Fifth Stage
Orthopedics
Dr. Haider – Lecture 1
1
Principles of Fracture Management
CONTENT
•
DEFINITION
•
PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
- classification of fractures
- displacement types
- fracture healing
- principles of treatment
•
COMPLICATIONS
DEFINITION
•
A fracture is a break in the structural continuity of bone.
CAUSES OF FRACTURES
1. Sudden trauma
–
Direct : ( Transverse fracture of the tibia caused by a car hit )
–
Indirect : ( spiral fractures of the tibia and fibula due to torsion of the leg,
vertebral compression fractures, avulsion fractures)
2. Stress or fatigue-repetitive stress(athletes, dancers, army recruits)
3. Pathological(osteoporosis, Paget’s disease, bone tumors)
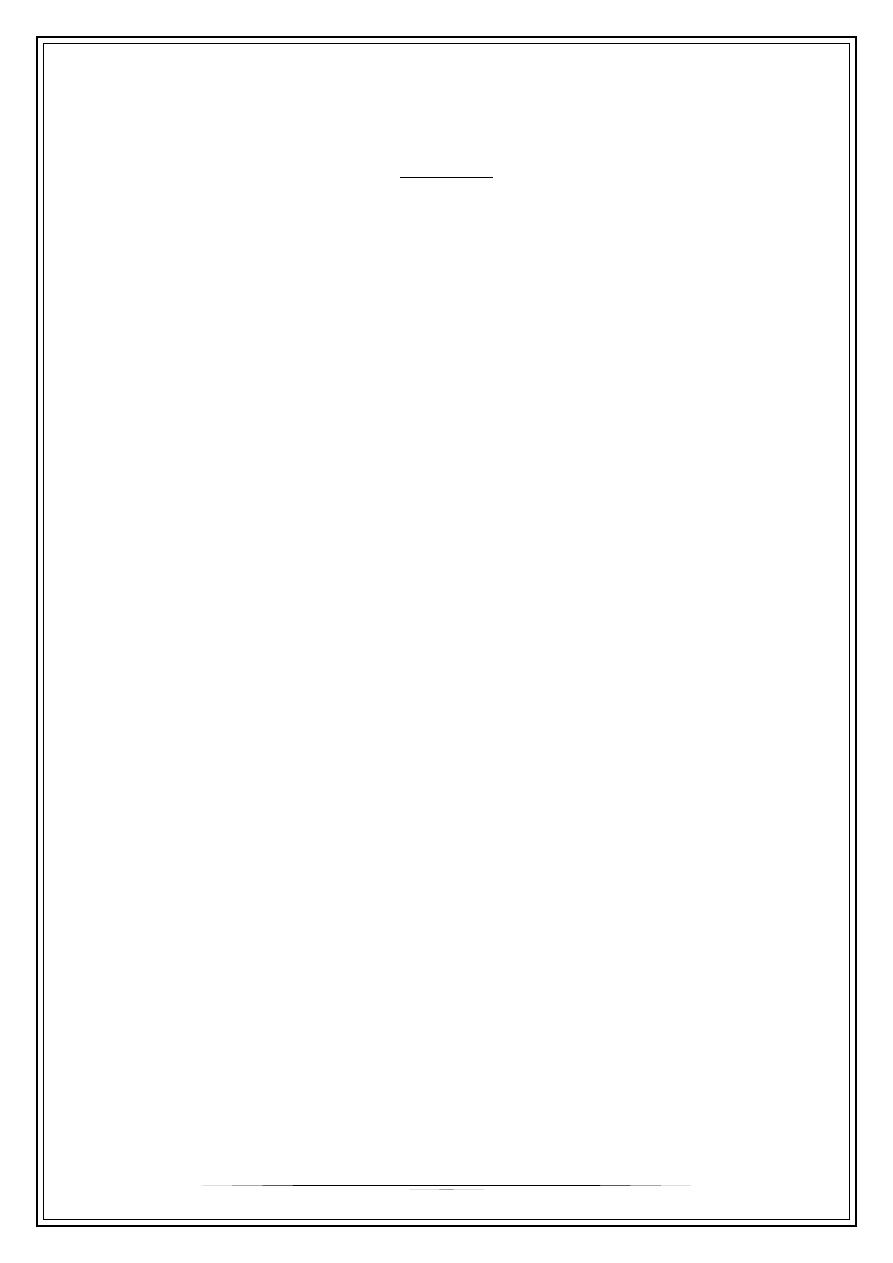
FRACTURE CLASSIFICATION
•
According to presence of a wound
- closed fractures
- open fractures
•
According to completeness
- complete ( subdivided according to the geometry into transverse , oblique ,
spiral , comminuted , segmental )
- incomplete
2
•
According to AO ( usually for academic purposes)
•
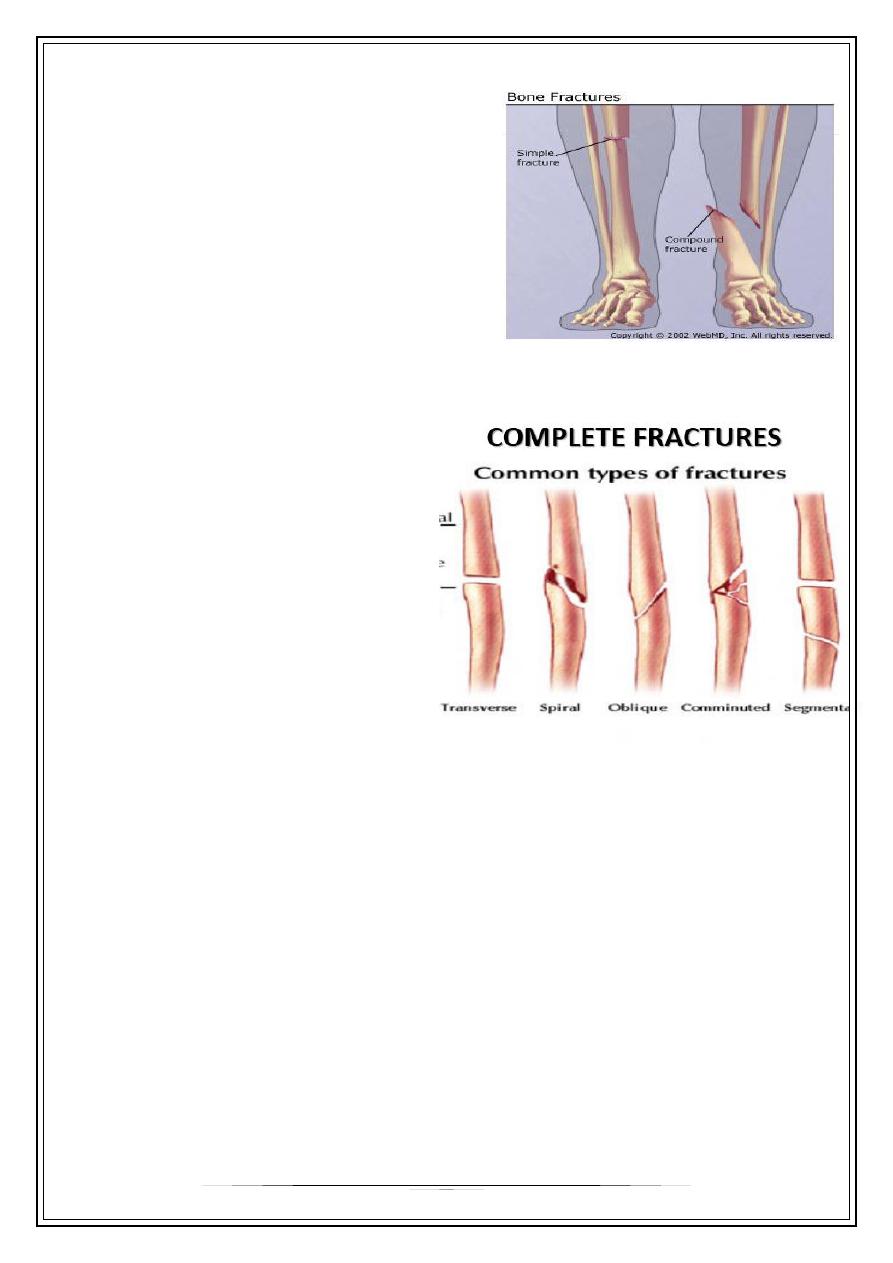
CLOSED/ SIMPLE
•
Fracture with no skin wound.
•
OPEN/ COMPOUND
•
fracture that is communicating
with the exterior
•
COMPLETE
•
bone is completely broken
into 2 or more fragments.
•
-eg:
•
transverse fracture
•
oblique fracture
•
spiral fracture
•
impacted fracture
•
comminuted
fracture
•
segmental fracture
•
INCOMPLETE
•
bone is incompletely divided and the periosteum remains in continuity.
•
-eg:
•
greenstick fracture
•
torus fracture
•
stress fracture
•
compression fracture.
3
FRACTURES DISPLACEMENT
•
Why complete fracture fragments displace :
–
by the force of injury
–
by gravity
–
by the pull of muscles attached to them.
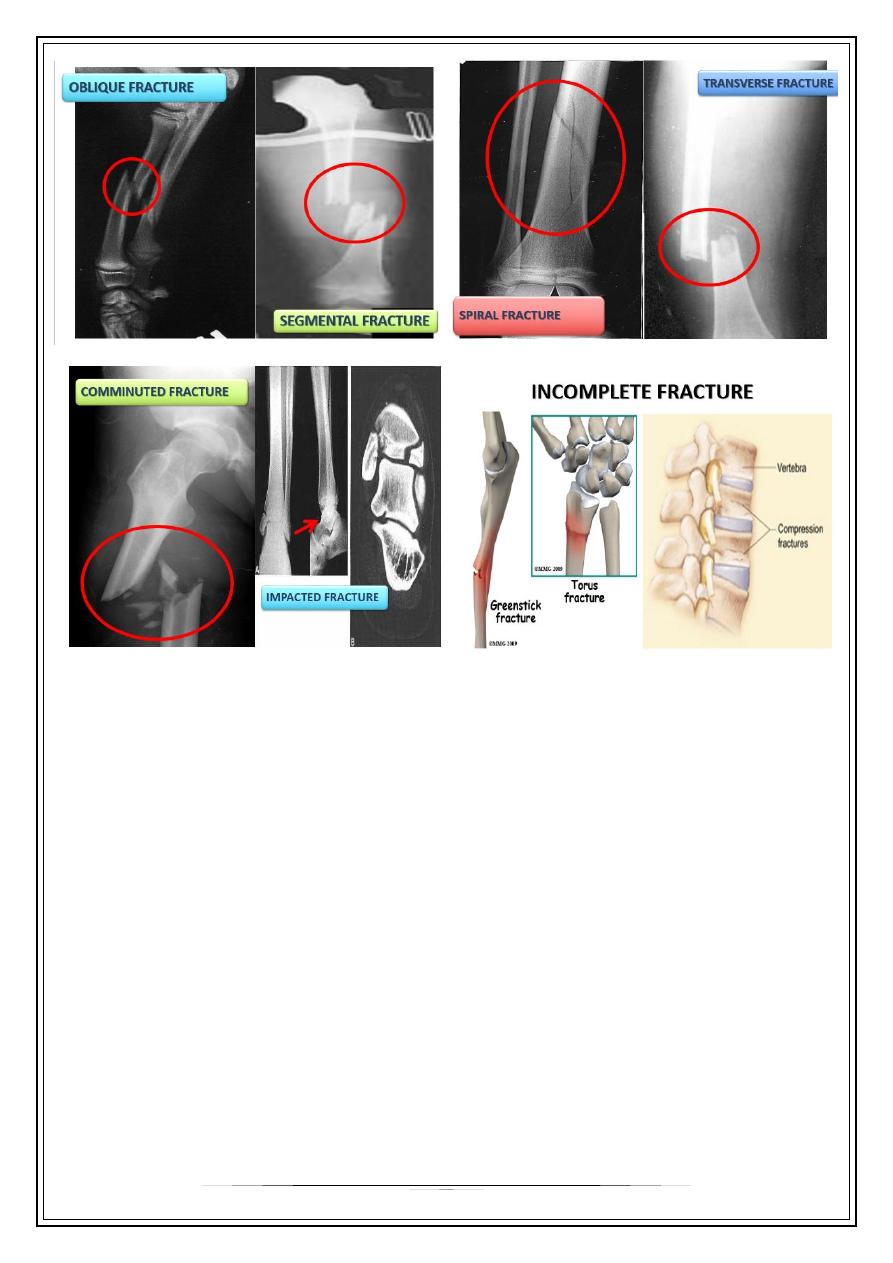
Types of fracture displacement
•
4 types :
–
Translation/Shift
–
Alignment/Angulation
–
Rotation/Twist
–
Altered length ( shortening or distraction )
4
FRACTURE DIAGNOSIS
Clinical assessment
-
Pain
-
Deformity
-
Swelling
-
Impaired function
-
Tenderness
Radiological assessment
1. Plain radiography : ( rule of 2 )
-
2 Views
-
2 joints
-
2 limbs
-
2 occasions
2- CT scan : such as in palvic and spine fractures and in intra articular fracures
3- MRI : to assess the associated injuries ( spine)
4- Bone scan : like in stress fracture
5
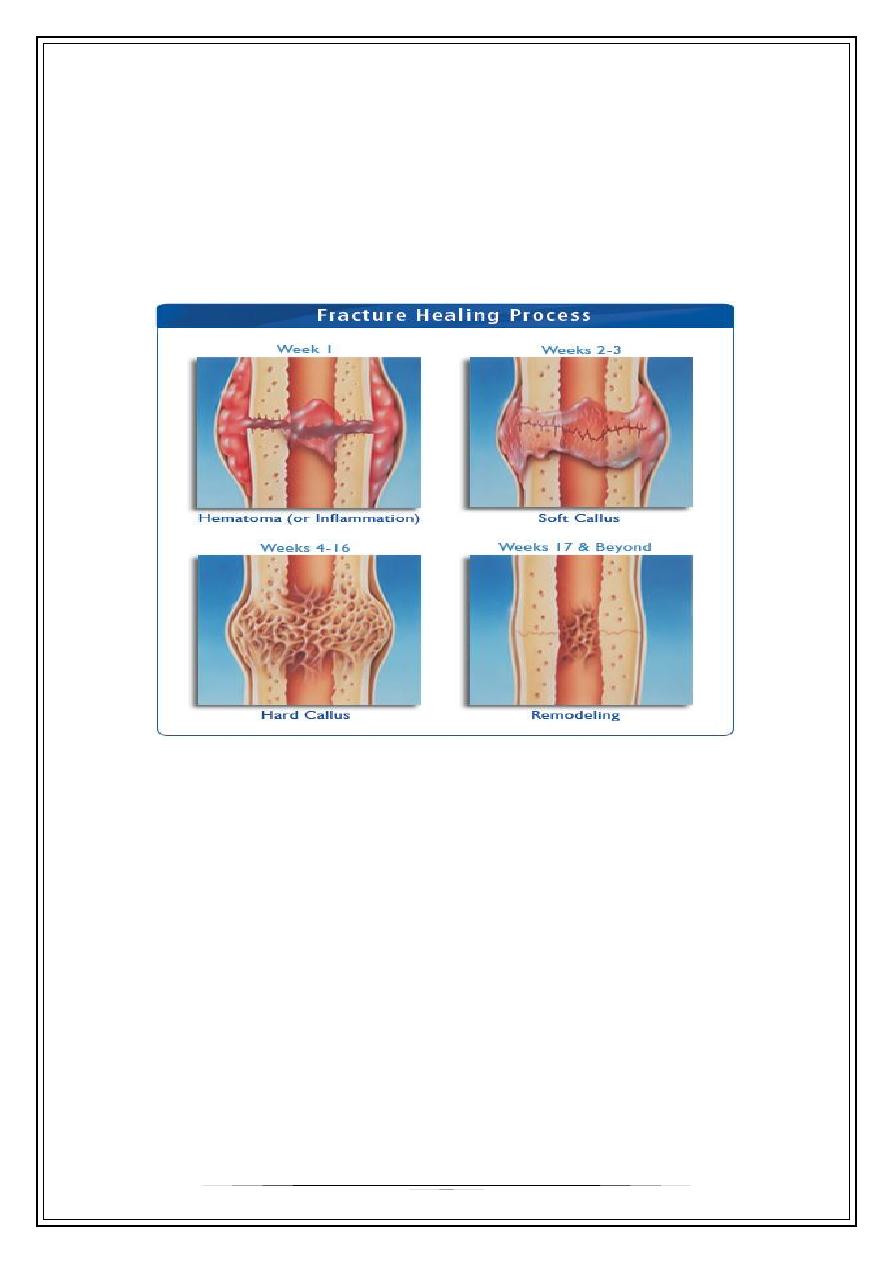
How fracture heals ?
•
Tissue destruction and haematoma formation.
•
Inflammation and cellular proliferation.
•
Callus formation: dead bone is mopped up & woven bone(immature) appears in
fracture callus.
•
Consolidation: woven bone(immature) is replaced by lamellar bone(mature).
•
Remodelling: Newly formed bone is remodelled to resemble the normal structure.
To be continued,,,
