
Dr.Safaa Hussain Alturaihy
2

Nasal resistance
The nose accounts up to half of the total airway resistance.
The resistance is made by two elements
A is essentially fixed made by bone,cartilage and attached muscle
B is variable made by mucosa
The nasal resistance is high in infants who initially are obligatory
nasal breathers
Removal of nasal resistance by tracheostomy reduce the dead space
but results in a degree of alveolar collapse

Factors decrease nasal resistance
Exercise
Sympathmymetic
Rebreathing
Atrophic rhinitis
Erect position

Factors increase nasal resistance
Infective rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis
Vasomotor rhinitis
Aspirin
Ingestion of alcohol
Cold air
Supine position
Hyperventilation
Sympthatic antagonists
Factors that influence nasal resistance is nasal cycle

Nasal cycle
Demonstrated in over 80% of adults but it is more difficult to demonstrate in
children.
The cycle consists of alternate nasal blockage between passages.
Cyclical changes occur between 4-12 hours;they are constant for each person
Various factors may modify the nasal cycle include
Allergy
Infection
Exercise
Hormones
Pregnancy
Fear
Emotiom

Autonomic nervous symptom vagal overactivity cause nasal
obstruction
Drugs the anticholinergic effects of antihistamine can block the
parasympthatic activity and produce an increase of sympthatic
tone ,hence improve airway

In the inf.meatus
Opening of nasalcrimal duct
In the mid.meatus
There is bulge called bulla ethmoidalis below it there is Uncinate
process between them there is a fissure formed called hiatus
similunaris
The following sinuses open in the middle meatus
Ant. Ethmoid air cell and frontal sinus in the anterior part of hiatus
simlunaris
Maxillary sinus ostium and sometime accessory ostia open in the
posterior part of hiatus simlunaris

In
the superior meatus
Posterior ethmoid sinus,sphenoid sinus drain in the sphenoethmoid
recess which is a small depression above and behind the superior
turbinate

The middle meatus is of special significance as it contains the
ostiomeatal
complex
(OMC).
This is an anatomical area in the bony
lateral nasal wall comprising narrow, mucosal lined channels
and
recesses into which the major dependent sinuses drain.
The
OMC
acts physiologically as an antechamber for the frontal, maxillary
and anterior ethmoid sinuses.
Irritants and antigens are deposited
there and may cause mucosal oedema. As the clefts in the OMC are
narrow, small degrees of oedema may cause outfl ow tract
obstructionwith impaired ventilation of the major sinuses
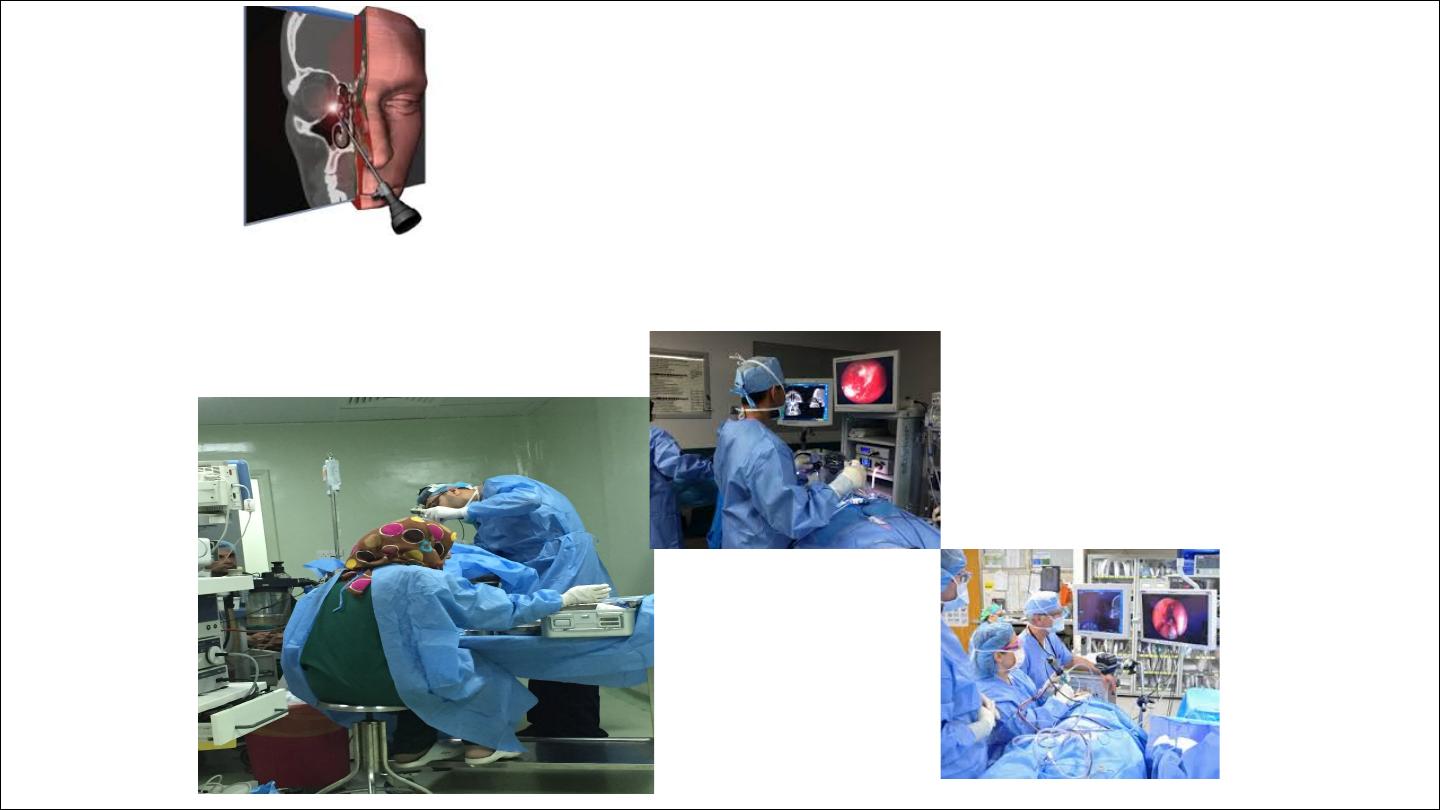
•
OMC lies in the middle meatus and
important for FESS

OMC
It is the site for the common pathway of the anterior
group of sinuses(frontal,anterior ethmoid,mawillary) structure
contribute to this area:
Uncinate process
Thin bony structure runs anterosueriorly to psteroinferioly.it
articulate with the ethmoidal process of inferior turbinate,it artly
cover the oening of maxillary sinuse
Hiatus similunaris
It is a semilunar groove which leads anteriorly to the ethmoidal
infundibulum
Ethmoidal infundibulum
It is a short passage at the anterior end of the hiatus
Frontal sinus,maxillary and anterior ethmoid drain into it
Bulla ethmoidalis
It ia a round prominence formed buldging of ethmoid sinus
Frontal recess
openng of frontal sinus
Maxillary sinus
Middle Meatus
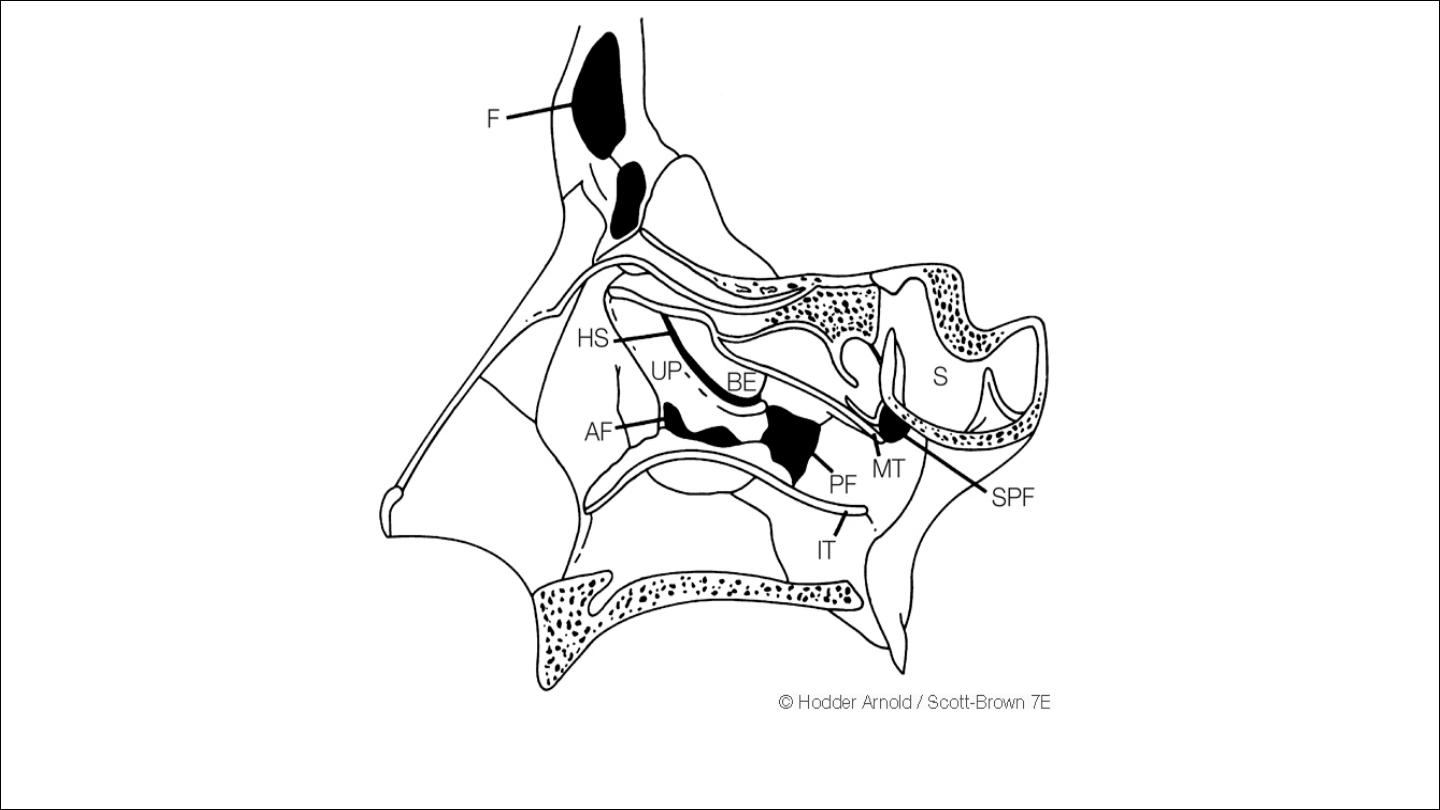
Bony structure of lateral nasal wall

The
configuration of the structure of the middle meatus are complex and
variable,in disarticulated skull ,the maxillary bone has a large opening in its
medial wall,the maxillary hiatus.
In articulated skull this is filled by adjacent bones
1
inferior: maxillary process of inferior turbinate bone
2
posterior:perpendicular plate of palatine bone
3
Anterosuperior:lacrimal bone
4
superior:UP and Bulla ethmoidalis
So portion of maxillary hiatus is left open these osseous attachment which in
life filled wth mucous membrane of
1 Mucous membrane ofMM
2Mucous membrane of maxillary sinus
3 Intervening connective tissue and membranous portion of lateral wall

Middle Meatus
Lies lateral to the MT
Structure important in the MM:
UP
HS
BE
Ethmoid infundibulum
Anterior and posterior fontanelle
:
Are membranous areas between the interior turbinate and uncinated
process,accessory ostia are found mostly in the posterior fontanelle
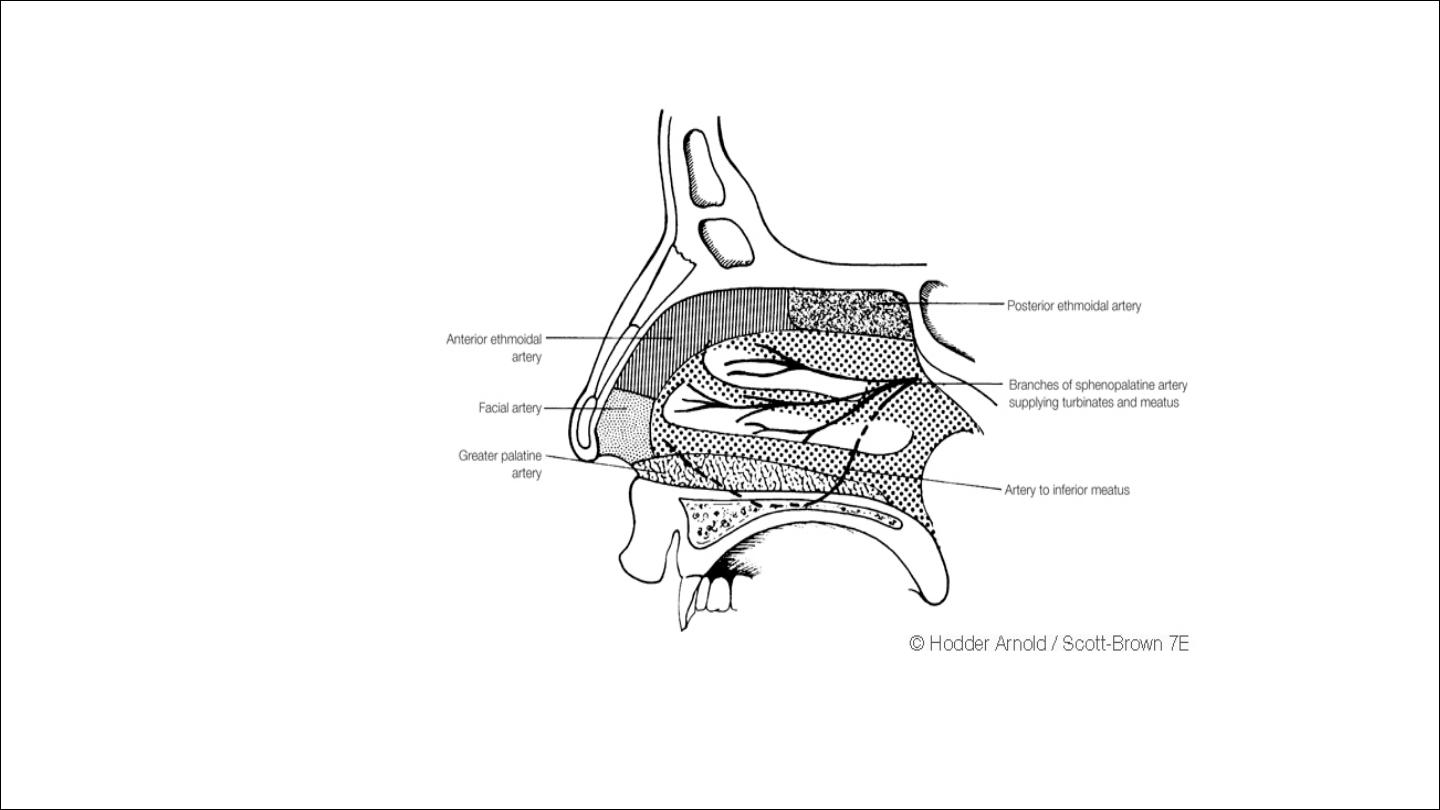
Arterial supply
external carotid artery-
facial artery-
superior labial artery
nasal branch
maxillary artery-
sphenopalatine
greater palatine artery
internal carotid artery-
anterior ethmoid artery
posterior ethmoid artery

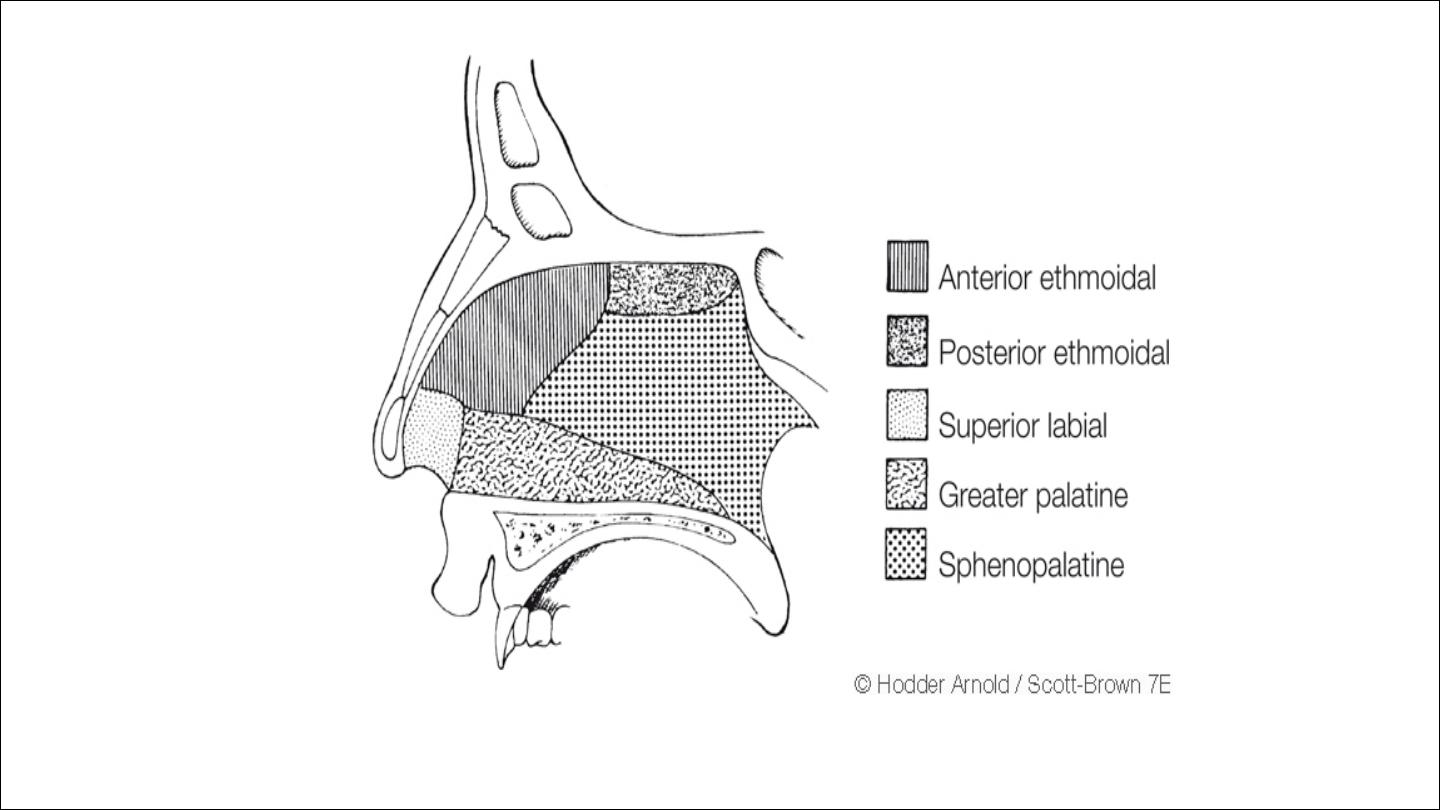
Little`s area or Kiesselbach`s plexus
It is an area in the anterior part of the septum just behind the skin
margin contain aggregation of poorly supported blood vessels
represents the most important and commonest site of epistaxis
It formed by anastamasis of
*
Septal br.of sphenopalatine artery
*
Superior labial artery
Greater palatine artery
*
*
Ant.ethmoid artery
Blood supply to the septum
Blood supply to lateral nasal wall
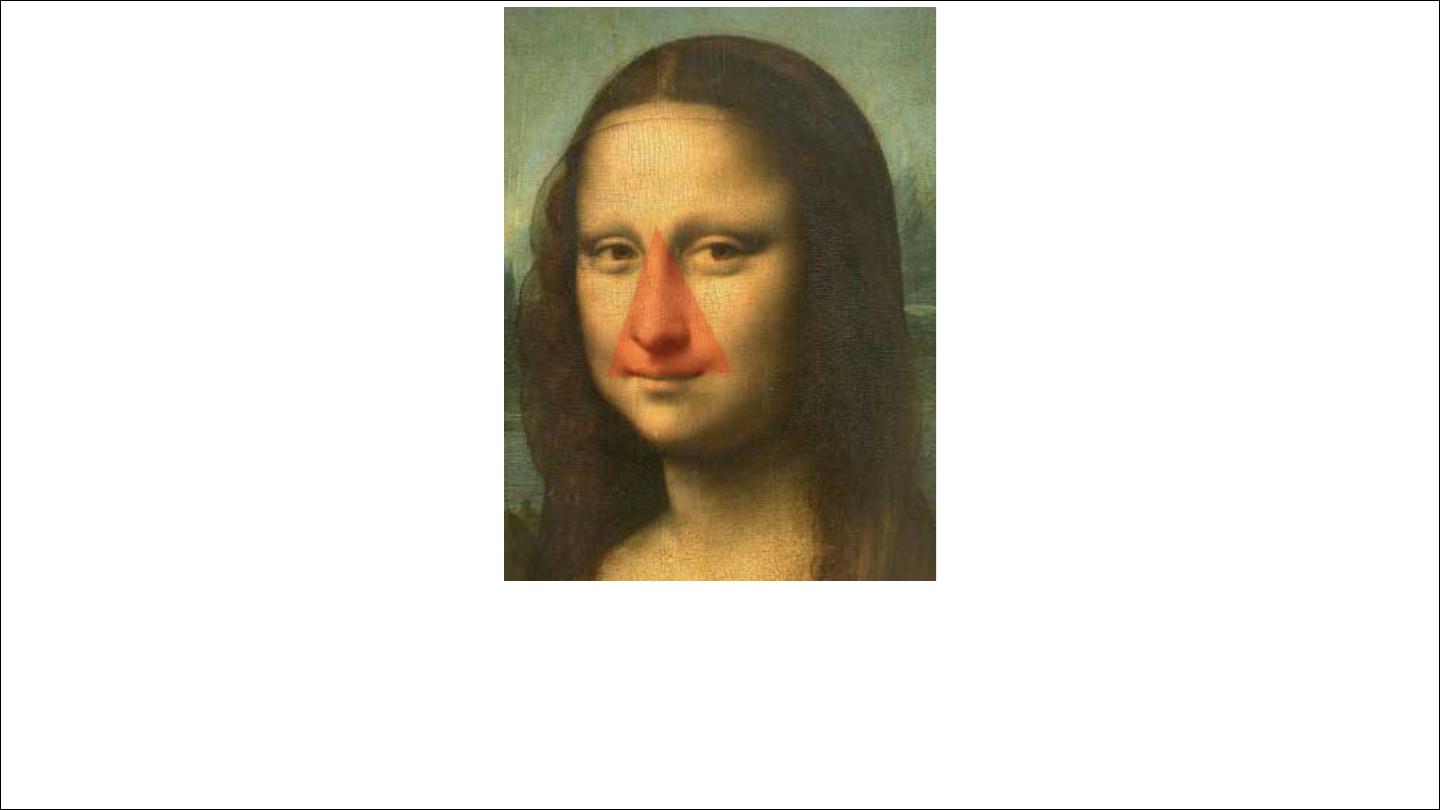

Dangerous area of the face is drained by anterior facial vein which
communicate with cavernous sinus via ophthalmic vein

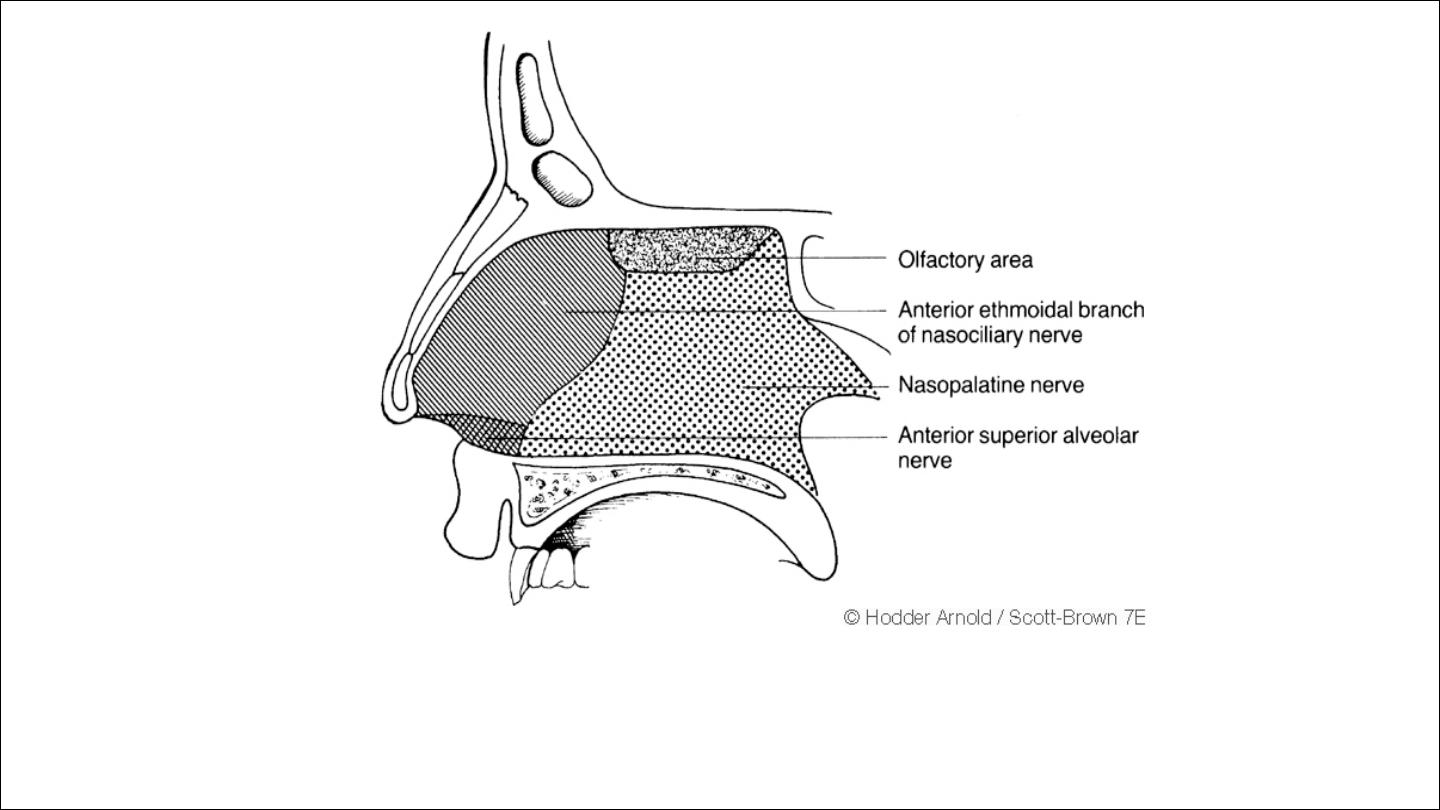
Nerve supply
Autonomic supply either
1
Sympthatic
Parasympthatic
Special sence
2
By olfactory nerve that supply olfactory mucosa which located in the
sup.portion of the nasal cavity
3
sensory supply
mainly by branches of trigeminal nerve
Anterior ethmoid nerve from ophthalmic division which has medial
branch supply ant.end of the septum and lateral branch supply mid.&sup.
Turbinate
Branches from sphenopalatine & greater palatine nerve which supply
most of turbinate
4
motor
nerves from facial neve for elevate and dilate nasal ala
Nerve supply to the septum

Thank you
