
Skull and brain imaging
By
Dr. Firas Abdullah
Thiqar college of medicine

Brain tumors
Glioma:
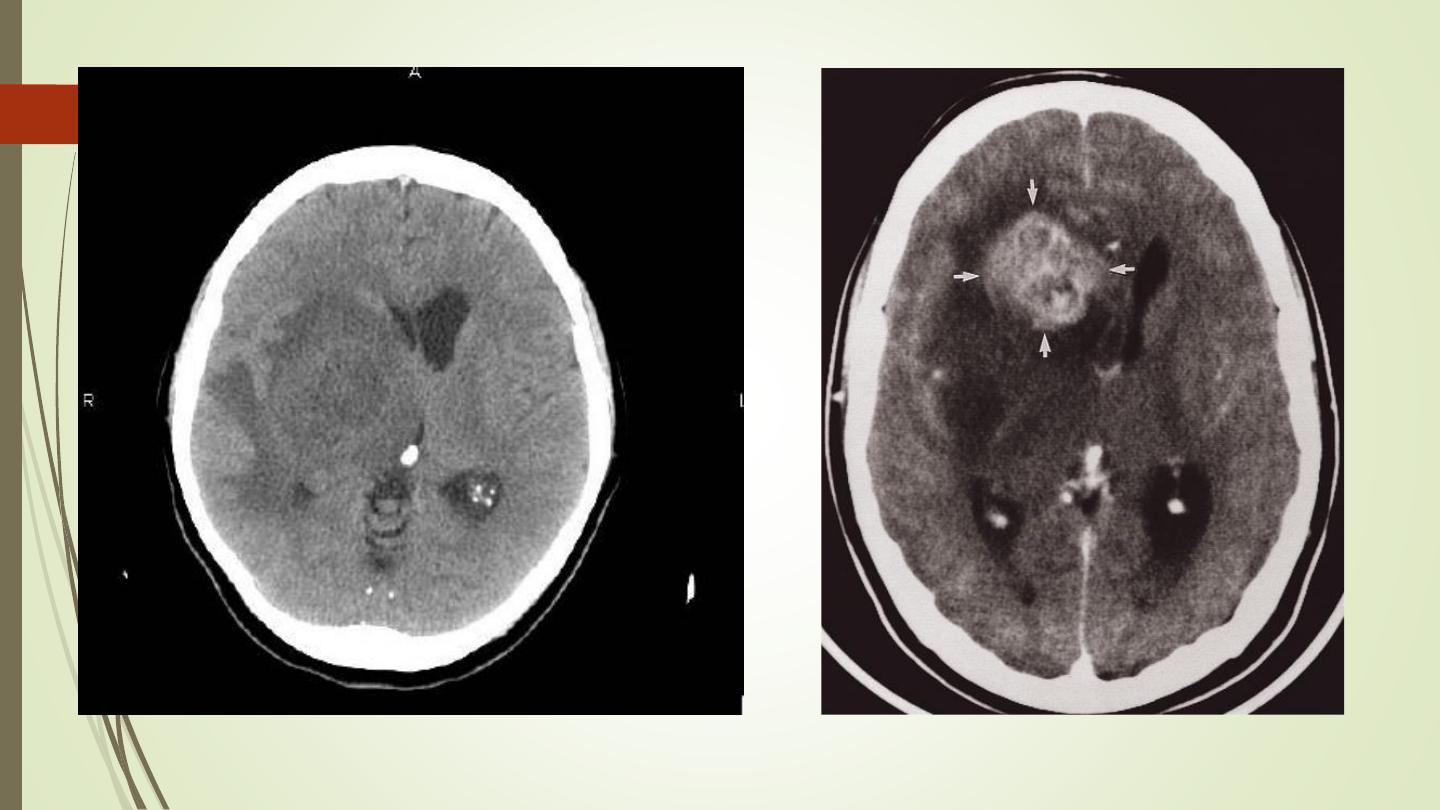
• Typically appears as a solitary, smooth or irregular mass, surrounded by
variable amount of edema
• Compression or displacement of the ventricles
• The CT attenuation values of the tumour itself are usually low, but may be
high or mixed.
• Some, particularly the low grade tumours, may be very densely calcified.
• Partial enhancement with intravenous contrast medium, sometimes only
the outer portion enhances, giving a so called ring enhancement pattern.

Brain tumors
Glioma:
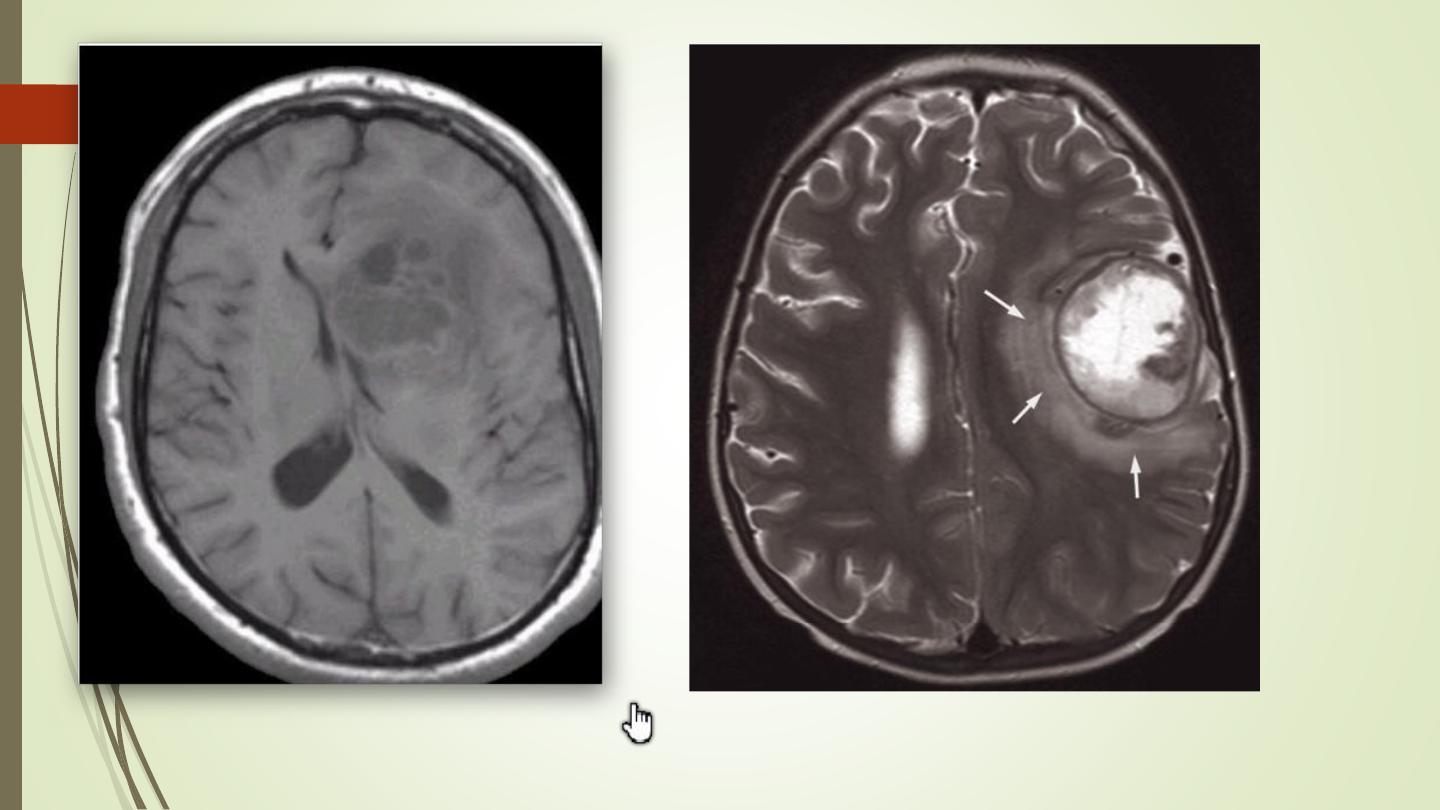
• AT MRI, same as for CT. The essential features are a
mass, often with adjacent oedema.
• Calcification is less evident than in MRI.
• In general, the tumour is lower in signal intensity than
the normal brain on the T1-weighted images and
higher in signal intensity on the T2-weighted images.

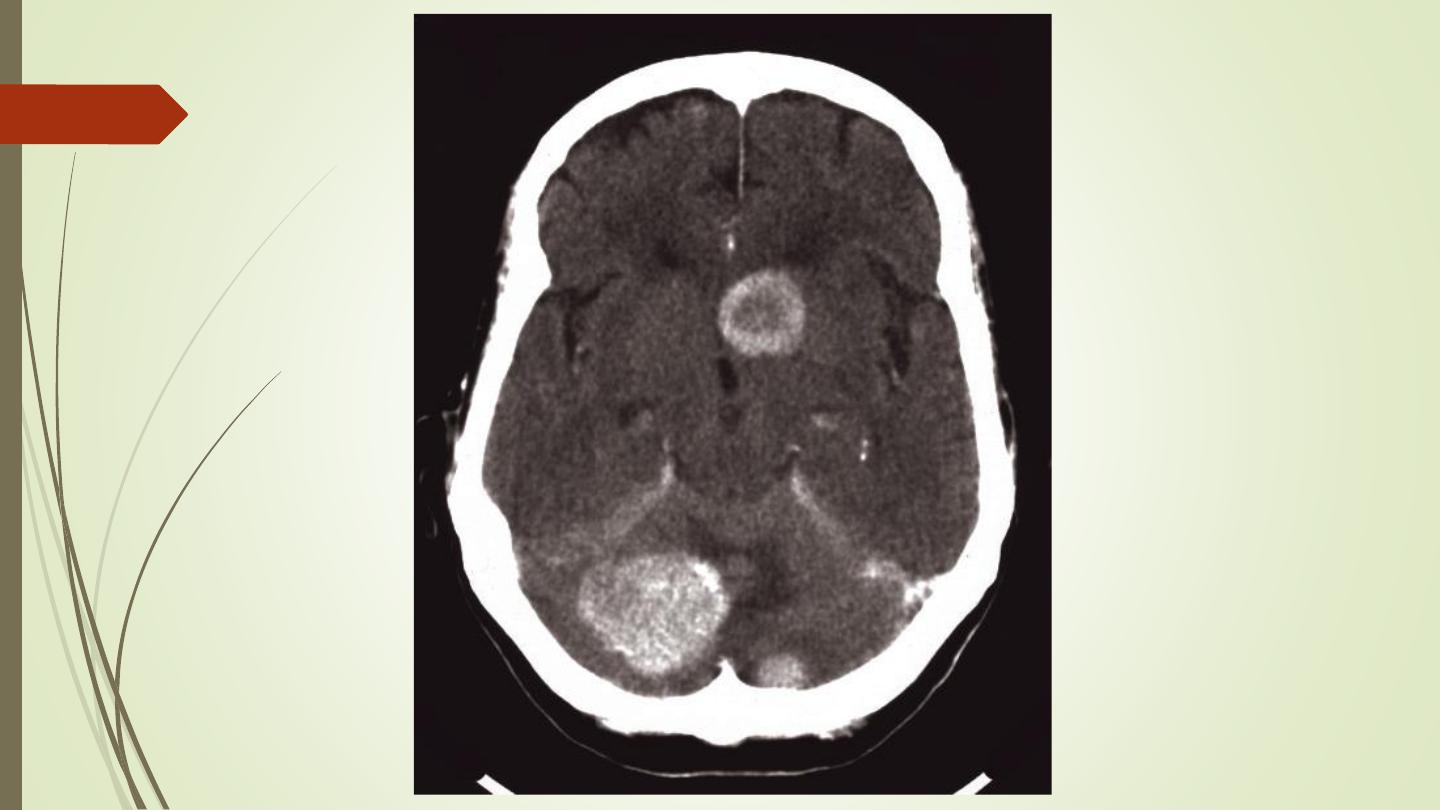
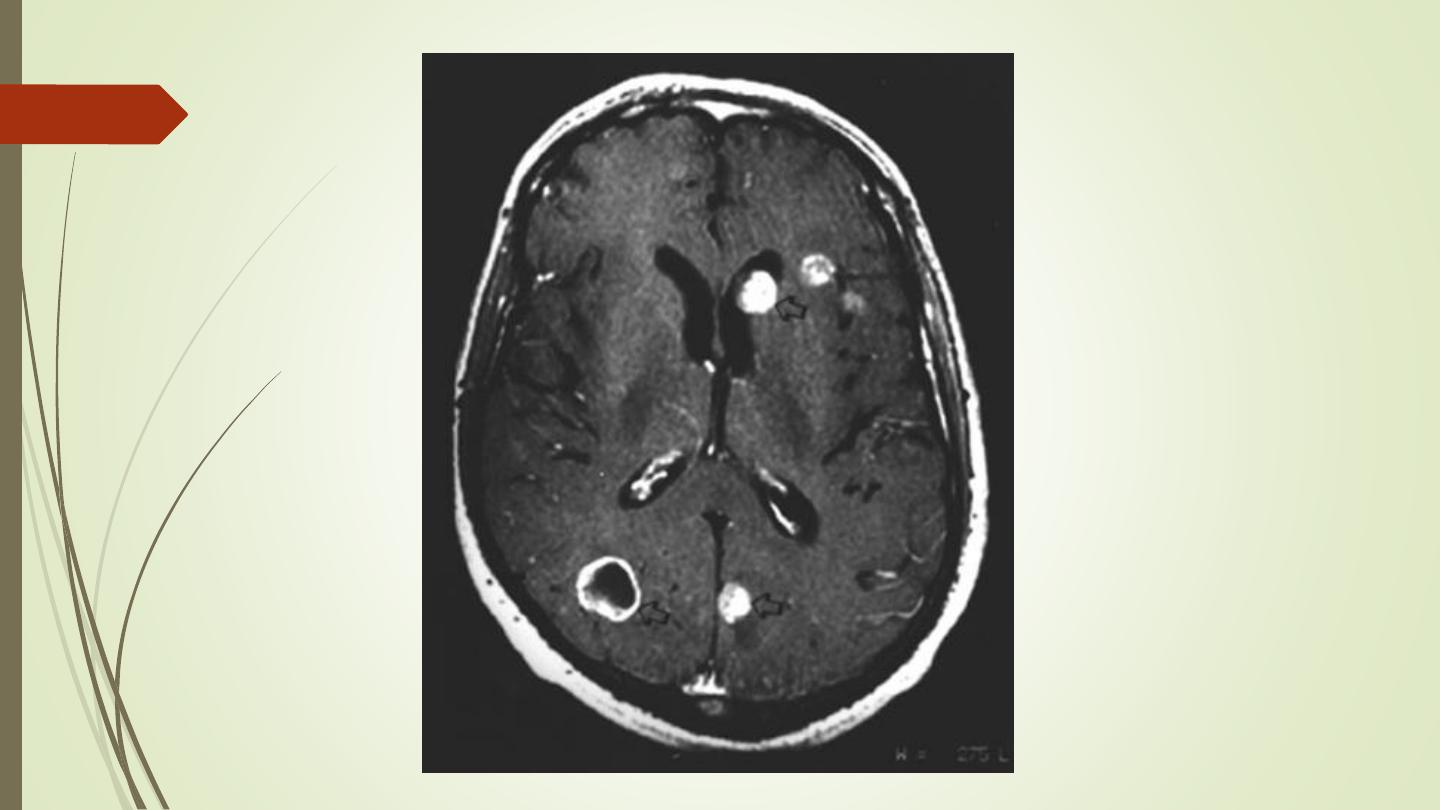
Brain metastasis
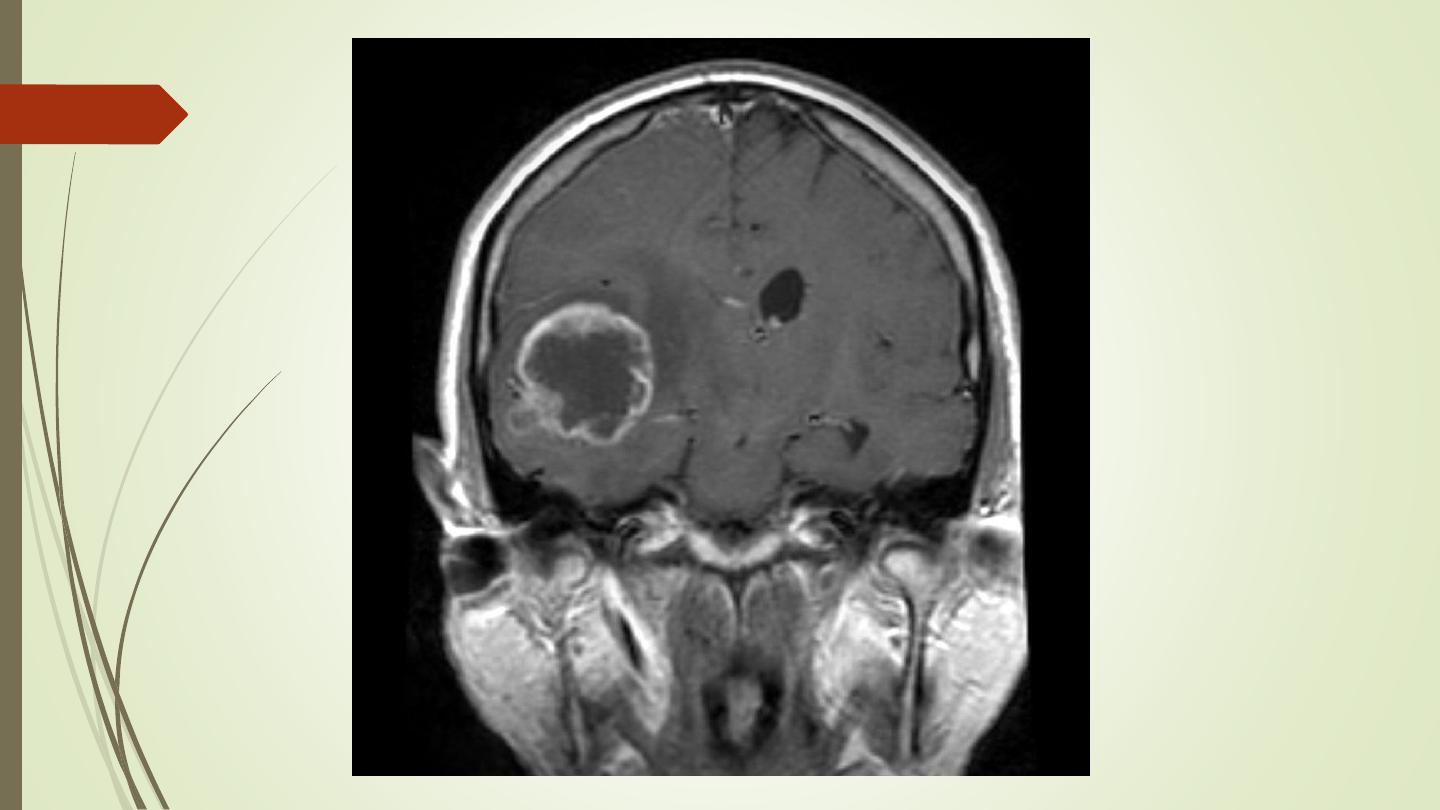
• Metastases in the brain may be of high, iso, or low
density
• They usually show contrast enhancement (ring
enhancement(
• They are often surrounded by significant oedema
• Metastases are typically multiple.
• A solitary metastasis is indistinguishable from a
primary intracerebral brain tumour
.

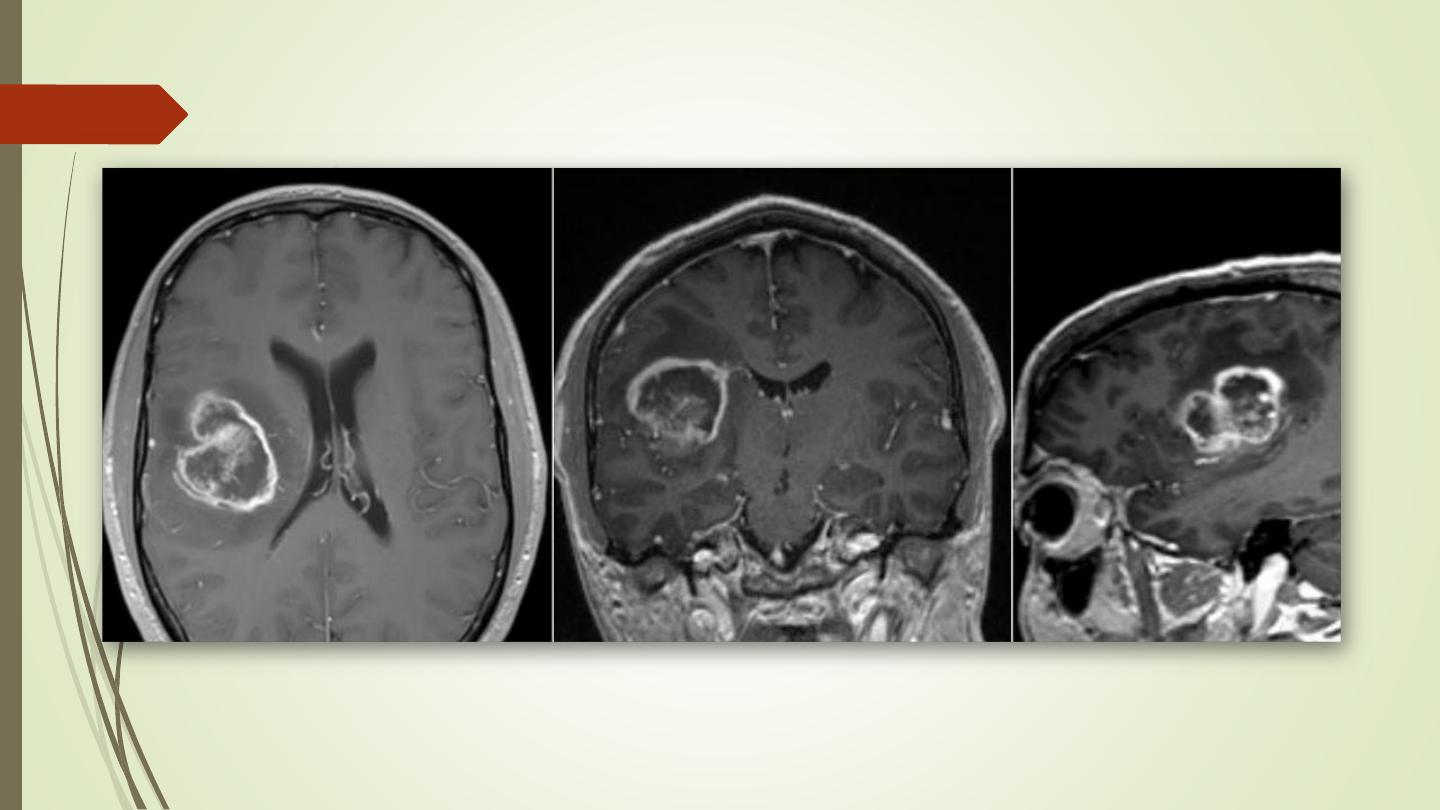
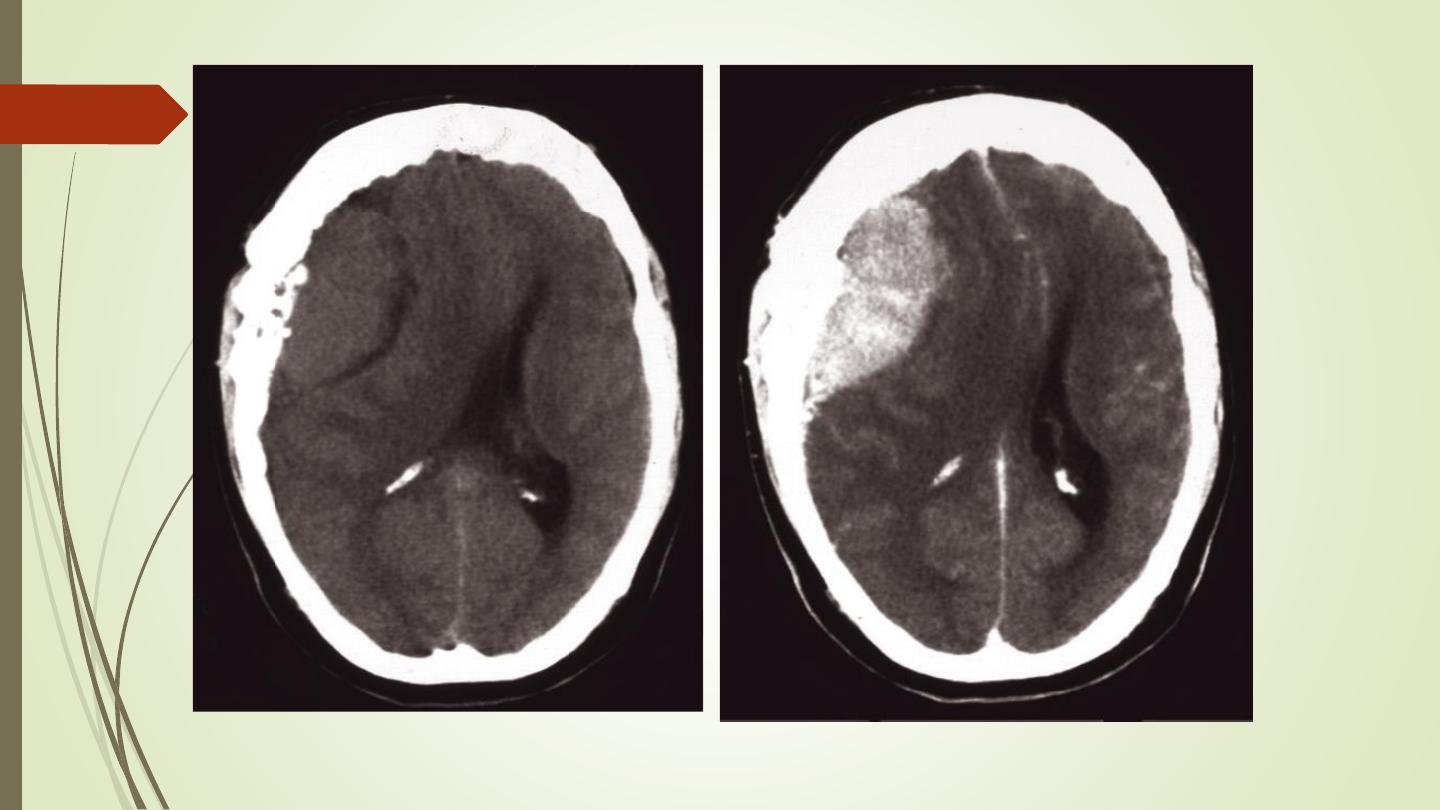
Meningioma:
• Arise from the meninges of the vault, falx, or tentorium
(extra-axial)
• Characteristic sites, the commonest being the parasagittal
region, over the cerebral convexities, and the sphenoid
ridges
• Unenhanced CT scan, a meningioma is slightly denser than
the brain
• The tumour shows marked enhancement post contrast
injection
• Sclerosis and thickening of the adjacent bone.
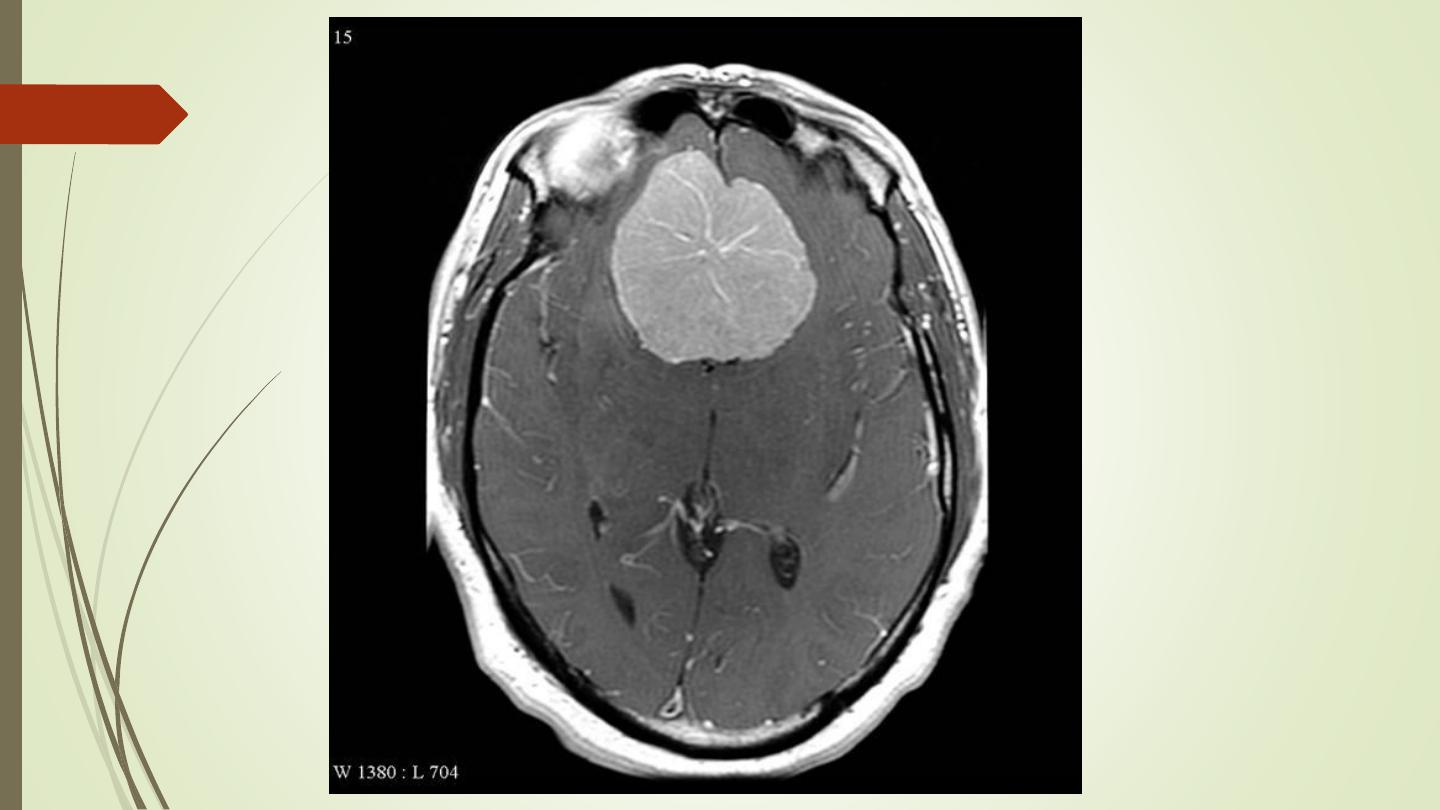
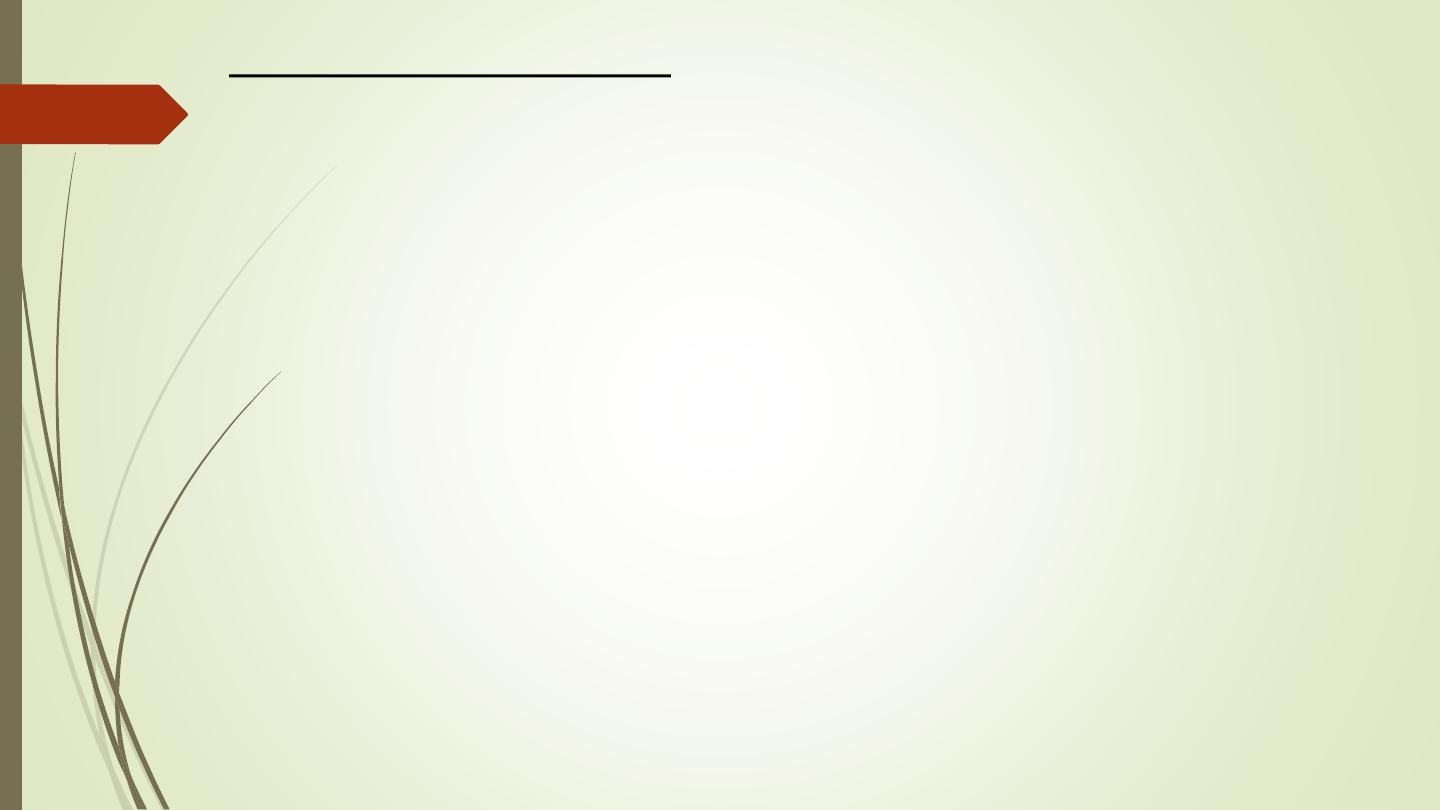
Acoustic neuroma:
• Neurofibromas of the acoustic nerve arise in the internal
auditory canal or immediately adjacent to the internal
auditory meatus in the cerebellopontine angle.
• When large, they can be recognized at CT or MRI. When
small, they may only be identifiable with MRI.
• Contrast enhancement improves their visibility with either
technique
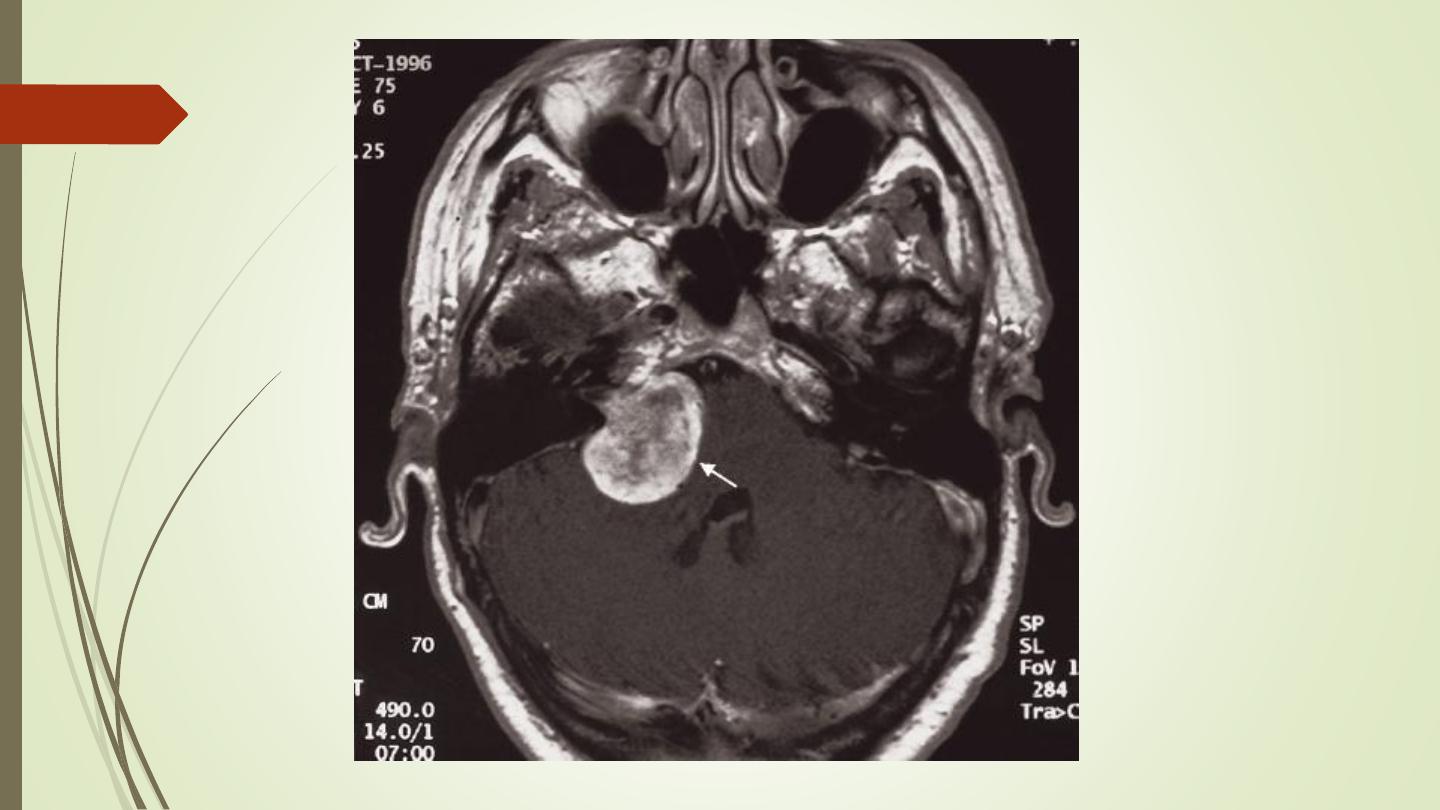
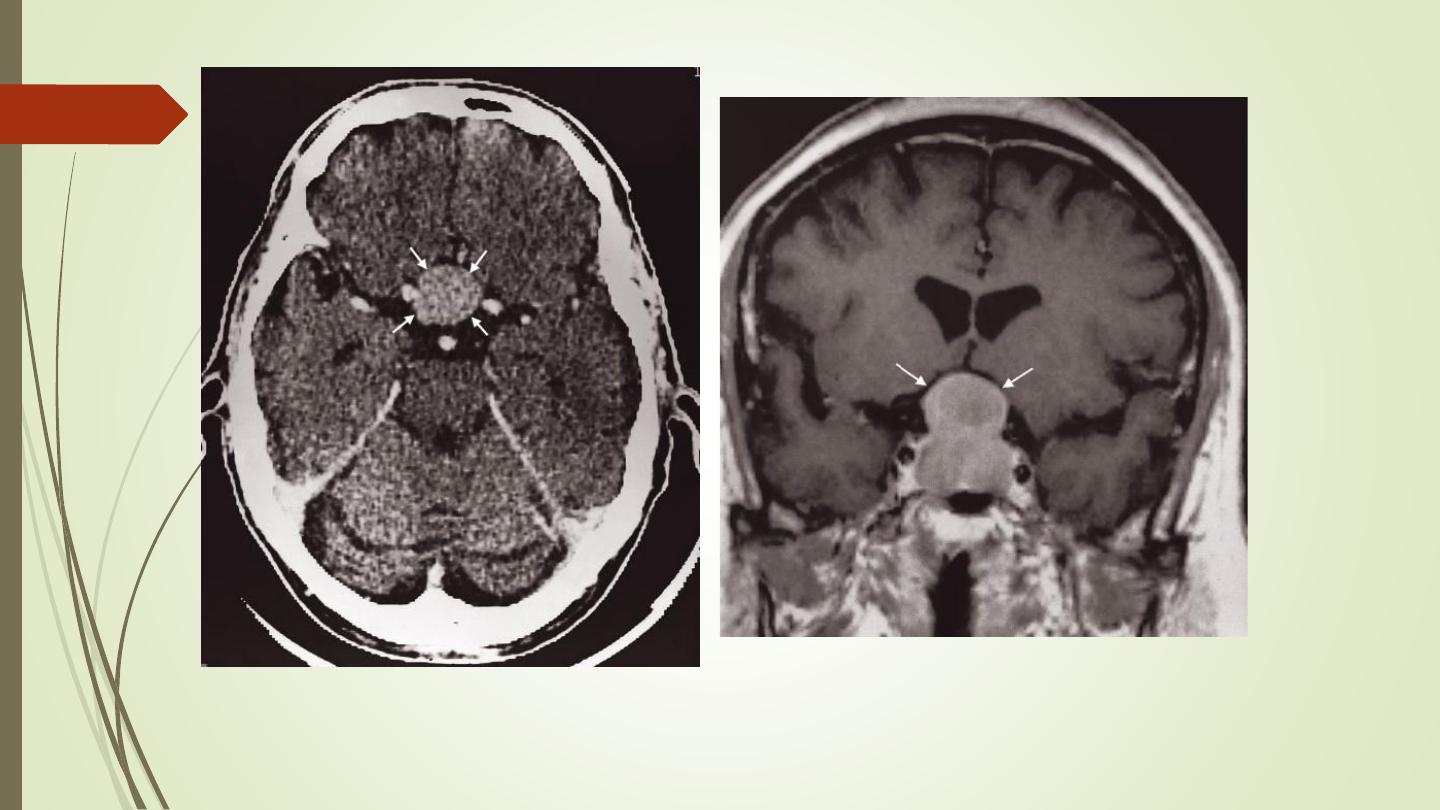
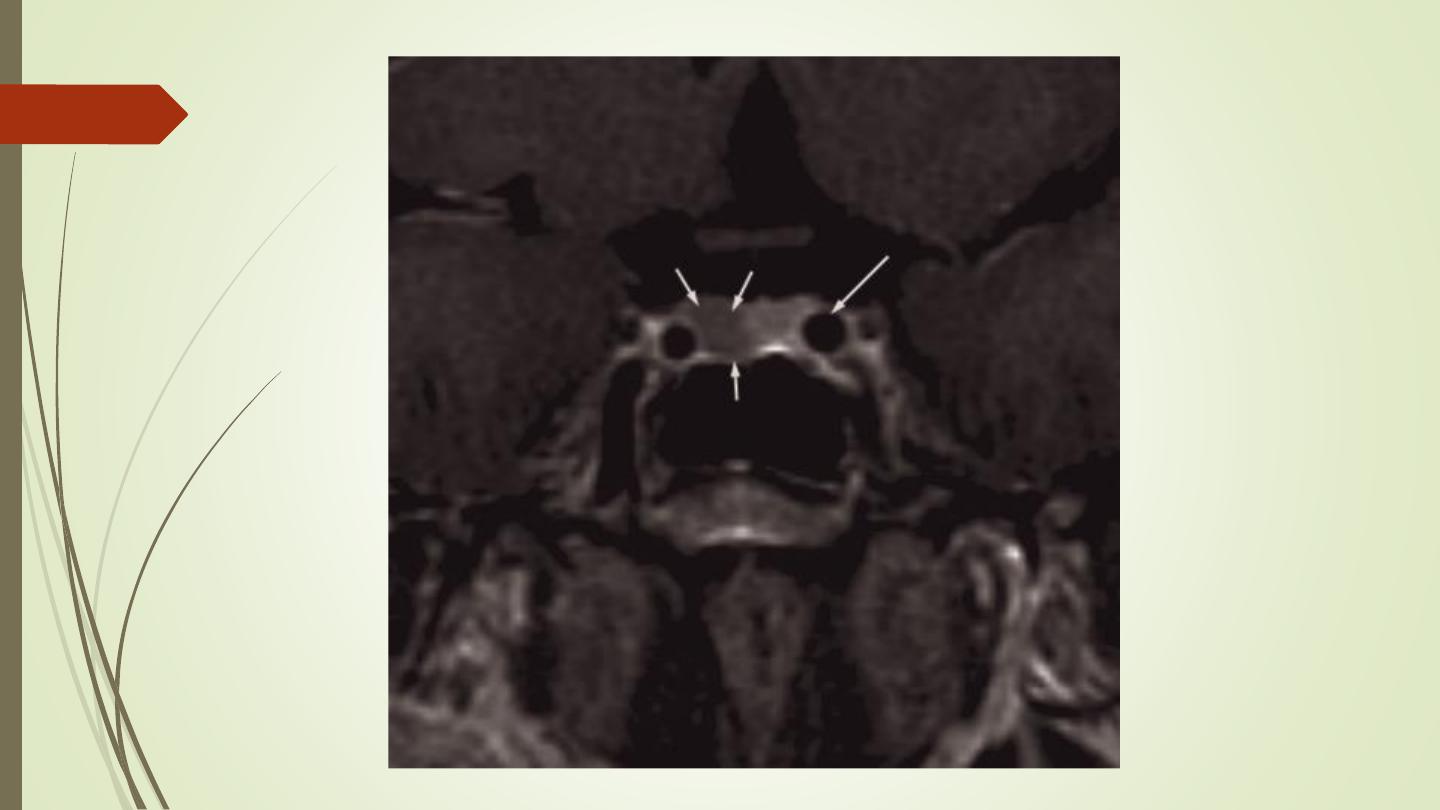
Pituitary tumours:
• Divided into macroadenomas (>1 cm), and microadenomas
(<1 cm).
• Large tumours may cause enlargement of the pituitary fossa.
• Computed tomography can show a pituitary tumour , but MRI
is the investigation of choice and can readily demonstrate its
relationship to the optic chiasm and optic nerves and can
show very small tumours

Infection
• In acute meningitis CT and MRI are usually normal.
• Encephalitis is caused by infection, usually viral or by an immune
reaction to infection. CT and MRI show unilateral or bilateral focal
abnormal areas, often in a characteristic distribution appearing as
low attenuation on CT and high signal on a T2-weighted MRI scan
• An abscess can be caused by pyogenic, tuberculous, fungal or
parasitic organisms. Necrosis and pus formation occur in the
center of the abscess, which appears as low density on CT. The
wall of the abscess enhances with intravenous contrast and may
be surrounded by oedema giving an appearance known as ring
enhancement
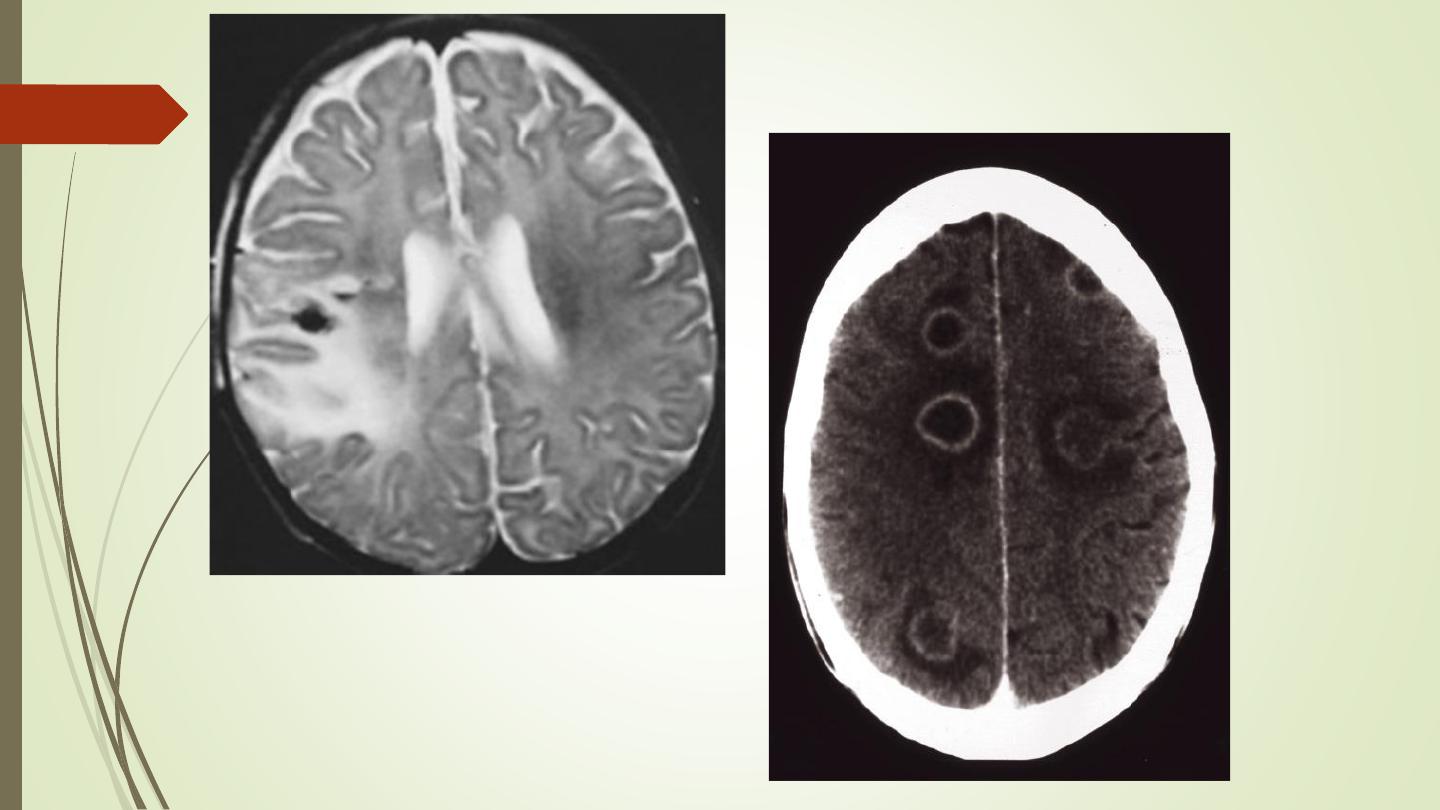
abscess.
Encephalitis

Thank you
