Introduction to Neuroanatomy
Done by
Dr. Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi
Clinical Radiology CABM ,DMRD,MBCHB,
1
المرحلة
:
الثانية
المادة
:
التشريح
ج
امعة ذي قار
كلية الطب
Part 1

Objectives:
2
By the end of this session you should be able to:
● List the anatomical terms used in neuroanatomy and the
difference in their use in gross anatomy and neuroanatomy.
● Describe the planes of sections.
● Describe the anatomical divisions of the nervous system.
● List the neuronal and non-neuronal cells of the nervous system
and their major functions.
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
2
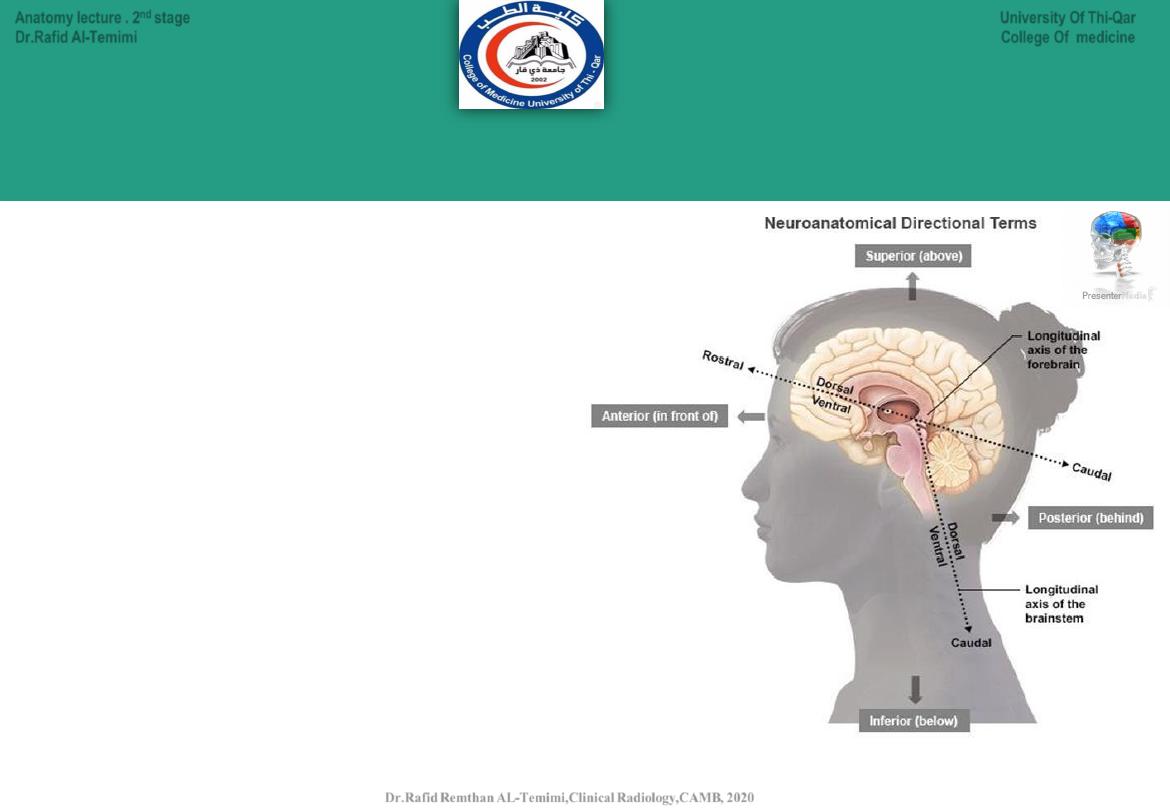
Anatomical Terms in Neuroanatomy:
● The terms
:anterior, posterior,
superior, and inferior are used in
reference with the body axis
(which doesn’t bend).
● The terms
:
dorsal,
ventral,
rostral, and caudal are used in
reference with the long axis of
the
nervous
system
(which
bends).
3
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
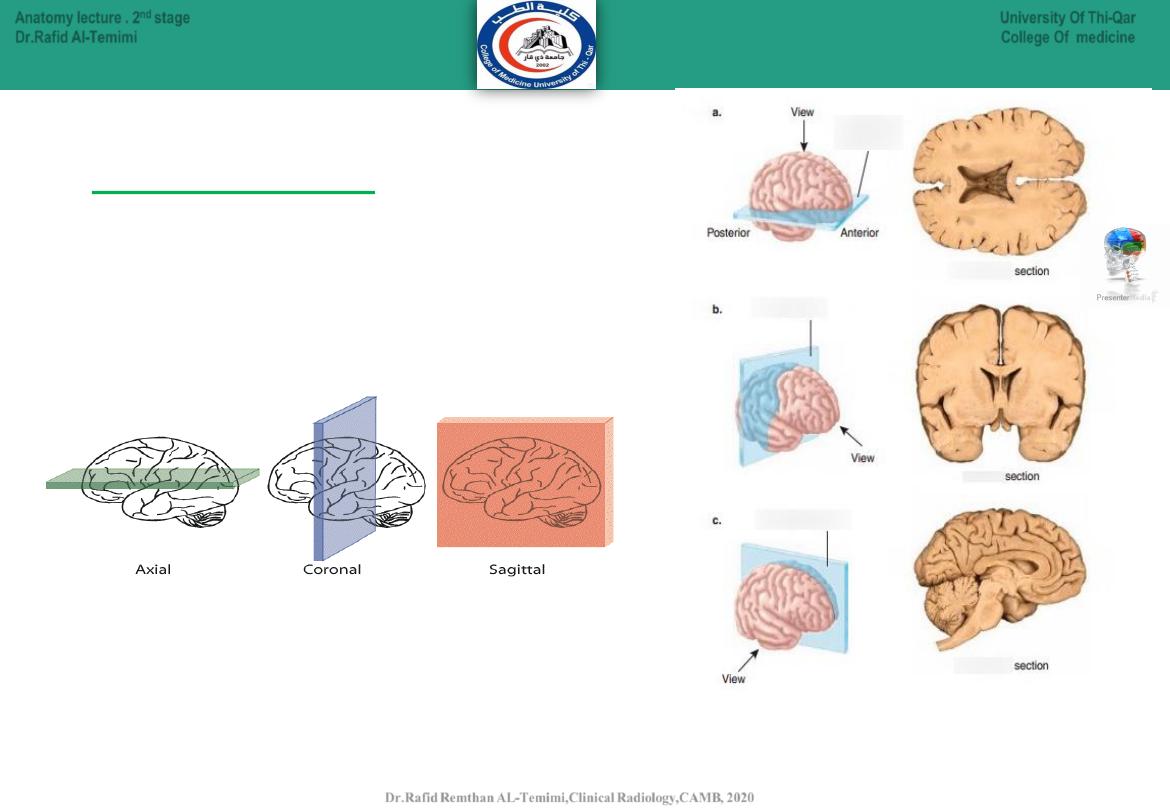
4
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
● Horizontal (axial):
divides into above and
below.(Transverse)
● Coronal (frontal):
divides into front and back.
● Sagittal:
divides into twos sides.
Anatomical planes:
Corona
l
Corona
l
axia
l
axial
sagittal
sagittal
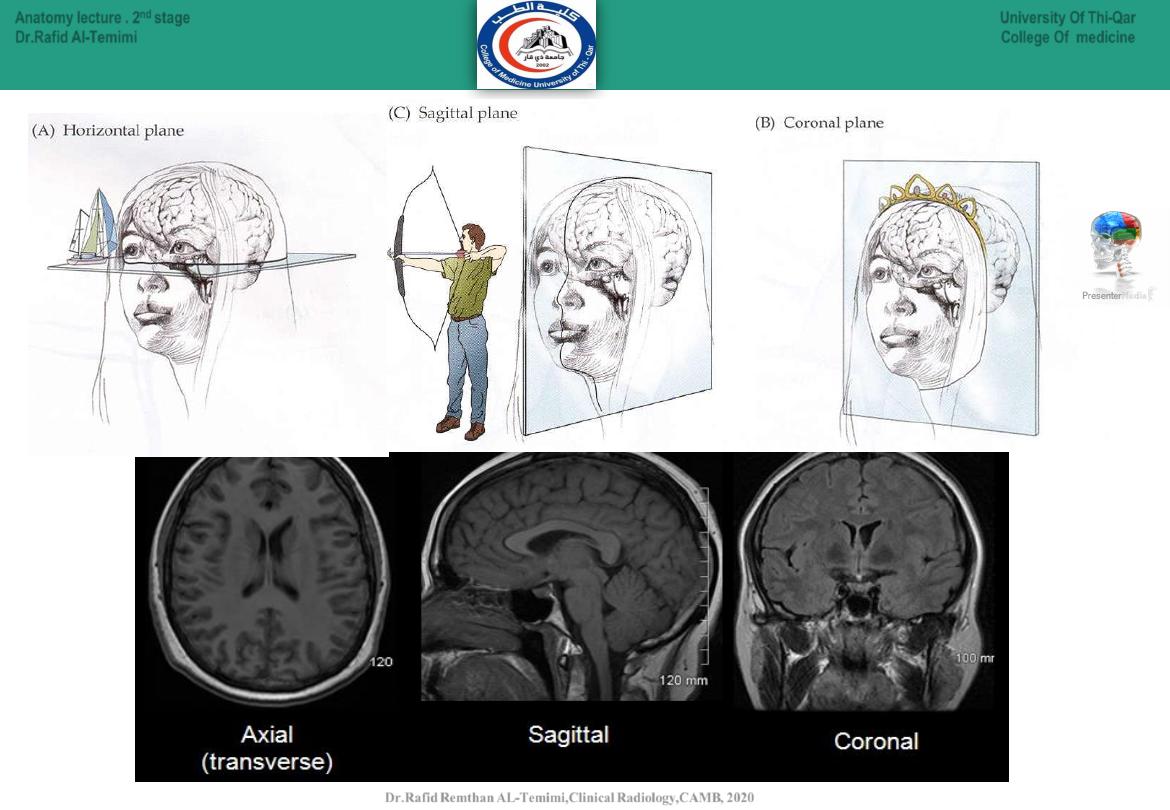
5
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
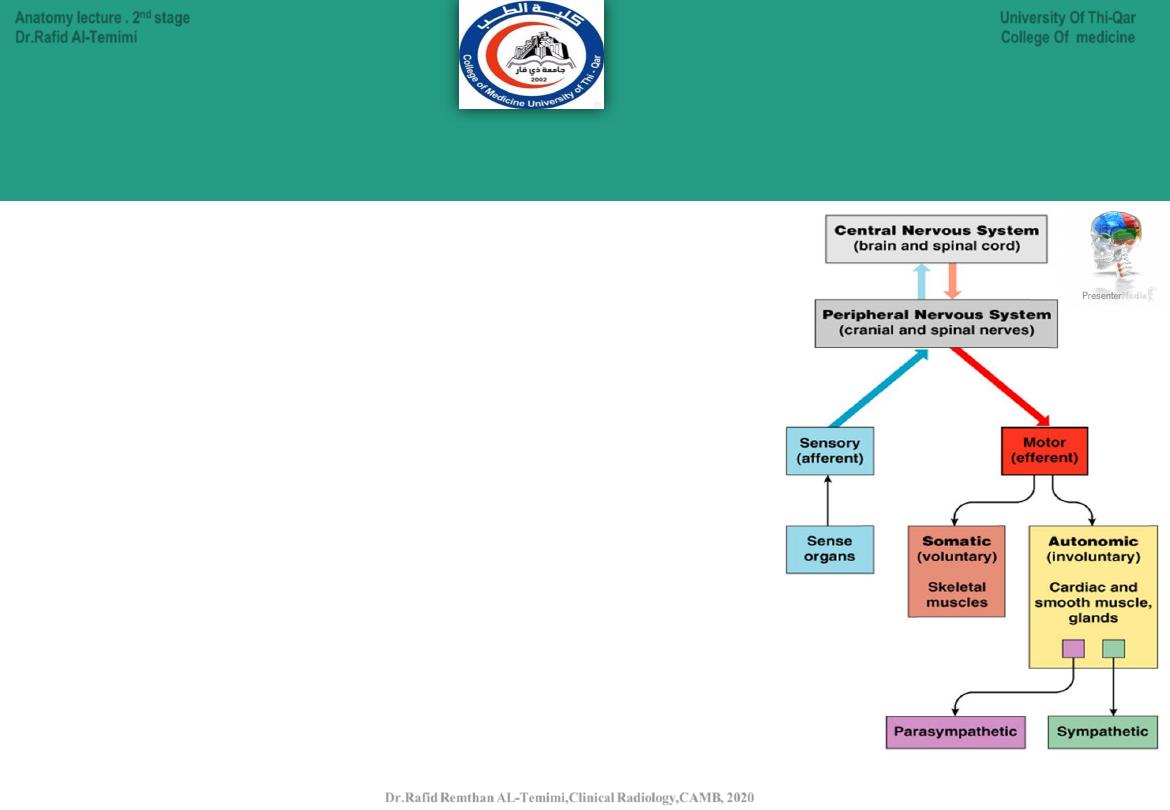
Anatomical Divisions of the Nervous System
There are Two Anatomical Divisions:
•
Central nervous system (CNS):
Brain
Spinal cord
•
Peripheral nervous system (PNS):
•
All the neural tissue outside CNS
•
Afferent division (sensory input)
•
Efferent division (motor output)
•
Somatic nervous system
•
Autonomic nervous system:
Sympathetic ANS
Parasympathetic ANC
6
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
The
central nervous system
(CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal
cord. These neurons
cannot
regenerate if damaged.
Dr. Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi ; Clinical Radiology ( CABM) 2020
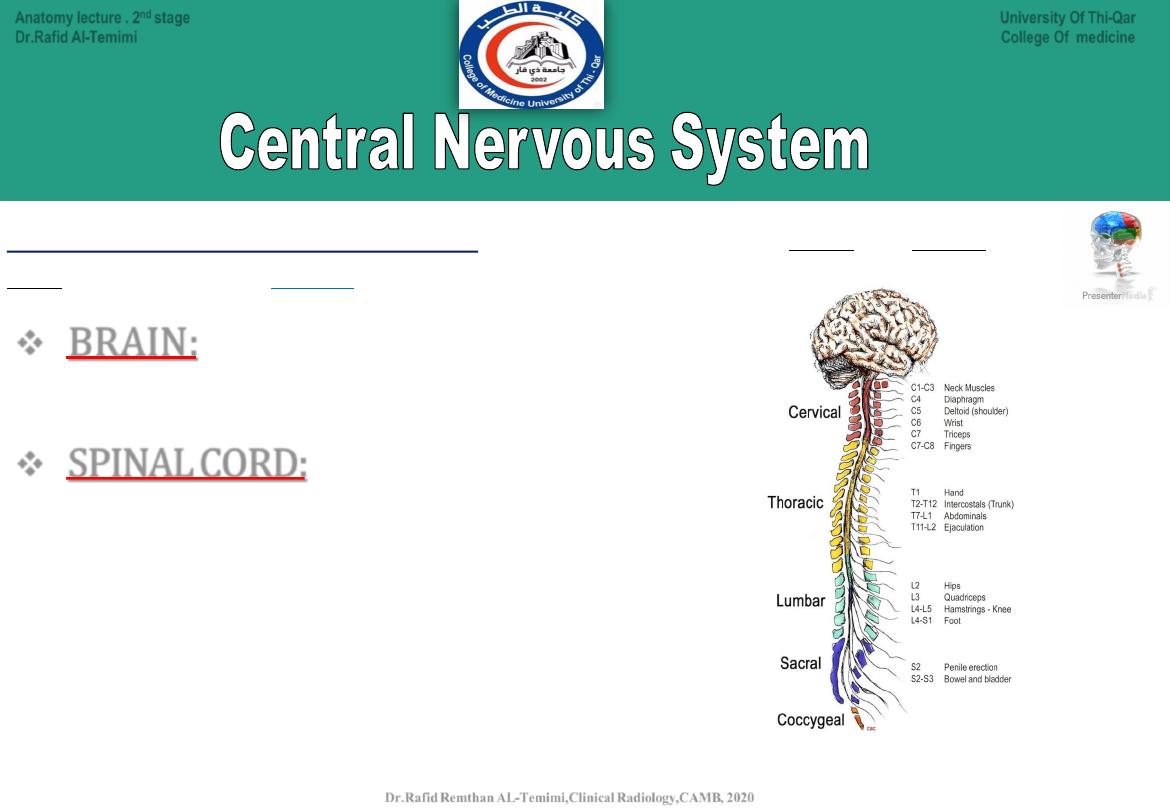
BRAIN:
•
Mass of nerve tissue
•
Protected by membranes & the cranium or skull
SPINAL CORD:
•
Goes down back of body from Medulla Oblongata
•
Surrounded and protected by vertebrae
•
Responsible for reflex actions
•
Carries sensory and motor messages
•
Spinal nerves are named for the region from which they arise
7
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
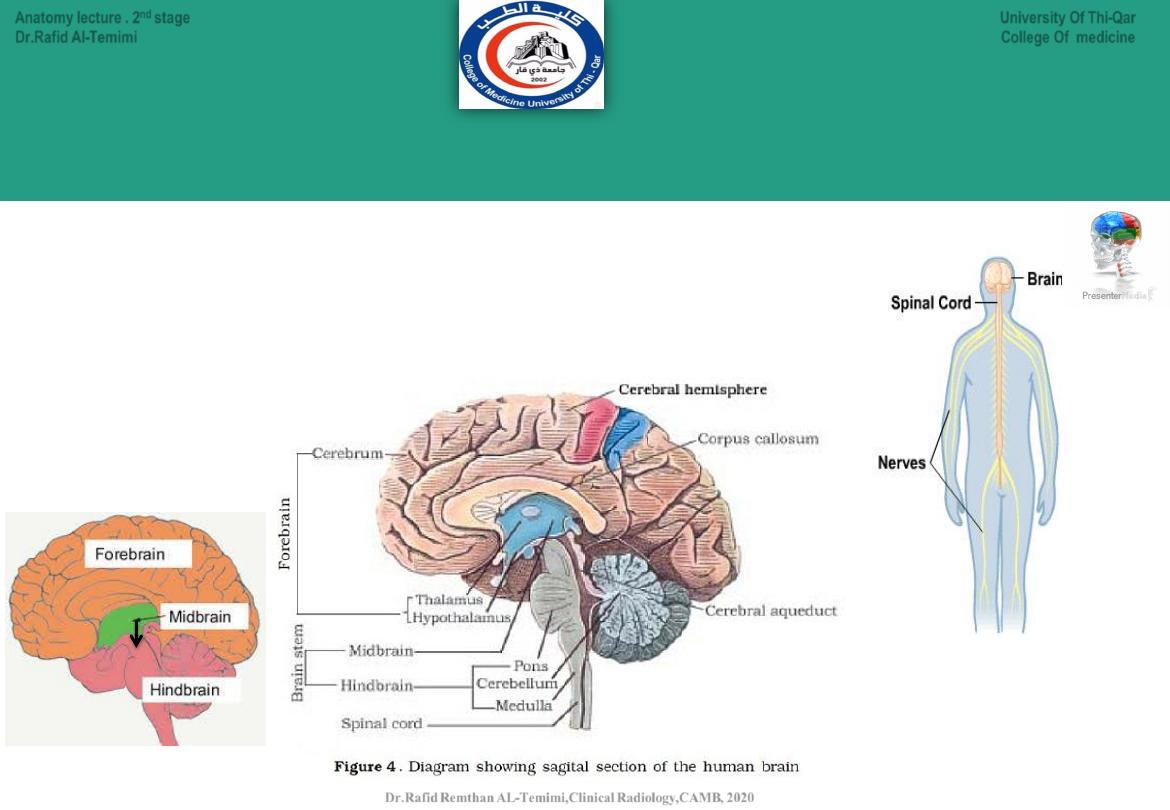
Main Divisions of the CNS: central nervous system
8
The CNS is divided mainly to the following:
● Brain.
● Spinal cord.
The Brain is divided to:
● Forebrain.
● Midbrain.
● Hindbrain.
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
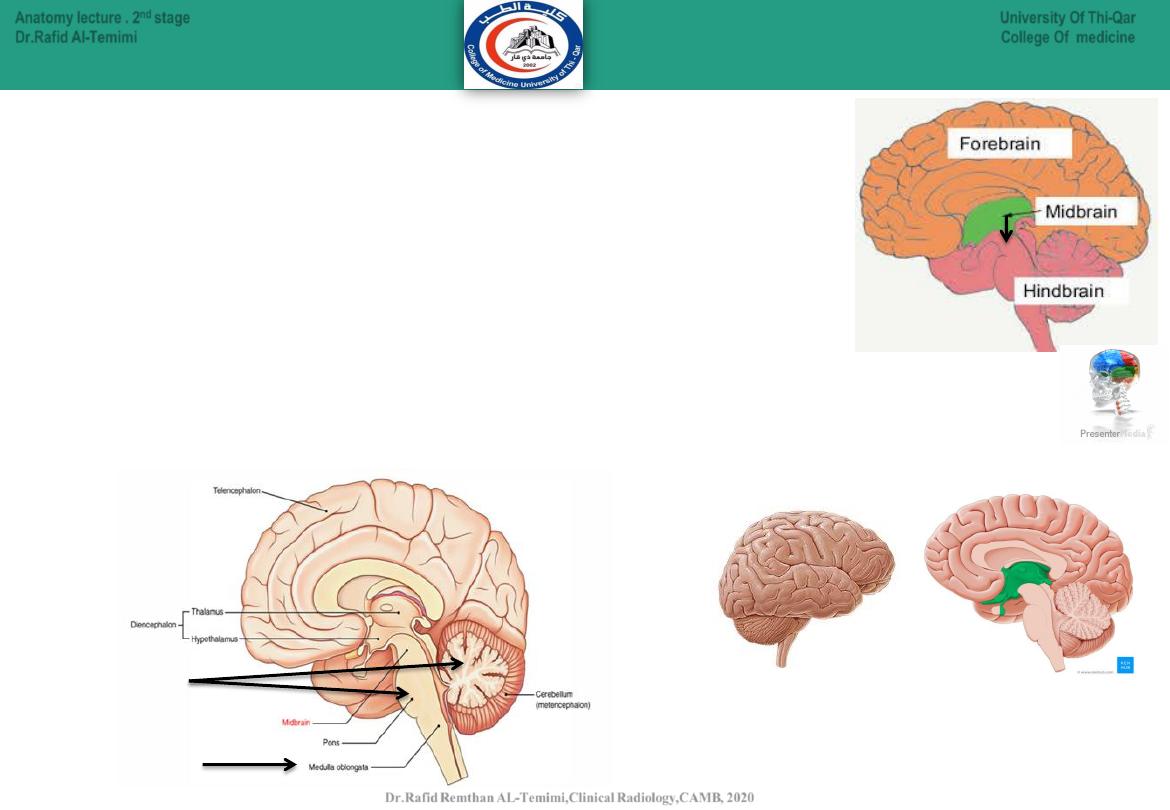
9
Early on in development, the neural tube forms three outpouchings
called
the primary brain vesicles
.
1.
The
Prosencephalon
will form --------------------the forebrain.
2.
The
Mesencephalon
will form --------------------the midbrain.
3.
The
Rhombencephalon
will form-----------------the hindbrain.
Shortly after these form, in the fifth week of gestation, the prosencephalon and
rhombencephalon undergo further divisions, such that :
1. The
Prosencephalon
gives rise to the
Telencephalon
and
Diencephalon
.
2. The
Rhombencephalon
gives rise to the
Metencephalon
and
Myelencephalon
.
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Myelencephalon
Metencephalon
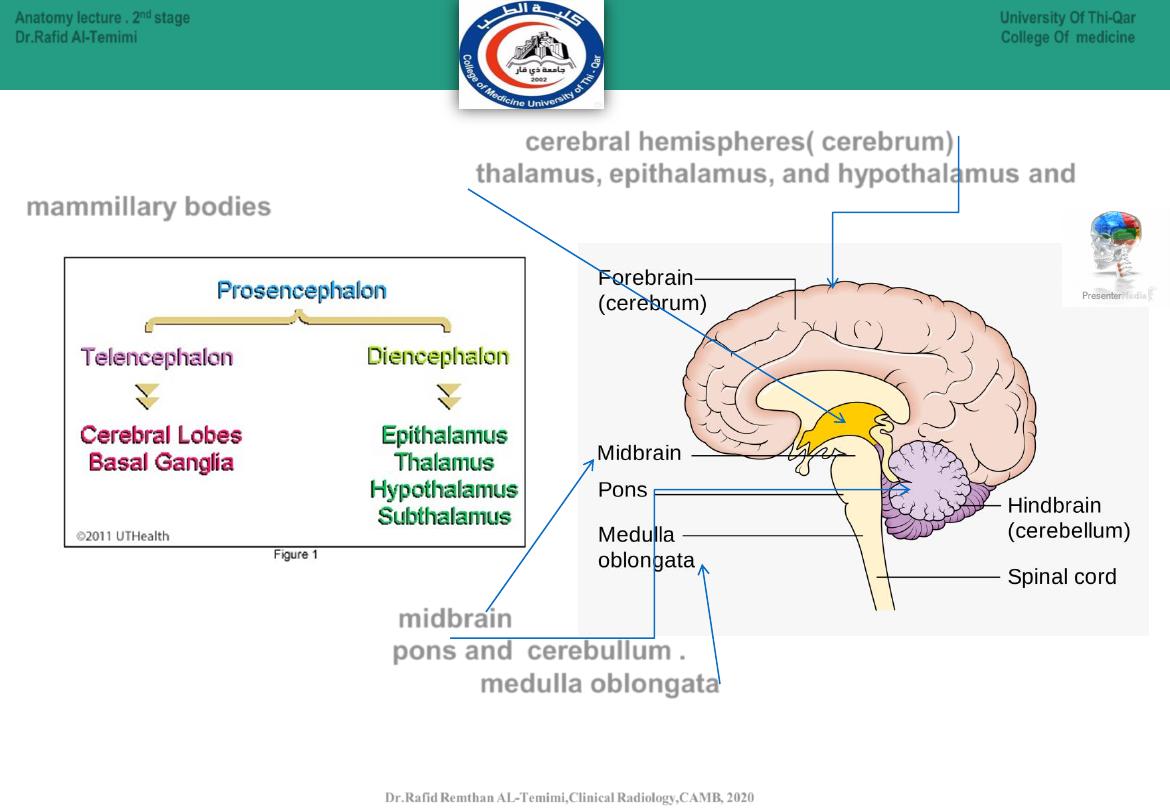
10
The
Telencephalon
eventually forms the
cerebral hemispheres( cerebrum)
.
The
Diencephalon
develops into the
thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus and
mammillary bodies
.
The mesencephalon forms the midbrain.
The metencephalon forms the pons and cerebullum .
The myelencephalon gives rise to the medulla oblongata.
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
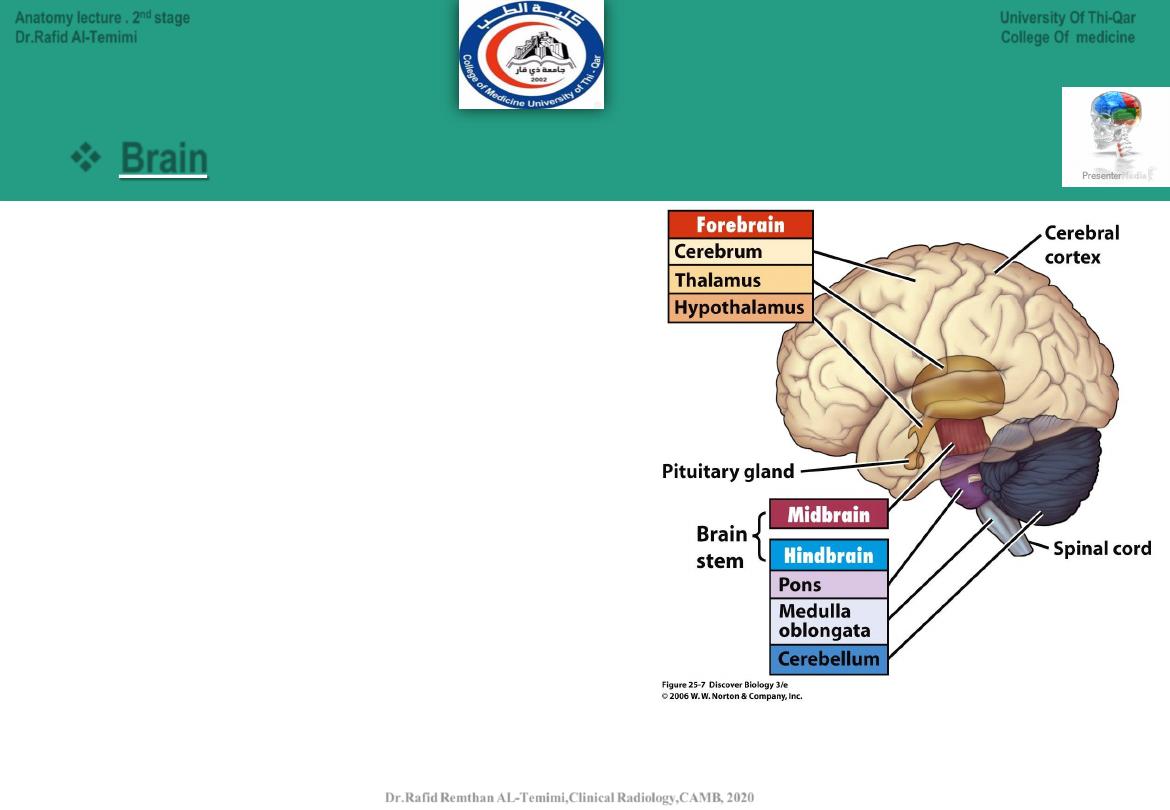
Main Divisions of the CNS:
11
The forebrain (prosencephalon) contains:
● Telencephalon
(cerebrum).
● Diencephalon.
(thalamus & hypothalamus
The midbrain (Mesencephalon )contains:
• Midbrain.
The hindbrain (Rhombencephalon) contains:
● Cerebellum.
(metencephalon)
● Pons.
(metencephalon)
● Medulla oblongata
.
(myelencephalon)
Brain
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
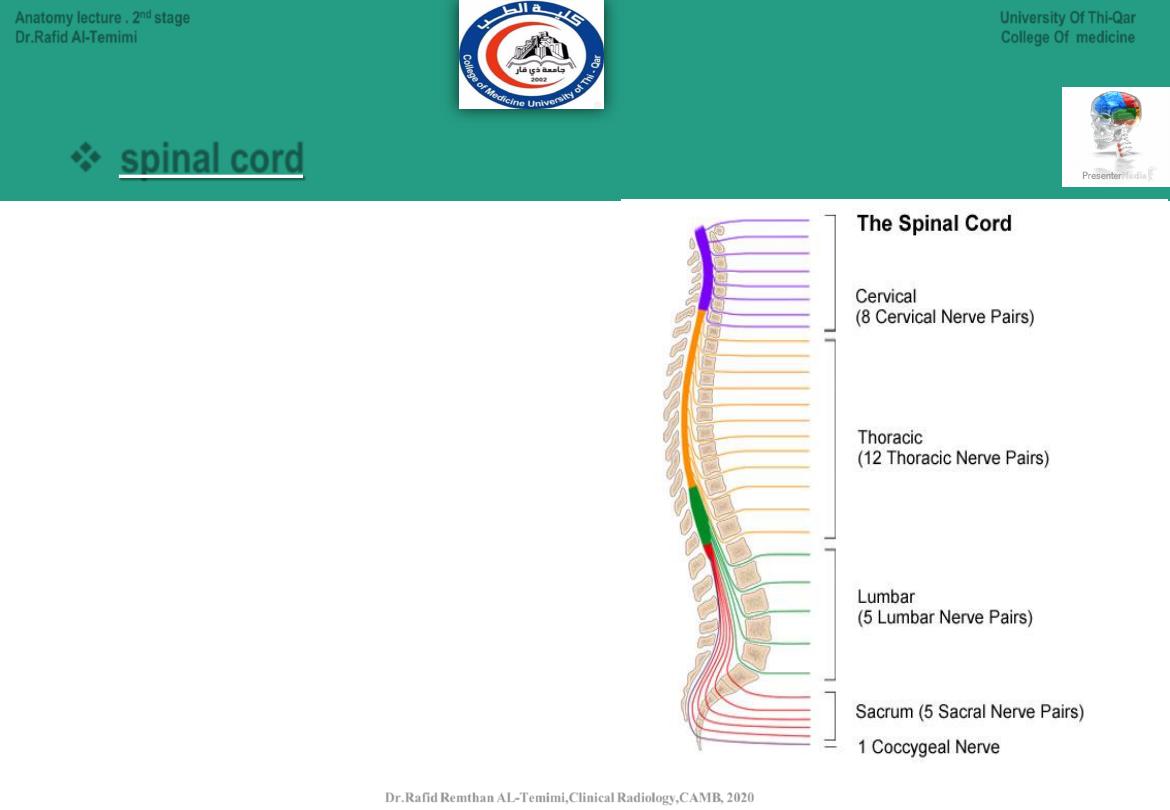
12
The spinal cord is divided to:
● Cervical spinal cord (8 pairs of nerves).
● Thoracic spinal cord (12 pairs of nerves).
● Lumbar spinal cord (5 pairs of nerves).
● Sacral spinal cord (5 pairs of nerves).
● Coccygeal spinal cord (1 pair of nerves).
Main Divisions of the CNS:
spinal cord
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
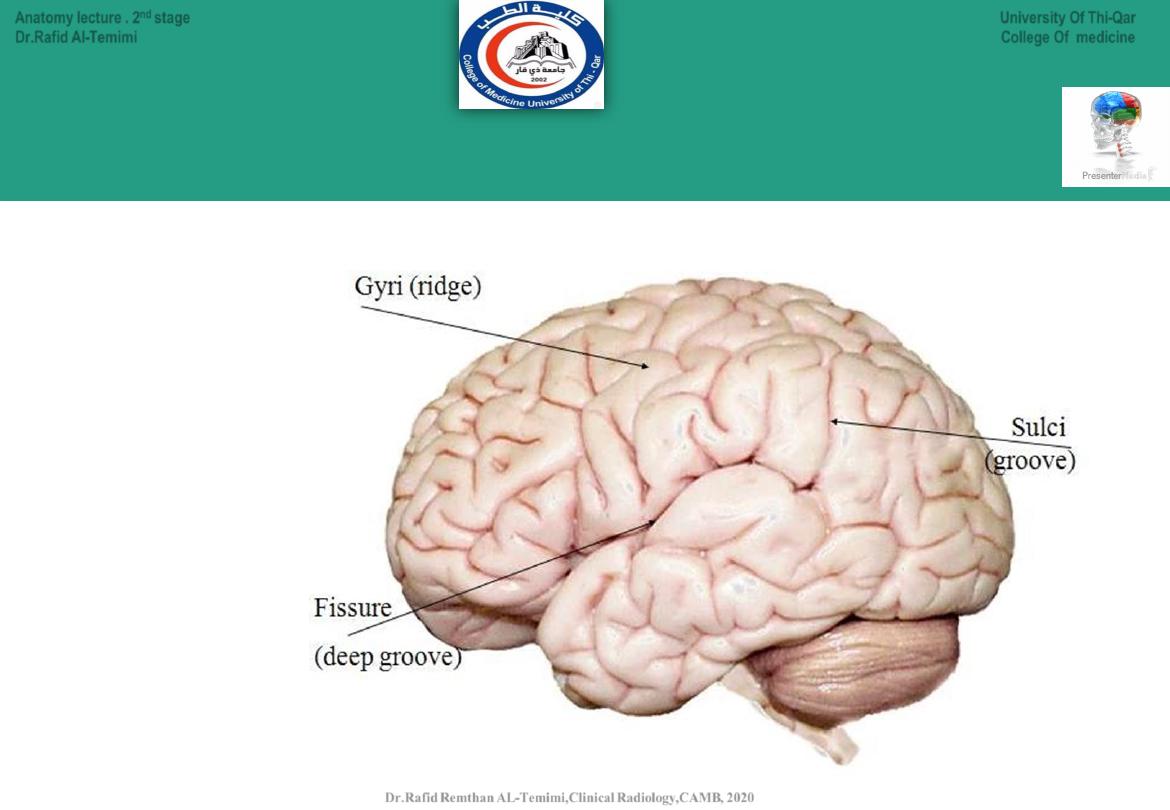
Gyri, Fissure & Sulci
13
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
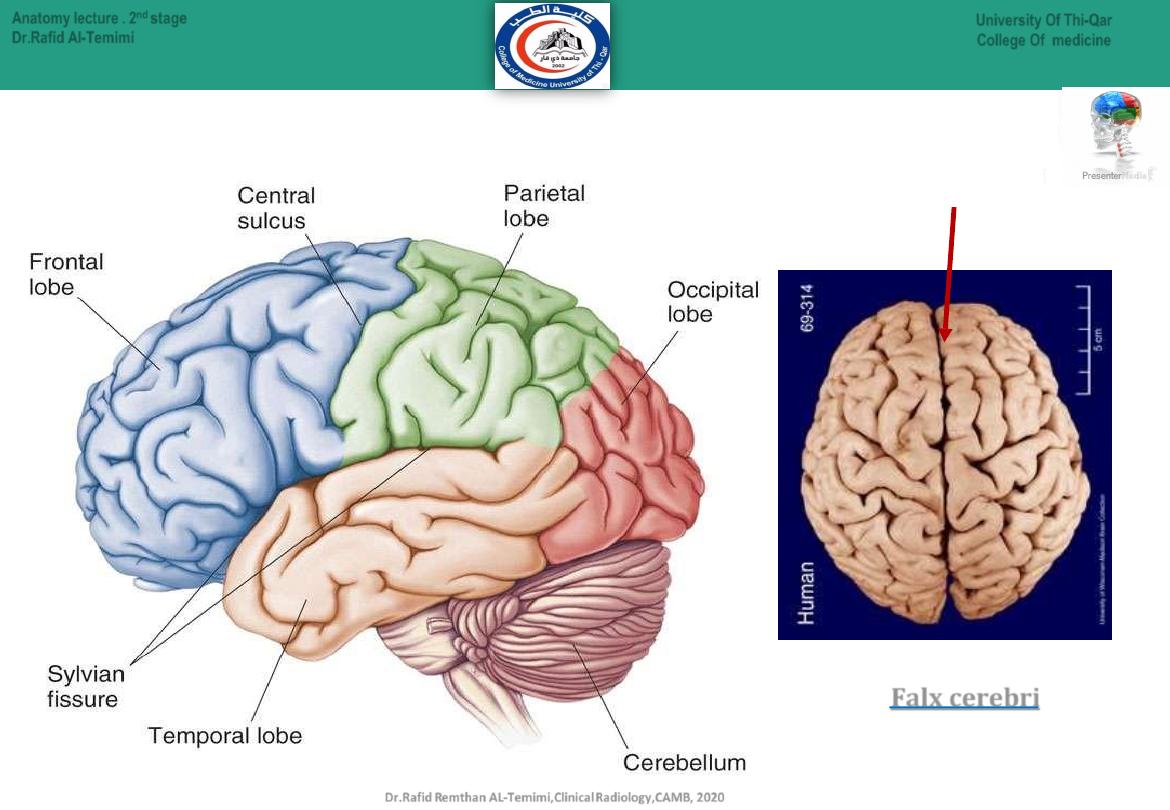
Longitudinal Fissure
Lobes of the Brain
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Paired (left and right) superior parts of the
brain divided by
Falx cerebri
Human Brain
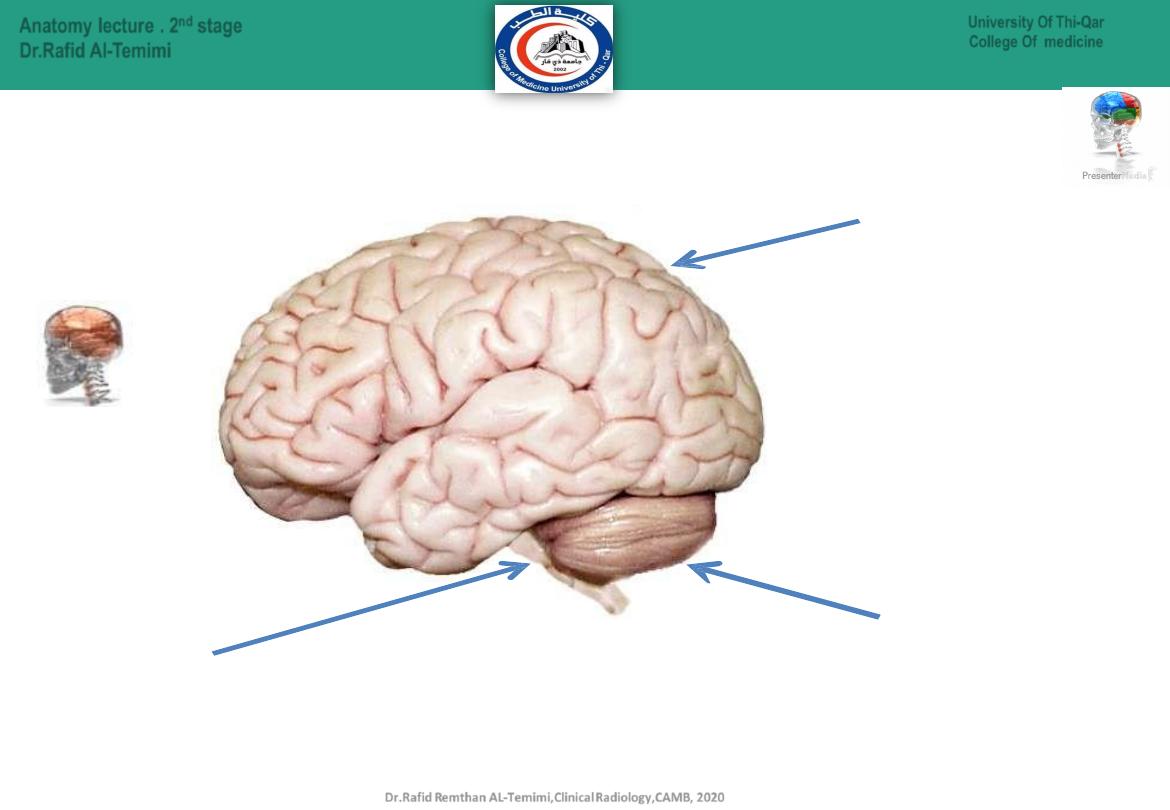
Cerebellum
(Co-
ordinate muscle
movements, maintain posture,
and balance.)
Cerebrum
( touch, vision, hearing, speech,
reasoning, emotions, learning & fine
control movements)
Brain Stem
(relay center connecting the cerebrum and
cerebellum to the spinal cord.
breathing, heart rate, body temperature,
wake and sleep cycles, digestion, sneezing, coughing, vomiting, and
swallowing )
15
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
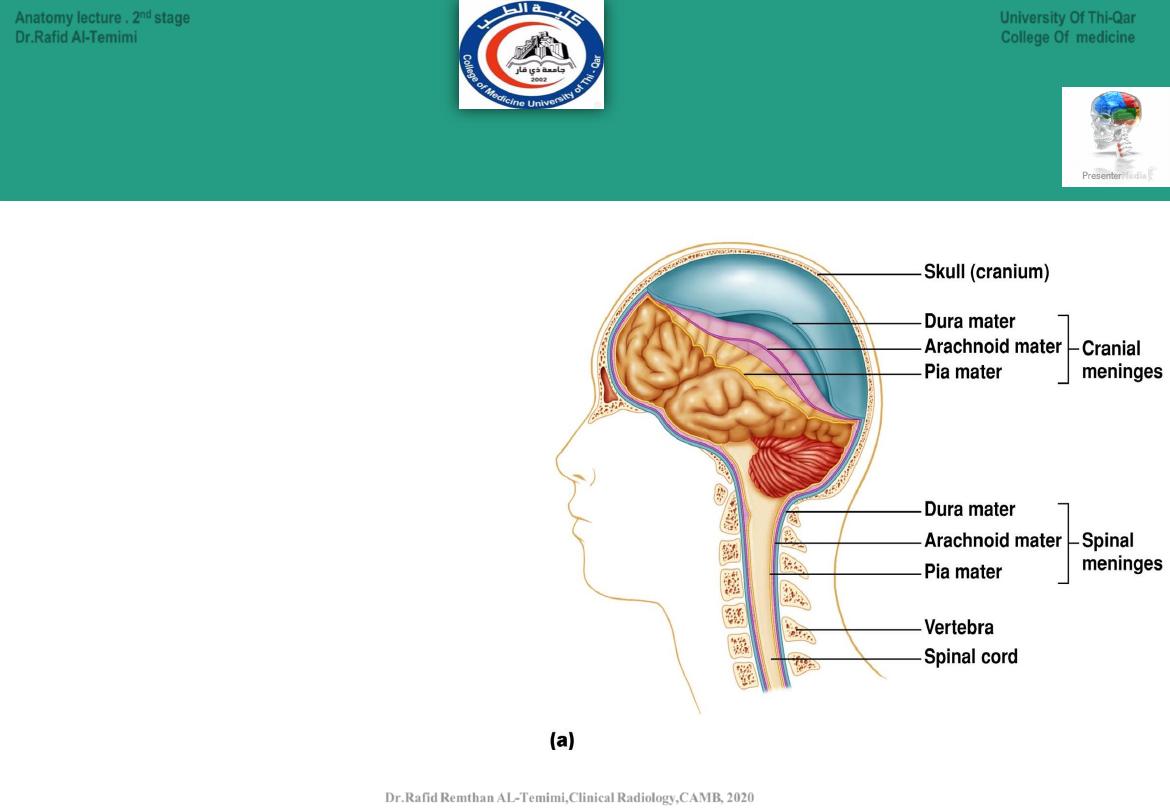
Meninges
Meninges
are layers of tissue that covers
and protects the brain and spinal cord
1.Dura mater:
thick, tough outer layer.
2.Arachnoid membrane
:
middle delicate
weblike layer.
3.Pia mater:
inner most layer with blood
vessels to nourish the nerves.
Consists of 3 membranes
16
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
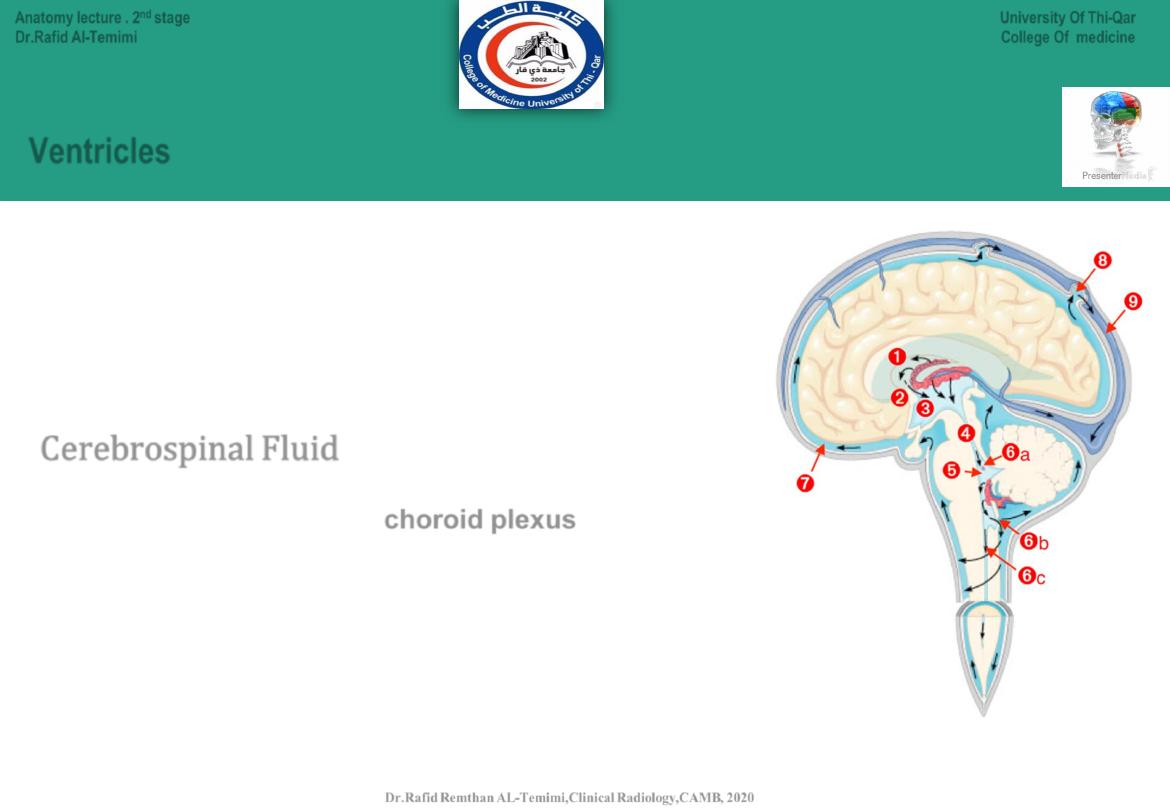
Ventricles
•
hallow spaces located in the middle of the brain.
•
Connected to each other
•
Filled with fluid called cerebrospinal fluid
Dr. Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi ; Clinical Radiology ( CABM) 2020
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Circulates continuously from
choroid plexus
in lateral venricle
Serves as shock absorber to protect brain and spinal cord.
Carries nutrients to parts of brain and spinal cord
helps remove metabolic products & wastes
after circulation, absorbed into the blood vessels of the dura mater.
17
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
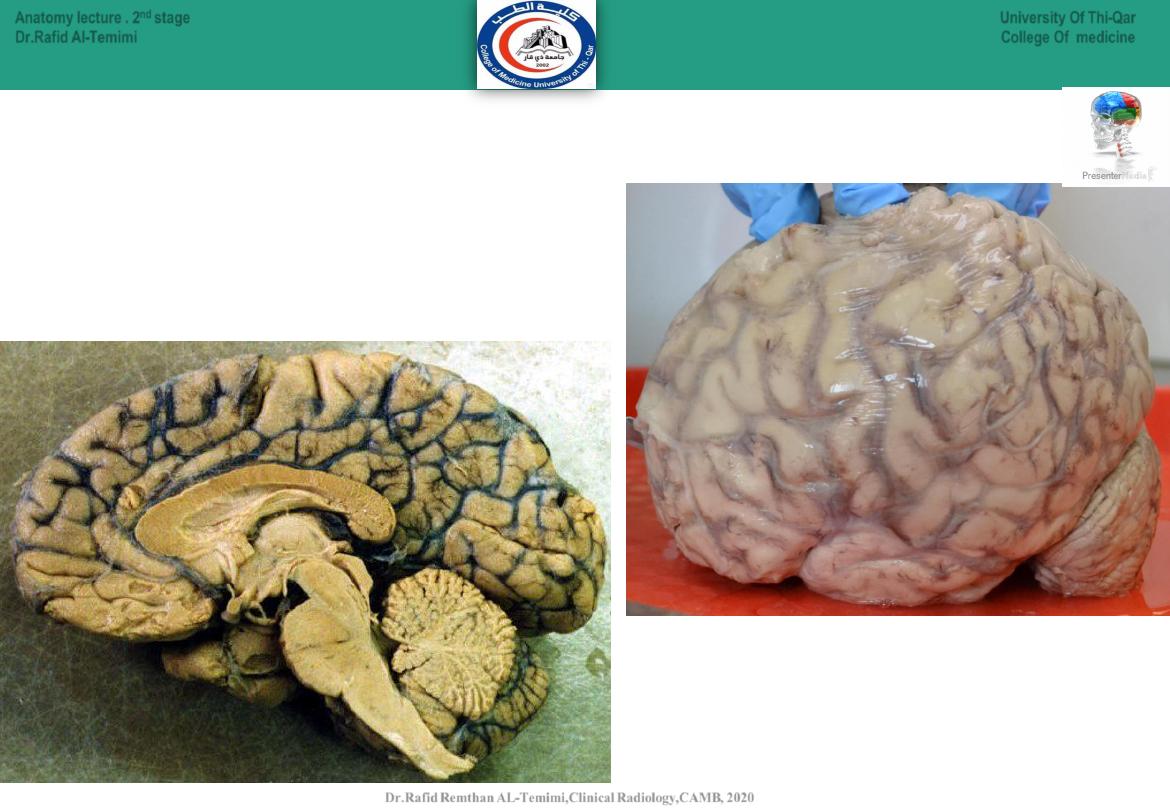
18
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
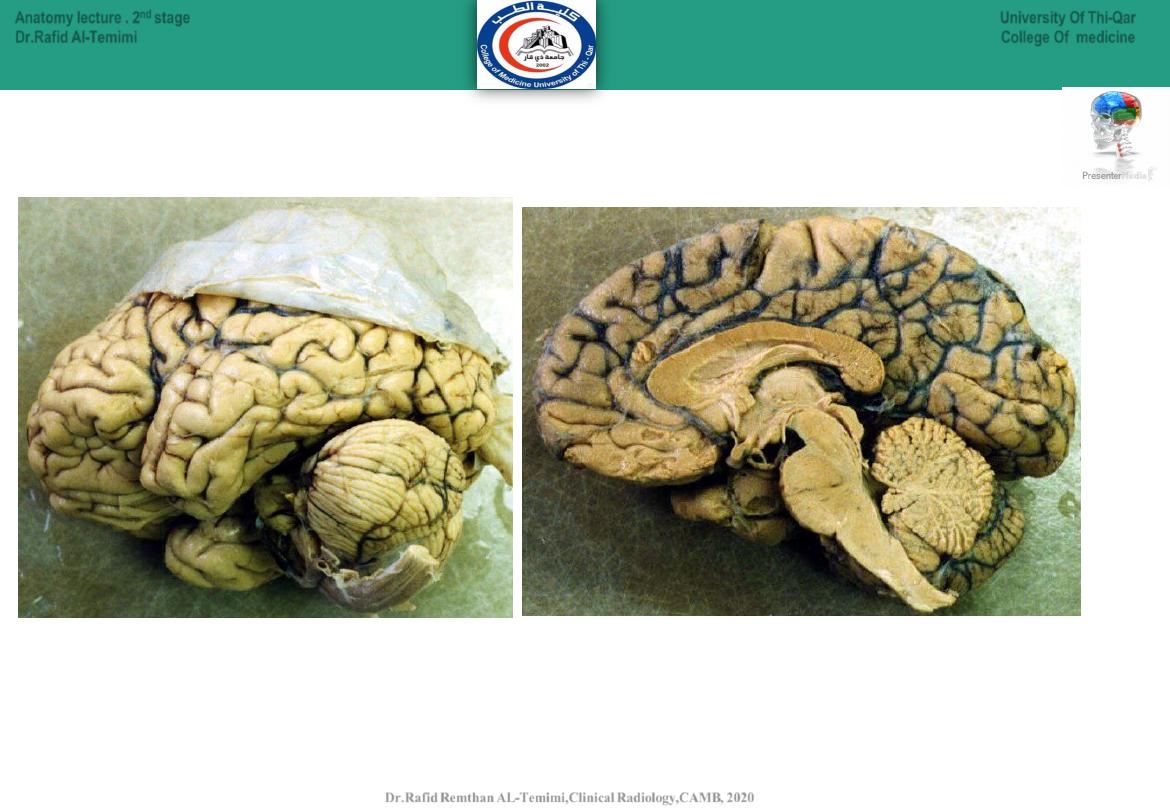
19
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
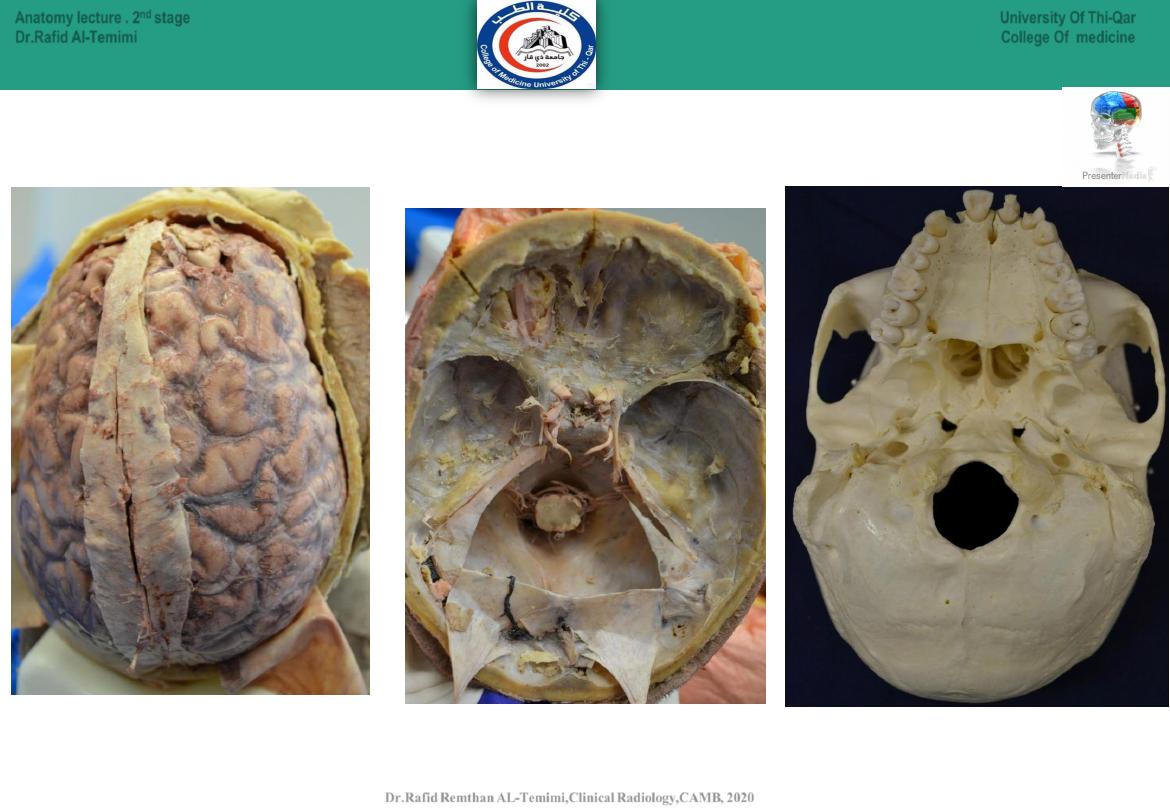
20
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
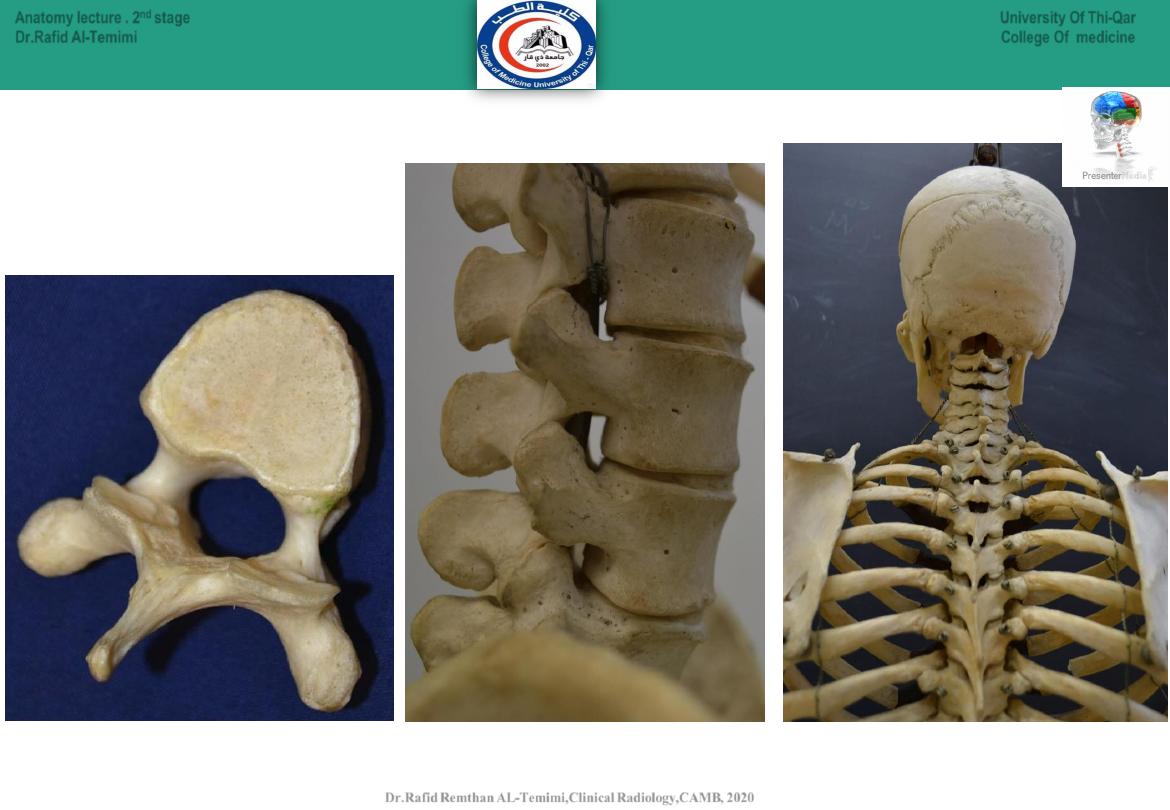
21
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020

22
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
