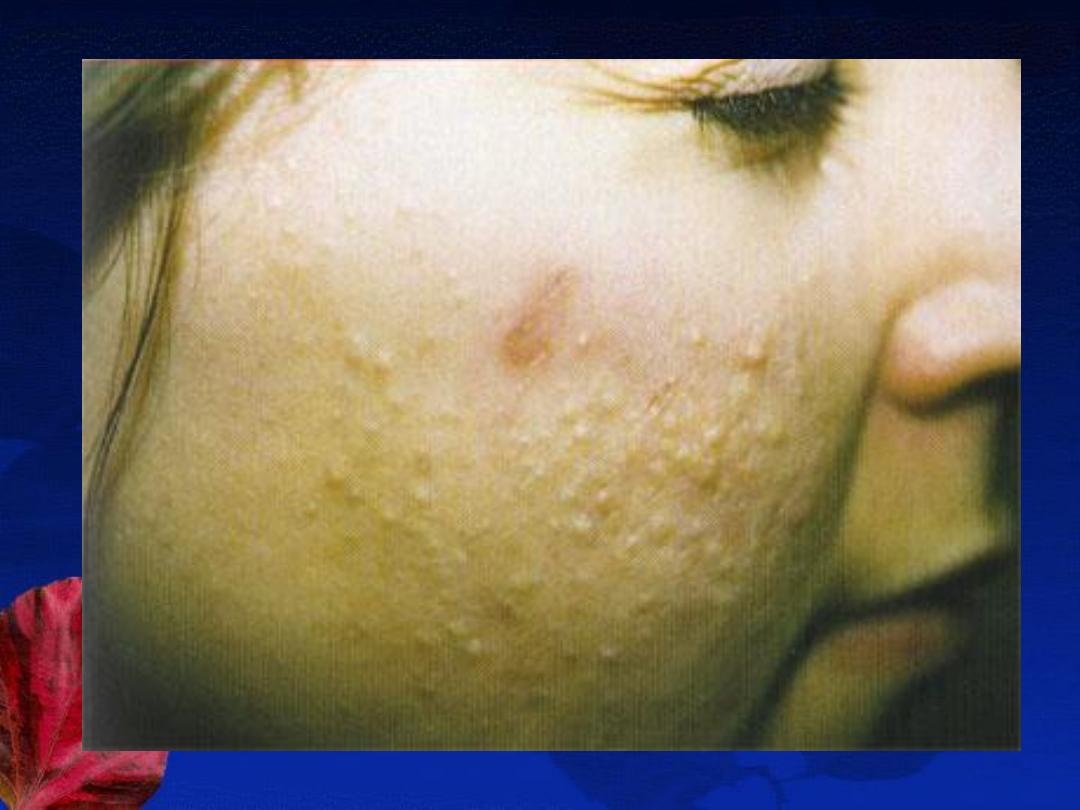
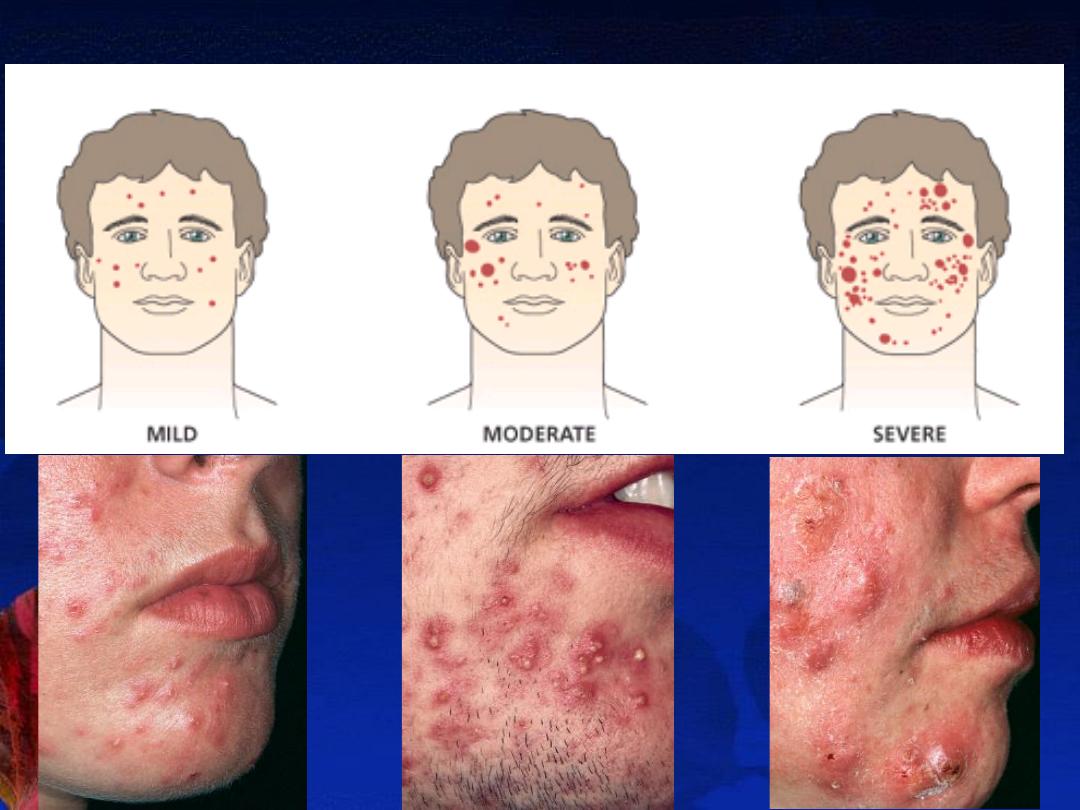
Severity:
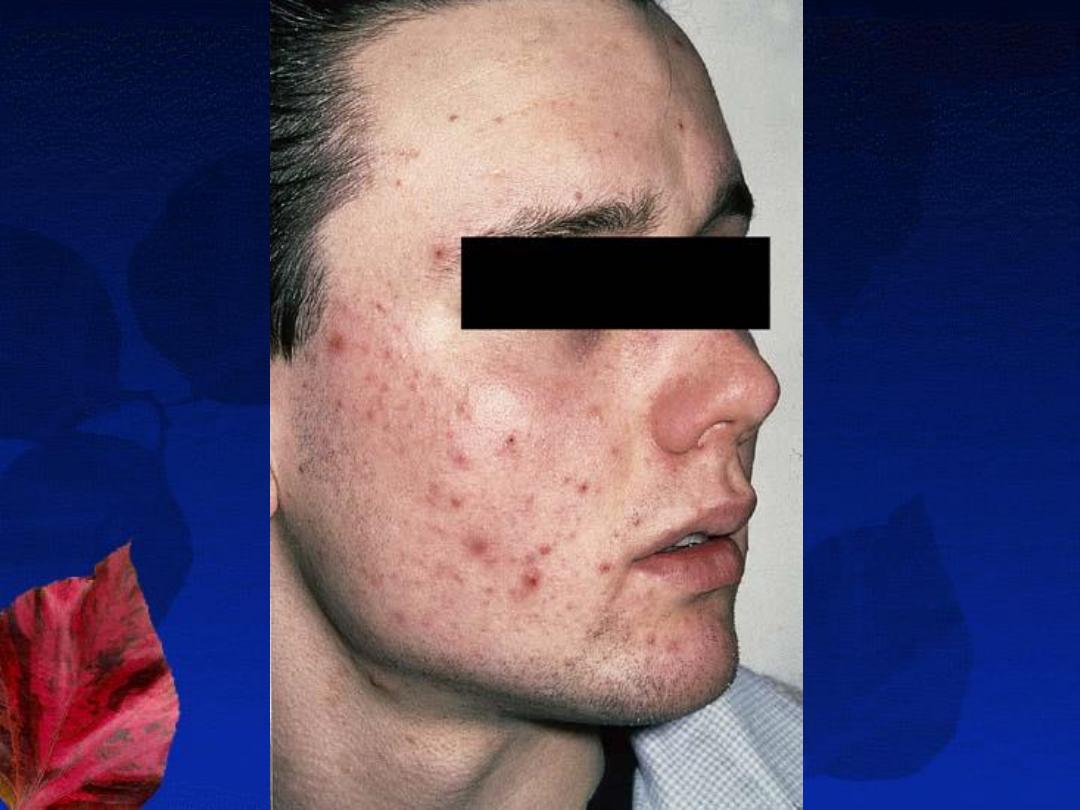
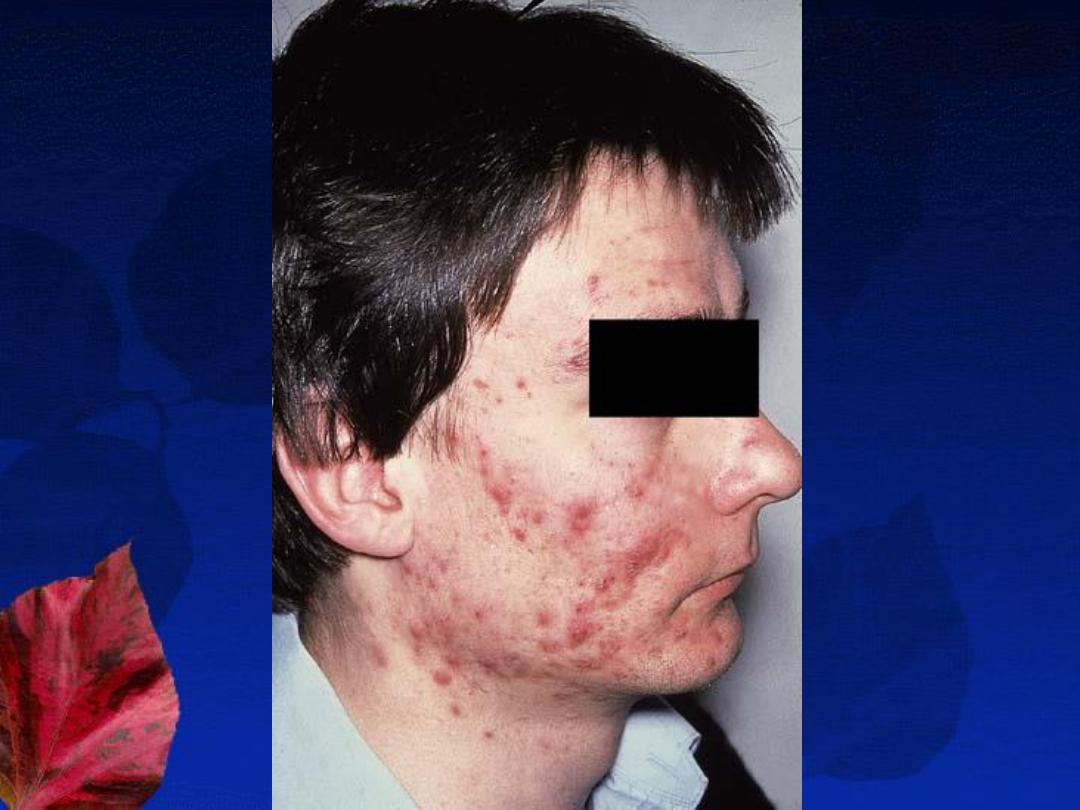
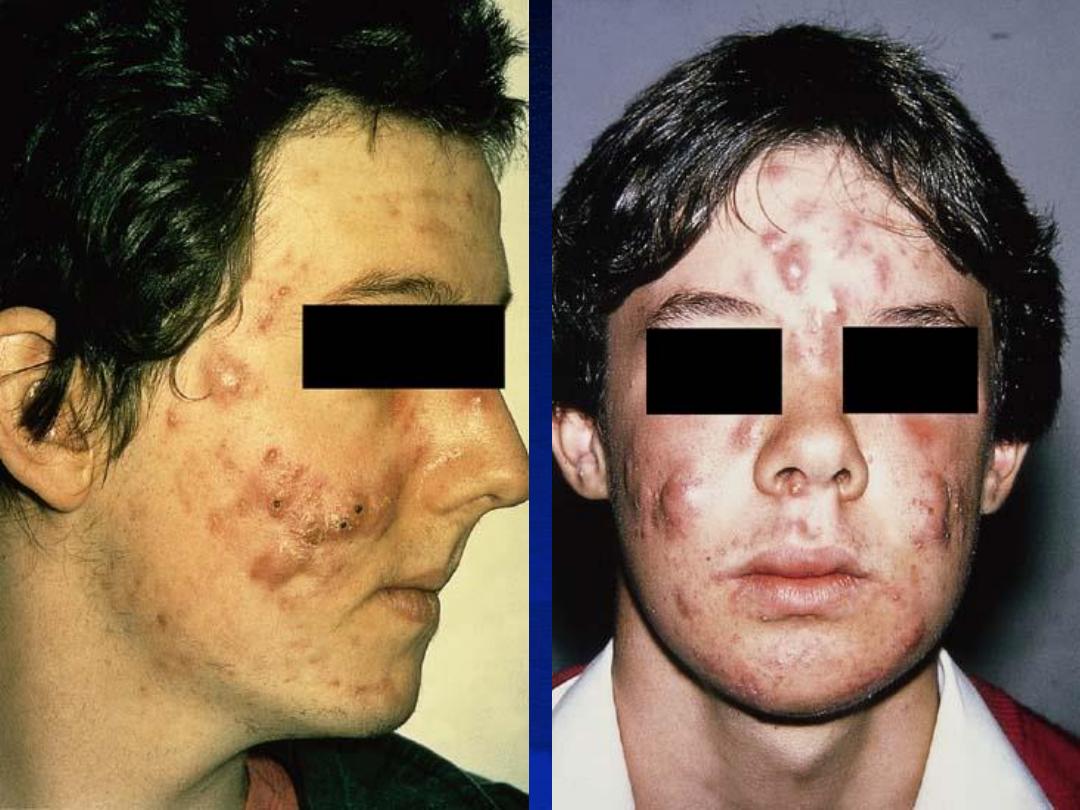

Acne Variants:
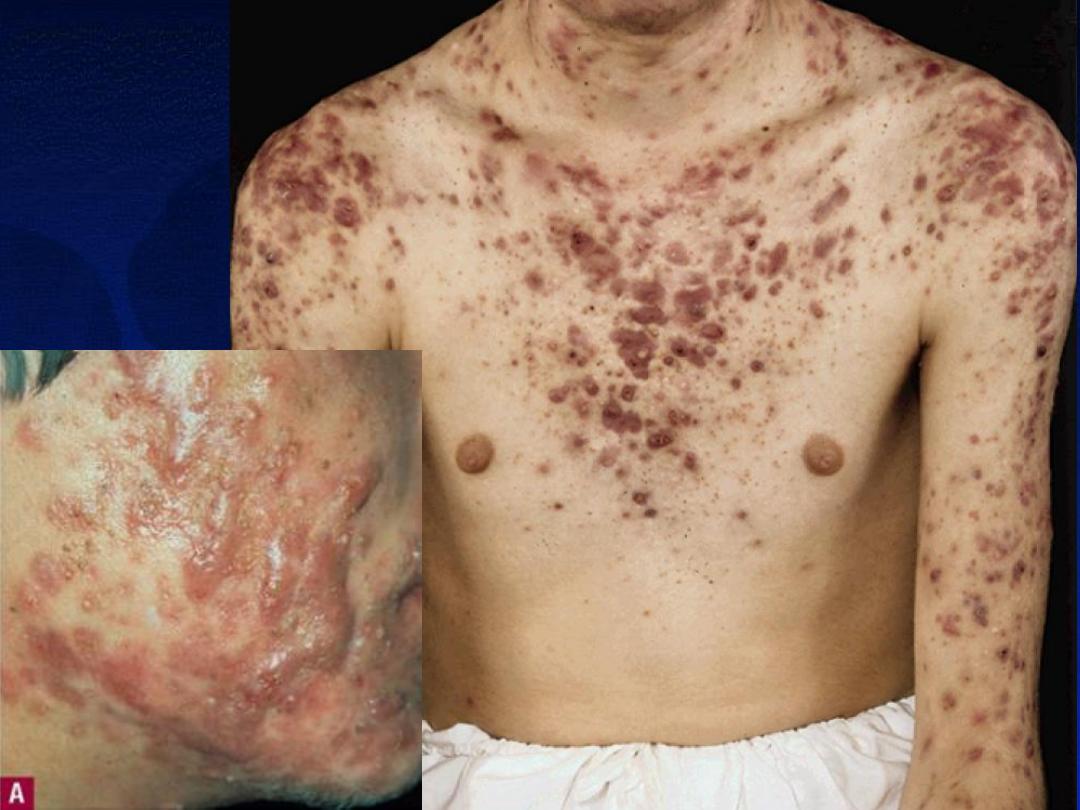
1-Conglobate
2-Fulminans
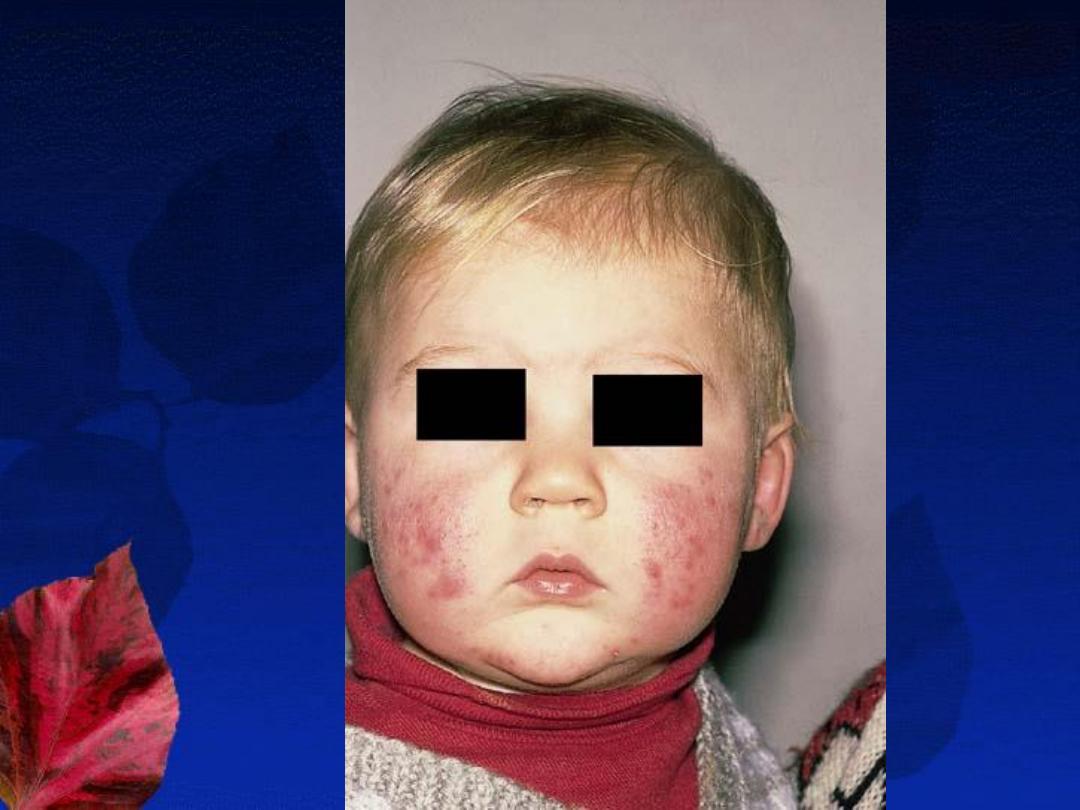
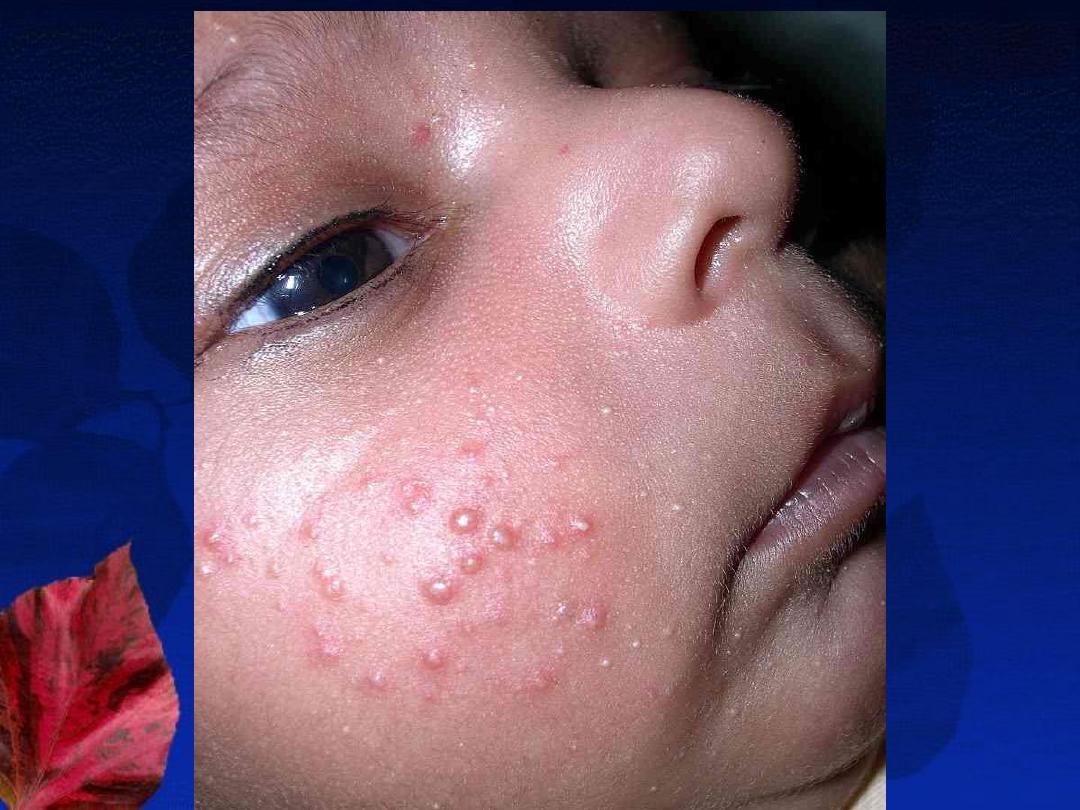
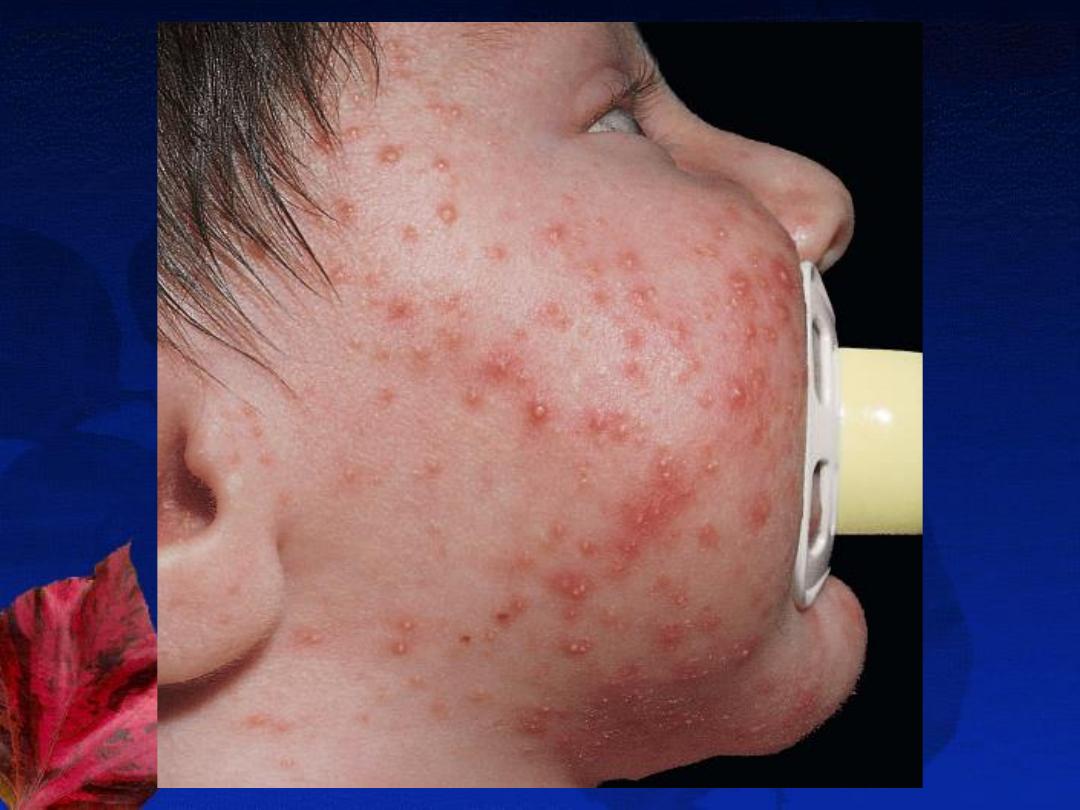
3-Infantile
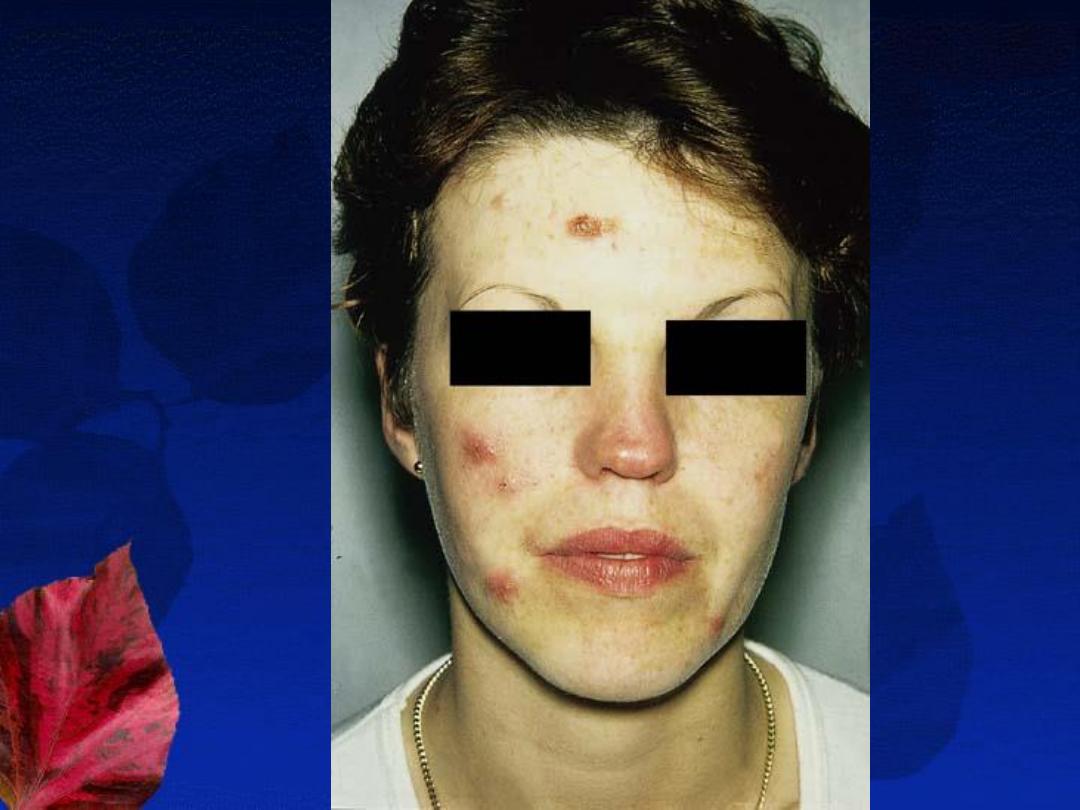
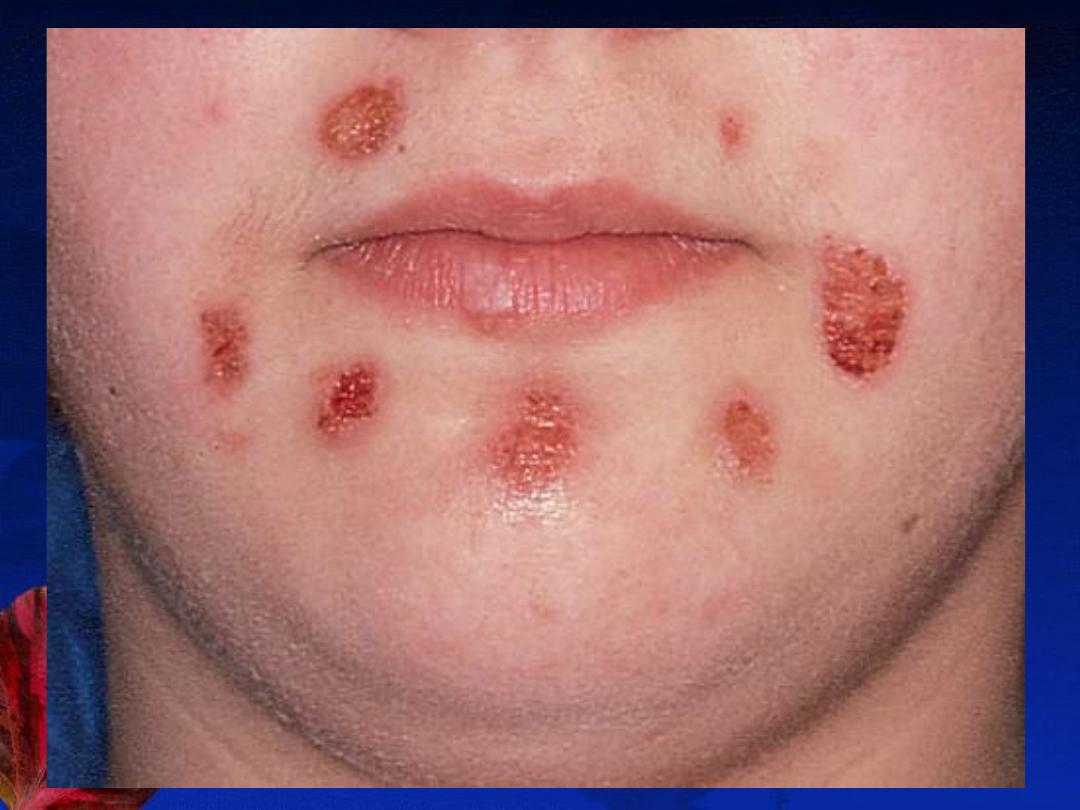
4-Excoriated
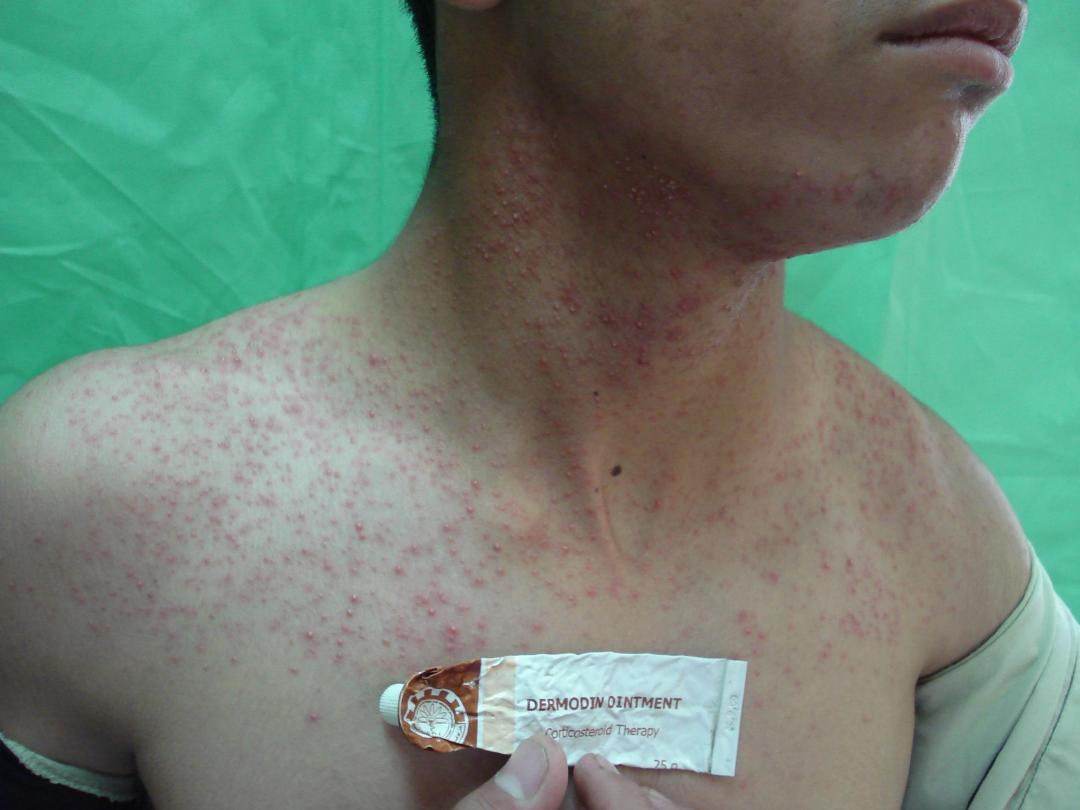
5-Drug-induced
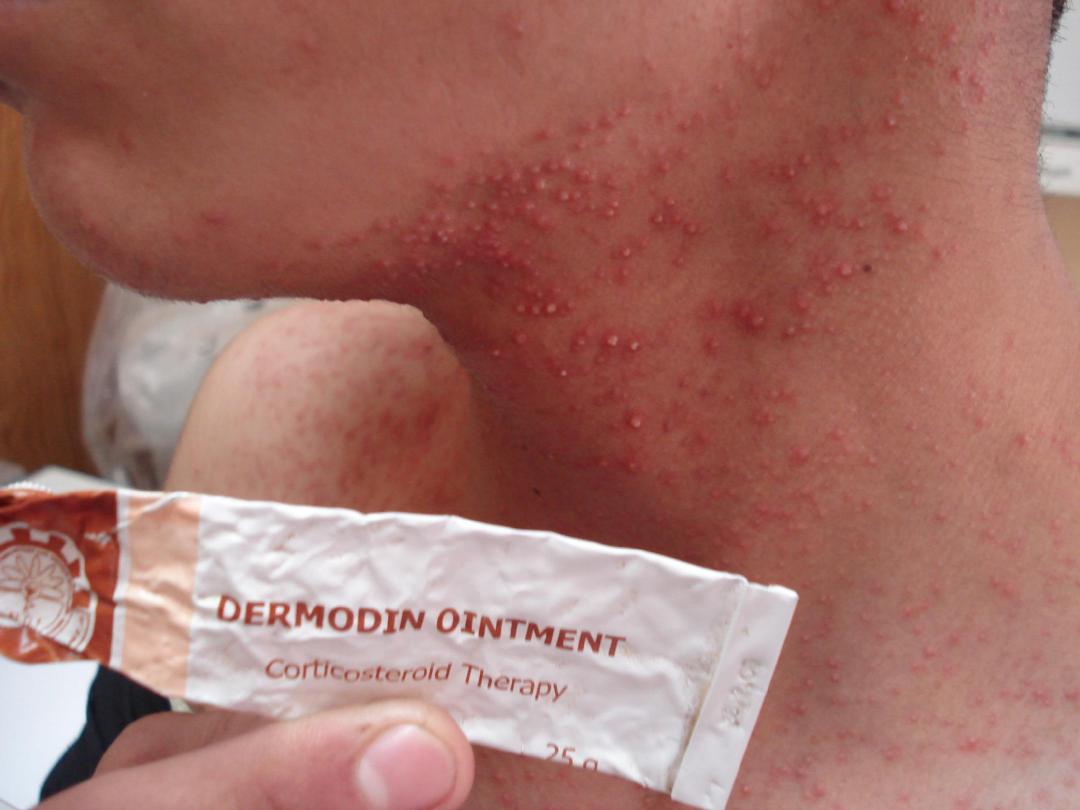
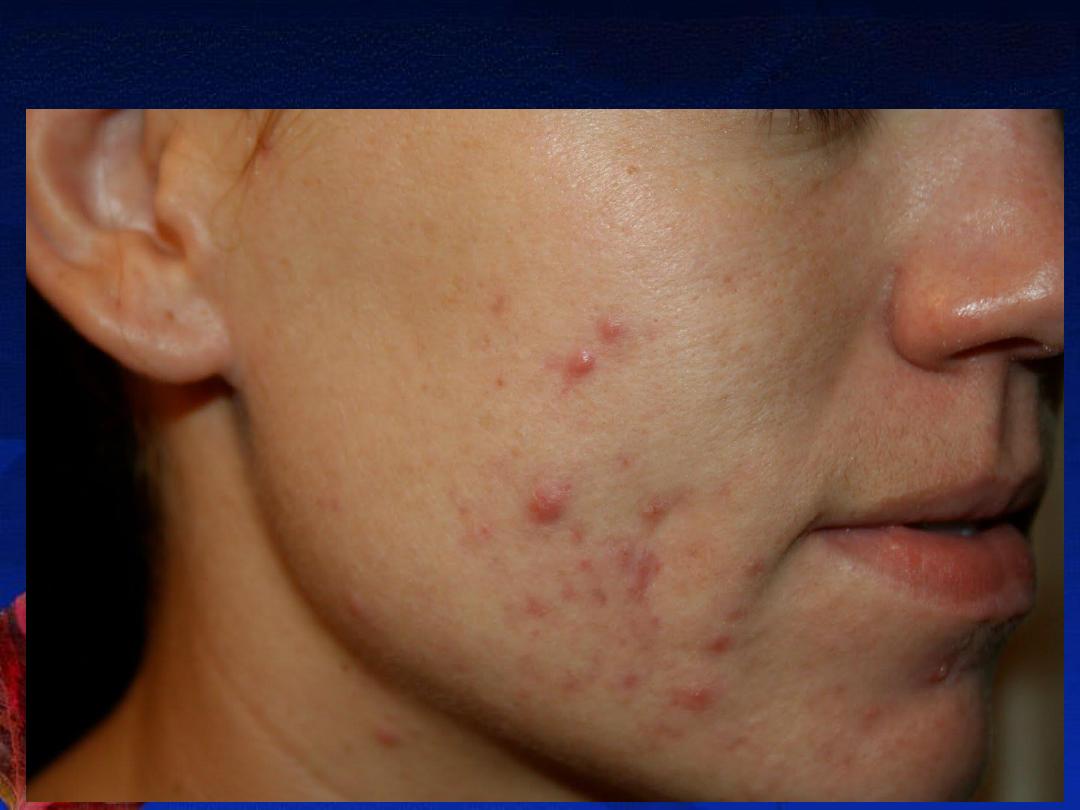
6-Late onset acne
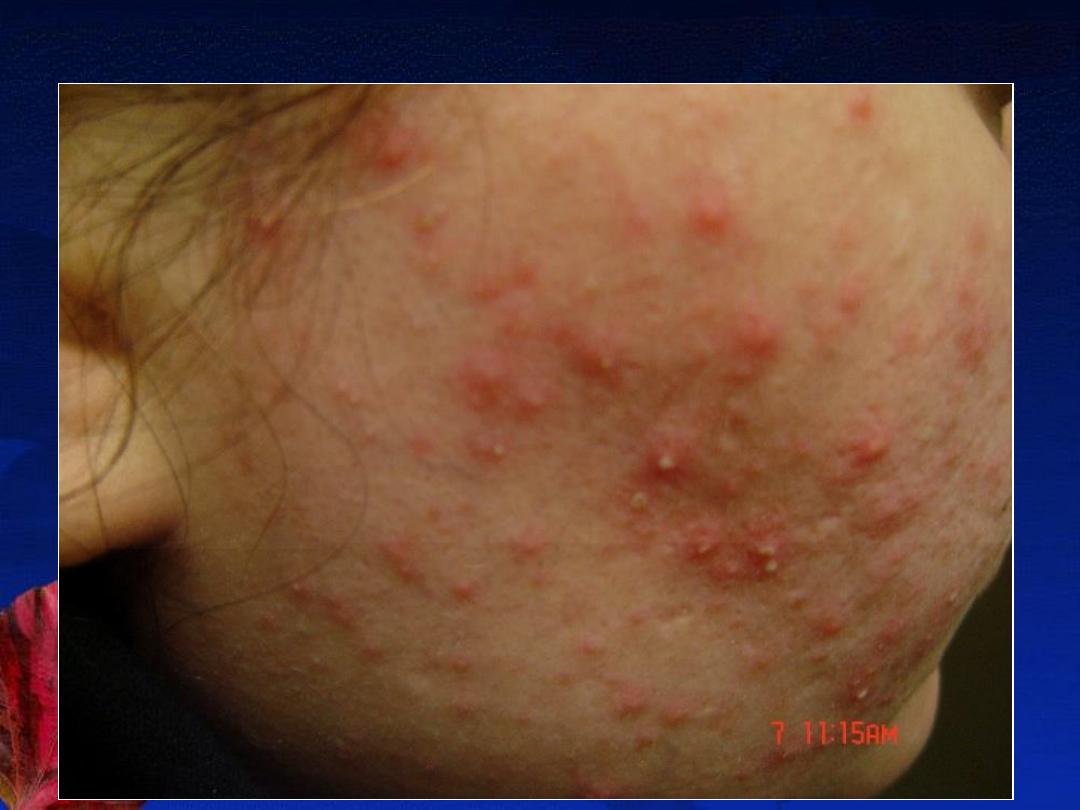
7-Post epilation acne

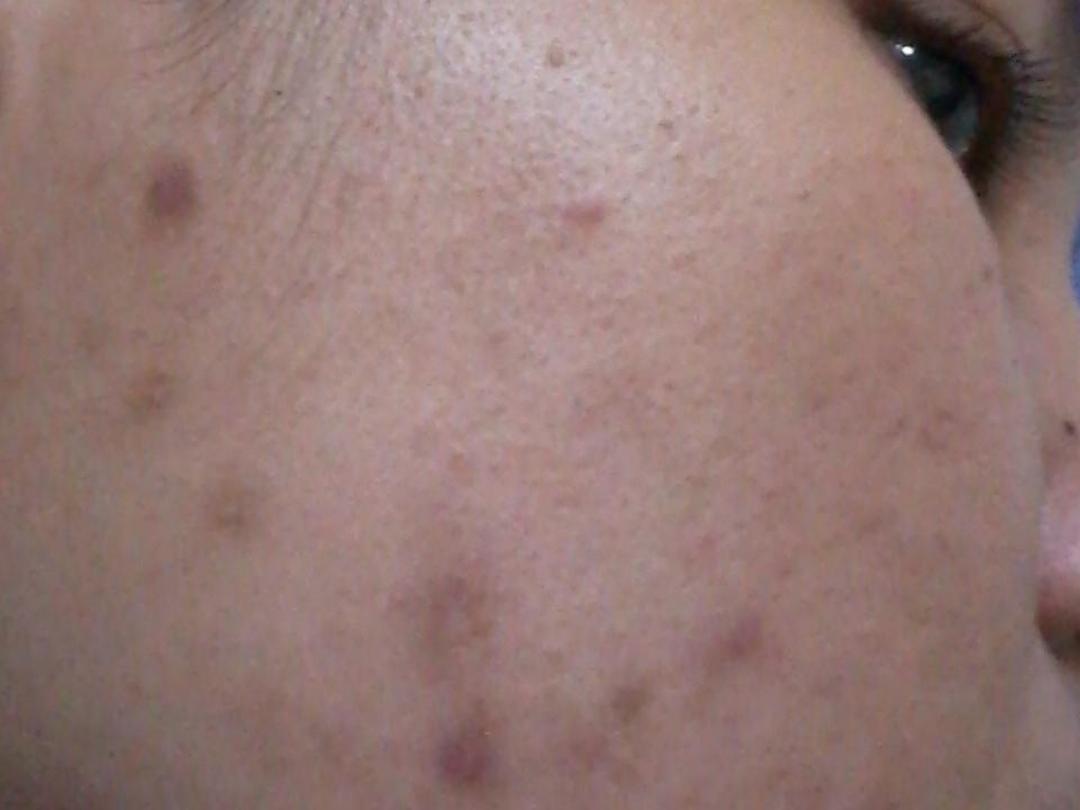
Complications:
1-Psychological disturbances &
depression
.
2-Transient macular
erythema
.
3-Post inflammatory
hyperpigmentation
.
4-Permanent
scarring
.
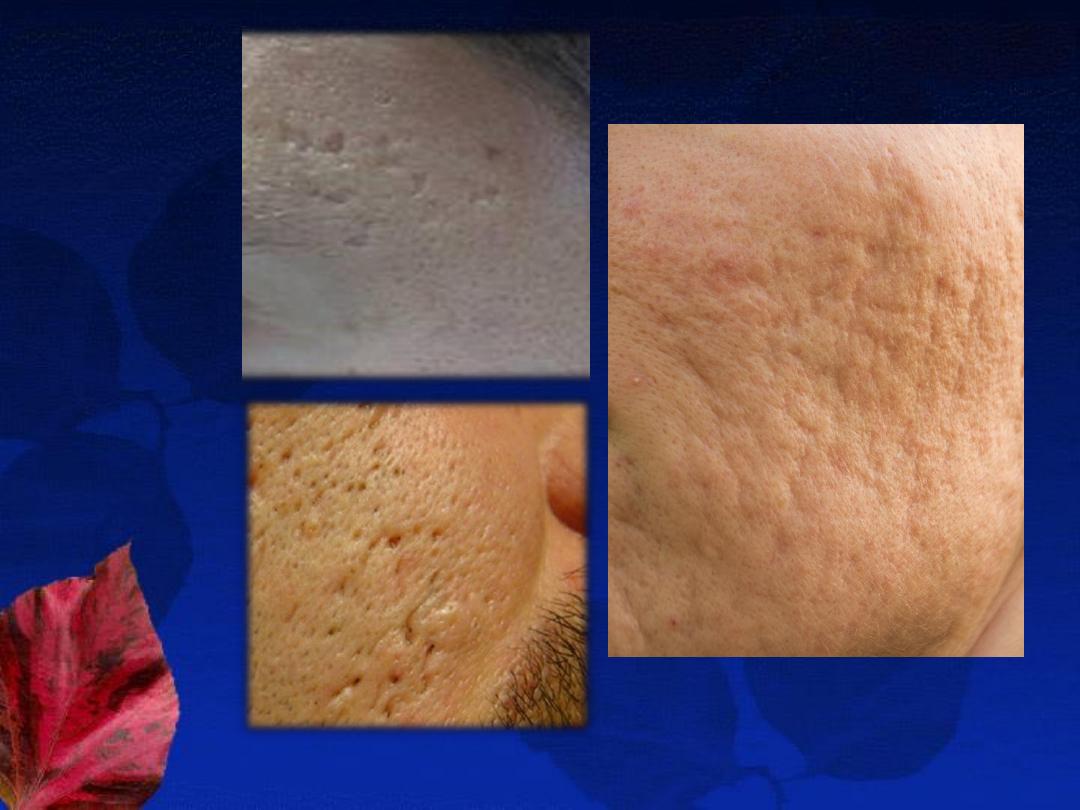
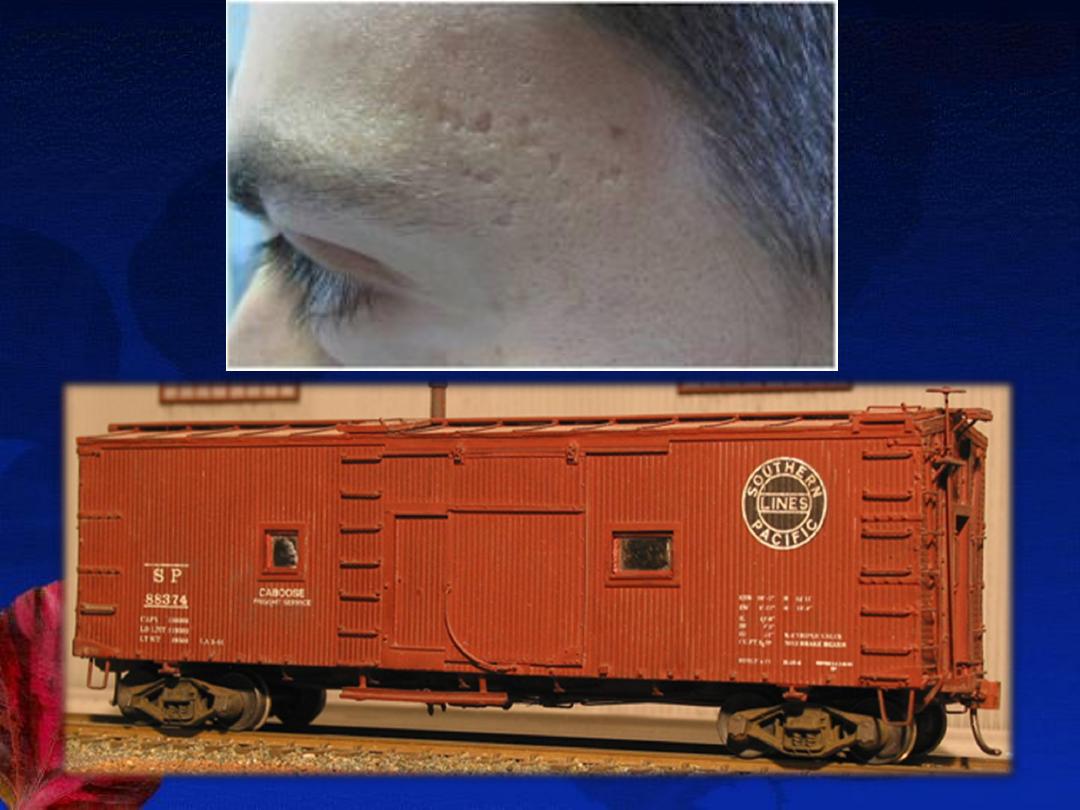

Treatment

A-General measures:
1-
Psychological support
.
2-
Underlying cause
should be
removed or treated.
3- Determine the
predominant lesions
(comedonal or inflammatory).
4- Determine the
severity
.

B-Topical treatment:
1
-Regular gentle cleansing.
2
-Benzoyl peroxide.
Benoxide
gel
3
-Local antibiotics
.
4
-
Retinoids: tretinoin, isotretinoin, & adapalene.
5
-Azelaic acid.
6-
Others: as Sulphur, zinc sulphate & AHA.
7
-Combinations.

C-Systemic treatment
1-Antibiotics
(3months)
I
-Tetracyclines
Tetracycline
Doxycycline
Minocycline
II
-Erythromycin
III
-Trimethoprim
IV
-Ampicillin & clindamycin
2-Isotretinoin
(4 months)
3-Hormonal.
4-Others ;dapson
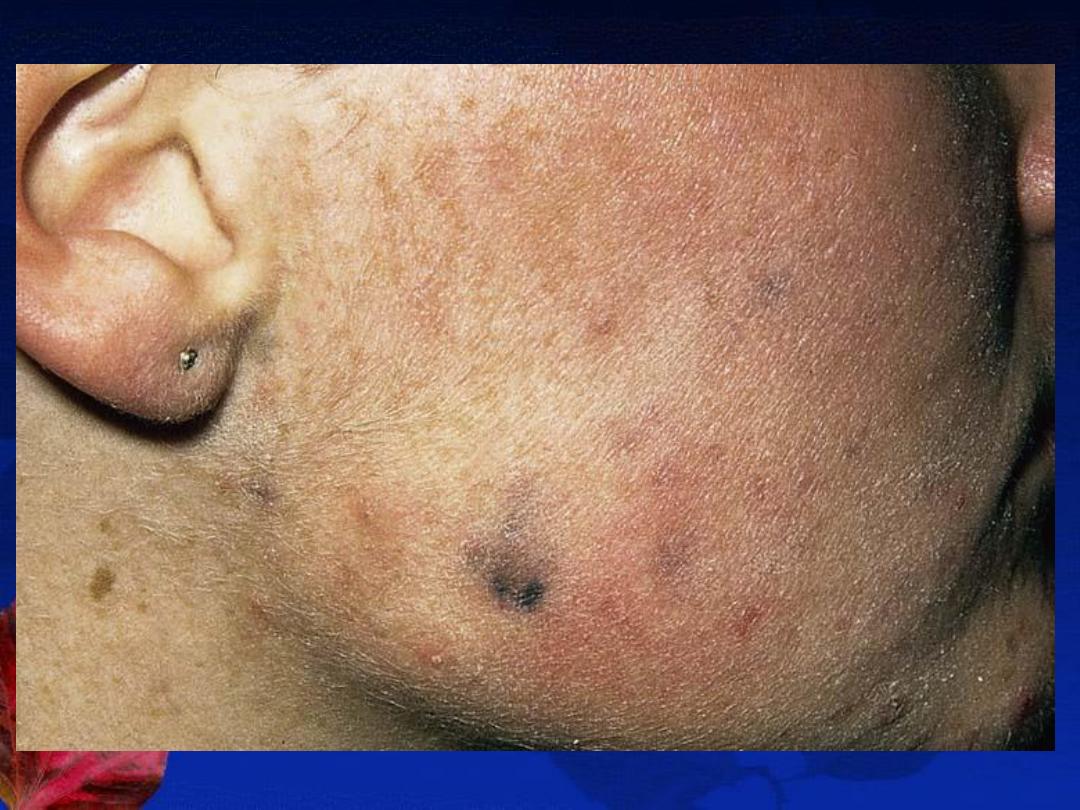

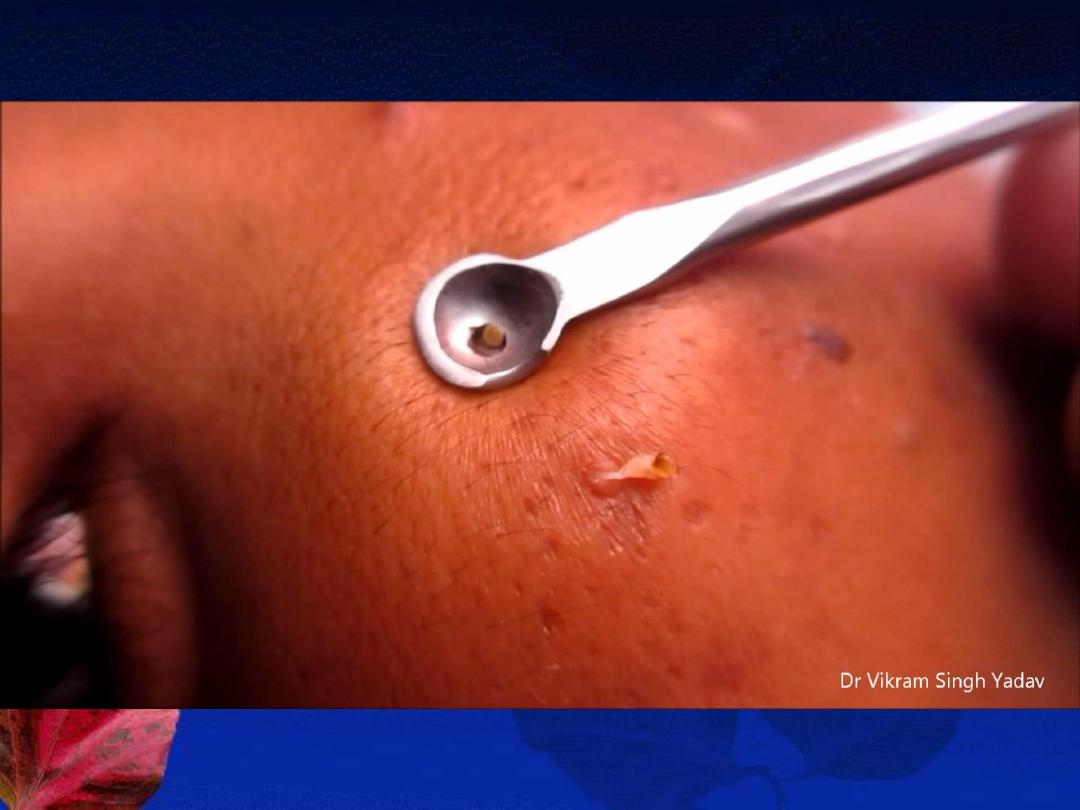
D-Physical treatment:
1- Comedone removal
2- Intralesional injections of steroid
3- Light therapy: lasers and intensive pulse
light (IPL), ultraviolet B radiation, and
photodynamic therapy (PDT).

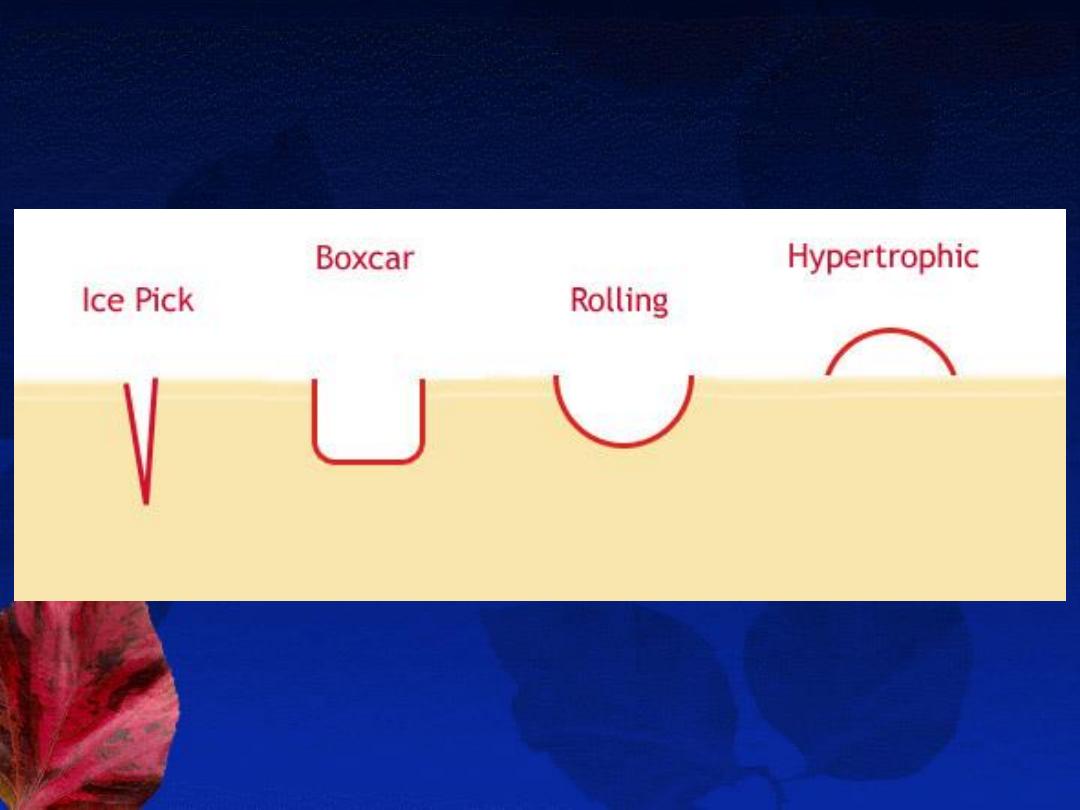
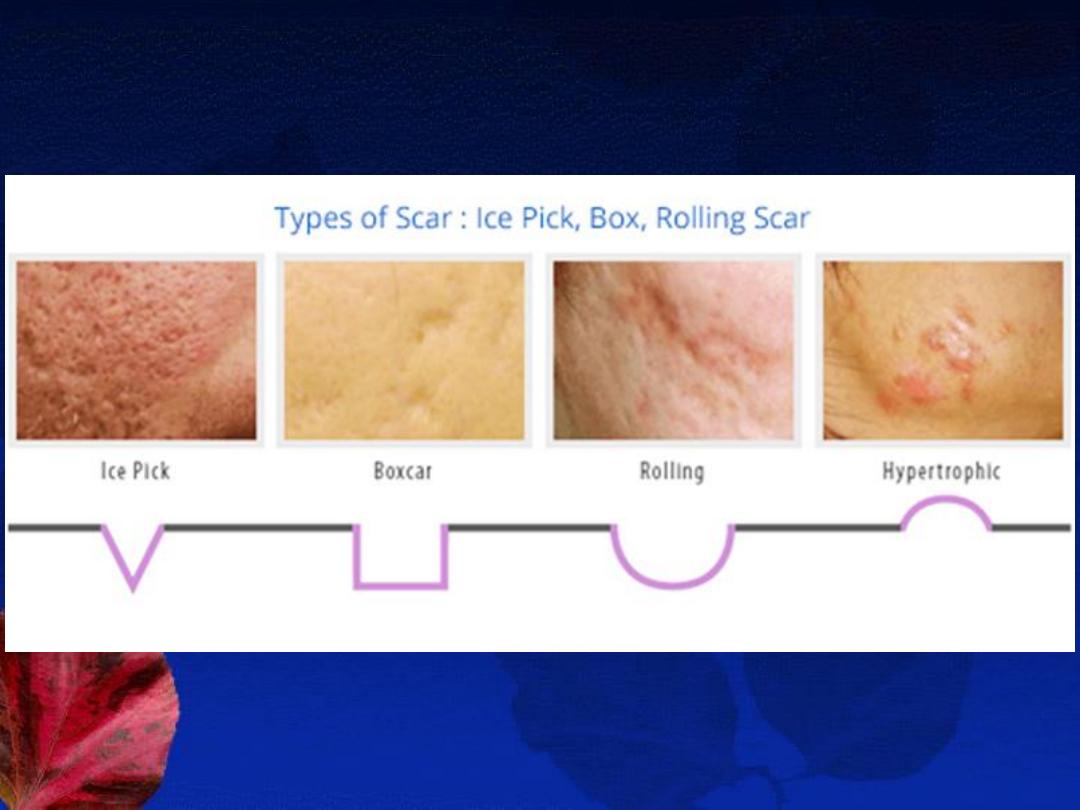
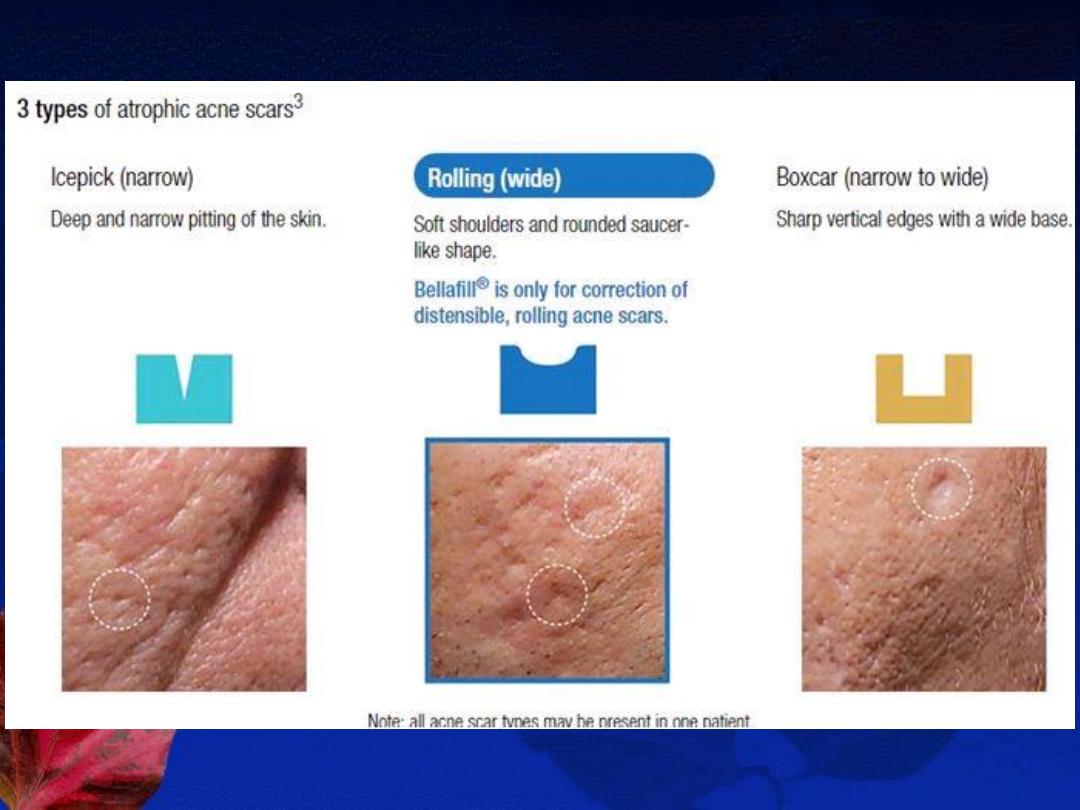
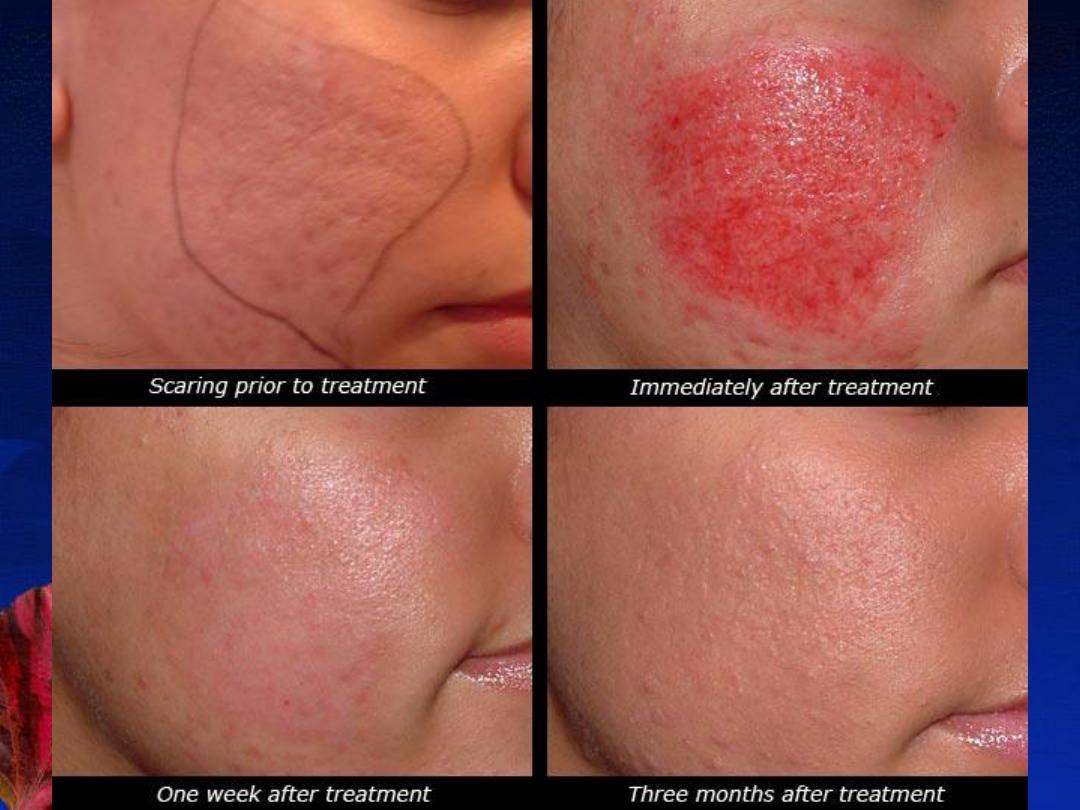
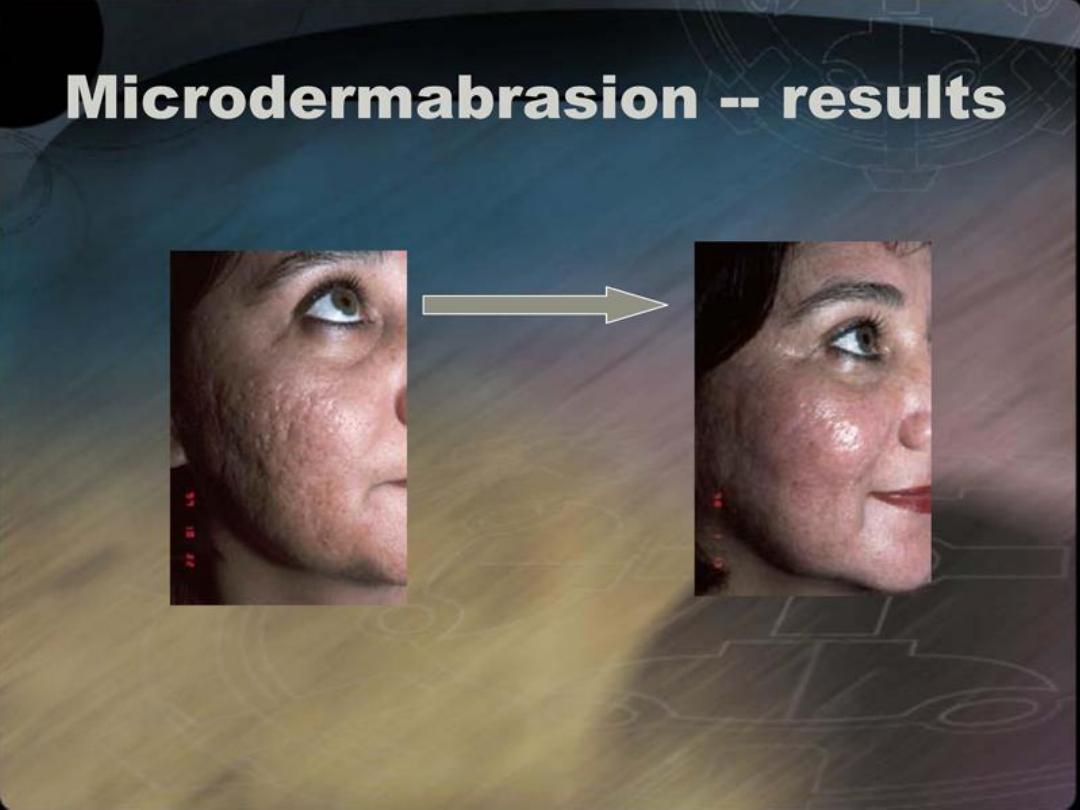
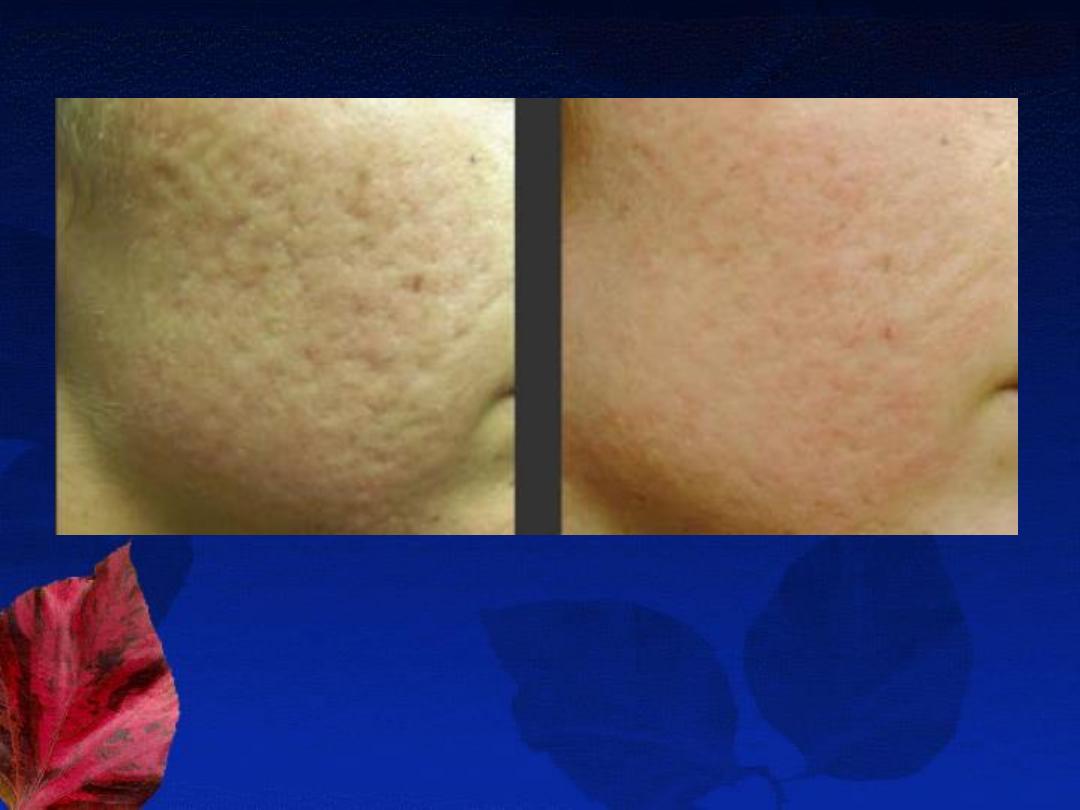
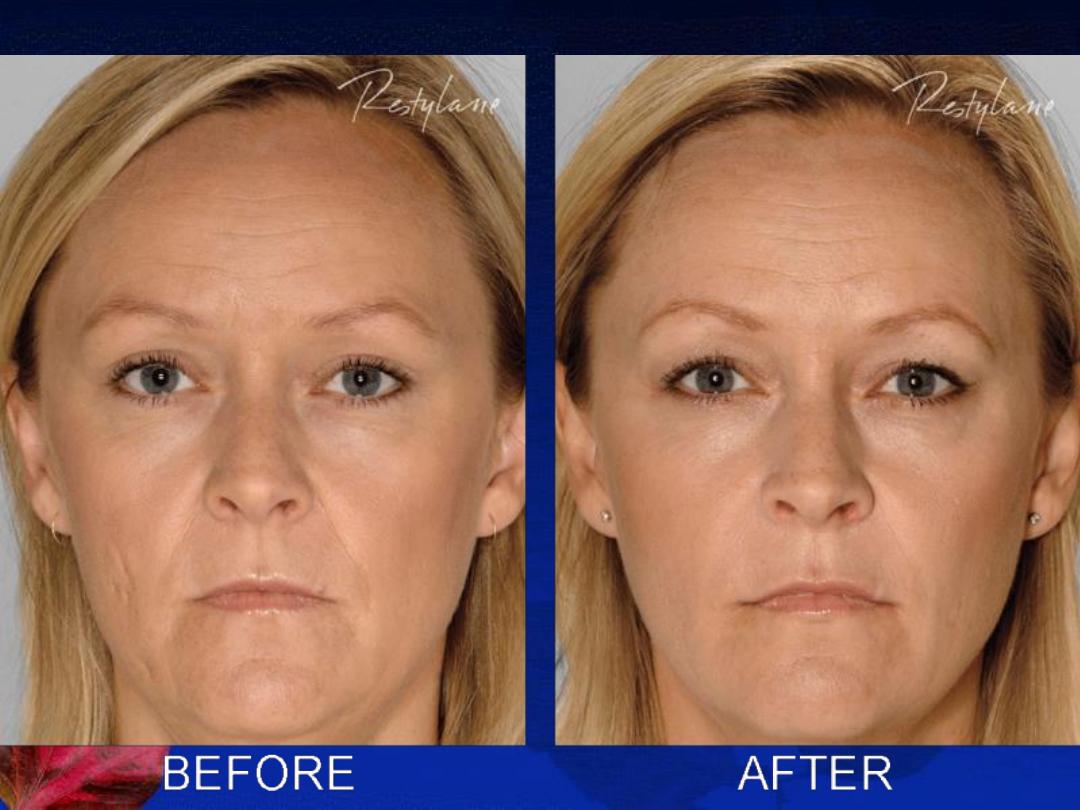
E- Treatment of acne scars:
1- Atrophic scars: (ice pick, rolling, or boxcar scars)
Chemical peels
Dermabrasion
Filler injections
Collagen induction therapy
Laser treatment
2- Hypertrophic scars: (hypertrophic & keloidal scar )
Sillicone ointments
Intralesional steroids
Radiotherapy
Surgery

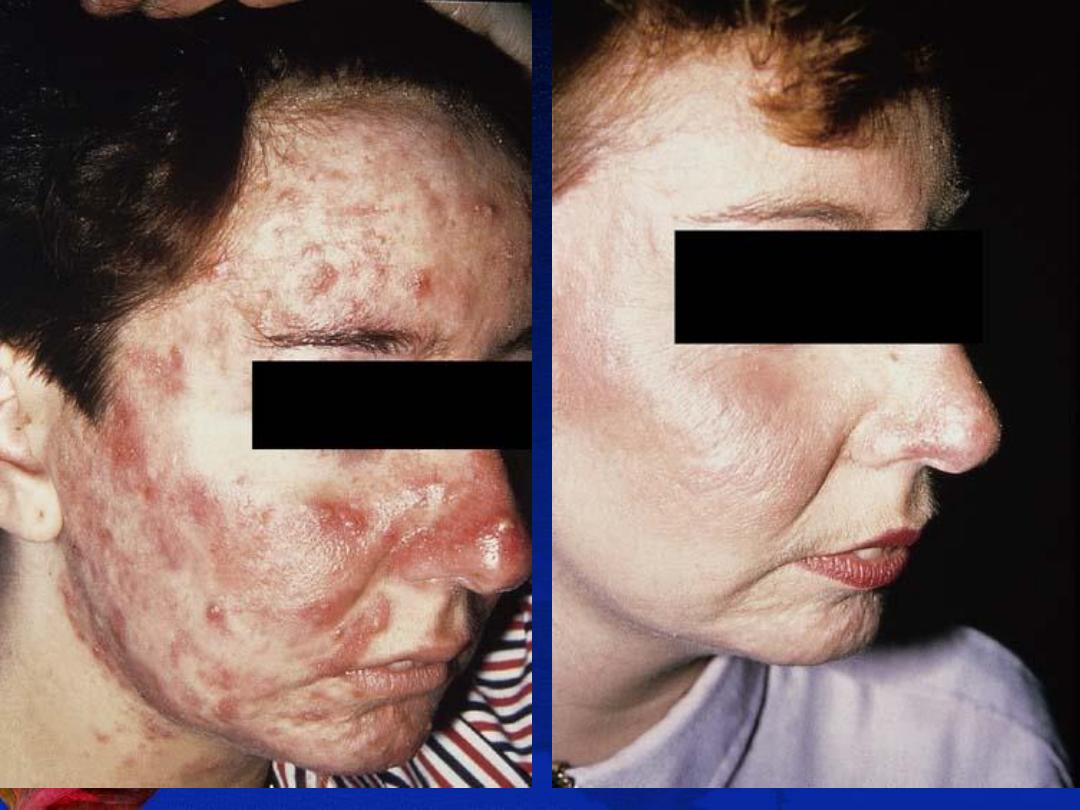
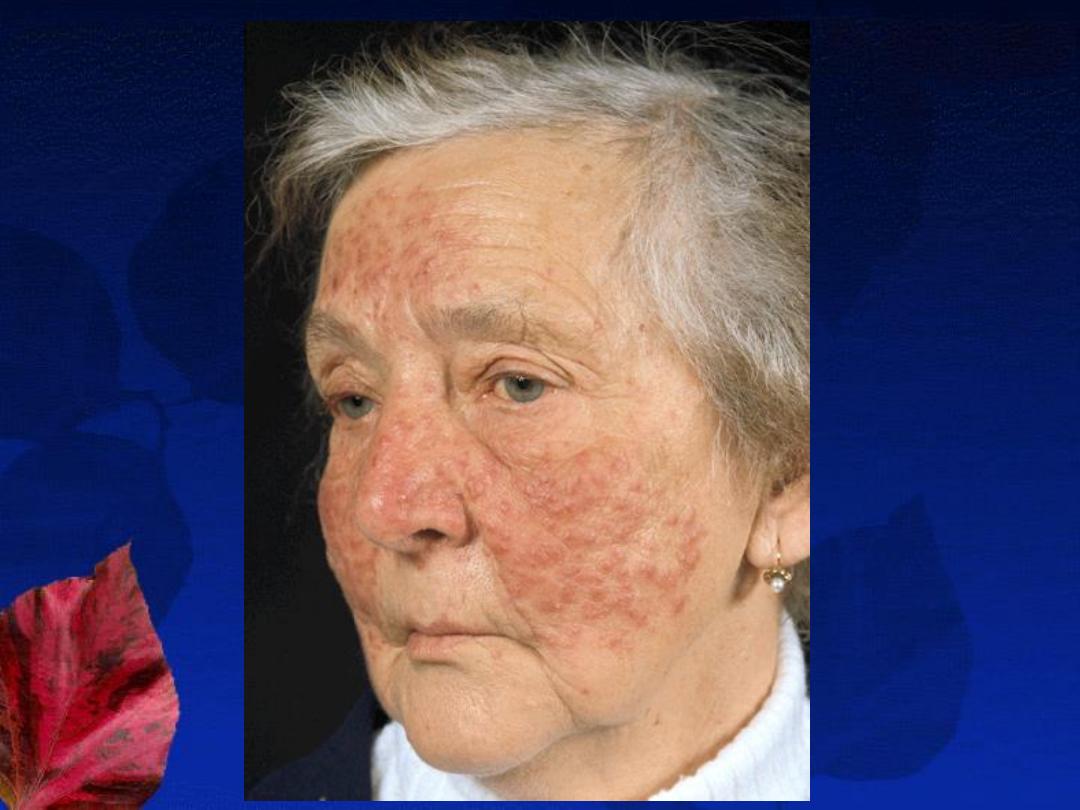
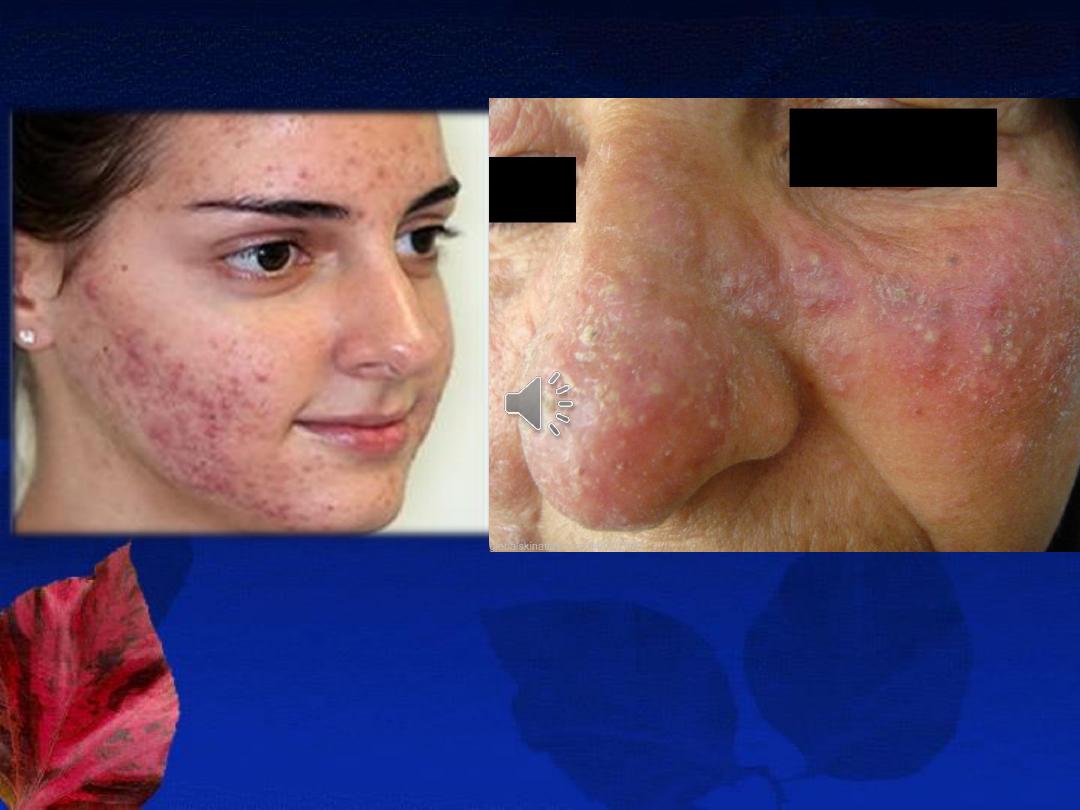
Rosacea

Definition
: is a
chronic inflammatory disorder
involving the skin of the nose, forehead, and
cheeks. (
center of the face
) that is characterized by
congestion, flushing, and telangiectasia
.
Epidemiology
: the vast majority of cases occur in
fair-skinned
individuals. It predominantly affects
middle age women
(30-50 years), however, children,
adolescents, and young adults may develop rosacea.

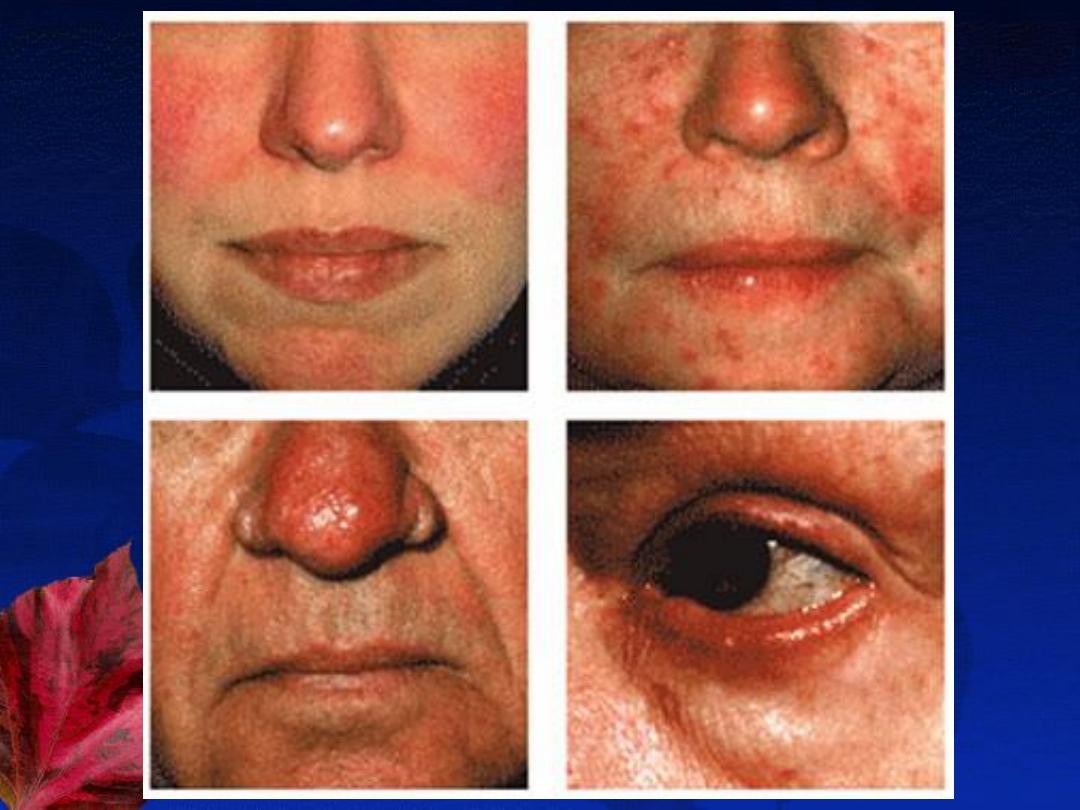
Types and Clinical Features:
1-
Papulopustular
2-
Erythematotelangiectatic
3-
Phymatous
4-
Ocular
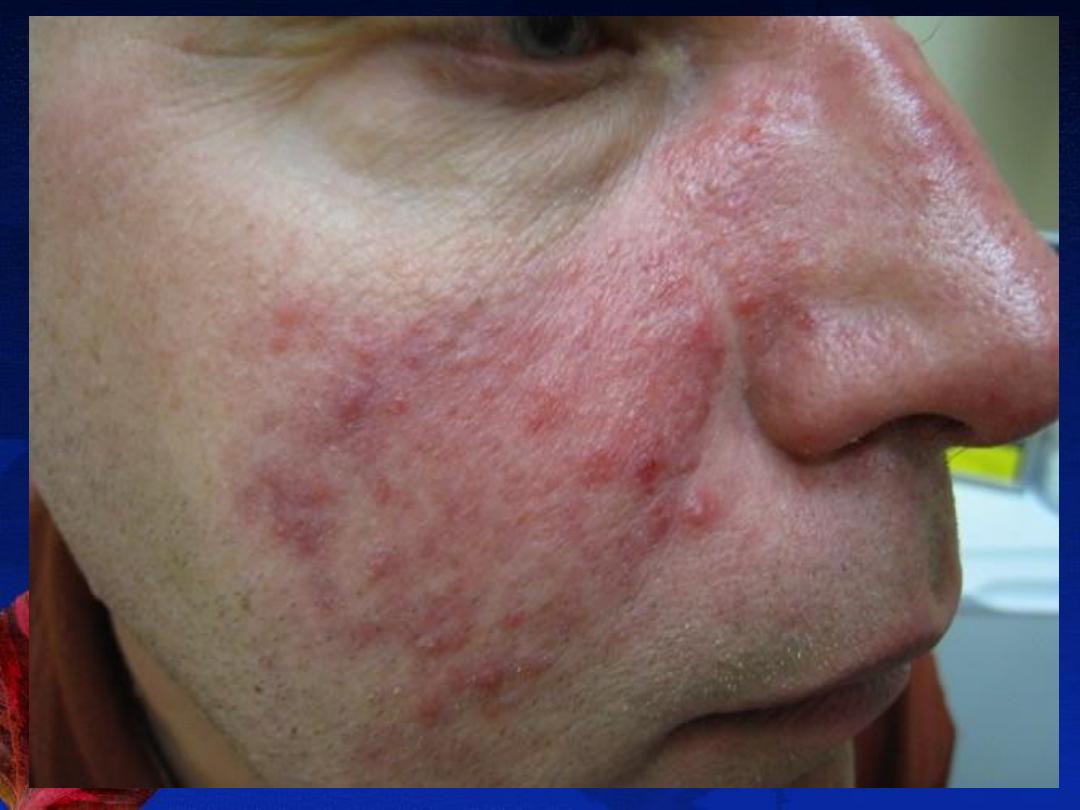
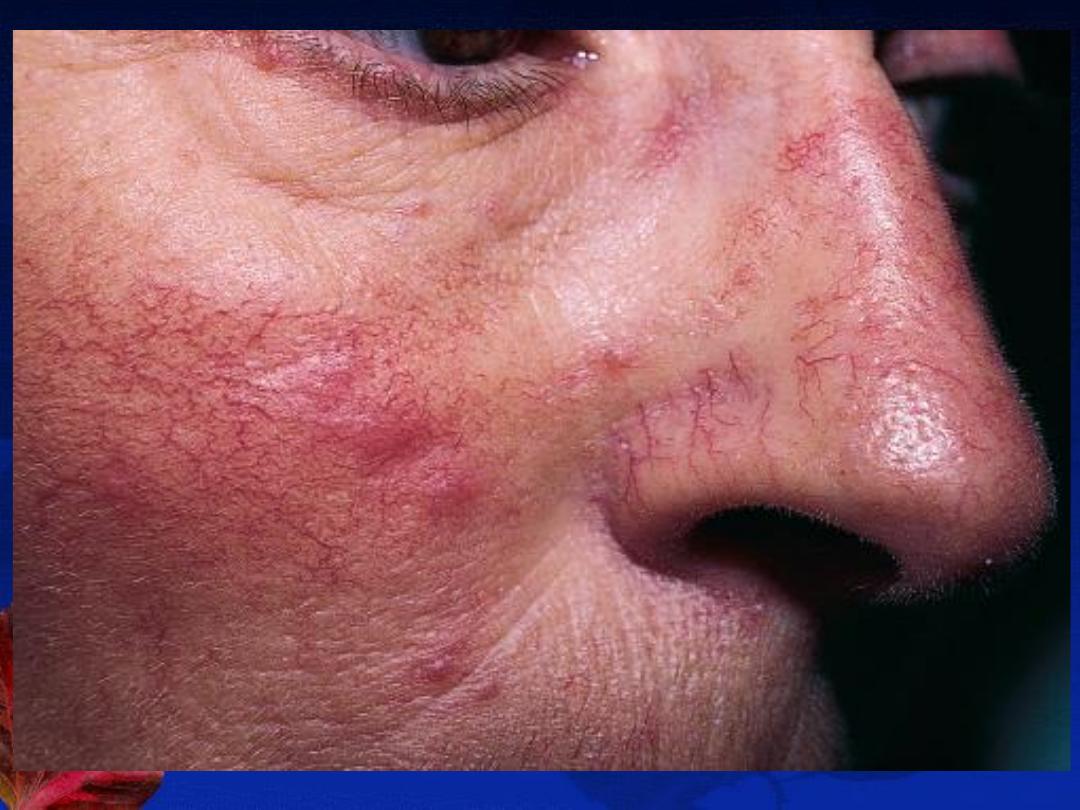
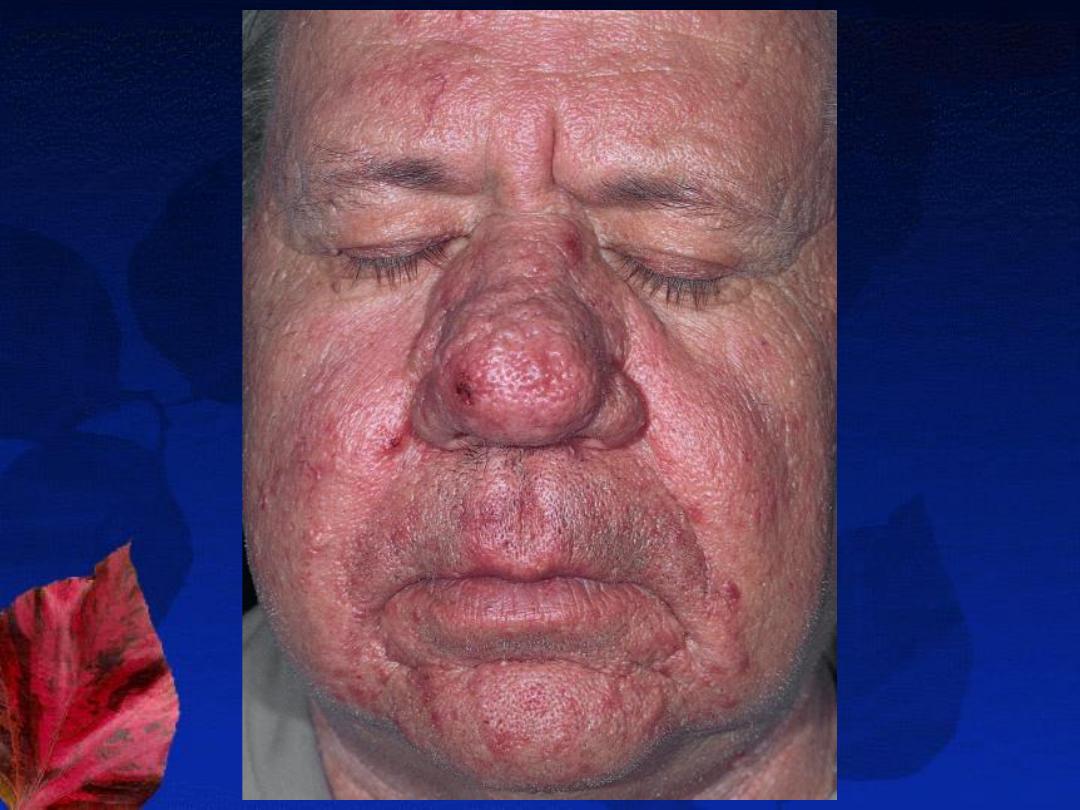
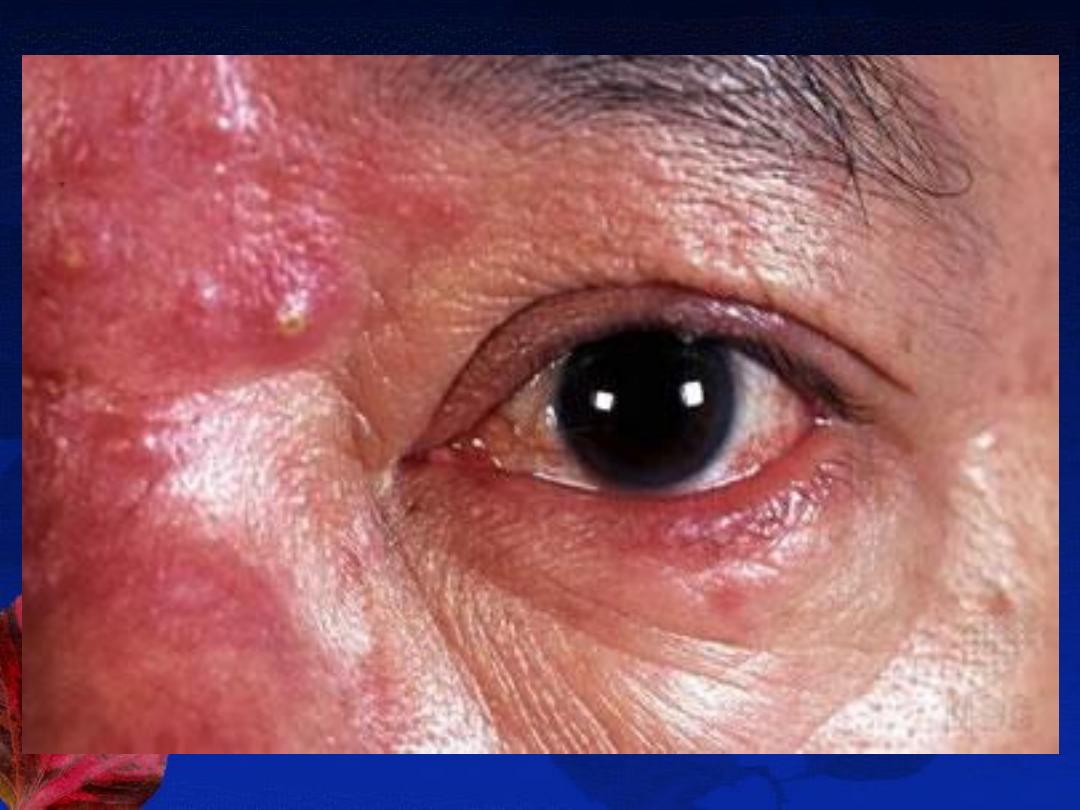

DDX
1- Acne vulgaris
2- SLE
3- photodermatitis
4- flushing
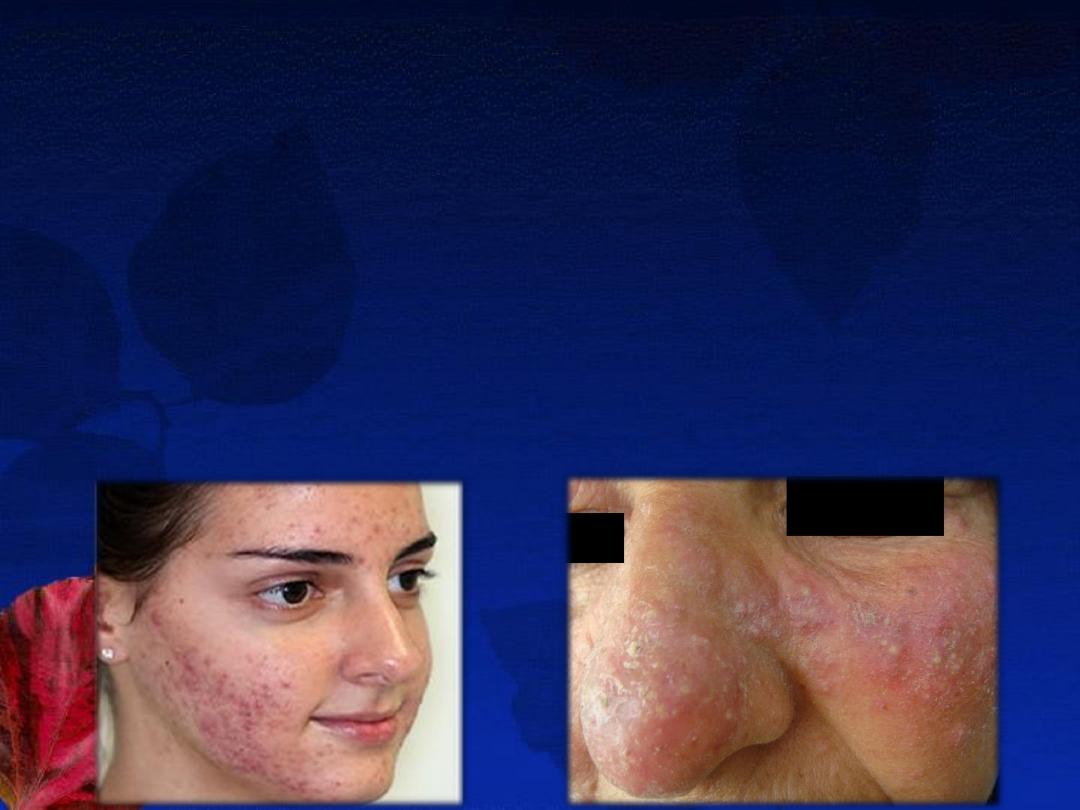
Acne Versus Rosacea
1-
More common
.
2-
adolescence.
3-
Male and female are affected equally.
4-
Affects fair and dark individuals.
5-
All the face can be affected.
6-
Extrafascial are common.
7-
Comedones and scars.

THANK
YOU



