Elderly physical and physiological change
Nutritional requirement, Problems of old age, Nutrients influencing aging process.Aging is a gradual, Continuous process of natural change that begins in Early adulthood. In elderly many bodily functions begins to change. WHO defines old age as age group of 60 or above.
Old age differ in three ways:
Chronologic age:
It is based solely on the passage of time. It is persons age in
years. Health problem increases as age increases.
Biological age:
It refers to changes in body that occur as people age.
Psychological age:
It is based on how people act and feel.
Gerontology :
It is the study of aging process, include physical,
mental and social changes.
Geriatrics:
It is the branch of medicine that specializes in the care of older people, which often involves managing many disorders and problems at the same time.
Geriatricians
have studied the aging process so they can better distinguish which changes result from aging itself and which indicate a disaster.
Physical Changes:
As the cell age, they function less. Sometimes the old cells die it is called apoptosis.
The reason for cell death are
They divide only a limited number of times.
Damage to a cell causes its death.
damage caused by harmful substances like radiation, Chemotherapy drugs, sunlight.
Bones and joints
Bones tend to become less dense. Bones become weaker and more likely to break.
In women after menopause, loss of bone density speeds up because Oestrogen is produced less.
The amount of calcium in body reduced because the absorption from food decreases. And also the amount of vitamin D also decreases slightly.
The most affected bones are thing bone (femur), end or arm bones at wrist (radius and ulna), Bones of the spine (vertebrae)
The older people becomes shorter because the vertebrae becomes less dense due to loss of fluid in the cushion of tissues and becomes thinner.
Cartilage tends to thin because of the wear and tear of years of
movement. This leads to osteoarthritis.
Ligaments and Joints tend to become less elastic, making joints feel tight or stiff. This make people less flexible.
Ligaments tend to tear more easily and they heal slowly because the cells maintain ligaments and tendons become less active.
Muscles and Body fat
The amount of muscle tissue and muscle strength tend to
decrease as age increases. Muscles cannot contract quickly.
However, aging effects reduce mass and strength by about 10 to
15 % than during an adults lifetime.
By the age of 75, the percentage of body fat typically doubles when compared to adulthood. This increase the risk of health problems in old age.
A healthy diet and regular exercise can help older people minimize increase in body fat.
Eyes:
As people age increases this occurs,
The lens stiffens, making focusing on close objects harder.
The lens becomes denser, making seeing in dim light harder.
The pupil reacts more slowly to changes in light.
The lens yellows, changing the way colors are perceived.
The number of nerve cells decrease, impairing depth perception.
The eyes produce less fluid, making them feel dry.
A change in vision is the first undeniable sign of aging.
Changes in lenses of the eyes can cause the following.
Loss of near vision.
Need for brighter light.
Changes in color perception.
Appearance of eyes changes in several ways:
The whites (sclera) of the eyes may turn slightly yellow or brown.
A gray-white ring may appear on the surface of the eye. The ring
is made of calcium and cholesterol salts.
The lower eyelid may hang away from the eyeball because the
muscles around the eye weaken and the tendons stretch.
The eye may appear to sink into the head because the amount of fat around the eye decreases
Ears:
Most changes in hearing are probably due as much to noise
exposure as to aging.
Exposure to loud noise over time damages the ear’s ability to
hear.
As people age, hearing high-pitched sounds becomes more difficult. This change is considered age-associated hearing loss (presbycusis). These changes tend to speed up after age 55.
In presbycusis for old people the words become harder to understand. Gradually, hearing lower pitches also becomes more difficult.
Thick hairs may grow out of the ears.
Mouth and Nose
The ability to taste and smell gradually diminish.
As people age, the taste buds on the tongue decrease in sensitivity. This change affects mostly tasting sweet and salt more than bitter and sour.
The ability to smell diminishes because the lining of nose becomes thinner and drier and the nerve ending in the nose detoriate.
At aging the gum recedes slightly. The teeth loss can occur.
With aging the nose tends to lengthen and enlarge and the tip tends to droop.
Skin:
The skin tends to be thinner, less elastic, drier and finely wrinkled.
with aging the body produces less collagen and elastin. so, the skin tears more easily.
The fat layer under the skin thins, this causes wrinkles to appear, and tolerance to cold decreases.
The number of sweat glands and blood vessels decreases, and blood flow to deep layer of skin decreases.
The number of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) decreases. As a result, the skin has less protection against ultraviolet radiation causes large, brown spots appear on skin.
The skin is less able to form vitamin D when it is exposed to sunlight. Thus, the risk of vitamin D deficiency increases.
Brain and Nervous system:
The number of nerve cells in the brain typically decreases.
However, the brain compensates it by
As cells are lost, new connections are made between the remaining nerve cells.
New nerve cells may form in some areas of the brain, even during old age.
3.The brain has more cells than it needs to do most
activities - a characteristic called redundancy.
Nerve cells may lose some of their receptors for messages.
Blood flow to the brain decreases.
Some mental functions—such as vocabulary, short-term memory, the ability to learn new material, and the ability to recall words— may be subtly reduced after age 70.
Therefore, in older people with damaged nerves, sensation and strength may be decreased.
Heart and blood vessels:
The heart and blood vessels become stiffer. The heart fills with blood more slowly.
The stiffer arteries are less able to expand when more blood is pumped through them. Thus, blood pressure tends to increase.
An Older heart cannot speed up as quickly or pump as fast or as
much blood like younger heart.
Respiration changes
The muscles used in breathing, such as the diaphragm, tend to
weaken.
The number of air sacs (alveoli) and capillaries in the lungs decreases. Thus oxygen absorbed is less from air breathed in.
The lungs become less able to fight infection.
The lungs become less elastic.
Reproductive organ changes
Women :
The effects of aging on sex hormone levels are more obvious in
women than in men.
In women, most of these effects are related to menopause
(termination of Menustration).
The decrease in female hormone levels causes the ovaries and uterus to shrink.
The tissues of the vagina become thinner, drier, and less elastic .( called Atrophic vaginitis)
Men :
In men, changes in sex hormone levels are less sudden.
Levels of male hormone testosterone decreases, resulting in
lesser sperm production
Blood production:
The amount of active bone marrow, where blood cells are produced, decreases.
Problems may occur when the need for blood cell is increased.
Immune system :
The cells of the immune system act more slowly.
This slowdown of immune system causes:
Cancer is more common among older people.
Vaccines tend to be less protective in older people.
Infections such as pneumonia and influenza, are more common among older people and result in death more often.
Allergy symptoms may become less severe.
Psychological changes of aging
Most elderly people seems to be most vulnerable to psychological
dysfunction when they experience change.
As a person ages, the inevitability of death becomes more real and can often be a source of uncertainty and dread.
As elderly people become less physically able to engage in their daily needs and activities, they often mourn their loss of independence.
Major changes can be scary and may lead to feelings of insecurity and/or loss of self-worth.
Age related changes.
losses that occur with aging
Chronic diseases.
Increased dependency..
Function impairment.
Lack of control over the person environment .
Memory loss is one of the most common psychological effects of
aging.
Remembering everyday things become more difficult.
Memory loss affects short-term memory more than long-term.
Absent mindedness is also a characteristic psychological effect of aging.
Clear, lucid thoughts become increasingly difficult.
Older people may repeat themselves in conversation.
Bereavement is a natural response to death of a loved one. It makes a older person to crying and sorrow, anxiety and agitation, sleep problems and eating problems.
Depression:
Depression occurs 16-65% of elders living in the community.
Depression including: sleep disturbance, lake of interest, feelings of guilt, lack of energy, decreased concentration and, loss of appetite.
Losses can lead to depression.
The ability to solve complex problems decline with age.
Hearing and visual deficits related to aging process can affect learning.
The elderly is more liable to distract attention by irrelevant information and stimuli.
The social changes that come with life are change in life style,
loss of other family members, neighbors and friends.
The main social problems which confront elderly are
Social isolation
Finance
Loneliness.
Rejection and loss of purpose in life.
Deterioration in housing standard and poor nutritional
level.
Poor adjustment to role changes
Family relationship problems
Nutritional Requirements of old age:
Nutrition plays an important role in the prevention, retardation and treatment of diseases affiliated with aging.
Adequate Nutrition and a well balanced diet is of vital importance in old age so as to prevent and control the common hazards of Aging.
Many factors like poor income, decreased mobility, social isolation and depression are known to affect the health and well being of the elderly.
Energy :
Energy requirements decline with increasing age, but it is essential that the nutrient density of the diet remains the same.
An energy intake reduced to less than the energy needs of the older person can result in poor nutritional status.
Energy need in the elderly may increase due to the diseases, injuries and fractions.
Inadequate nutrition increases the frequency of the chronic
diseases and the number of deaths caused by these diseases.
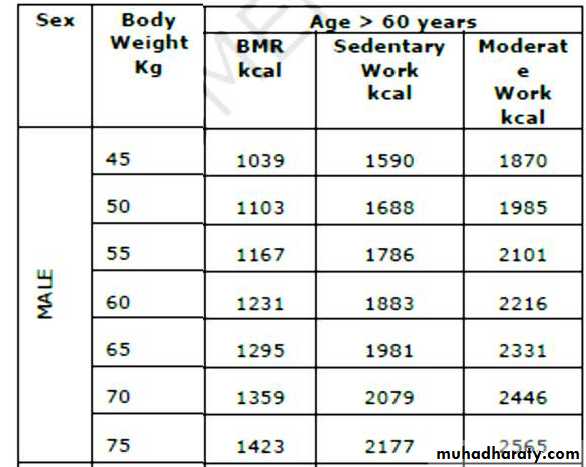
Energy requirement of Indian men (> 60 years)
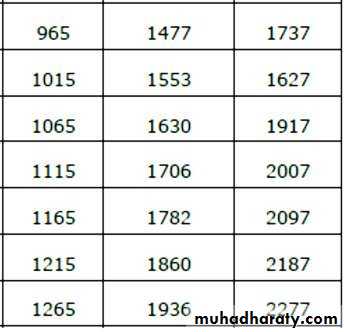
Energy requirement of Indian women (> 60 years)
Carbohydrates:
Nearly 60% of the daily energy intake is supplied from the carbohydrates.Carbohydrates consumed more than the necessary amount are
turned into fat and cause obesity.
Sugar and Starch are just carbohydrates and they may lead to
diabetes by increasing the blood sugar very quickly.
Because of these factors, the well-sugared and starchy nutrients should not be consumed excessively and cereals, cereal flours its brans are not separated, fruits and vegetables should be consumed as sources of carbohydrates.
Protein :
The recommended intake is difficult to apply to all older people but a figure of 0.75-0.8g of protein per kilogram of body weight should meet all requirements.
It is essential that any older patient with a medical condition requiring an increase in protein is provided with an adequate intake.
In conditions like chronic kidney disease where the daily protein intake should be decreased, the daily requirements must be determined by the experts on the basis on the condition of the disease.
Fats:
Minimum 25% of the daily energy intake should be provided from fats.
Avoid excessive consumption. Because it causes obesity, cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Solid fats like margarine and butter should be avoided because
that causes hypertension, high cholesterol and CVD.
Sufficient intake of omega -3 fatty acids helps in visual acuity, Hair loss, tissue inflammation, improper digestion, poor kidney function and mental depression.
Water :
The body contains 60% water in adult period this amount reduces to 50% in the elderly.
The reduction in body water may create risk.
The reduction of sense of thirst in the aging period may cause failure in the recovery of lost water. This causes serious health problems which may result in death.
In old age at least, 8-10 glasses of water (1500ml) per day should
be consumed.
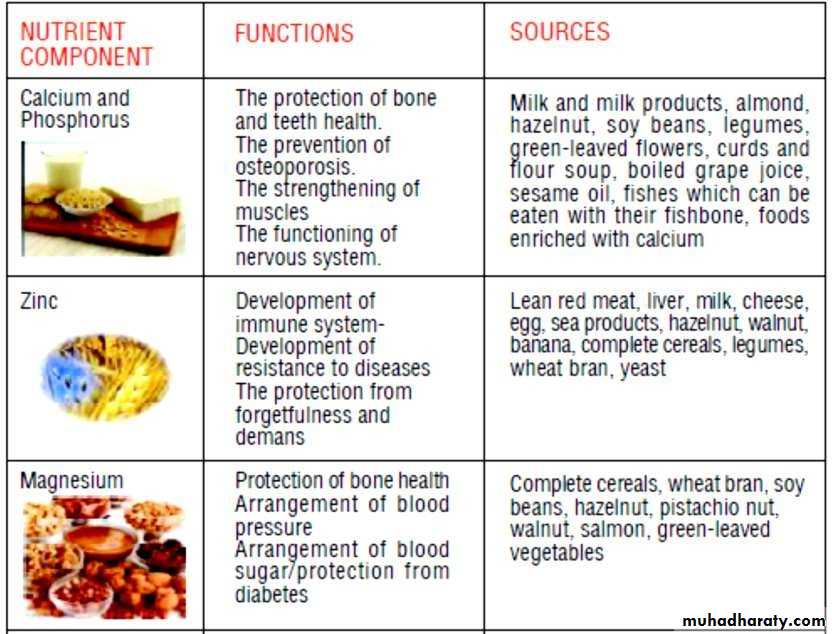
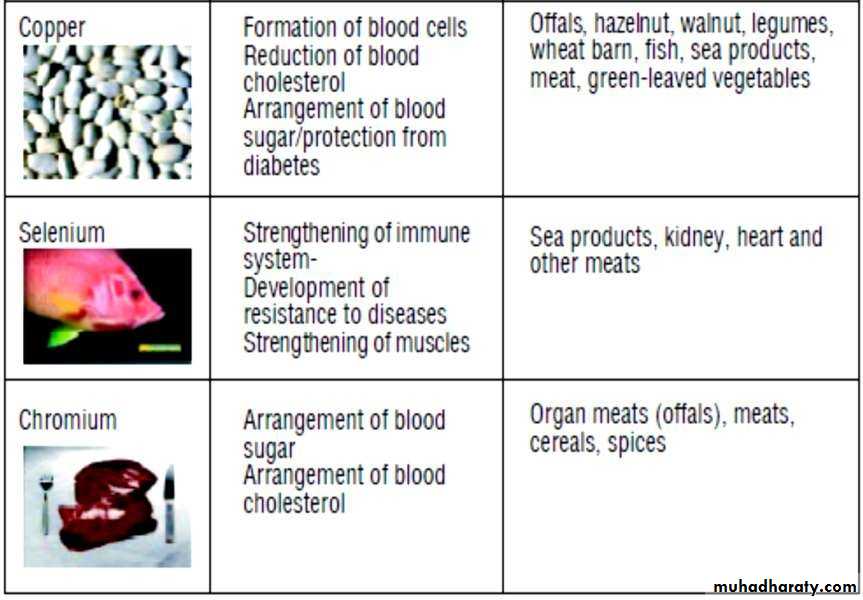
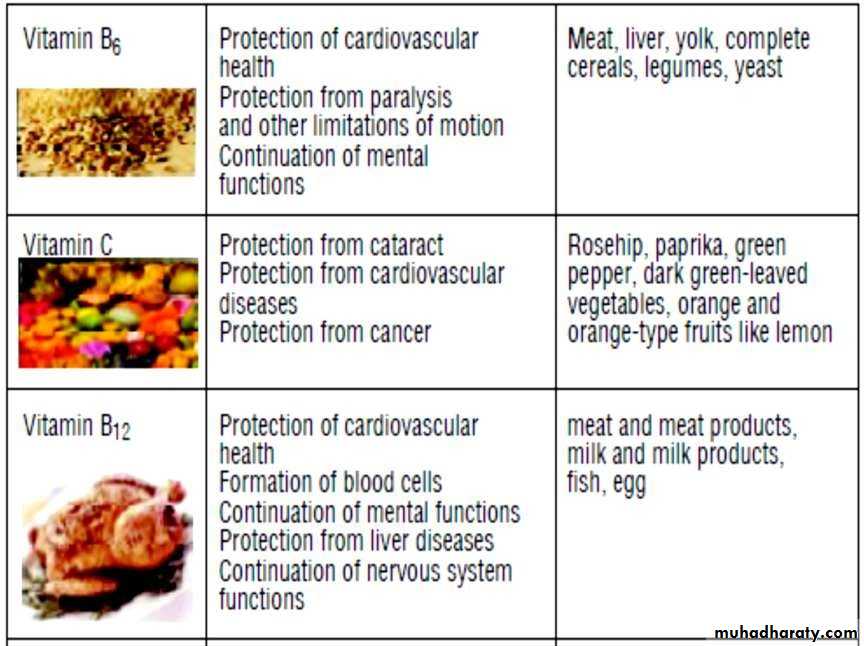
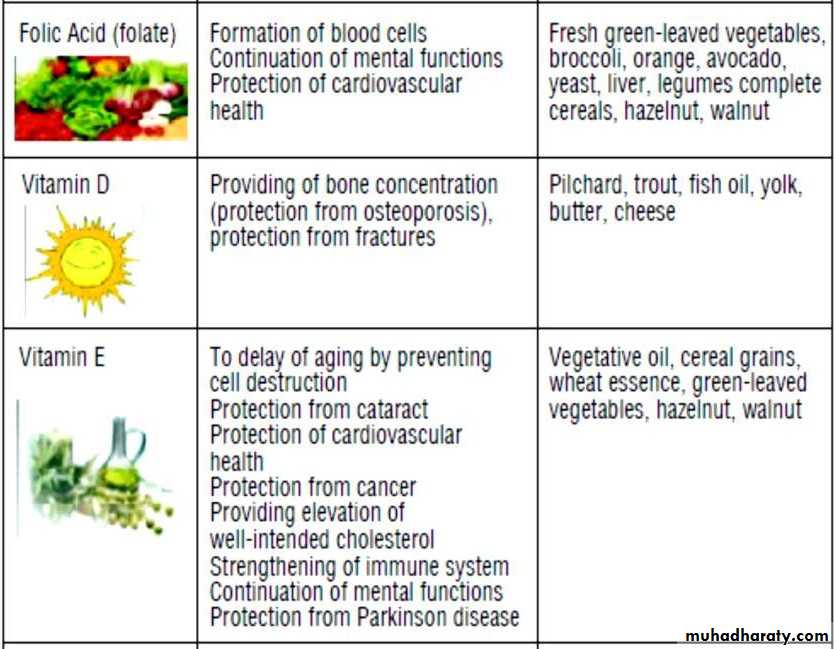
Nutrients help in elderly their function and sources
Recommended Nutrient intake for Older persons by WHO
Protein : 0.91 g/kg/ day.Fat : 30% E for sedentary older persons
35% E for active older persons.
Saturated fat should not exceed 8% of E
Calcium : 800- 1200 mg /day
Iron : 10mg/day
Selenium : 50-70 microgram/ day
Zinc : Men - 7 mg/day , women – 4.9 mg/day.
Riboflavin : Men – 1.3 mg , Women – 1.1 mg
Folate: 400 microgram/day.Vitamin B12: 2.5 microgram/day.Vitamin C: 60-100 mg/day.Vitamin A: 600-700 microgram retinol equivalents /Day.Vitamin D: 10-15 microgram/day.Vitamin E: 100-400 IU/day.
Problems in old age:
ObesityCardiovascular diseases.
Hypertension
Diabetes mellitus
Osteoporosis
Cancer
Under nutrition and Malnutrition.
Anorexia
Vision problems.
Gastro-intestinal problems.