Diabetes in children L5
Diabetes mellitus in children (type 1 DM ):Definition :Common chronic metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical features .
Etiological classification of DM
1-Type 1 DM (beta cell destruction )
Immune mediate
Idiopathic
2-type 2DM (insulin resistance &deficiency )
Typical
Atypical )
3-enetic defect of beta cell
Mody (maturity onset diabetes of young )
Wolfram syndrome (DDMOD diabetes mellitus ,diabetes insipidus optic atrophy &deafness)
Mitochondrial DNA mutation
Thiamine responsiveness megaloplastic anemia with diabetes
4-drug or chemical induced
L-asparginase
Anti rejection .cyclosporine …..
Phenytoin
Diazoxide
Beta blockers
α interferone
5- disease of exocrine pancreas
Cystic fibrosis
Trauma to pancreas
Pancreatitis
6-infection (CMV ,Rubella .HUS)
7-genetic syndromes
Prader willi syndrome
Downs syndrome
Turner syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome
8-Gestational diabetes
9-Neonatal diabetes
Transient
Permanent
Type 1 diabetes mellitus :
Insulin dependent or juvenile diabetes characterized by low or absent level of endogenously produced insulin & by dependence on exogenous insulin ; insulin act on movement of glucose into cells to subdue hepatic glucose production & halt movement of fatty acid from periphery to liver
the natural history include 4 stages :
Preclinical Beta cell autoimmunity with progressive defect of insulin production
Clinical diabetes
Transient remission ,honeymoon period
Established diabetes
Its account about 10 % of cases of diabetes affecting >10 million people in the world ,over all incidence of type 1 DM varies from 0.7/100 000 /year [in Pakistan to 40/100 000/year In Finland. Girls and boys are equally effected ,no apparent correlation with socioeconomic status .
Age incidence ,2 peak group 5-7 yrs and time of puberty .there is a familial clustering inT1DM with prevalence in sibling approaching 6% but in general population is 0.4%in US .
HLA system mostly associated with DR3/4-DQ2/8
Natural history of diabetes involve some or all of the following stages :
Initiation of autoimmunityPreclinical of autoimmunity with progressive loss of beta cell function
Onset of clinical disease
Transient remission
Established disease
Development of complications
nfluence of high insulin vs low insulin on some metabolic processes in liver, muscle &adipose tissues :
High plasma insulin(postprandial state )
Low plasma insulin (fast state )
Liver
Glucose uptake
Glycogen synthesis .lipogenesis
Absence of ketognesis
Glucose production
Glycogenolysis
Gluconeogenesis
Muscles
Glucose uptake
Glucose oxidation
Glycogen synthesis
Protein synthesis
Absence of glucose uptake
Fatty acid &ketone oxidation
Glycogenlysis
ProteolysisAdipose tissues
Glucose uptake
Lipid synthesis
Absence of glucose uptake
Lipolysis & fatty acid release
Diagnosis
Impaired glucose toleranceDiabetes mellitus
Fasting glucose 100-125mg/dl
Or
2hrs plasma glucose during OGTT more or equal 140mg/dl but <200mg/dl
Symptoms of diabetes +random plasma glucose more or equal to 200mg/dl
Or
Fasting (at least 8 hr )plasma glucose more or equal to 126mg/dl
or
2hrs plasma glucose during OGTT more or equal to 200mg/dl
Or HA1c >or equal to 6.5%
DM should suspected in any child with polyuria & dehydration ,poor weight gain ,hyperglycemia ,glucosuria & ketonuria
Random serum sugar >200mg/dl with typical symptoms with or without ketonuria is diagnostic
Initial management of type1 DM
Most newly cases of DM are alert and able to eat and drink and can manage with subcutaneous insulin alone .
iv fluid required if the child vomiting or dehydrated . intensive educational programme is needed for the parents and child to cover
1.Basic understanding of pathophysiology ofDM
2.Insulin injection technique &sites
3.Diet , regular meal & snacks ,reduced refined CHO .healthy diet no >than 30% fat intake
4-match food intake with insulin &exercise
5-blood glucose monitoring
6-recognition and treatment of hypoglycemia
7-the psychological impact of lifelong condition with serious short & long term complications
INSULIN THERAPY
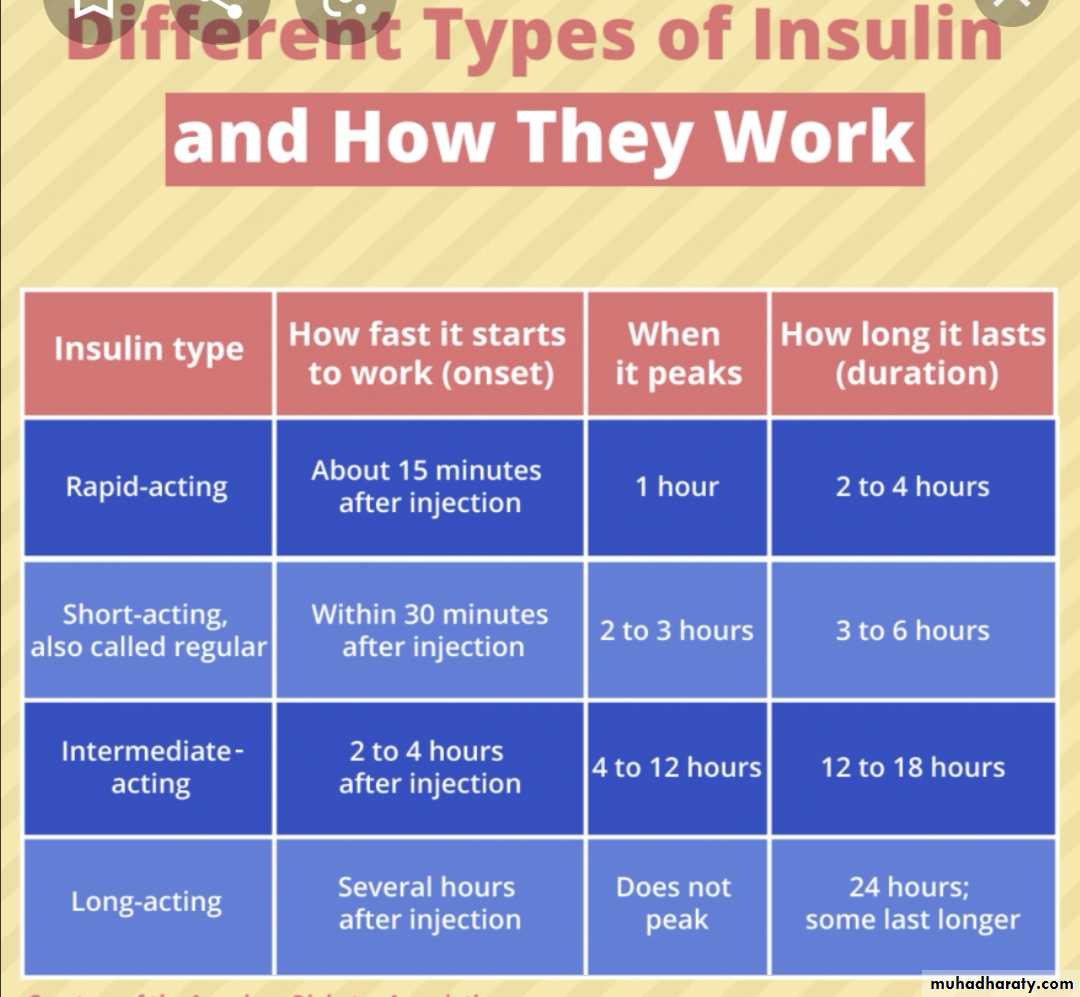
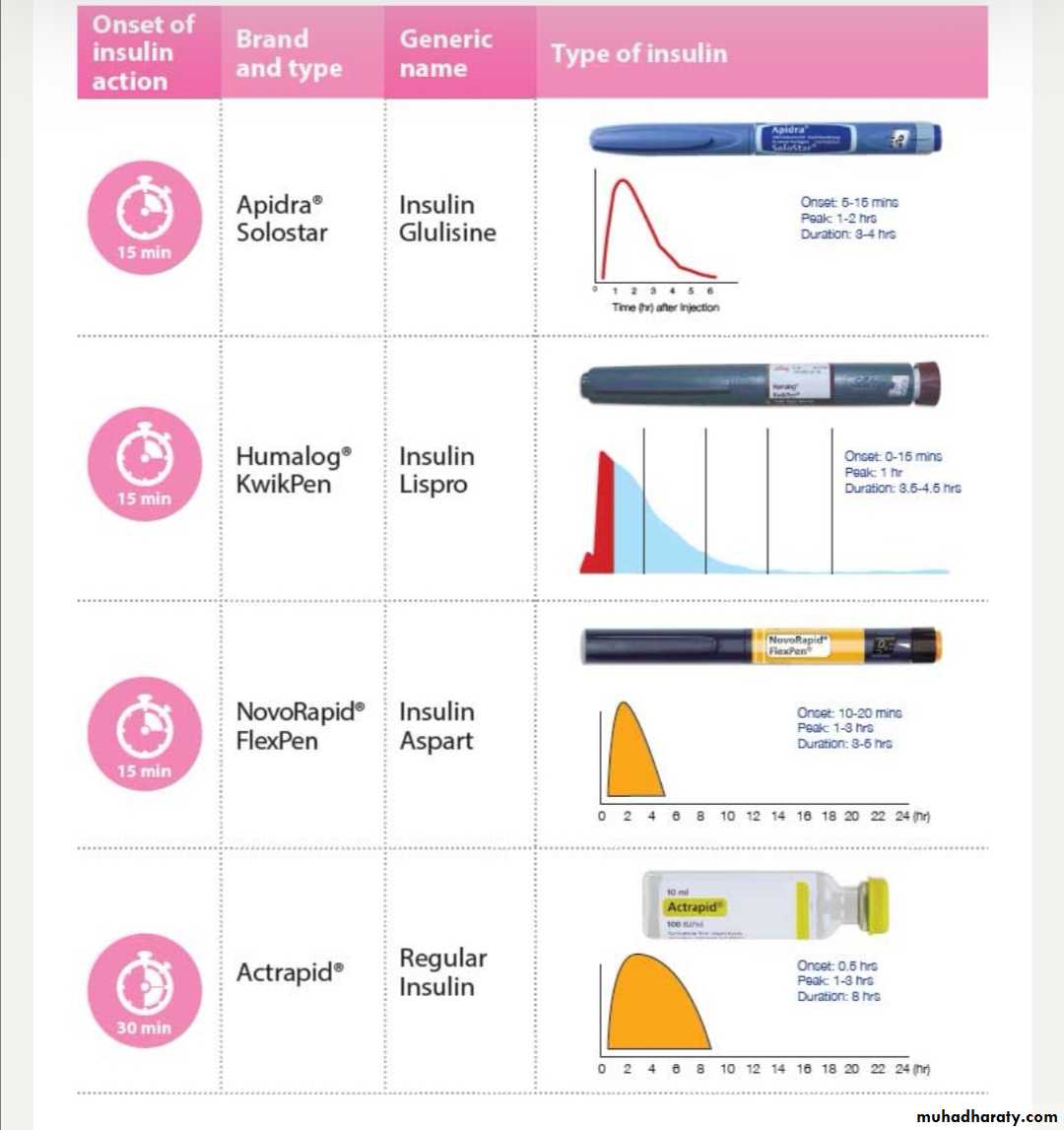
Most insulin used in Iraq for children is humen with concentration 100U/ml with different types includes:
human insulin analogues . rapid acting like lispro &aspart within few minutes
short acting soluble insulin onset 30-60 min. peak 2-4 hrs. duration up to 8 hrs. given 15-30 min.before meal
intermediate acting insulin onset 1-2 hrs . peak 4-12 hrs( insulin with protamine )
mixed short & intermediate 30/70 mixtard
very long acting insulin analogues e.g glargine (lantus)
teenager preferable to use bolus & basal (basal .lantus at night and short acting before each meal )
Factors affecting blood glucose
Increase blood glucoseDecrease blood glucose
omission of insulin
refined food
illness
menstruation
growth hormone
corticosteroids
sex hormones at puberty
stress of an operation
insulin
exercise
anxiety (marked )
some drugs
DIET : healthy diet recommended with high complex CHO &relatively low fat content ,diet should be high in fiber
Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA :
End result of metabolic abnormalities result from sever deficiency of insulin or insulin ineffectiveness. It is occur in 20-40 % of children with newly diagnosed diabetes & DKA consider when serum sugar >300 mg .acidosis .+S/S of DM with ketosis .Classification of DKA
Normal
Mild
Moderate
Sever
Co2)meq/l venus
20-30
16-20
10-15
<10
pH venous
7.35-7.45
7.25-7.35
7.15-7.25
<7.15
Clinical
No changes
Only fatigue
Kussmaul ,oriented but sleepy
Kussmaul or depress respiration ,sleepy to coma
Treatment
Time
Therapy
Comment
1st hr.
10-20ml/kg IV bolus 0.9%NaClor LR
Insulin drip at 0.05-0.1unit/lg/hr
Volume expansion ,NPO monitor I/O,use flow sheet prepare manitol 1g/kg at bed side if cerebral edema developed
2nd hr. until DKA resolution
0.45% Nacl plus continue insulin drip
20meq/l KPhos &20 meq/l K Ac….5%glucose if blood >250mg/dl
85ml/kg +maintenance -bolus
IV rate =
23 hr
If K <3meq give 0.5-1 meq as oral solution or increase iv K to 80meq/l
Maintenance =100ml/kg for 1st 10 kg+50ml/kg for 2nd 10 kg +25 ml/kg for remaining kg
Initial bolus fluid consider part of total fluid allowed & subtracted before calculating iv rate
Sample calculating for 30 kg child
1st hr 300 ml iv bolus 0.9% NaCl or LR2nd & subsequent hrs= (85ml × 30)+1750ml -300ml =
23hr
= 175 ml
hr
I/O input output, NPO nothing by mouth ,KAc potasium acetate ,kphos=potasium phosphate ….LR lactated Ringer..NaCl sodium chlodide
Long term management of DM
Aim of long term management :
normal growth & development
normal home & school life as possible
good diabetic control through knowledge & technique
encourage children to be self- reliant
avoidance of hypoglycemia
Assesment of a child with DM summary
Assessment of diabetic control :any episode of hypoglycemia
school absence
interference with normal life
HbA1C result
Insulin regimen ---appropriate
Diet –healthy diet
General overview :
Normal growth and pubertal development , ovoid obesity
Blood pressure checking
Renal for microalbuminuria
Eye ---cataract
Feet –care
Screening for celiac and thyroid disease
Knowledge &psychological aspects
Good understanding of diabetes
Becoming self-reliant but appropriate supervision at home
Taking exercise ,sport?
Smoking ???
Is hypo treatment readily available ?
What shall I eat?
Breakfasta bowl of cereal with semi-skimmed milk
wholegrain toast with spread and/or jam
yogurt and fruit
a cereal bar and a glass of milk.
Lunch
a chicken or ham salad sandwich...
a small pasta salad...
soup and a roll...
...with a piece of fruit and a yogurt.
Dinner
salad
roast chicken with potatoes and
vegetables
beef stir fry, vegetables and rice
chicken tortillas and salad
salmon and noodles
curry and rice
What sort of snacks do I need to eat?
The healthiest snack choice is definitely a piece of fruit, but rice cakes, crackers, a couple of biscuits, a small bag of crisps, a cereal bar, or a yogurt are good snack choices too.
Foods to avoid for a type 1 diabetes diet include
sodas (both diet and regular),
simple carbohydrates - processed/refined sugars (white bread, pastries, chips, cookies, pastas),
trans fats (anything with the word hydrogenated on the label), and high-fat animal products.