

U-shaped
Valley
V-shaped
Valley
Cave
Atoll

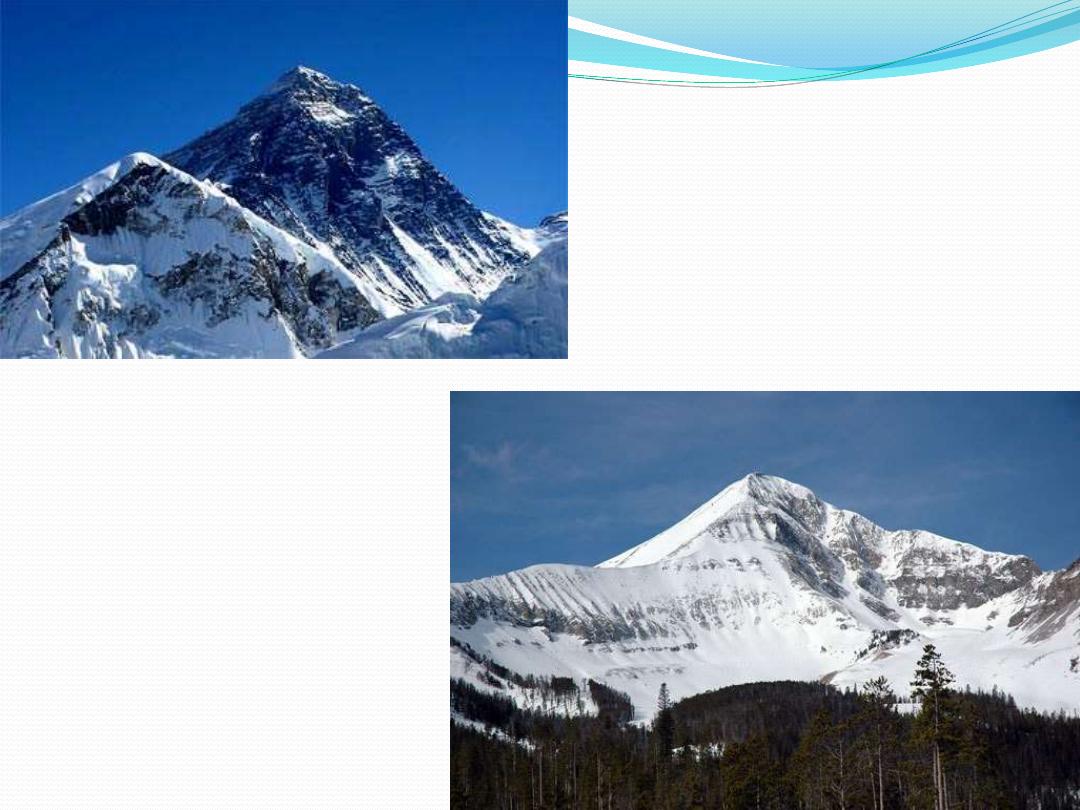
Tectonic and Structural Landforms
Both endogenic
Create large-scale landforms
Tectonic
produced by deep Earth process without erosion
Structural
the result of exogenous forces acting on tectonic
landforms


Structural Landforms
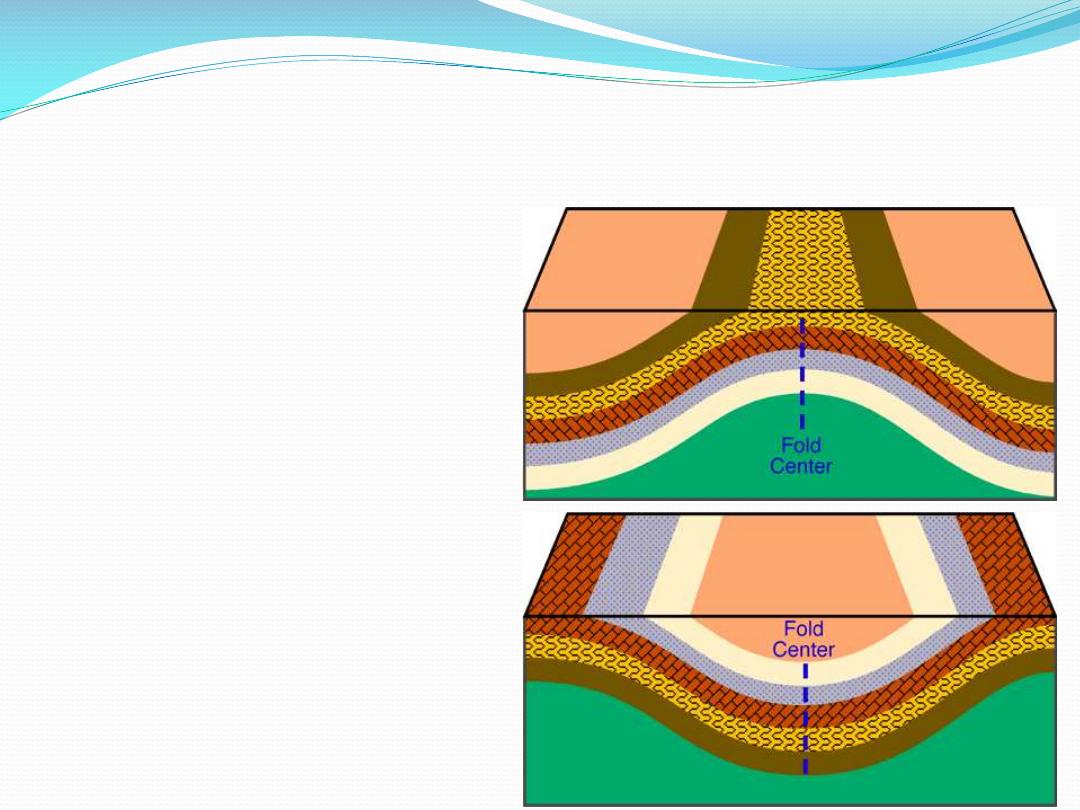
Convergent tectonic forces produce fold structures
anticlines, synclines, monoclines, dome, basins
Compressive or tensional forces produce faulting
fault scarps, horsts, grabens
Faults and folds impart relief to the landscape
(until erosion gets to them)

Structure
the attitude of a bed or stratum of beds or strata of
sedimentary rocks, as indicated by the dip and strike.
the disposition of the rock formations; i.e., the broad
dips, folds, faults, and unconformities at depth
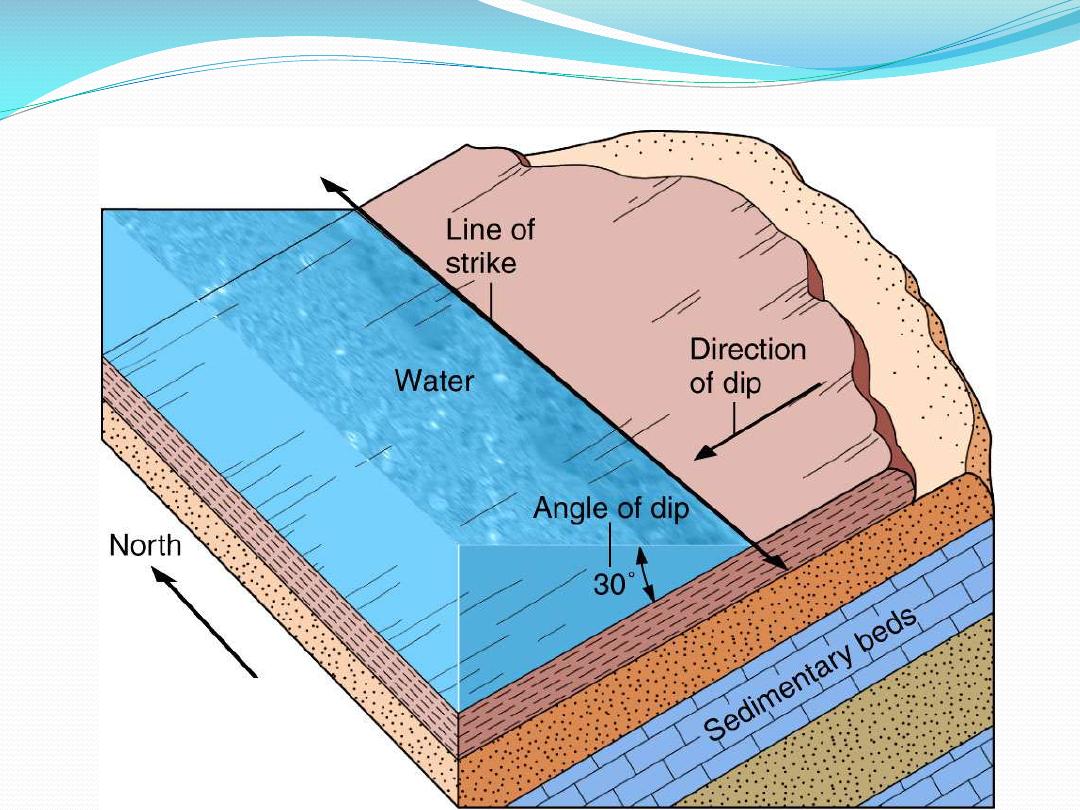
Strike and dip

Lithology
Relative erodibility
Layered rocks = wide range
Sedimentary
Volcanic
Massive rocks = narrow range
Metamorphic
Intrusive igneous
Erodibility is not absolute
typically shale > limestone > sandstone ~ gneiss
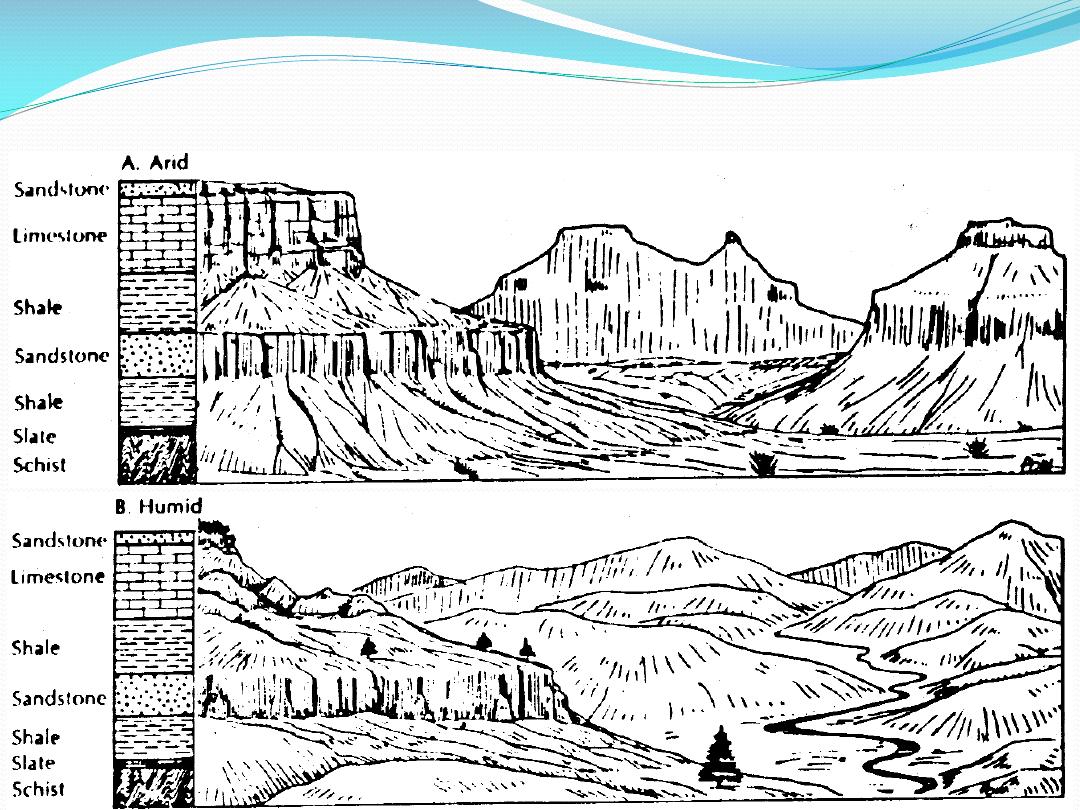


Lithology/Climate

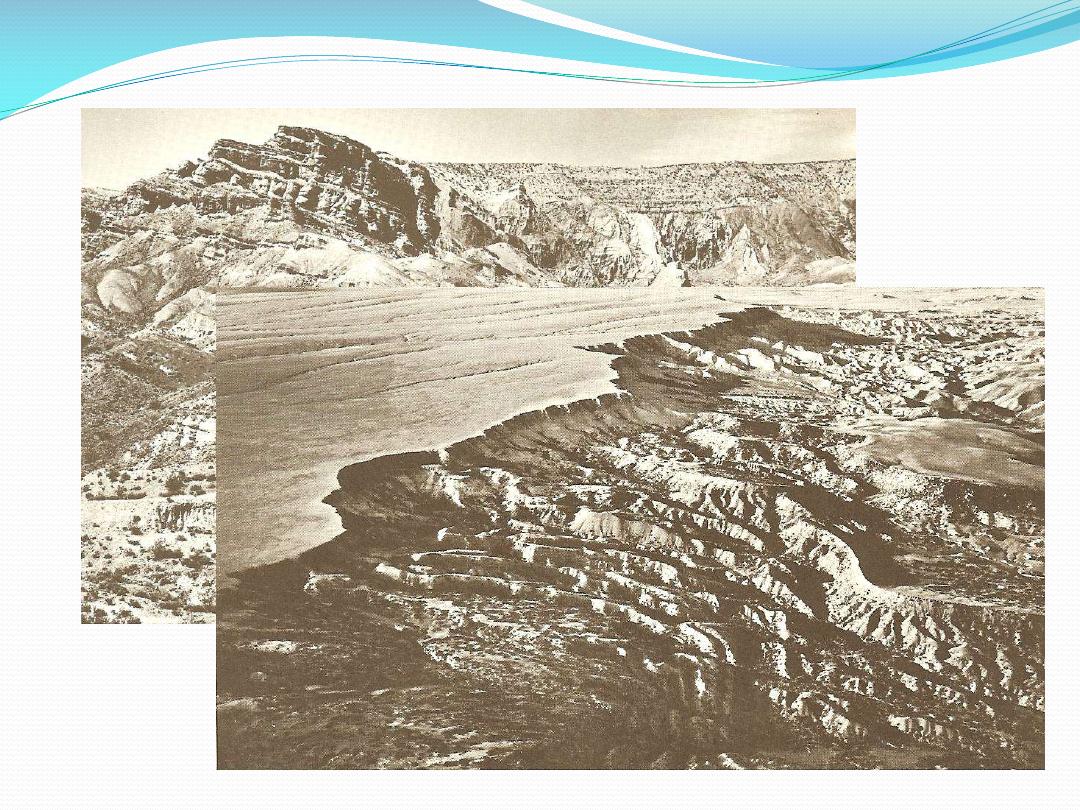
Landforms assoc. with sedimentary rocks
Horizontal beds
plateau, mesa, table, butte
Folded beds
anticline (arches in strata), syncline (trough in strata),
cuesta, hogback

Tablelands
Plateau/mesa/butte/chimney
Tilted Layer Cakes
Monoclinal folding
beds are flexed from one
level to another
Feature = f(dip angle)
Cuesta (gentle)
Hogback (steep)
Flatiron (very steep and
supported)
Also f(rel. erodibility)
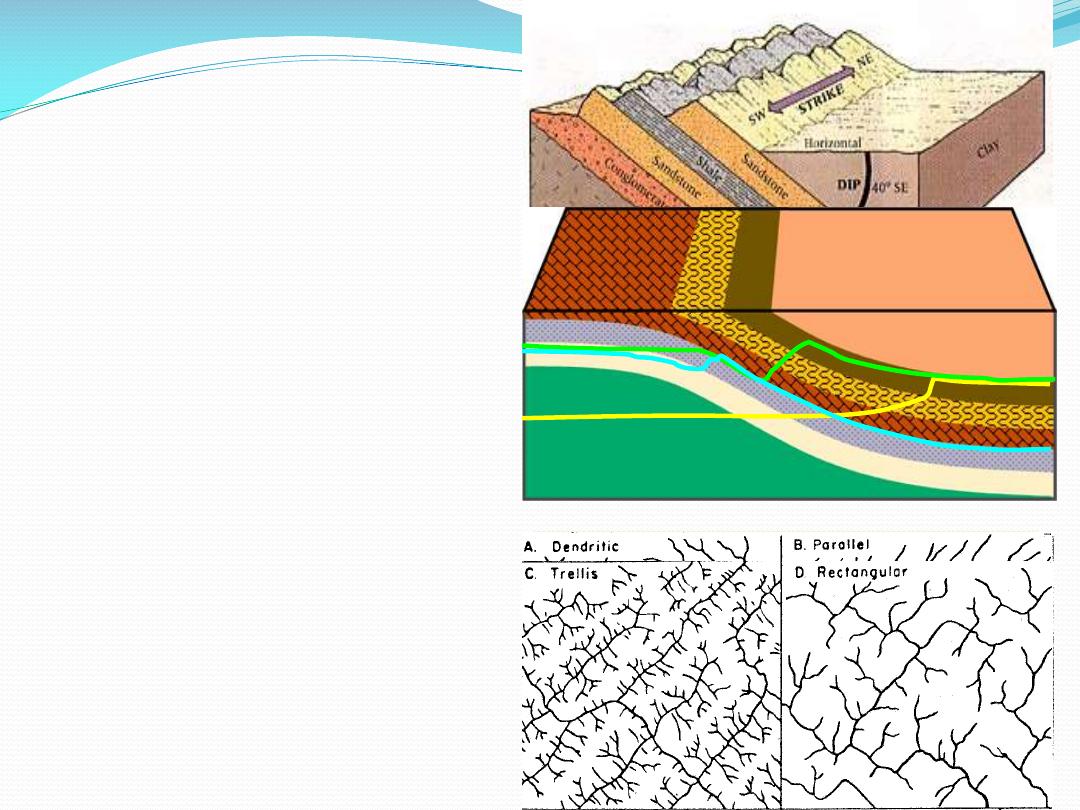
Drainage patterns
Parallel
Trellis
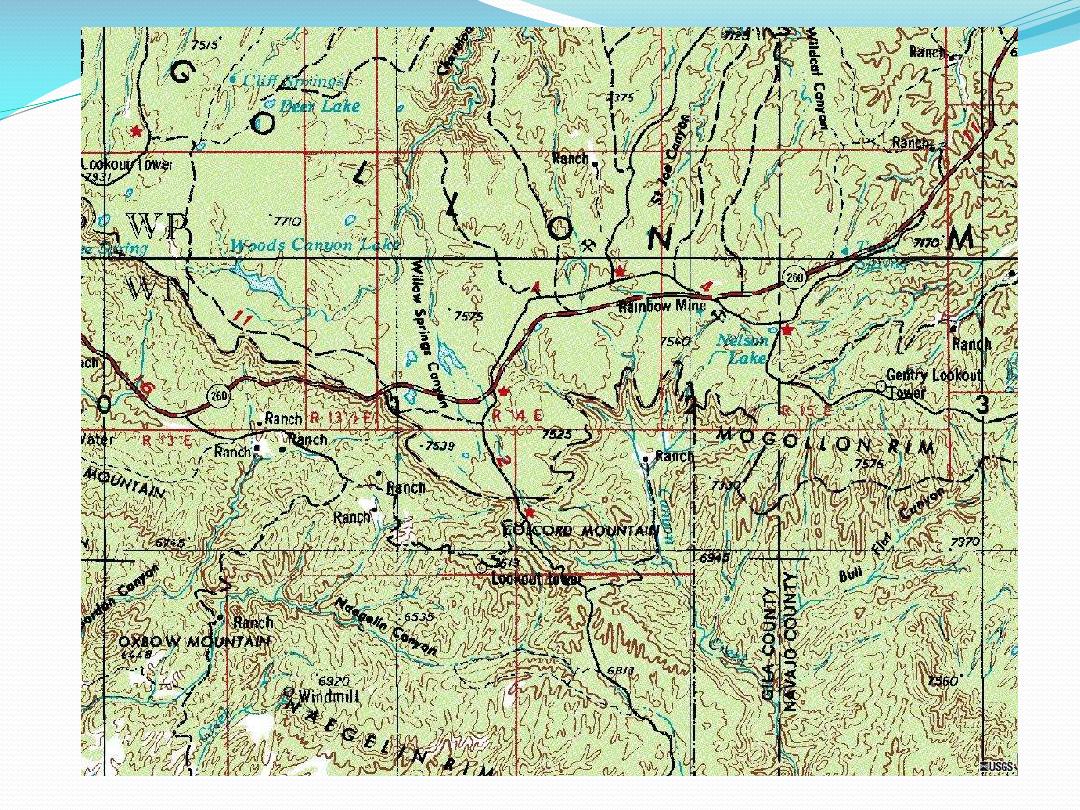
Landforms Associated with Sedimentary Rocks
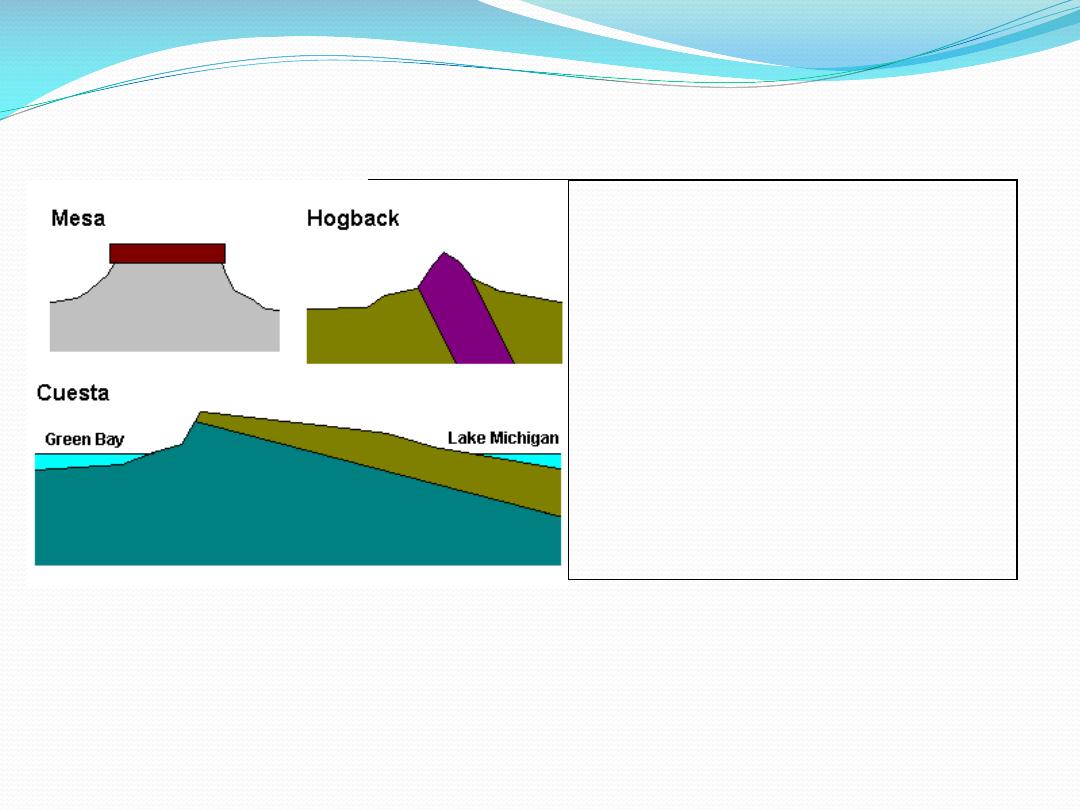
Mesa
Flat-topped hill capped with hard
rock
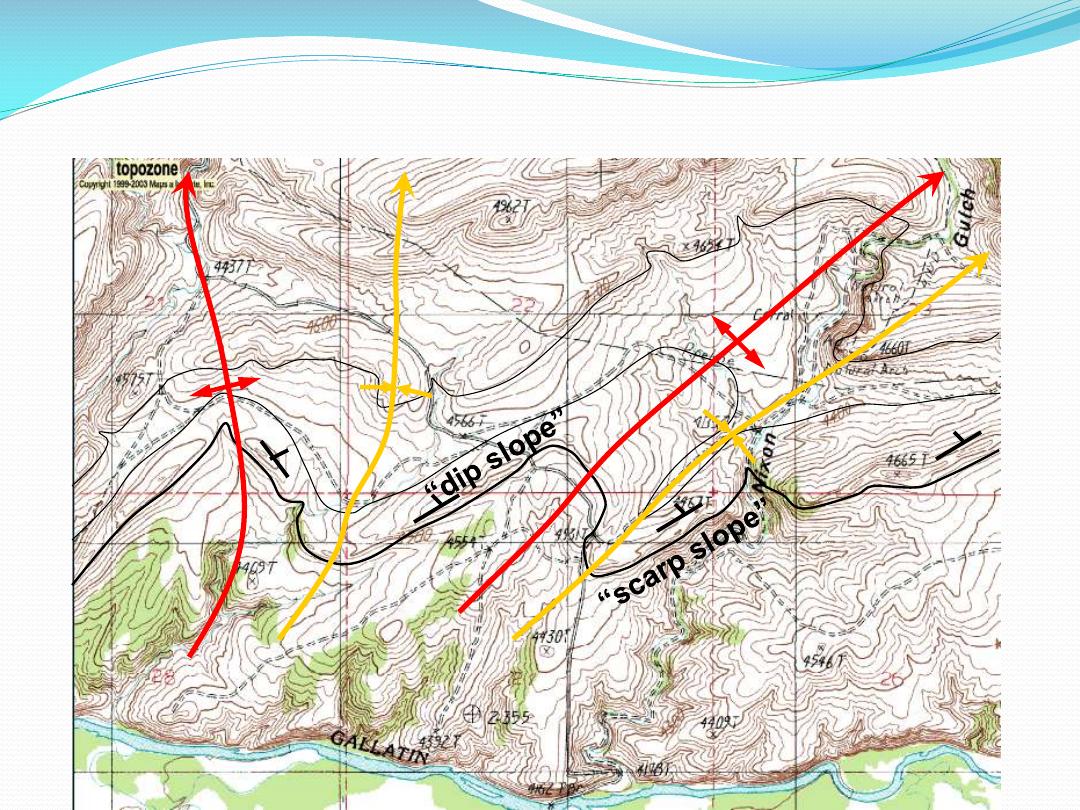
Cuesta
Gently-tilted layer of hard rock. The
gentle upper slope, on top of the
layer is called the dip slope
Hogback
A sharp ridge of hard rock, edge of
a steeply-dipping layer
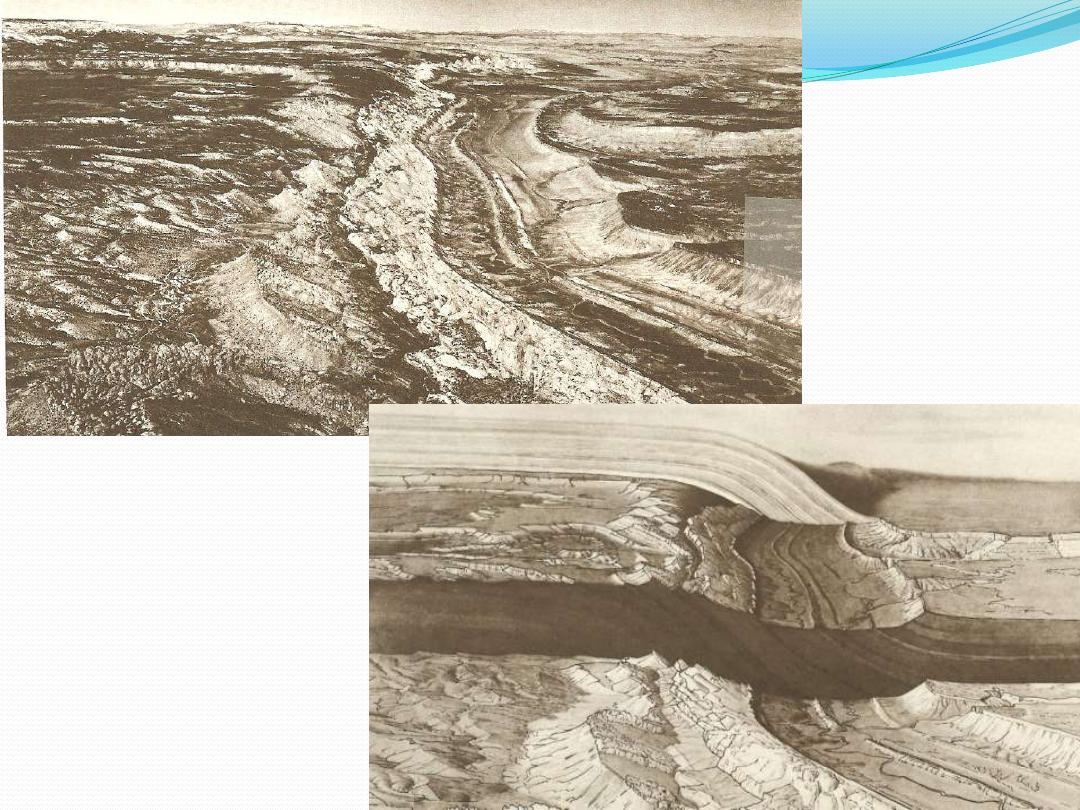
Monocline:
“A double flexure connecting
strata at one level
with the same strata at
another level
”

Dip
Slope
Back
Slope
Kd
Kd
Jm
Jm
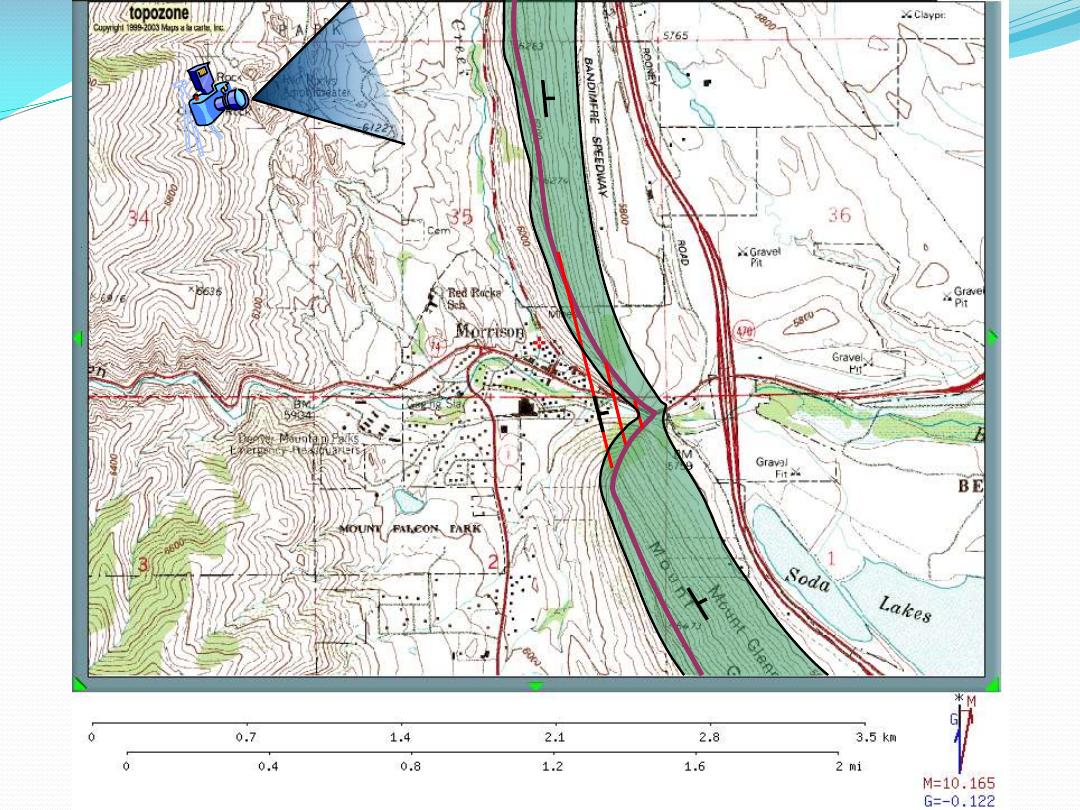
Delaware MI
Res
is
tant uni
ts
are
ty
pi
c
al
ly
<
100
’
thi
c
k
and
di
p
N
at
10
-16
°
16
10
15
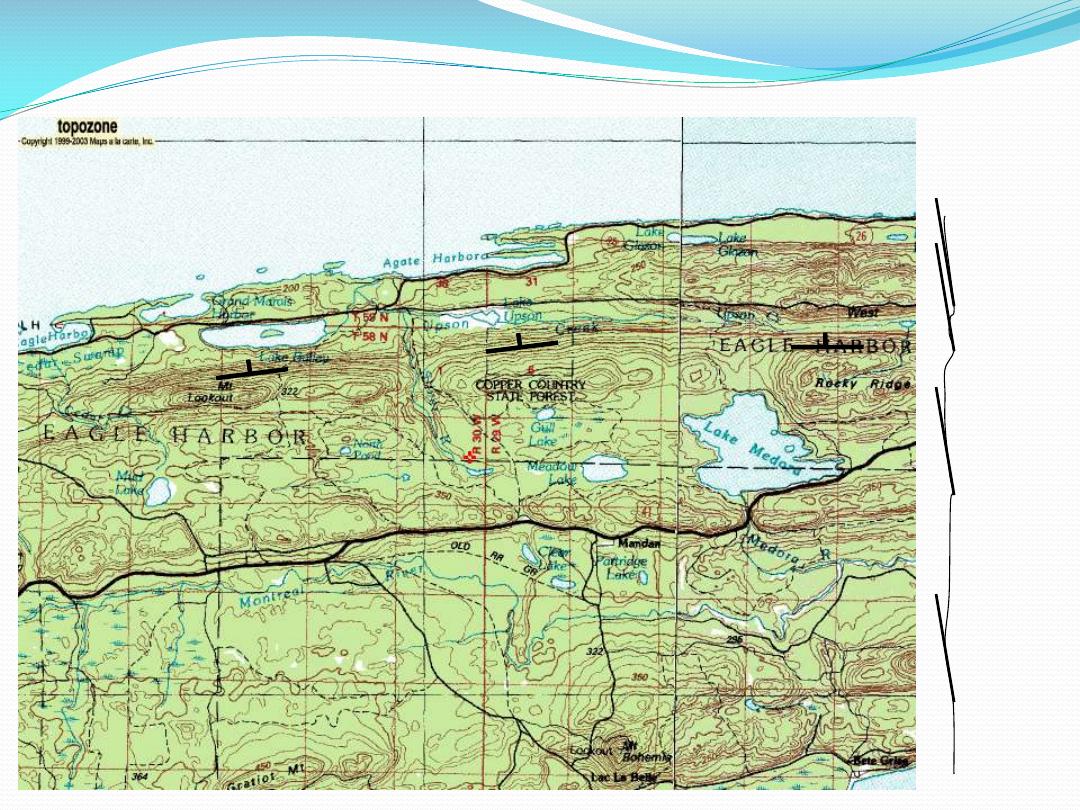
Folded Rocks – Simple
Anticline/syncline
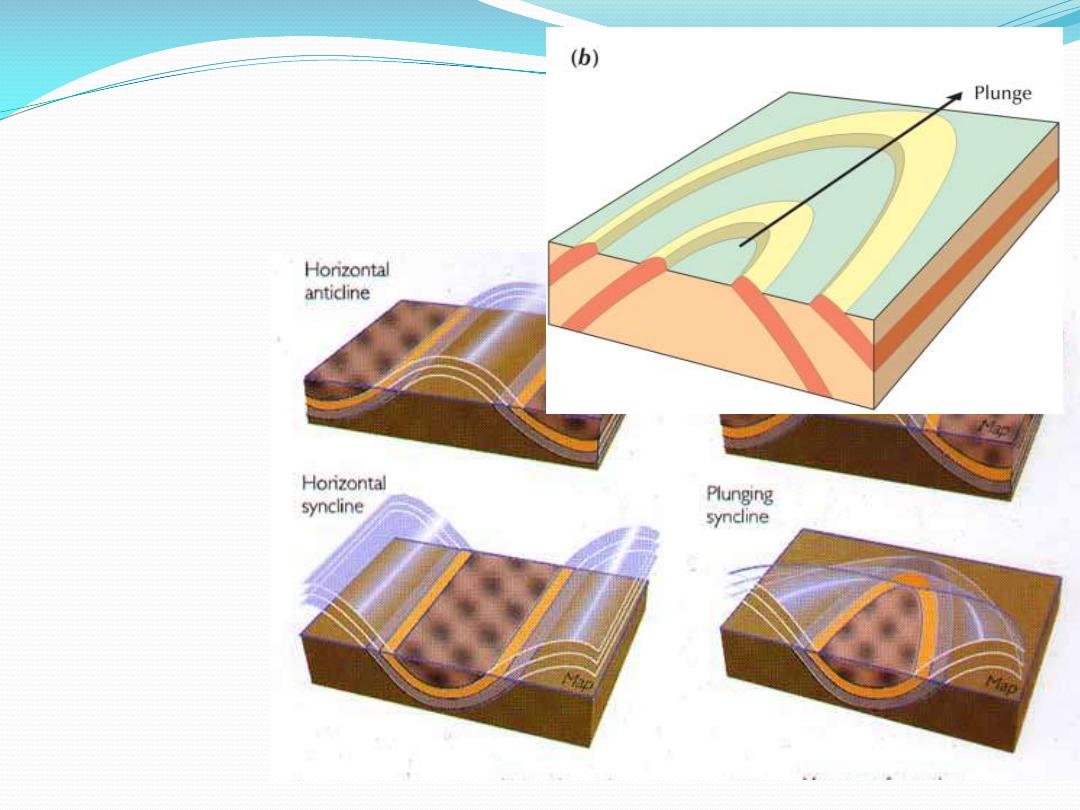
Folded – still
simple
Plunging
Z-folds


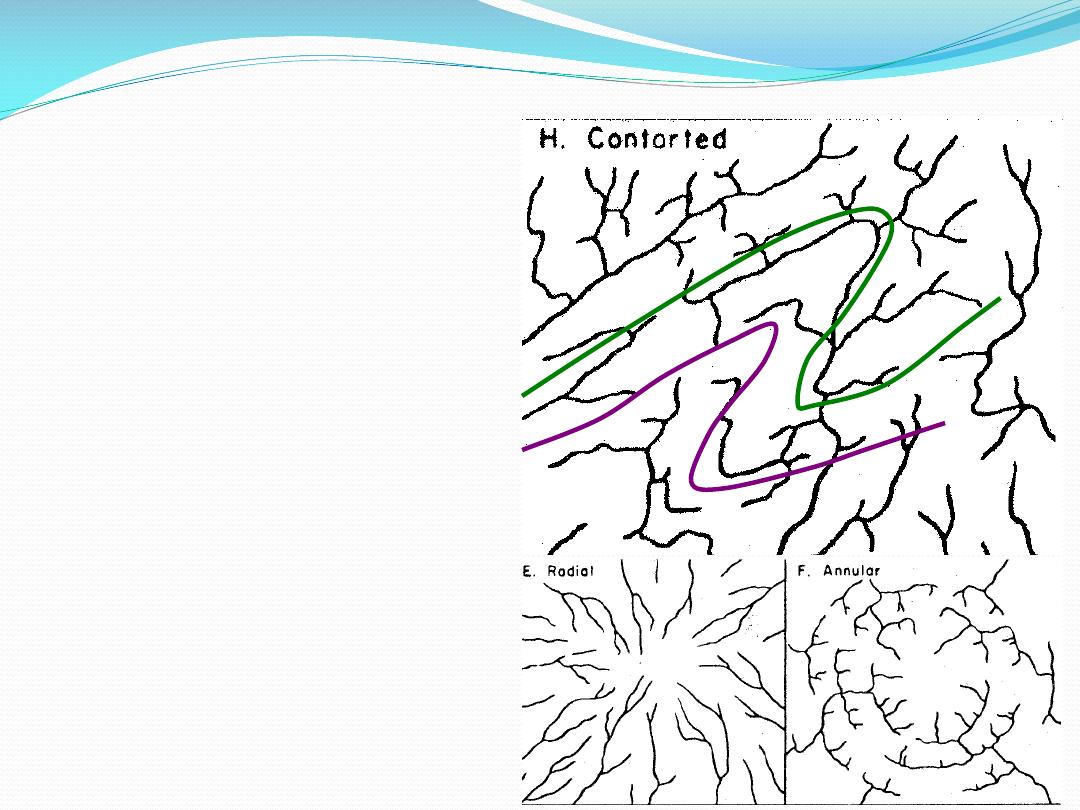
Simple folds -
drainage
Contorted
Metamorphic?
Inward/outward
Radial
Centripetal
Ringlike - annular

Folded Rocks - Complex
Folded Rocks - Complex
Weak
Strong
Weak
Strong
Ho rsesh oe Hills.kmz
Horseshoe Hills
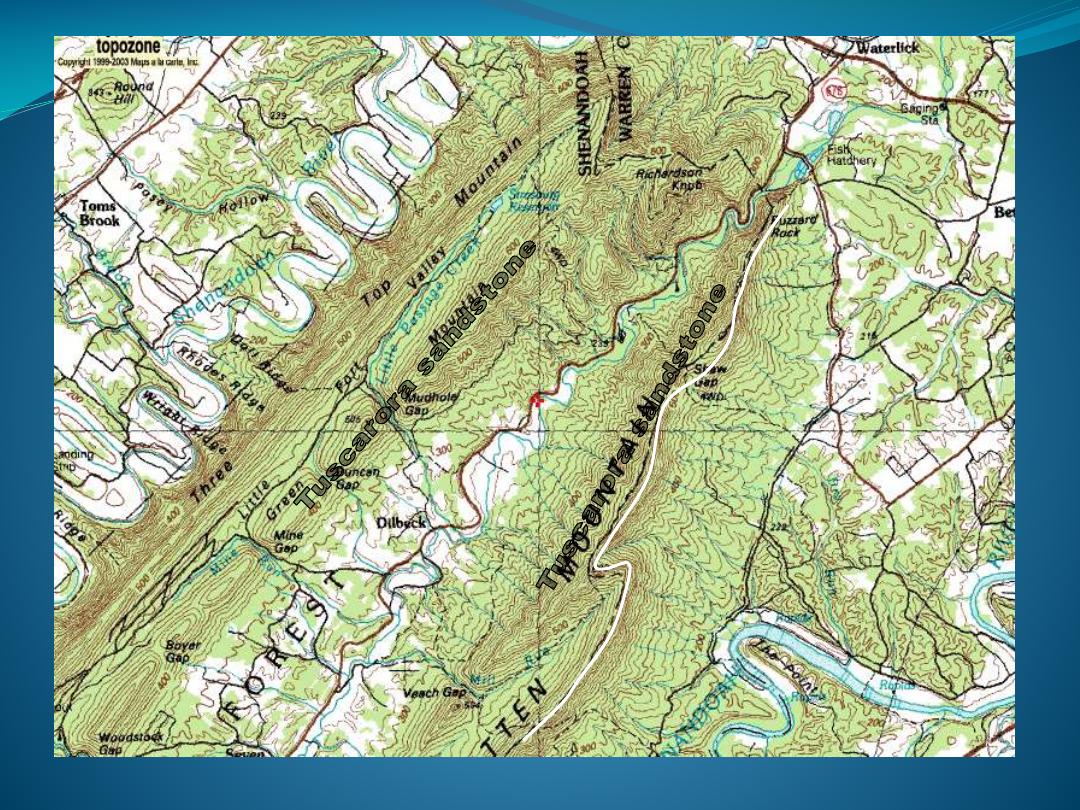
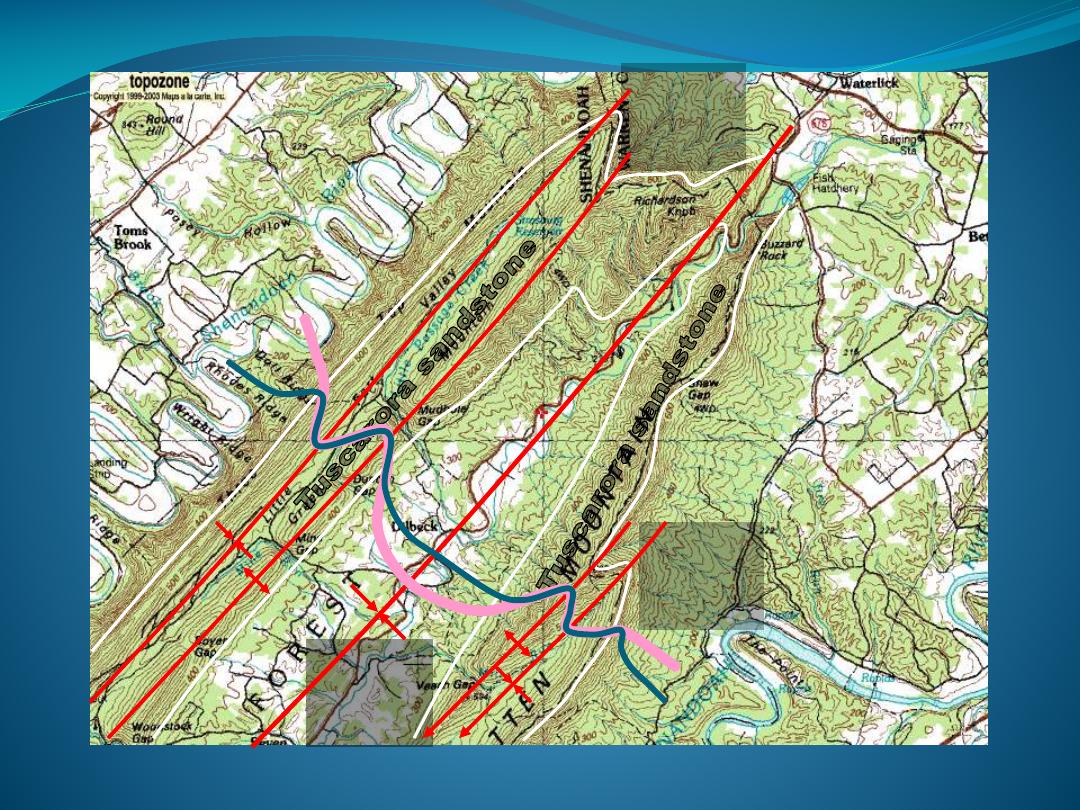
Blunt
synclinal
nose
Blunt
synclinal
nose
Sharp
anticlinal
nose
TOPOGRAPHY
S
Tss
