Injuries of the pelvis
Injuries of the pelvis
•Pelvic Fractures account for less than 5% of all skeletal injuries.
• Important : because of serous complication
associated Soft tissue injuries
severe blood oss
Shock
Sepsis
A.R.D.S(adult respiratory distress syndrom)
• About two-third of all Pelvic Fractures occur in road traffic accident.
•10 % will have a visceral injuries with mortality rate is probably 10%.
Structures liable for injury
Pelvis transmits weight from the trunk to the lower limbs and provide
protection for the pelvic viscera, vessels and nerves
: In females the urethra is much more mobile so less
prone to injury .
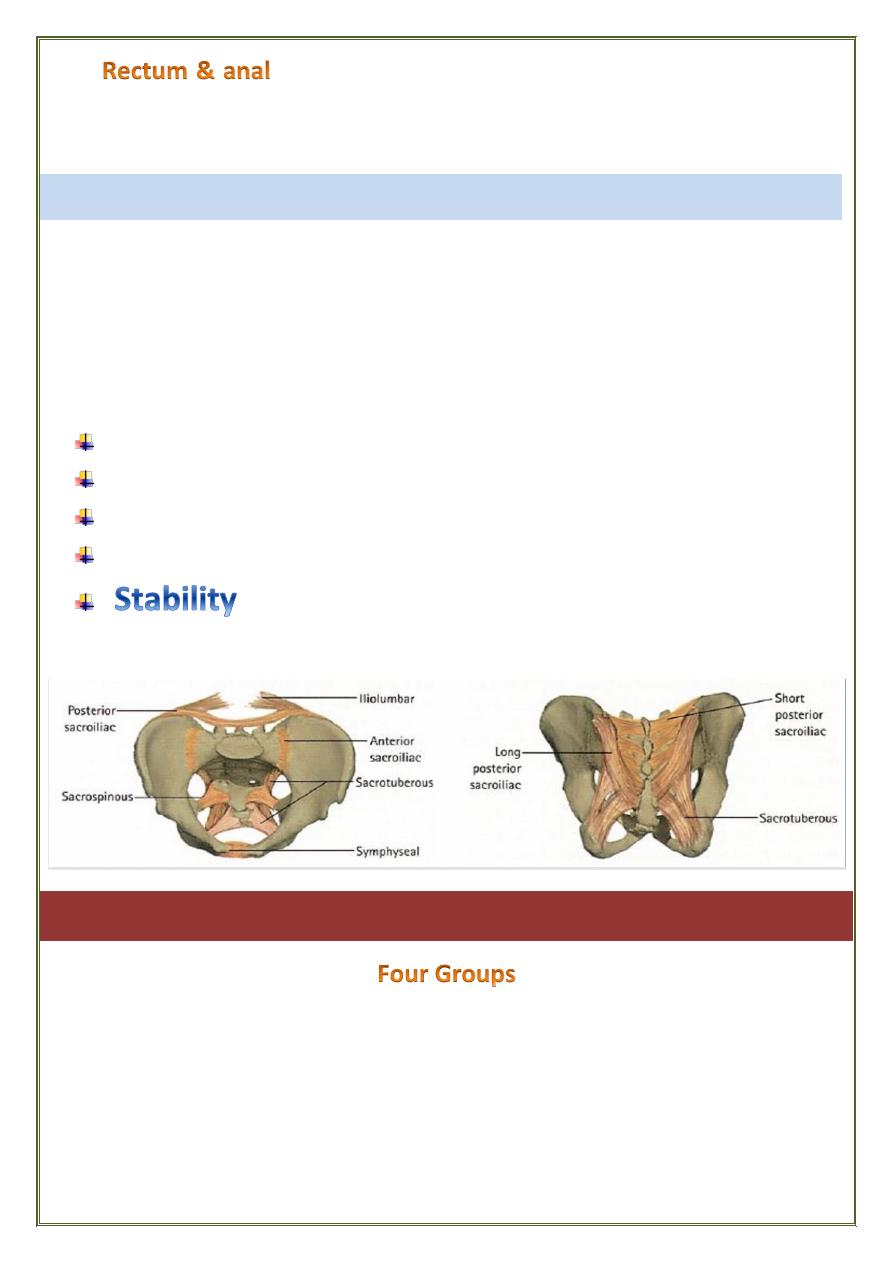
The rectum and anal canal are more firmly tethered, so
vulnerable to injury. The pelvic colon , with its mesentery , is a mobile
structure and so not readily to injury.
Surgical anatomy
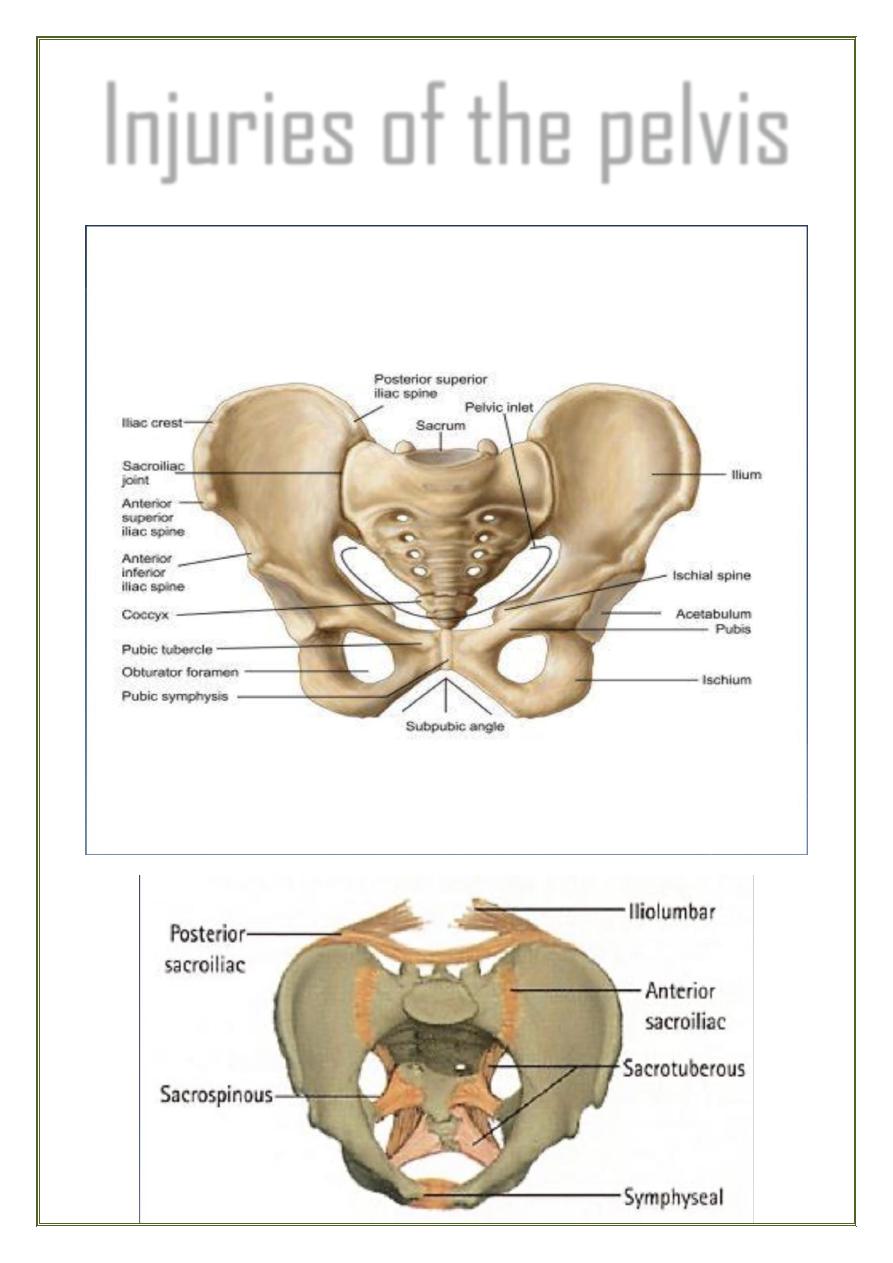
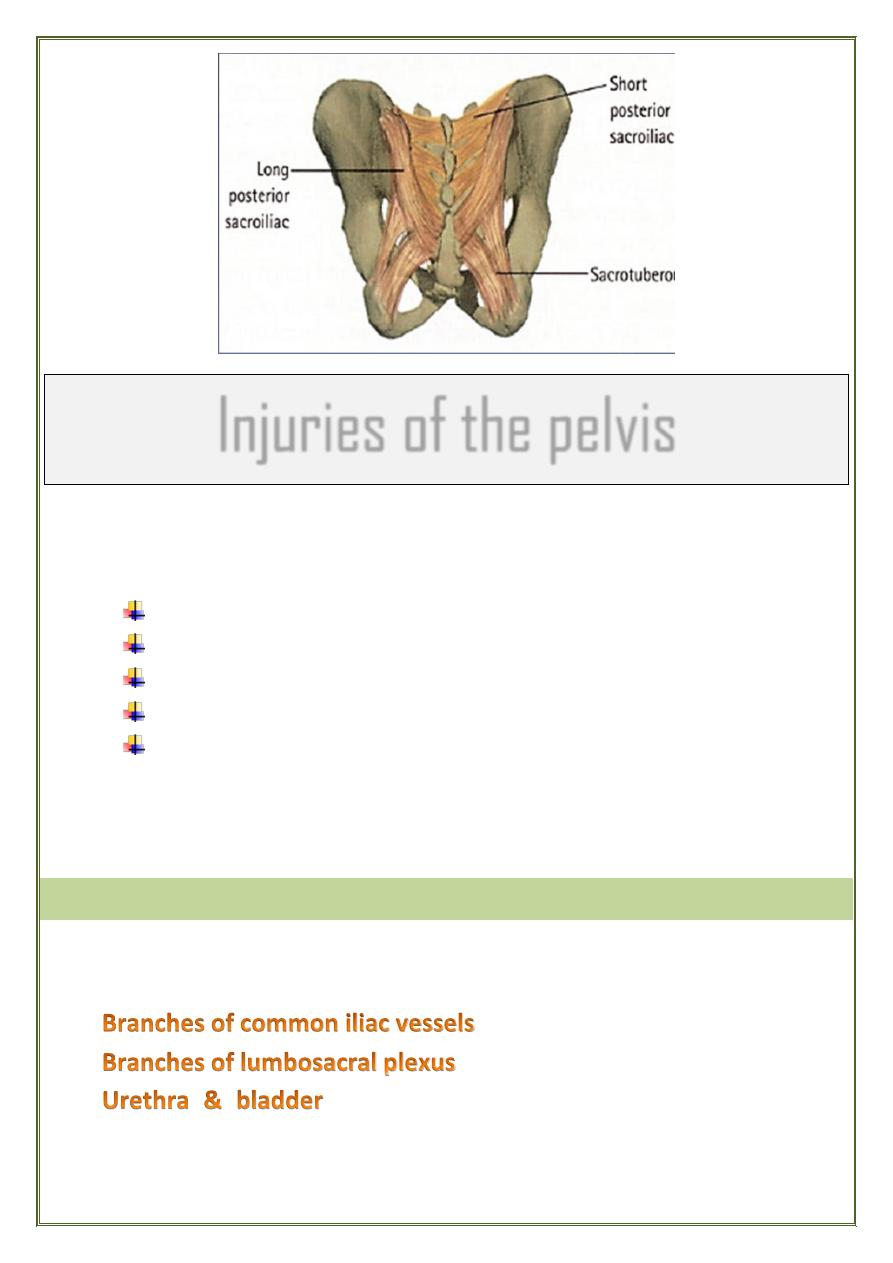
Pelvic ring: is made up of the 2 innominate bones + the sacrum,
articulating in front at the symphysis pubis and posteriorly at the
sacroiliac joint.
The stability of the pelvic ring depends upon the rigidity of the
bony parts and the integrity of the strong ligaments.
Sacroiliac ( anterior & posterior )
Sacro-tuberous
Sacro-spinous
Ligaments of symphysis pubis
:Stable pelvis : can withstand weight bearing
without displacement
Types of pelvic injuries
Isolated fractures with an intact pelvic ring
Fractures with broken ring (stable or unstable)
Fractures of the acetabulum
Sacrococcygeal fractures
Isolated fractures : 3 types
Avulsion #s
A piece of bone is pulled off by violent muscle contraction seen in
sportsmen and athletes. e.g.:-
• ASIS(anterior superior iliac spine): Sartorius
• AIIS :(anterior inferior iliac spine): rectus
• Pubic tubercle : adductor longus
• Ischial tuberosity : hamstrings
:
Direct fractures
A direct blow to the pelvis , usually F.F.H may fracture the ischium or
the iliac blade. need only bed rest until pain subsides.

Stress fractures
• Fracture of the pubic rami are common.
• In osteoporotic or osteomalacic patients
• Cause of sacroiliac pain in elderly osteoporotic individuals.
• Stress fractures are best demonstrated by radioisotope scan.
Fractures of pelvic Ring
Pelvis is a rigid ring fracture in one point must be associated
with disruption at another point except in children
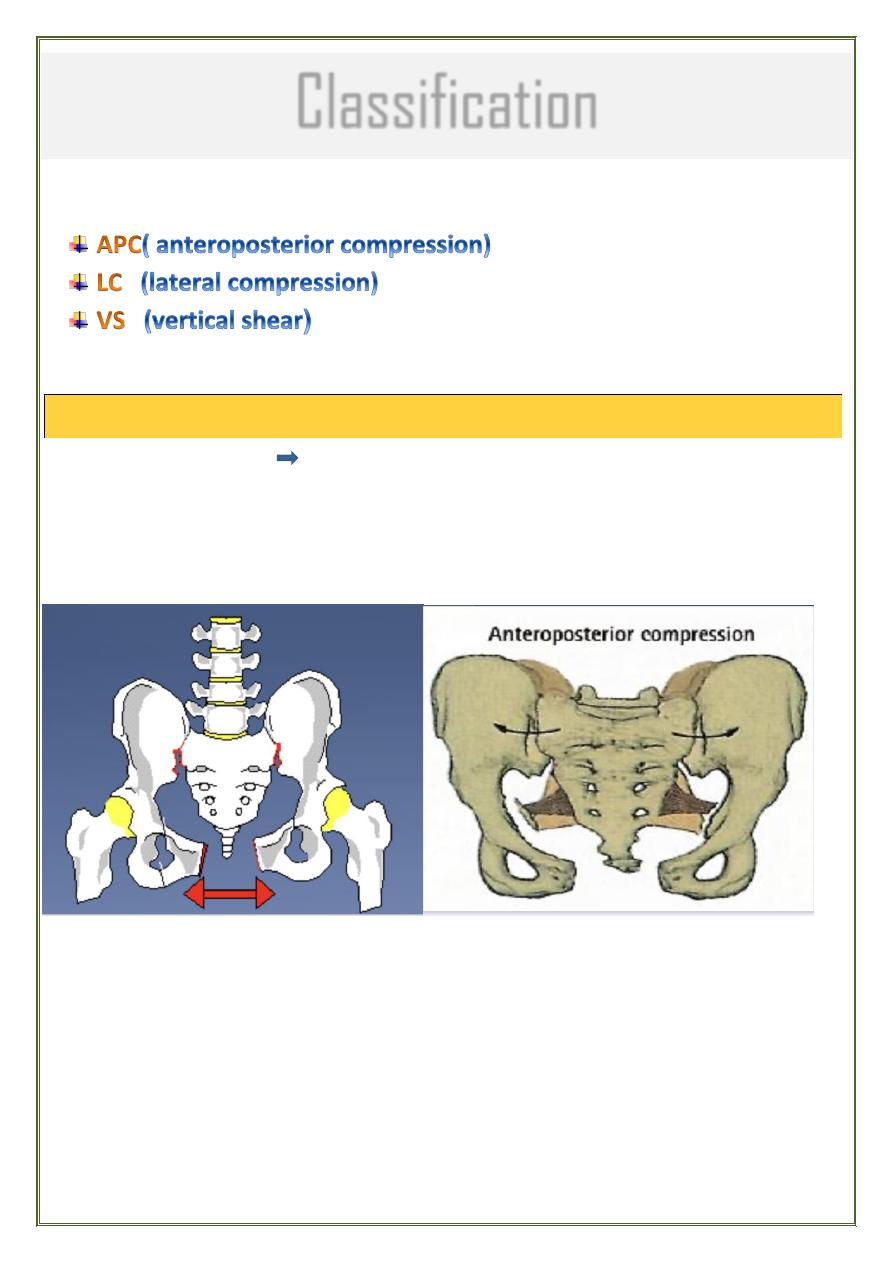
Classification
According to direction of force :
APC
frontal collision open - book injury : diastasis of symphysis
pubis or # of pubic rami
innominate bones are externally rotated
Posteriorly : injury of ligaments of sacro-iliac joint
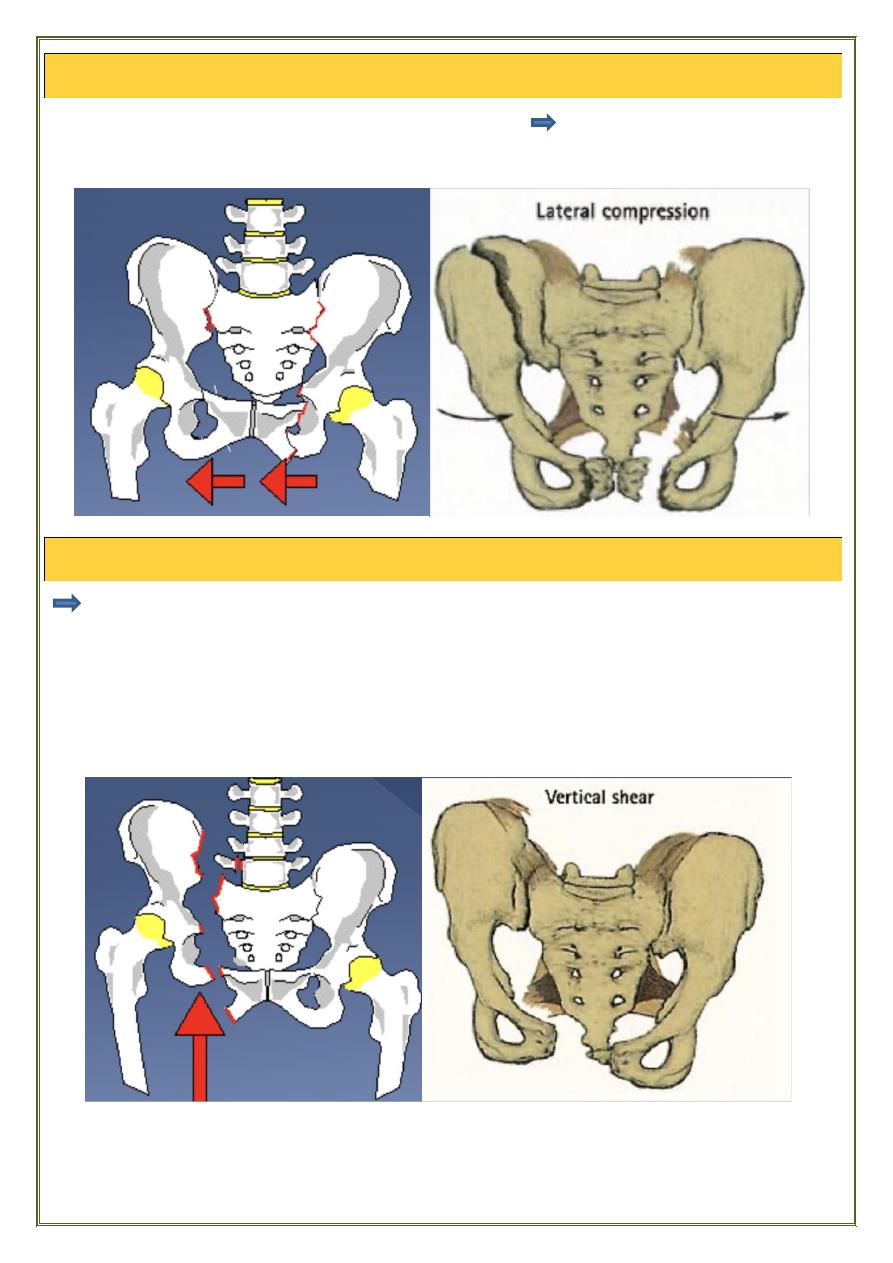
LC
•Side to side compression, causes (buckling # of pubic rami + a
severe sacroiliac strain or a fracture of the sacrum or ilium. .
VC
• upward displacement of the hemipelvis
Occur typically when someone falls from a height onto one leg.
•These are usually severe, unstable injuries with gross tearing of the
soft tissues and retroperitoneal haemorrhage.
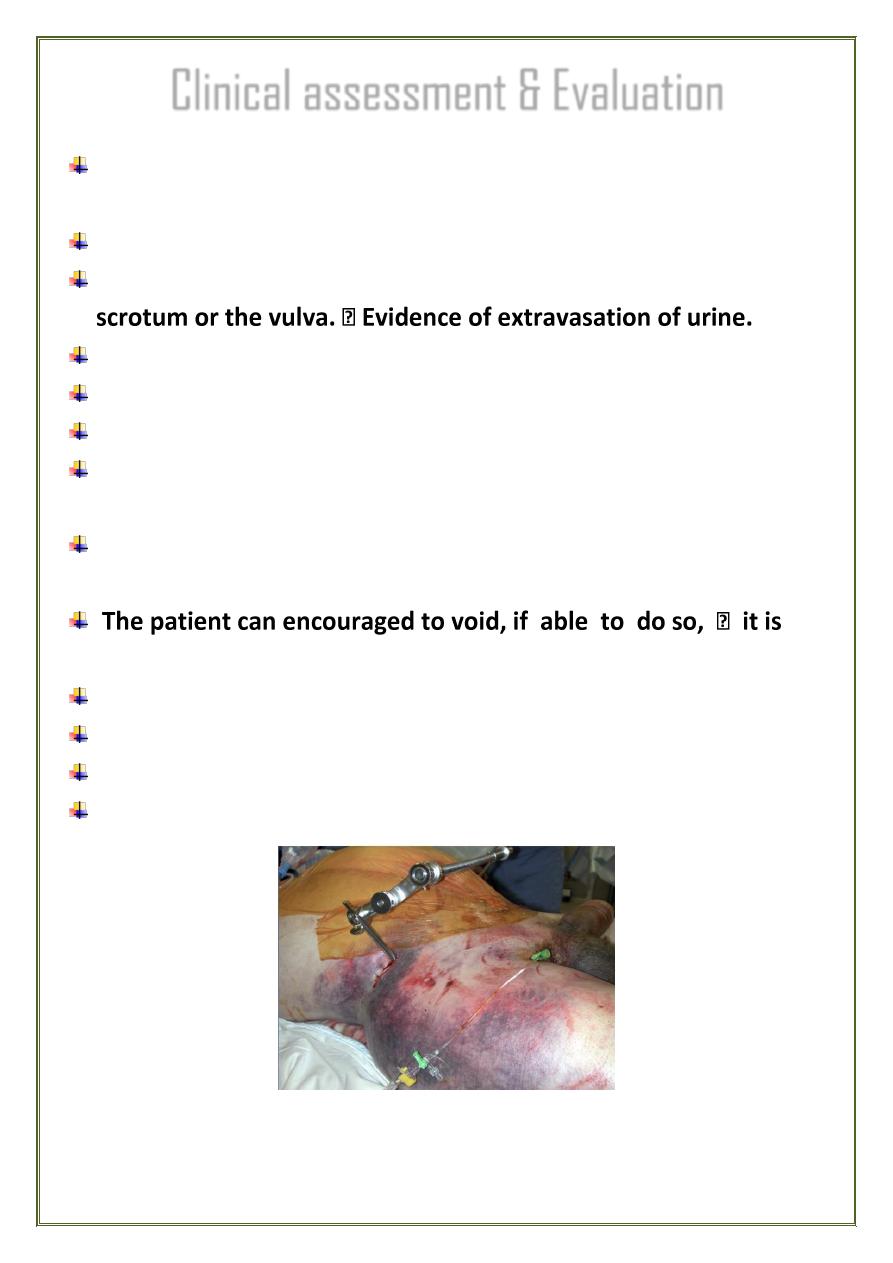
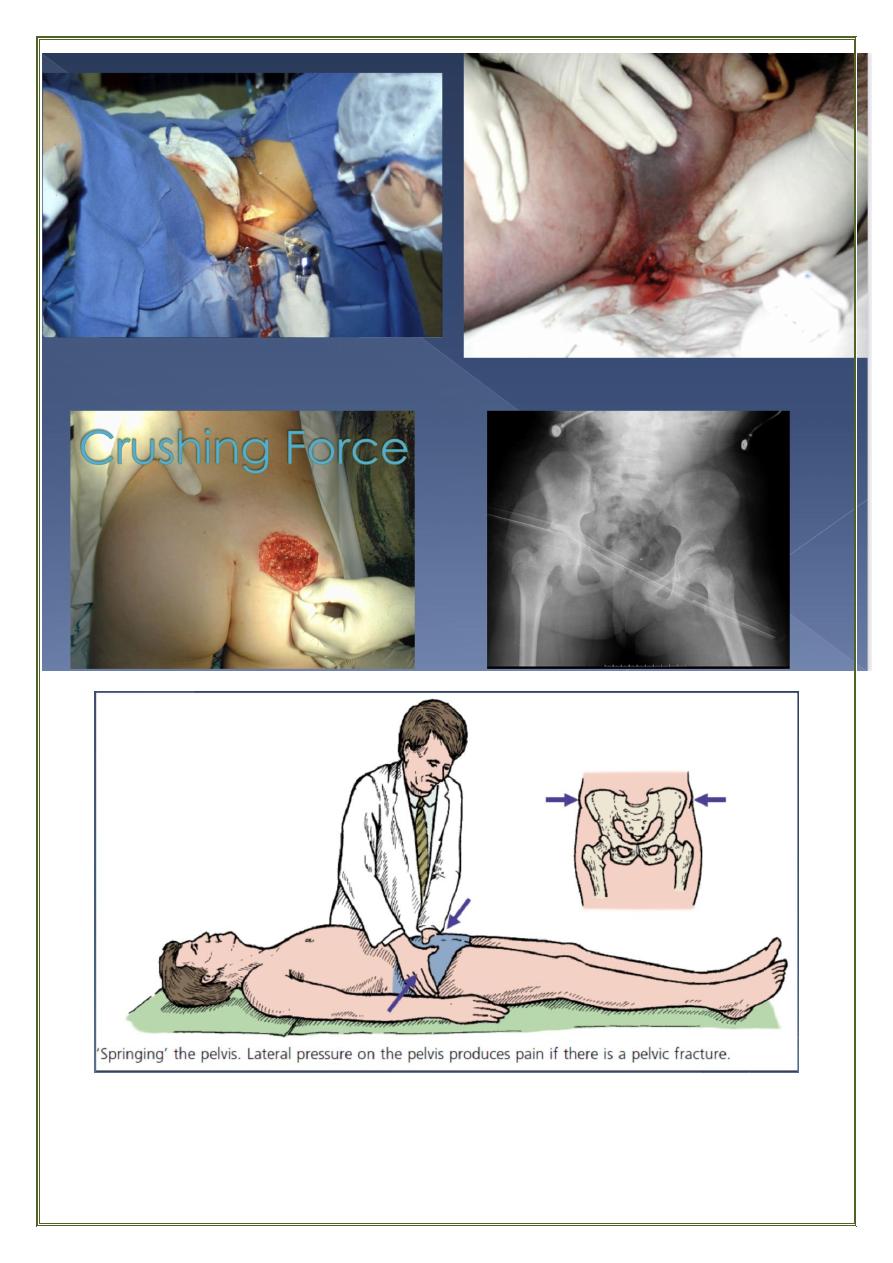
Clinical assessment & Evaluation
suspected in every patient with serious abdominal or lower limb
injuries
History of R.T.A. F.F.H, Crush injuries
Swelling or bruising of the lower abdomen, thighs, perineum,
Rectal examination.
Coccyx, sacrum can be felt and tested for tenderness.
High prostate suggests a urethral injury
Inability to void urine and blood at the external meatus are the
classic features of a ruptured urethra,
absence of blood at the meatus does not exclude a urethral
injury.
either the urethra is intact or there is only minimal damage.
No attempt catheterization.
retrograde urethrography.
Neurological examination is important .
If the patient is unconscious , the same routine is followed.
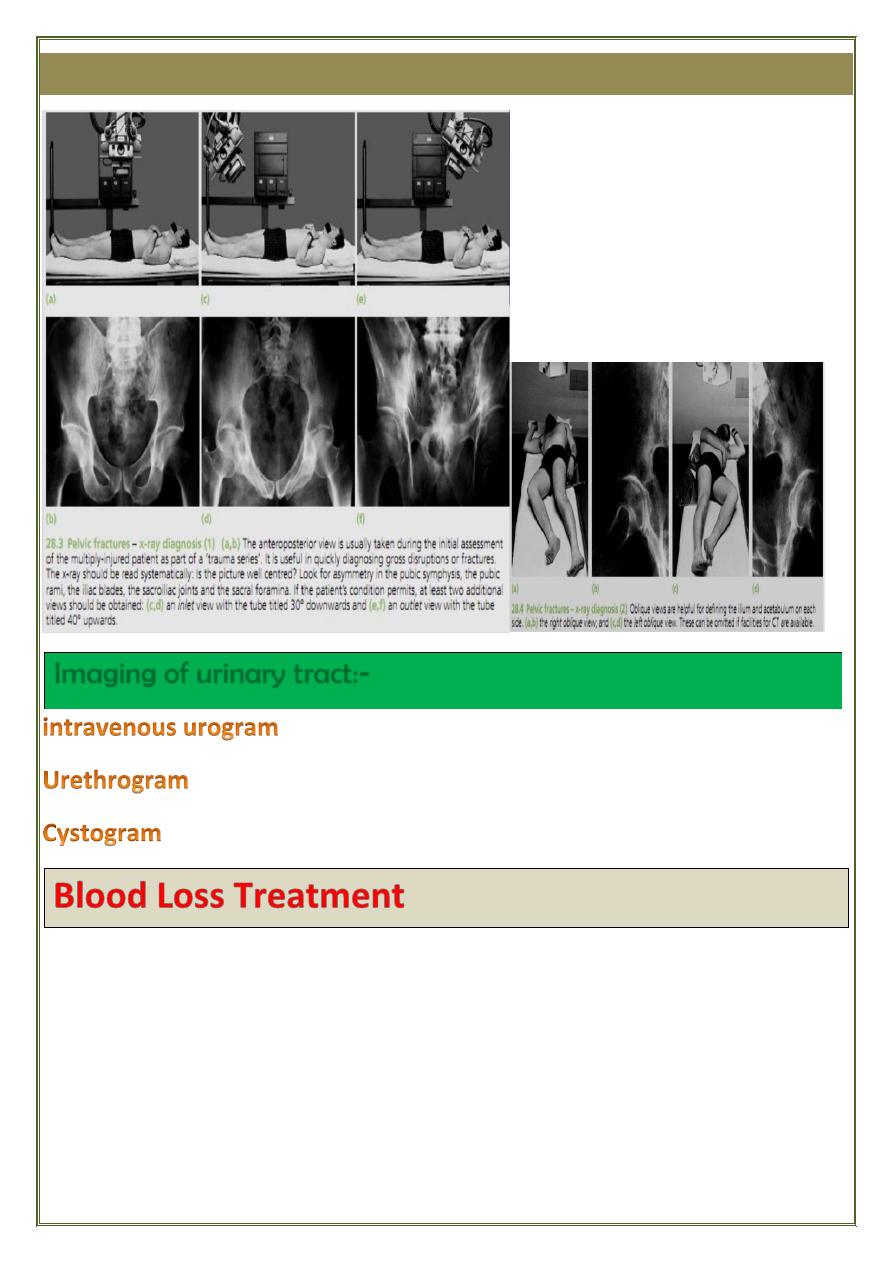
Imaging of the pelvis
Imaging of urinary tract:-
:- renal injury.
:- urethral injury.
:- rupture of the bladder
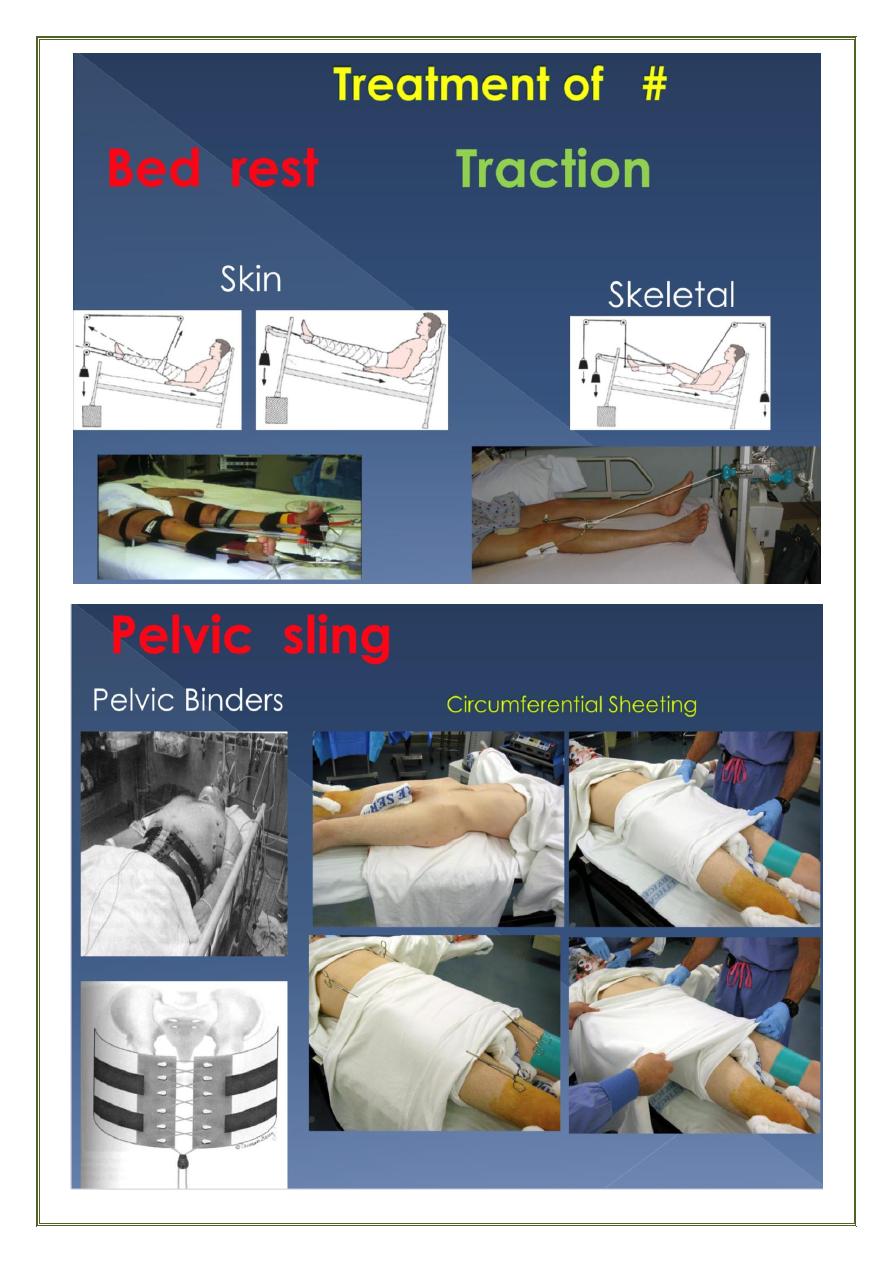
General treatment of shock
Pelvic sling
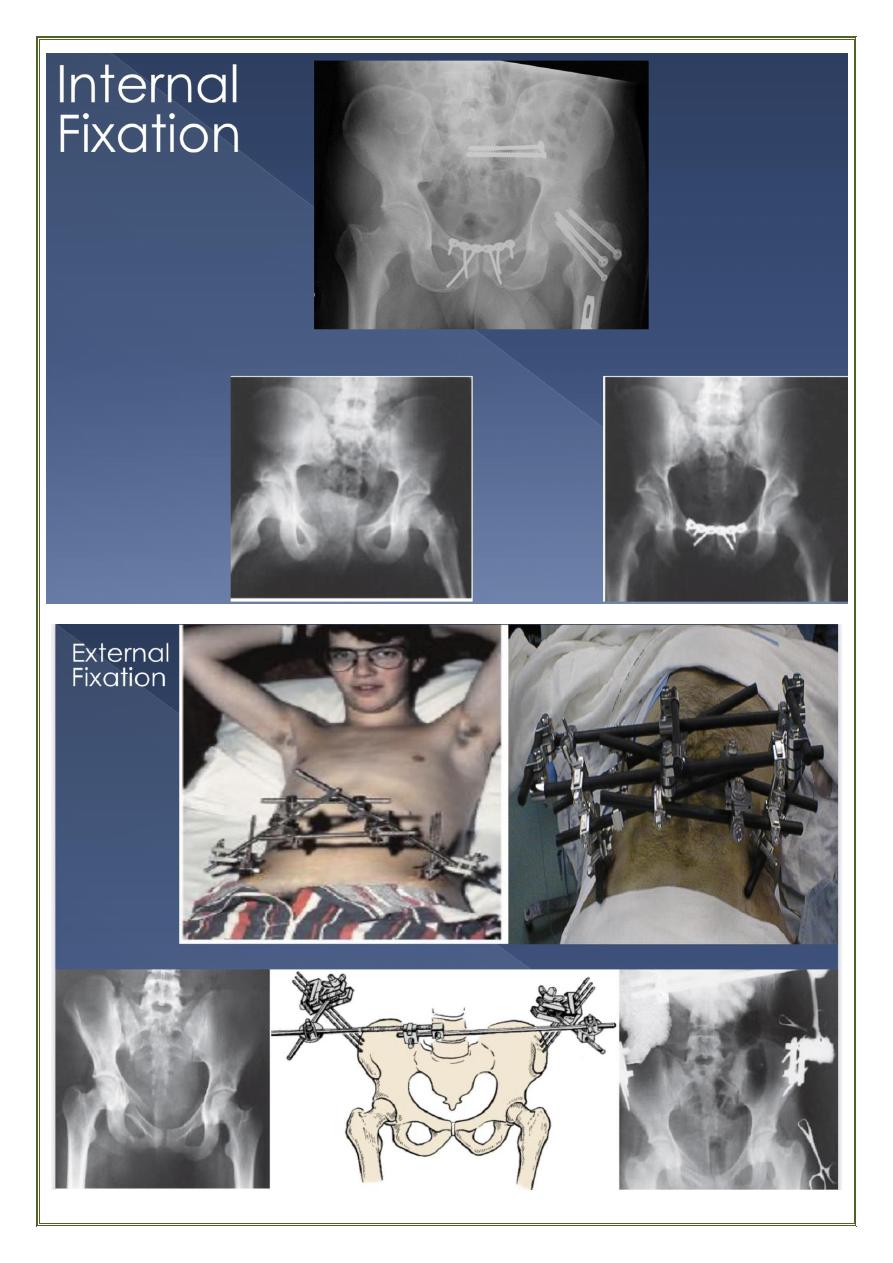
External fixation
Laparotomy
Embolization
Retroperitoneal haemtoma should not be evacuated