CRYSTAL-ASSOCIATED
DISEASE
•
COMMON: MSUM, CPPD,BCP.
•
UNCOMMON: CHOLESTROL, CA OXALATE,
EXTRINSIC, SEMI-CRYSTILLE, SYNTHETIC CRY.,
PLANT THORN/SEA, URCHIN SPINES.

Gout:
The pathological reaction of joint or periarticular tissue
to presence of mono sodium urate monohydrate
crystal(MSUM) .
M/F: > 5/1.
It is one of most common inflammatory arthritis of men
and of older women. The prevalance increases with
increase of serum uric acid and with age, positively
associated with body weight and with increase of
metabolic syndrome in which hyperuricemia is an
integral component.

Hyperuricaemea :
Is a serum uric acid level greater than 2 SD
above the mean for a population. 0.40
mmol/l or 6.7 mg/dl for men. 0.35 mmol/l or
5.9 mg/dl for women.
Only a minority of patient with
hyperuricemia develop gout.

Aetiology
:
Primary gout:
1/3 of serum uric acid source from diet. And 2/3
from endogenous metabolism of purines.
The level depend on the balance between
synthesis and elimination by the kidneys and
gut(2/3 renal, 1/3 gut)
Hyperuricaemia can result either from
:.

Diminished renal excretion:
-inherited renal tubular defect
-renal failure
Chronic drug therapy(thiaizides and loop
diuretics, low dose aspirin, ciclosporin
,pyrazinamide
-lead toxicity
-lactic acidosis(alcohol)

OR
Increase production:
-increase purine turnover(chroonic
myeloproliferative or lymphoproleferative
disorders(e.g polycythemia ,chronic lymphatic
lukemia)
-increase de novo synthesis
unidentified abnormality.
specific enzymatic defect(Hypoxanthine-guinine ---
-phosphoribosyl transferase(HGPRT) deficiency
-Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase over-
activity(PRPP).
Lesch
–Nyhan syndrome
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency.
.

RECENT STUDIES HAVE IDENTIFIED
POLYMORPHISMS
IN SEVERAL GENES THAT ENCODE URATE
TRANSPORTERS.
VERY RARELY (<1%) HAVE
INHERITED
DEFECT IN
PURINE METABOLISM, WHICH SUSPECTED IN:
1-UNDER AGE OF 25 YEARS.
2-RENAL CALCULI
3-STRONG FAMILY HISTORY OF EARLY-ONSET
GOUT.

INTER-RELATED ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS:
APART FROM HYPERURICAEMIA OTHER RISK
FACTORS AND INTER-RELATED CONDITIONS,
CAN ASSOCIATED WITH PRIMARY GOUT
INCLUDE METABOLIC SYNDROME (INSULIN
RESISTANCE, DYSLIPIDAEMIA,
HYPERTENSION), AND HIGH ALCOHOL INTAKE
ESPECIALLY BEER.
WHEREAS IN SECONDARY CHRONIC-DIURETIC
INDUCED GOUT, OA IS FURTHER RISK FACTOR
ESPECIALLY IN WOMEN.

Clinical feature
:
Acute gout
: almost the first attack is single distal
joint affected .The 1
st
MTP joint affected
. in more than 50% of cases. Other joints can be
affected in 1
st
attack: ankle, mid-foot, knee, small joint
of the hand, wrist and elbow.
The axial skeleton and proximal large joints rarely
affected and may be never as the first sites.
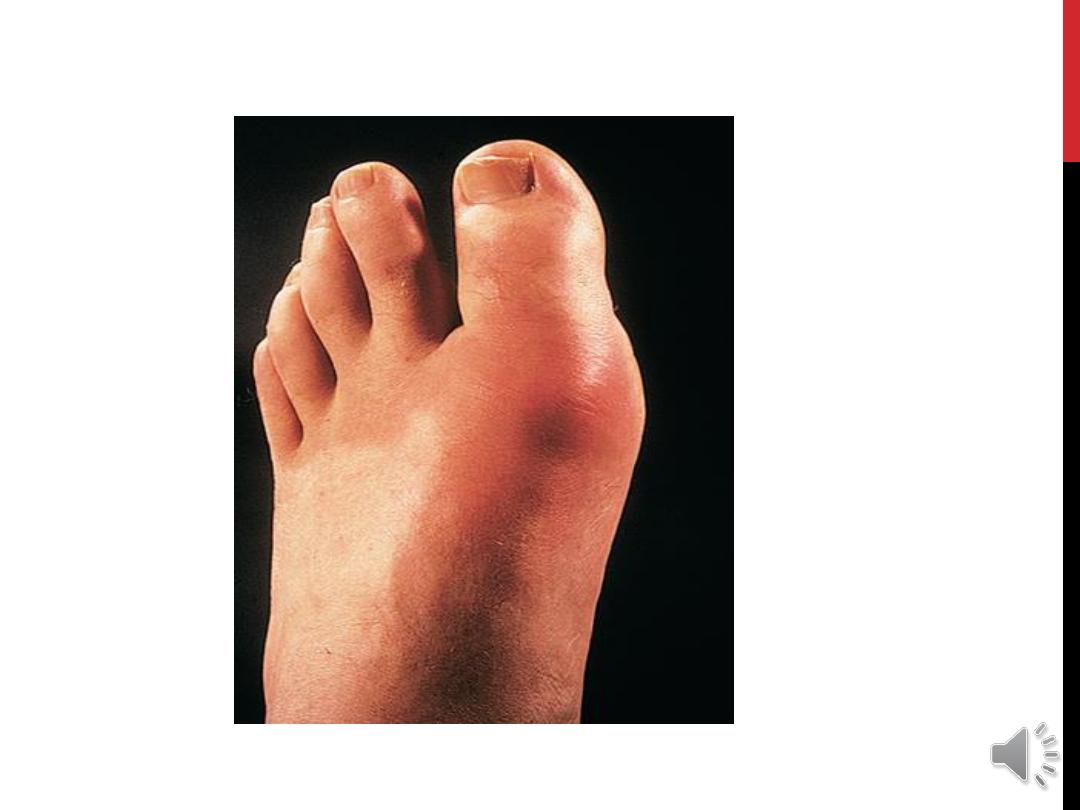

THE ONSET
IS RAPID (ABRUPT), WITHIN FEW HOURS
REACH THE MAX. SEVERITY. THE PAIN IS
OFTEN SEVERE, WITH MARKED TENDERNESS
WITH MARKED SWELLING,
REDNESS OF OVERLYING SKIN. THE ATTACK
IS SELF LIMITING USUALLY RESOLVE WITH 5-
14 DAYS WITH DESQUAMATION OF OVERLYING
SKIN. THE ATTACK IS USUALLY ACCOMPANIED
WITH FEVER, MALAISE , THE ERYTHEMA MAY
EXTEND BEYOND THE JOINT
.

The acute attacks vary in severity from milder to severe
attack. Acute attack may presents as acute bursitis,
tenosynovitis or cellulites.
Some attacks affect more than one joint, but polyarticulars
are rare.
S.T. the acute attack triggers acute phase which triggers
attacks in other joints few days later “cluster attacks”.

The main DDX :
septic
arthritis and
other crystal
deposition dis.
Sepsis mostly less abrupt in onset and progress, if untreated
, however if you in doubt, synovial fluid should be sent for
direct smear and culture.

PROVOCATIVE FACTORS
:
TRAUMA, INTER-CURRENT ILLNESSES,
ALCOHOL INGESTION, INITIATION OF S. URIC
ACID LOWERING AGENTS, DRUGS (DIURETIC ,
LOW DOSE ASPIRIN)

Recurrent
,and
chronic gout
:
However most people have recurrence, the second attack within 1
year, some people have only single attack, never to have other
attacks, and some people have the second attack after years.
With time, attacks of gout may become more frequent and involve
more joints, and to be more severe. With continued crystal
deposition leading to joint damage and chronic pain, occasionally
with marked deformity and marked functional impairment.
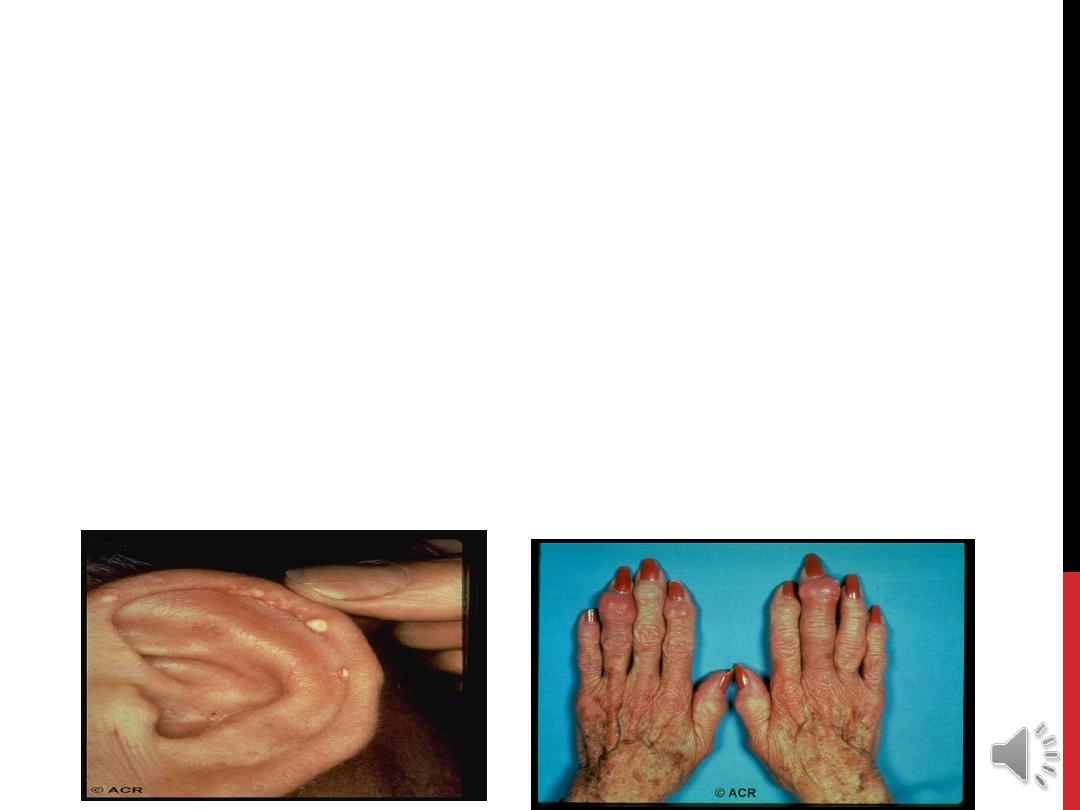
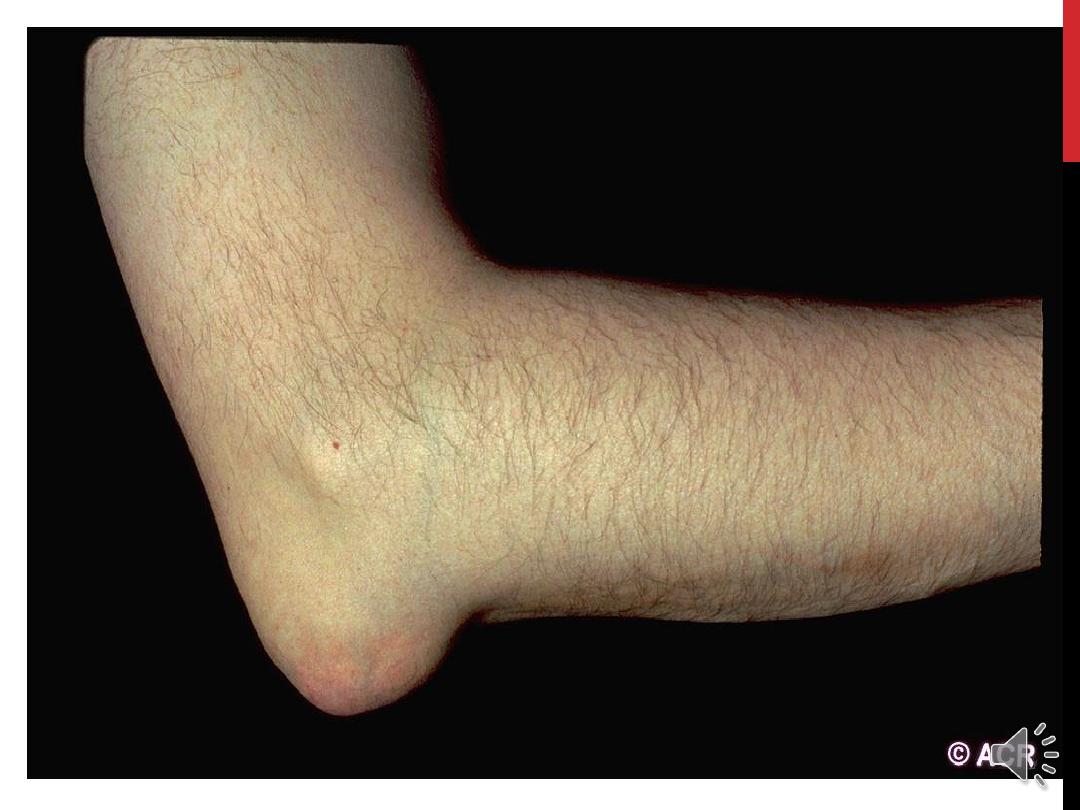
CHRONIC TOPHACEOUS GOUT
:
LARGE CRYSTALS DEPOSITION MAY OCCUR IN JOINTS
AND OTHER SOFT TISSUE FORMING IRREGULAR
SOMETIMES SMOOTH, FIRM NODULES (
TOPHI
), USUALLY
AROUND EXTENSOR SURFACE OF FINGER, HAND,
FOREARM, ELBOW, ACHILIS TENDON AND HELIX OF EAR.
THE
WHITE
COLOR OF TOPHI DIFFERENTIATE IT FROM
THAT OF RA NODULES.

s.t. the large nodule may be ulcerated with local inflammatory
signs even in the absence of secondary infection.
S.T the patient present with tophi even in the absence of
preceding attacks , this occur especially in female on
chronic diuretic therapy with nodal OA in which tophi
occur in and around osteoarthritic joint.

URATE RENAL STONE AND URINARY TRACT
MANIFESTATION
:
THE INCIDENCE OF URATE RENAL STONE FORMATION
INCREASE IN
HOT CLIMATE
,
PURINE OVER PRODUCER
,
URICOSURIC DRUGS
,
DEFECT IN TUBULAR REABSORPTION
AND DEHYDRATION.
MSUM CRYSTAL DEPOSITION IN
MEDULLA
AND
PYRAMID
IS
ANOTHER RENAL COMPLICATION LEADING TO
CHRONIC
INFLAMMATION,
FIBROSIS
,
GLOMERULO-SCLEROSIS
AND
POSSIBLE
SECONDARY PYLONEPHROSIS.

Investigation:
Diagnosis of gout is definitively established by
aspiration
and identification of MSUM in fluid from joint, bursa or
tophus.
In acute attack, synovial fluid is inflammatory, turbid, due to
elevated WBC count (>90% neutrophil).
In chronic gout, the fluid is usually
white
(due to high
crystal) , even in remission the joint fluid may have crystals.
In acute attack ,synovial fluid should be sent for
bacteriological study , because attack give similar picture of
septic arthritis and s.t. even both sepsis and crystal
deposition dis. can co-exist.

Although
hyperuricaemia
is usually present in some
stage , but by itself alone not confirm the diagnosis
(because most of the hyperuricaemic individuals are
asymptomatic) , on the other hand during acute
attack s.uric acid fall,
So normal s.uric acid level during acute attacks does
not exclude the gout.
Estimation of 24 hr urinary uric acid (on low purine
diet) to determine which patient is over producer.
Assessment of associated condition as
hypertension, lipid profile, renal function test and
blood glucose.
CBP and ESR for detection of Myeloproliferative
dise.
CRP and neutrophilia increase in acute attack.
ESR moderately rise in toph. Gout.

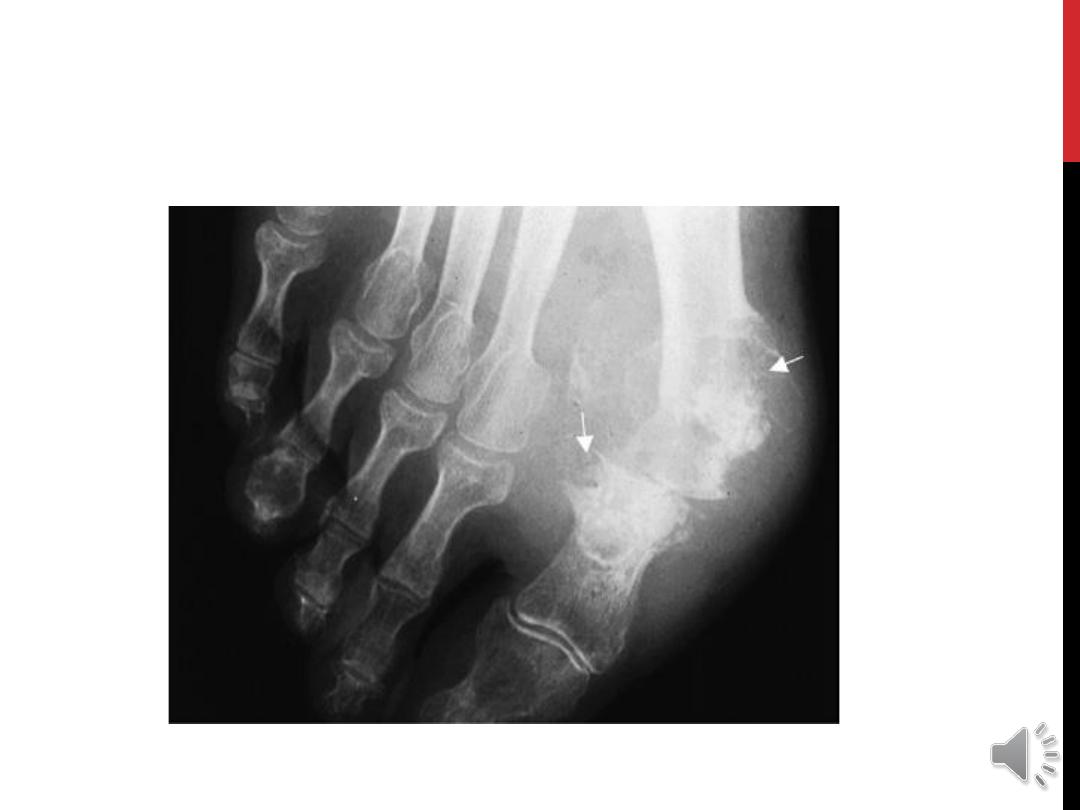
X-ray findings
:
Early attack normal apart of soft tissue swelling.
In chronic gout , joint changes of secondary OA.
Although bony tophi less common but has specific
appearance on x-
ray as Gouty erosion “
punched-out
defect
”.
Ultrasound
can detect subclinical microtophi and crystal at
1
st
MTP joint even at fist clinical presentation.