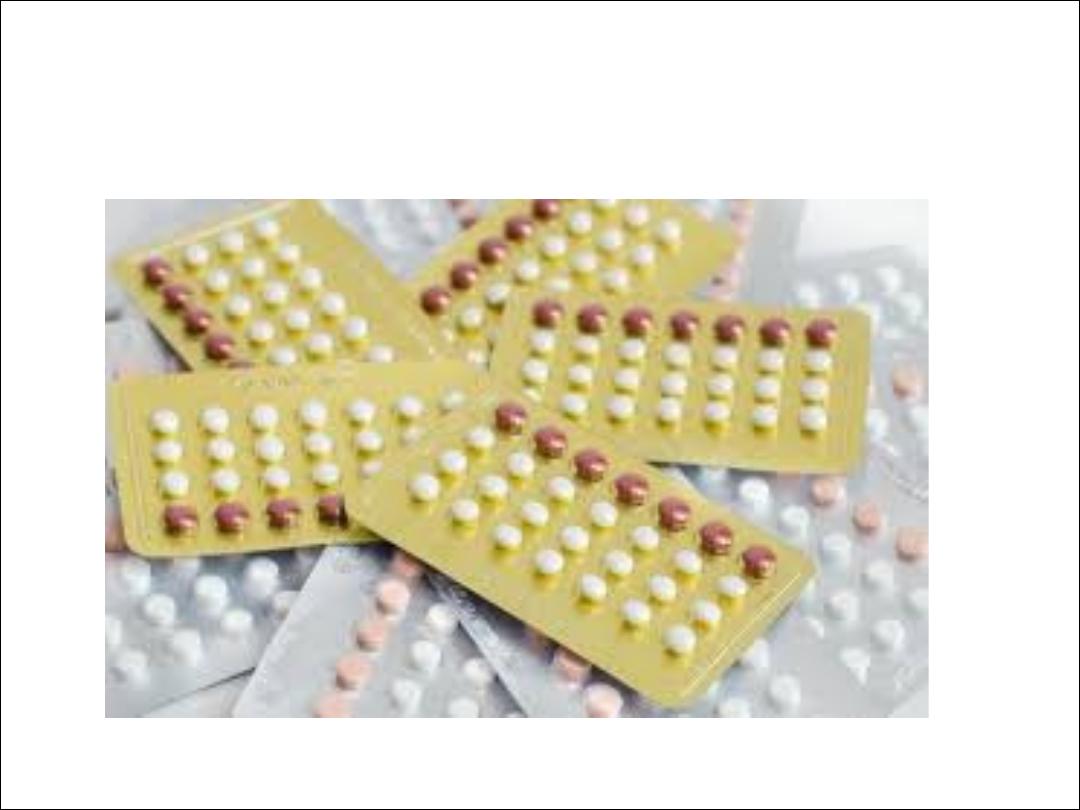
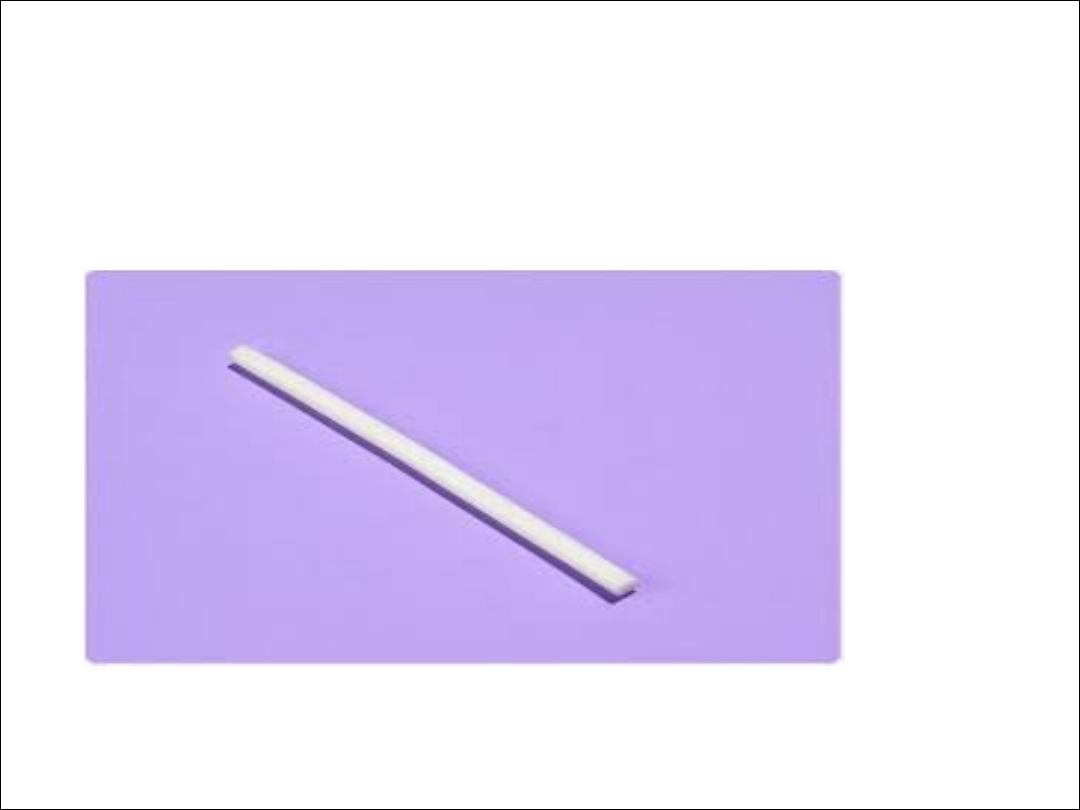
Oral contracep,ve pills

Learning objectives
•
To know types, mechanism of action, and side
effects of combined contraception.
•
2. to understand medical eligibility criteria of
missed pills.
•
To know types and side effects of progesterone
only contraception.

Ti is a widely accepted, effective, & usually
reversible method of contraception. It’s
introduced in 1956. 3 types:
1. combined oral contraceptive (COC).
2. Progesterone- only (minipills); contain either
Norgestril or Norethisterone, taken each day.
3. Seqential oral contraceptives.

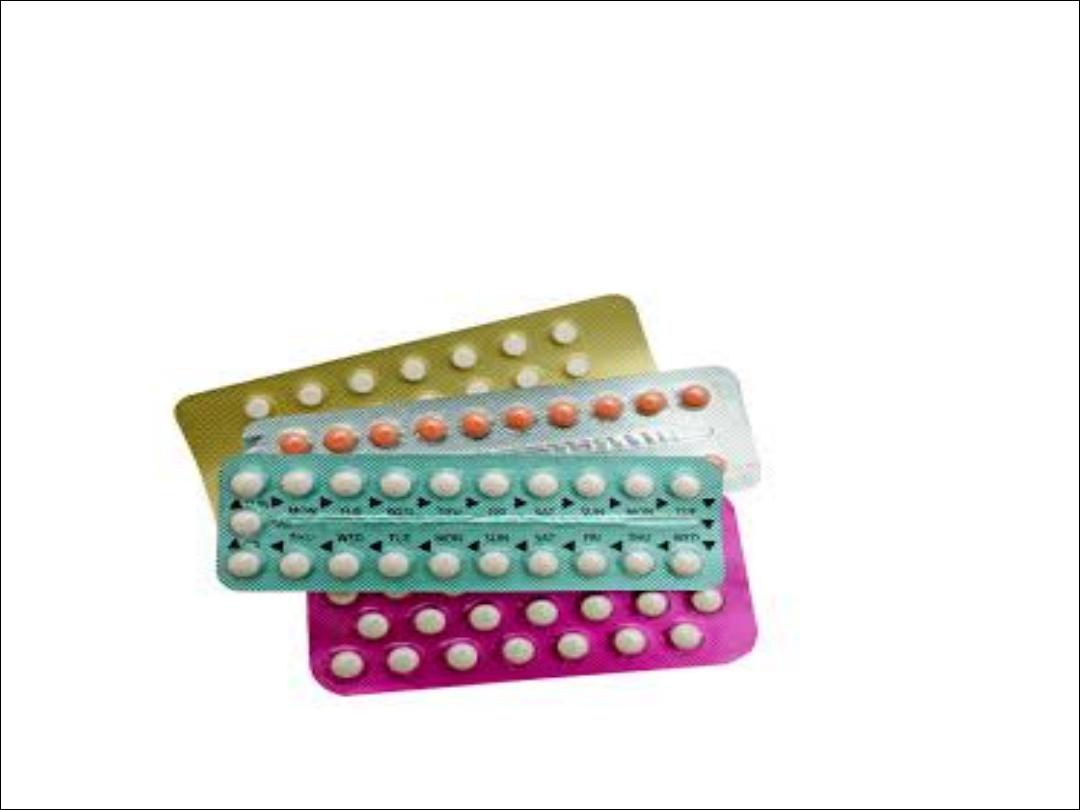
1. COC:-
Formulations:- It contains both estrogen(usually
Ethinyl oestradiol or Menstranol) & a progesterone.
Previously use high dose pills (100 ug of estrogen),
but now decrease the dose of estrogen to 20-50 ug;
most women use 30-35 ug estrogen (low- dose pills).
The progesterone either 1
st
or 2
nd
or 3
rd
generation

•
The pill is taken for 21 days followed by a 7-day
break during which time withdrawal bleeding usually
occurs. The pill should be taken at the same time
each day, bed time is convenient. If the woman
forgets to take the pill one night she can take it the
next morning.
•
Combined pills are available as monophonic
(preparation in which every pill in the pocket
contains the same dose of steroids); & biphasic &
triphasic pills ; in which the dose of both steroids
changes once or twice during the cycle so that the
regimen will mimics the normal cycle.

Mode of ac9on:-
•
The principle mode of action of COC is the
inhibition of ovulation. Estrogen inhibits FSH
(suppressing the development of ovarian follicles,
while progestogens inhibit the development of LH
surge.
•
Additional contraceptive effects include changes in
the cervical mucus characteristics interfering with
sperm transport, a possible alteration in the tubal
motility, endometrial atrophy with impaired
uterine receptivity.

Advantages:-
1. Menstrual periods are usually lighter, shorter &
more regular during the pill use, less painful &
premenstrual symptoms less troublesome.
2. Decrease the incidence of iron deficiency anemia
by decreasing menstrual blood loss.
3. Decrease incidence of benign breast lumps,
functional ovarian cysts, endometriosis, acne &
possibly PID.
4. COC use protects against ovarian & endometrial
cancer (due to decrease in the number of ovulations
& therefore rupture of ovarian capsule).

•
There is also a 50 per cent reduction in ovarian and
endometrial cancers which continues for 15 years
after stopping the CHC.
•
5.There is a possible protective effect against
rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease and duodenal
ulceration.

WHO medical eligibility criteria category 4 for combined
hormonal contracep9on
•
CHC: UKMEC Category 4 – Unacceptable health risk and should not
be used
•
Breastfeeding – <6 weeks postpartum
•
Smoking – aged ³35 years and smoking ³15 cigarettes per day
•
Cardiovascular disease – multiple risk factors for arterial
cardiovascular disease
•
Hypertension – blood pressure ³160 mmHg systolic and/or ³95 mmHg
diastolic; or vascular disease
•
VTE – current (on anticoagulants) or past history
•
Major surgery with prolonged immobilisation
•
Known thrombogenic mutations
•
Current and history of ischaemic heart disease
•
Stroke

•
Valvular and congenital heart disease – complicated by
pulmonary hypertension, atrial fibrillation, history of
subacute bacterial endocarditis
•
Migraine headaches – with aura at any age
•
Breast disease – current breast cancer
•
Diabetes – with nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy or
other vascular disease
•
Viral hepatitis – active or flare
•
Cirrhosis – severe decompensated disease
•
Liver tumours – benign hepatocellular adenoma and
malignant hepatoma
•
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) – positive or
unknown antiphospholipid antibodies

Risks & side effects:-
A-Minor S/E :-
1.Disturbances of the menstrual cycle: either slight
bleeding or frank break through bleeding especially
with low dose pills. If frank through bleeding ˃ 2
times the can be controlled by increasing the dose of
estrogen or change to another preparation contains
different proportion of estrogen to progesterone.
Amenorrhea when high –dose pills. Exclude pregnancy
& sometimes can be treated by induction of
ovulation.
2.Weight gain, fluid retention, headache, nausea, &
vomiting, chloasma, mood changes, loss of libido,
mastalgia, breast enlargement & greasy skin.

B-Serious S/E :
•
1.CVS: on venous side; increase risk of venous
thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. In dose-
dependent pattern related to the amount of
estrogen in the pill. Estrogen increase platelet
count & platelet adhesiveness & decrease ant
thrombin in blood.
•
This risk is the most during the first year of CHC
use.
On arterial side: including hypertension, CVA,&
coronary heart disease. Increase risk was only seen
on smoker woman on the pill.

2.Carbohydrate metabolism: high dose pills will
decrease carbohydrate tolerance.
3.Malignancy: small increase in breast cancer &
that the risk persisted for 10 years after stopping
the pills especially if she take the pills before the
birth of the first child.
Also small increase in the risk of carcinoma of
cervix.
Liver cancer; benign hepatic adenoma is rare
complication.

Interac9on with drugs:
•
Effectiveness of the combined oral contraceptive pill
(COCP) (and all other methods) is not affected by
administration of most broad-spectrum antibiotics.
•
Barbiturates, sulphonamide, rifampicin, phenytoin &
most anticonvulsants will increase activity of liver
enzymes that metabolize the steroids.
•
Effect on pregnancy: no increase in the incidence of
congenital abnormality in woman who has taken the
pills after pregnancy has started.
•
Follow up: B.P checked at 6, 12 months, then annually,
Pap smear annually .examine breast each year.

Missed-pill guidelines for COC
•
If ONE pill has been missed (more than 24 hours and
up to 48 hours late) .
•
Con$nuing contracep$ve cover
•
• The missed pill should be taken as soon as it is
remembered • The remaining pills should be
con$nued at the usual $me.
•
Minimizing the risk of pregnancy
•
Emergency contracep$on (EC) is not usually
required.

If TWO OR MORE pills have been
missed (more than 48 hours late
•
Continuing contraceptive cover •
•
The most recent missed pill should be taken as
soon as possible •
•
The remaining pills should be continued at the
usual time •
•
Condoms should be used or sex avoided until
seven consecutive active pills have been taken.

•
Minimising the risk of pregnancy
•
If pills are missed in the first week (Pills 1 - 7) .
•
EC should be considered if unprotected sex occurred
in the pill-free interval or in the first week of pill-taking
•
If pills are missed in the second week (Pills 8 - 14)
•
No indication for EC if the pills in the preceding 7 days
have been taken consistently and correctly (assuming
the pills thereafter are taken correctly and additional
contraceptive precautions are used).

•
If pills are missed in the third week (Pills 15 - 21)
•
OMIT THE PILL-FREE INTERVAL by finishing the pills
in the current pack (or discarding any placebo
tablets) and starting a new pack the next day.

Evra patch
•
With this patch 20 μg of ethinyl estradiol and 150 μg
of norelgestromin are released every 24 hours.
•
It is the first transdermal contraceptive applied once
weekly for 3 weeks followed by a patch-free week (3
weeks on, 1 week off).
•
The Pearl index is 1.24 per 100 WY

NuvaRing
•
releases 120 μg of etonogestrel (ENG) and 15 μg of
ethinyl estradiol daily. It is 54 mm in diameter and 4 mm
thick.
•
It is placed vaginally once every 3 weeks and following a
1-week ring-free interval a new ring is inserted.
•
Efficacy and cycle control are comparable to the COCs.
Side-effect profile is also similar to that of COCs.
•
However, women have reported more vaginal
symptoms of vaginiSs, leukorrhoea, foreign body
sensaSon, coital problems and expulsion.

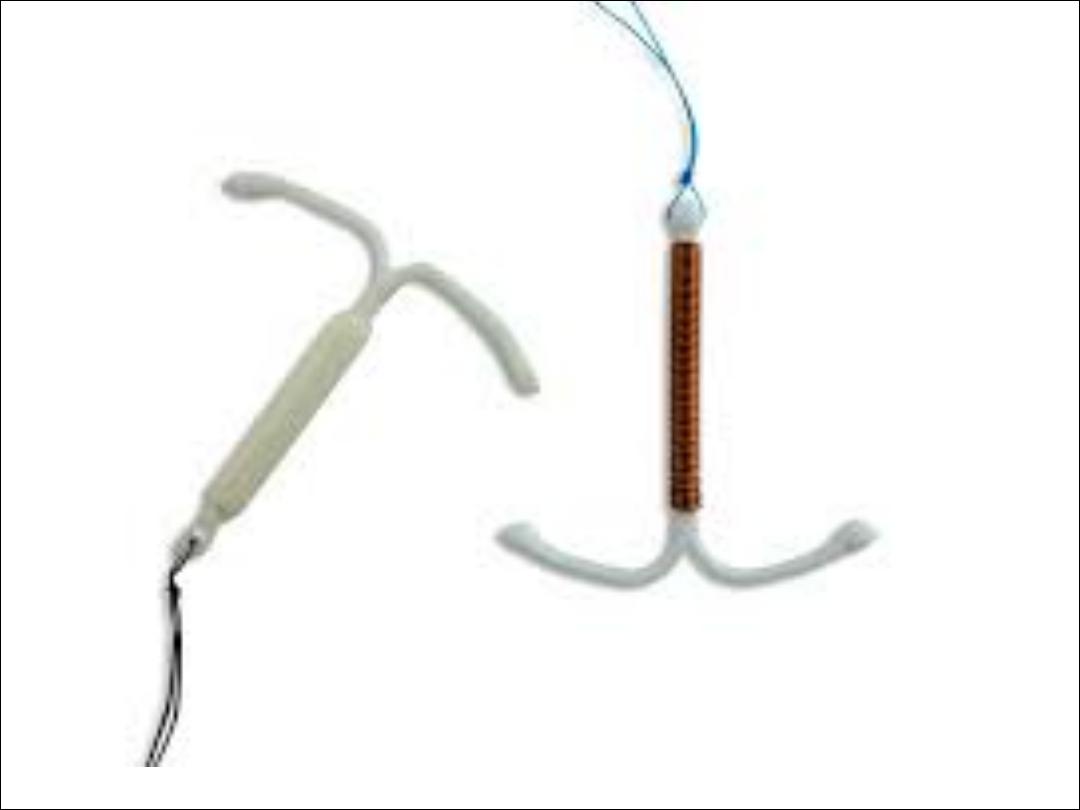
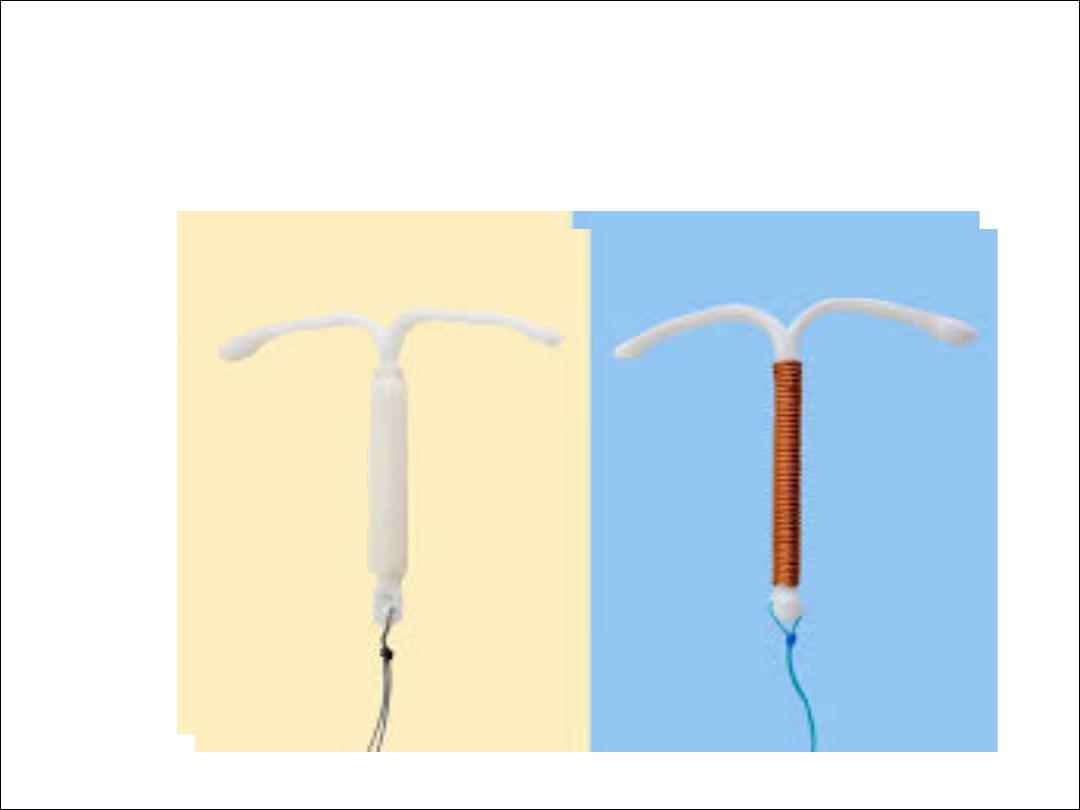
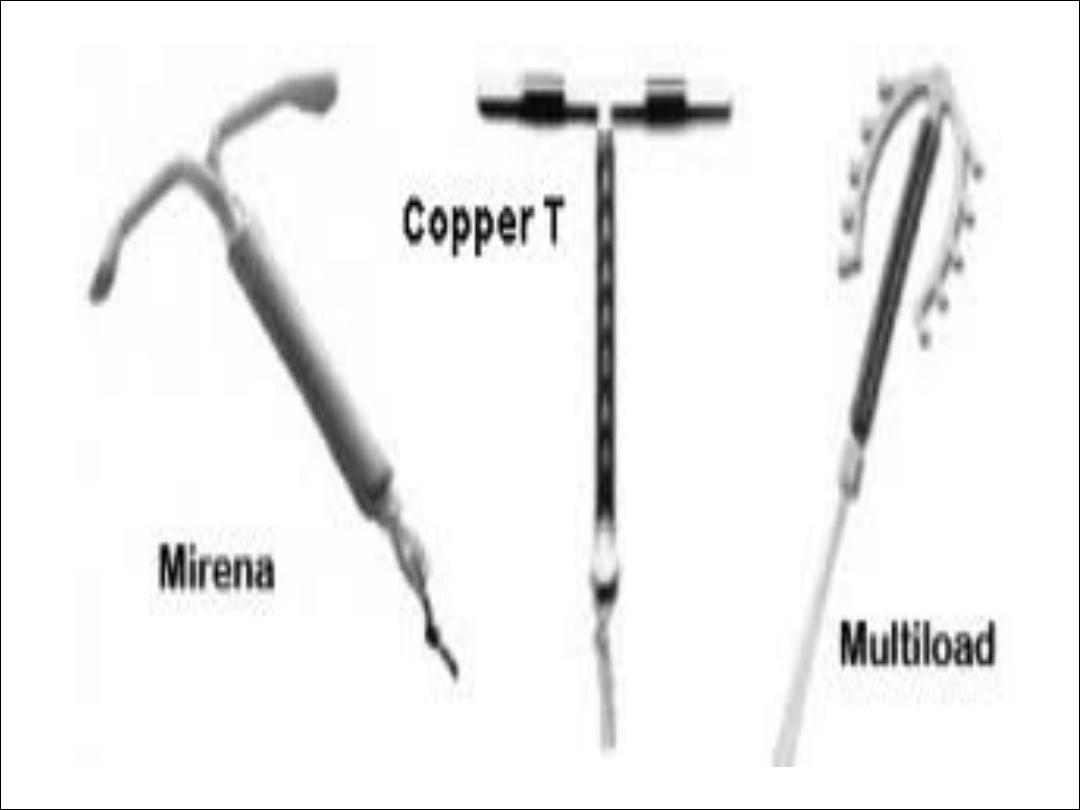
Progesterone- only contraception:
Available as oral pills, implants, long acting
injectables, & recently hormone – releasing IUCD.
Mechanism of action:
Given in high doses e.g. injectables, progestogens
inhibit ovulation. In low doses; ovulation may be
inhibited often inconsistently. By all routes
progestogens affect cervical mucus reducing sperm
penetrability & transport & all have an effect on the
endometrium which probably compromises
implantation.

S/E:
All low dose progesterone – only methods are
associated with high incidence of irregular
bleeding because ovulation inhibited
inconsistently .Also progestogens may alter the
vasculature of the endomrtium increase the
chance of bleeding.
Efficacy:
•
POP has a higher failure rate than COC.
•
Failure rates for traditional POPs vary from 0.3 to
8.0 per 100 WY. The decrease efficacy is due in
part that many women continue to ovulate & in
part because the POP has a shorter half- life in the
circulation.

Indications of POP:
1.In women in whom estrogen is absolutely or
relahvely contraindicated as women with CVS risk
factors, migraine, D.M or mild hypertension.
2. Lactahng women since estrogen impairs milk
produchon.

•
POP: UKMEC Category 3 – Risks generally outweigh
benefits
•
Current and history of ischaemic heart disease and
stroke – continuation of the method
•
Past history of breast cancer and no evidence of
recurrence for 5 years
•
HIV – on antiretroviral therapy (drug interactions)
•
Cirrhosis – severe (decompensated)
•
Liver tumours – hepatocellular adenoma and
malignant hepatoma
•
SLE – positive or unknown antiphospholipid
antibodies

•
POP: UKMEC Category 4 – Unacceptable
health risk and should not be used
•
Breast disease – current breast cancer

S/E:
1.Irregular vaginal bleeding.
2.High incidence of functional ovarian cysts due to
effect on ovarian activity.
3.Headache, nausea, bloating, breast tenderness &
mood changes, oily skin & acne.
4.Long –term risks: very small increase in the risk of
carcinoma breast after prolonged use of POP
(Depo-Provera confers a high degree of protection
against endometrial ca.).

Missed-pill guidelines for POPs
•
TRADITIONAL POPS (Micronor*, Noriday*,
Norgeston*, Femulen
•
>3 hours late (>27 hours since the last pill was taken)
•
Take a pill as soon as remembered.
•
If more than one pill has been missed just take one
pill. Take the next pill at the usual time. This may mean
taking two pills in one day. This is not harmful. An
additional method of contraception (condoms or
abstinence) is advised for the next 2 days (48 hours
after the POP has been taken).

DESOGESTREL-ONLY (Cerazette*)
•
>12 hours late
•
(>38 hours since the last pill was taken)
•
Take a pill as soon as remembered. If more than one
pill has been missed just take one pill. Take the next
pill at the usual hme. This may mean taking two pills
in one day. This is not harmful. An addihonal method
of contracephon (condoms or abshnence) is advised
for the next 2 days (48 hours aker the POP has been
taken).

Inject able progestogens:
2 types: 1. Depo-Provera (medroxy-proesterone
acetate given in a dose of 150 mg every 12 weeks.
2.Norethisterone –enanthate 200 mg given every 8
weeks.
Subcutaneous DMPA (Sayana Press) 104 mg given
subcutaneously every 13 weeks. It can be injected
into the upper anterior thigh or anterior abdomen .


S/E:
1.Irregular vaginal bleeding (treated by administration
of estrogen simply by adding the combined pills).
2.Amenorrhea.
3.Delayed fertility; it may take 1 year for normal
fertility to return following cessation of depo
provera.
•
4.Decrease bone marrow density (BMD);
Amenorrhea →hypooestrog. →↓BMD.
•
5.Weight gain
•
The average weight gain among women using DMPA
is between 2 and 6 kg.

PROGESTOGEN-ONLY IMPLANT
•
Nexplanon
•
is the only POI available in the UK. It has replaced Implanon.
•
It is a single rod which contains 68 mg of etonorgestril ENG in
a membrane of ethylene vinyl acetate. It is licensed for 3
years.
•
Nexplanon is radio-opaque
•
. Nexplanon® is a flexible rod (40 mm × 2 mm) and is inserted
•
subdermally 8 cm above the medical epicondyle, usually of
the non-dominant arm.
•
Insertion
•
is conducted under local anaesthesia using a specially
designed insertion device.

Mode of action
•
The main mode of achon is inhibihon of ovulahon .
•
Thickening of the cervical mucus prevents sperm
penetrahon into the upper reproduchve tract.
•
It also brings about changes in the endometrium
making the environment unfavourable for
implantahon .

Side effects
•
irregular bleeding and oligomenorrhoea/
amenorrhoea.
•
Weight gain .
•
Mood changes and loss of libido can occur.
•
Acne can improve, occur or worsen whilst using the
implant.
•
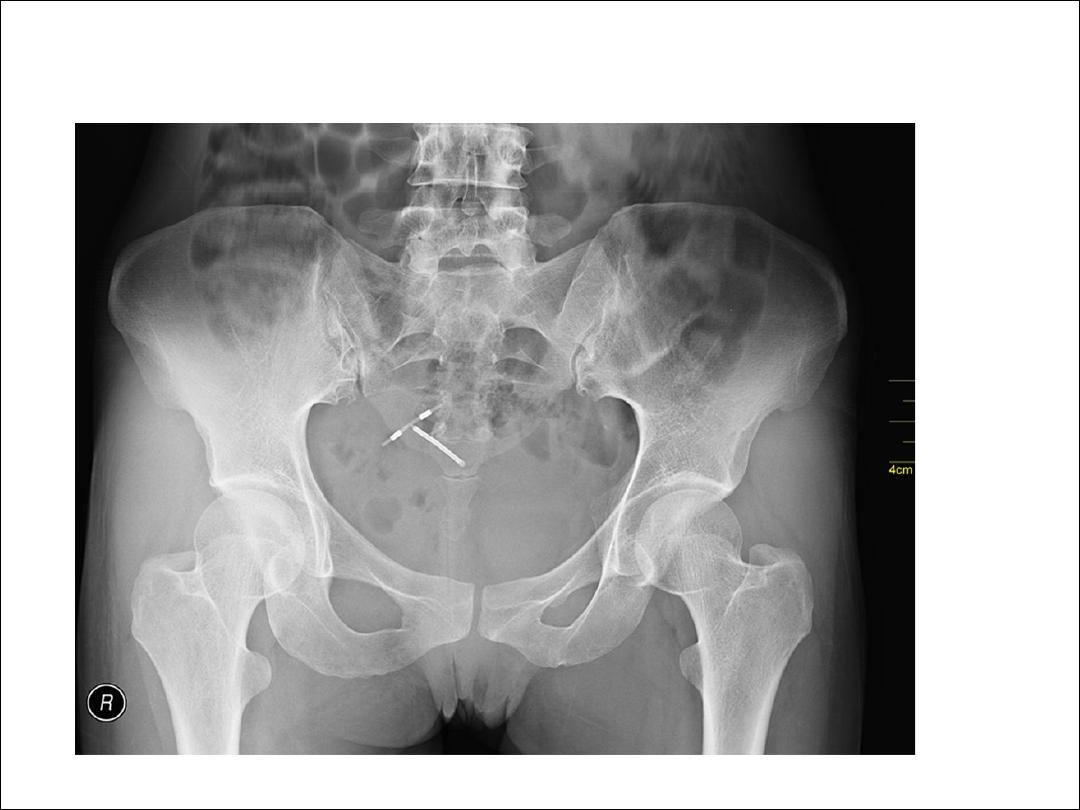
Complications with removal
•
include deeply sited, non-palpable, broken or
migrated implants. As Nexplanon contains barium
sulphate it is radio-opaque. Hence it can be identified
on X-rays. Ultrasound and MRI can also be used to
locate the implants.
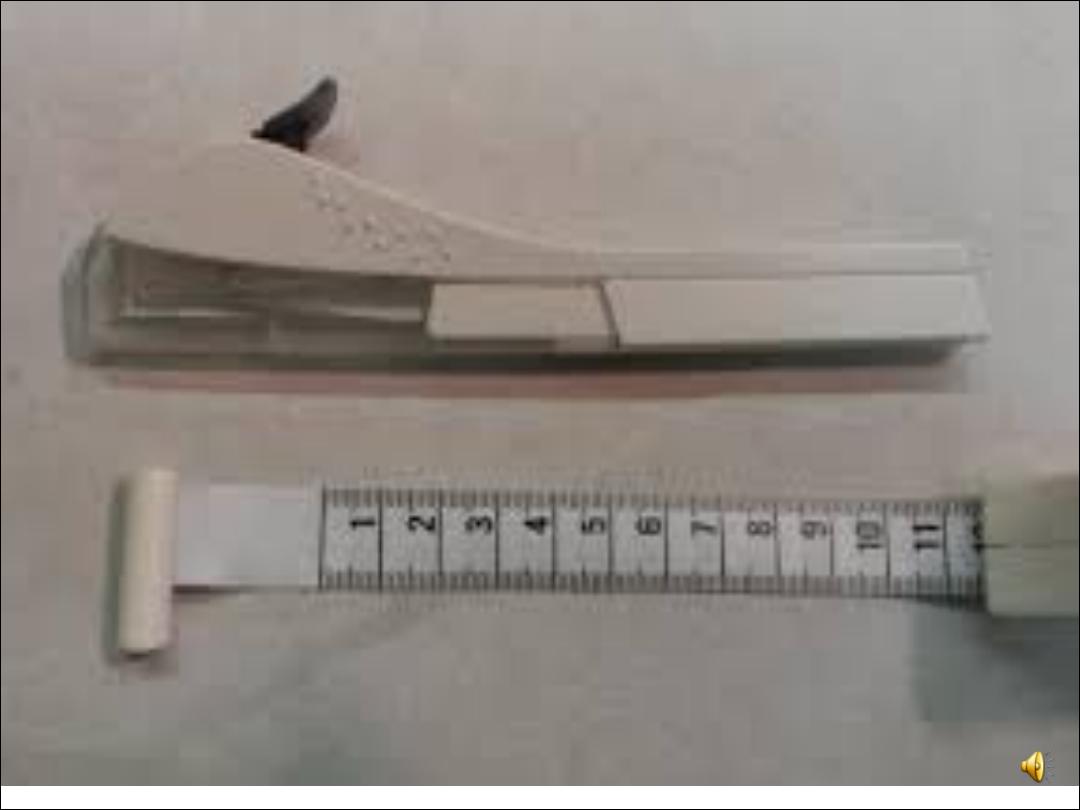


Emergency contracep9on
Is any drug or device used after intercourse to prevent pregnancy, to
prevent implantation of a fertilized egg.
1Yuzpe regimen. 2 tablets of high –dose estrogen (100ug) & 500ug
levonorgestrel repeated after 12 hours. S/E nausea & vomiting. The
dose should be given within 72 hours of coitus.
•
2.Levonorgestrel 1.5 mg once up to 3 days. Replace yuzpe regimen.
•
it works mainly by inhibiting ovulation. It prevents follicular
rupture.
•
It can be used more than once in a cycle.
•
3.IUCD is highly effective postcoital contraception with failure rate <
1%. It is used up to 5 days after coitus.or 5 days after ovulation
•
should be the first-line choice, particularly if the woman intends to
continue the IUD as long-term contraception .
•
When used for EC, its effect on the endometrium is thought to
prevent implantation if fertilization has occurred

•
4. ellaone-ulipristal acetate
•
30mg single dose tablet
•
If vomiting occurs within 3 hours, another tablet should be taken.
Ulipristal is not recommended to be used more than once per cycle
as the safety of efficacy of repeated exposure has not been
assessed
•
.
•
Is progesterone receptor modulator .
•
Its primary mode of action is thought to be inhibition or delay of
ovulation. It can prevent ovulation after the LH surge has started.
•
Effective up to 120 hours after coitus.
•
Levo norgestrel effective 69%
•
Ulipristal 85%.
•
Oral EC is much less effective than the Cu-IUD for EC and is
estimated to prevent only two-thirds of pregnancies.
•
• Effective ongoing contraception should be started after EC.

Sterilization:
•
Sterilisation is a permanent and usually an
irreversible method of contraception .
1-Female sterilization
•
It involves blocking both fallopian tubes by
laprotomy, mini-laprotomy, & more commonly by
laparoscope or
via hysteroscopy.
Bilateral salpingectomy or hysterectomy may be
preferable when there is coexistent gynecological
pathology.

Methods of tubal occlusion:
•
1.Ligation (using absorbable or non- absorbable
sutures)
•
The Pomeroy technique is the most widely used
ligation technique .
2.Electrocautery.
3.Rings.
4.Clips.
5.Laser (co2 laser).
•
6.Chemical agents instilled into fallopian tubes e.g.
quinacrine.
•
The failure rate for female sterilisation is 1 in 200.

Hysteroscopic sterilisation
•
Micro-inserts made from nickel–htanium and stainless
steel are inserted hysteroscopically through the cornual
ends of both tubes.
•
This can be performed under local anaesthesia and/or
intravenous sedahon. These generate fibrosis around the
devices and the tubes are occluded by 3 months aker the
procedure.
•
Addihonal contracephon needs to be used unhl a
hysterosalpingogram is performed at 3 months to confirm
full occlusion of the tubes.
•
It is an irreversible procedure and the failure rates
quoted are the same as for the other methods of tubal
occlusion.

Complications:
A-Immediate complications
1. Complication of G.A.
2. Vascular damage or damage to bowel or other
internal organs especially with electrocautery.
3. Gas embolism.
4. Thrombo-embolism.
•
5. Wound infection.

B- Long –term complications
•
1.Menstrual disorders. There is no evidence to
suggest that there is an increased incidence of
bleeding problems and consequently an increased
hysterectomy rate after tubal occlusion.
2.Abdominal pain & dysparunia (more common after
cautery).
3.Psychological problems & psycho-sexual problems.
4.Bowel obstruction from adhesions (very rare).

Vasectomy (male sterilization)
Division or occlusion of the vas deferens prevents the passage of
sperm using clips or diathermy or injechon of sclerosing agents
as silicone.
•
Efficacy: failure rate is 1 in 2000.
•
The procedure can be carried out under a local anaesthehc and
is safer than female sterilisahon. Following the procedure, men
should be advised to use effechve contracephon unhl two
consecuhve semen samples 4 weeks apart confirm azoospermia.
(The first sample should be taken at least 8 weeks aker surgery.)
Complicahons
A-Immediate
1. Scrotal hematoma, wound infechon.
2. Up to 2 % men fail to have azospermia in which case vasectomy
repeated.

B- Late complications
1.Antisperm antibody; it is harmless unless
restoration of fertility is desired.
2.Small inflammatory granuloma.
•
3.Cancer
•
There is no increase in testicular or prostatic
cancers following the vasectomy operation [B].
•
4.Heart disease
•
There is no increased incidence of heart disease
associated with vasectomy.