
Spine Imaging
By
Dr. Firas Abdullah
Thiqar college of medicine

Aims of our lecture:
To know the different radiological techniques used in
spine imaging
To know the signs of abnormality seen at spine
To discuss some spinal pathologies

I) Radiological techniques used in
spine imaging:
Plain X ray
MRI
Radionuclide bone scanning
CT scan
Myelography
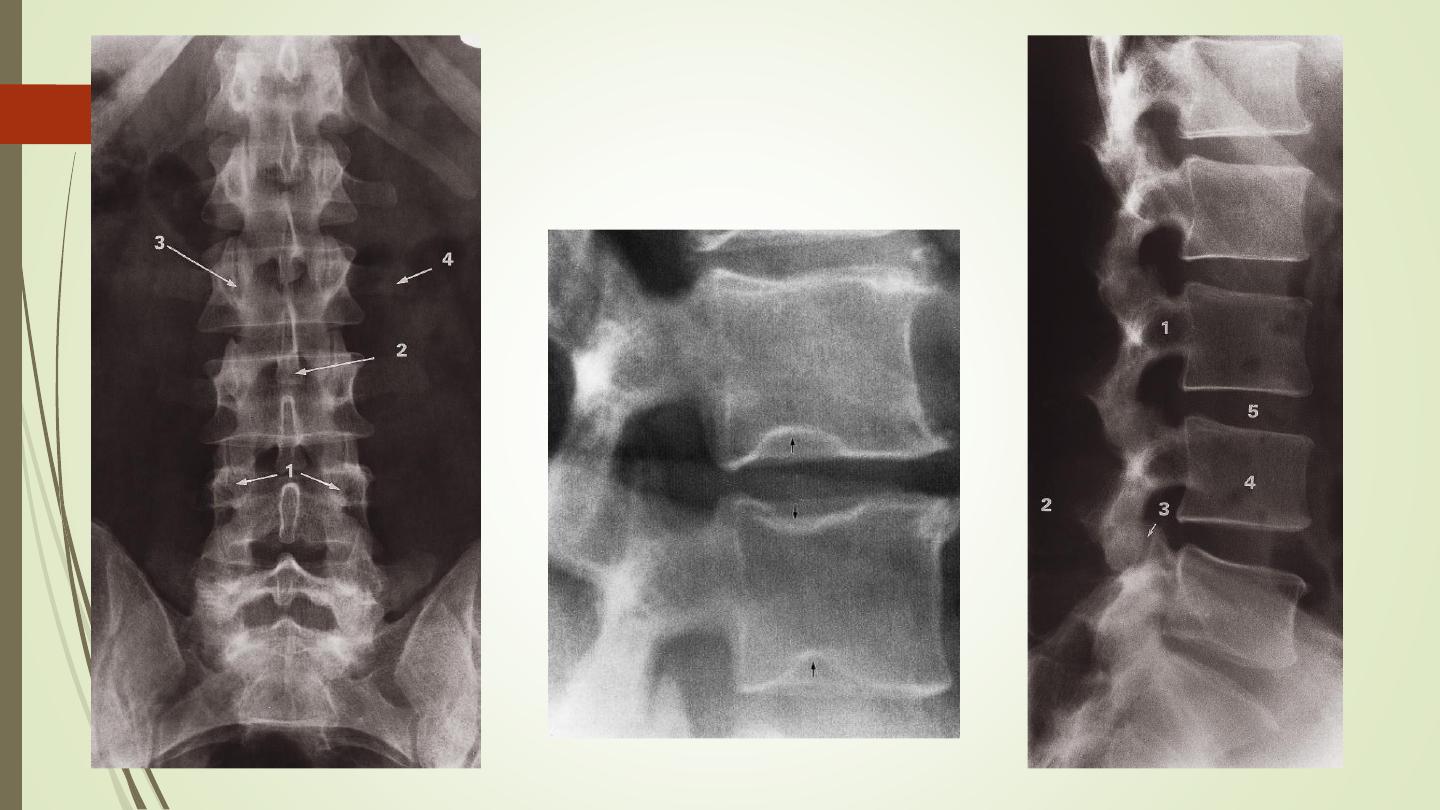
Plain X ray
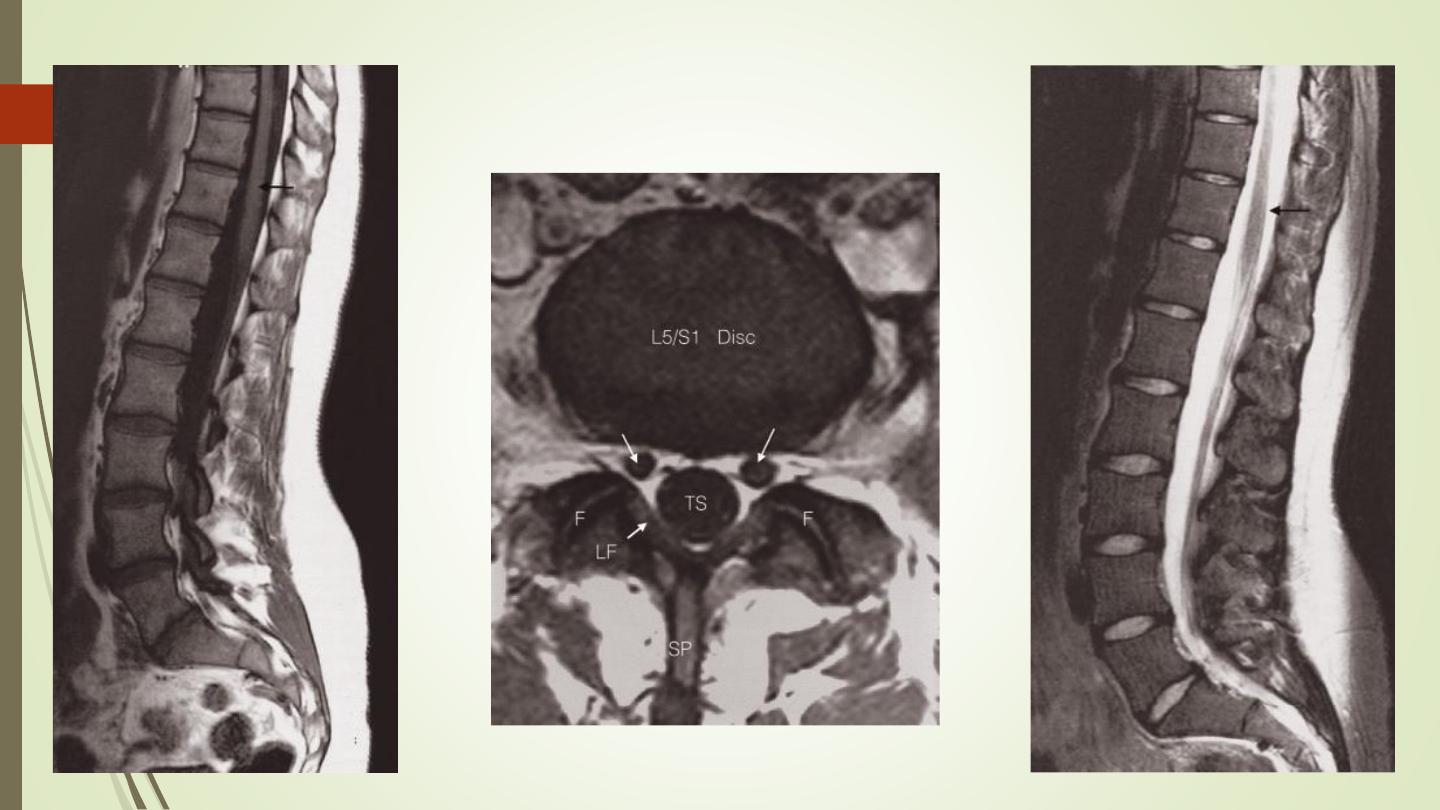
MRI

II) Signs of abnormality:
Disc space narrowing:
Collapse of vertebral bodies: most easily appreciated on
plain lateral radiographs of the spine, look to the
adjacent disc and pedicle. Common causes include:
❖
Metastases and myeloma.
❖
Infection
❖
Osteoporosis and osteomalacia
❖
Trauma
❖
Eosinophil granuloma: vertebra plana

II) Signs of abnormality:
Pedicles:
Dense vertebrae:
❖
Metastases‚
❖
Malignant lymphoma.
❖
Paget’s disease
❖
Hemangioma
Lysis within a vertebra: metastasis, MM, infection,
lymphoma.
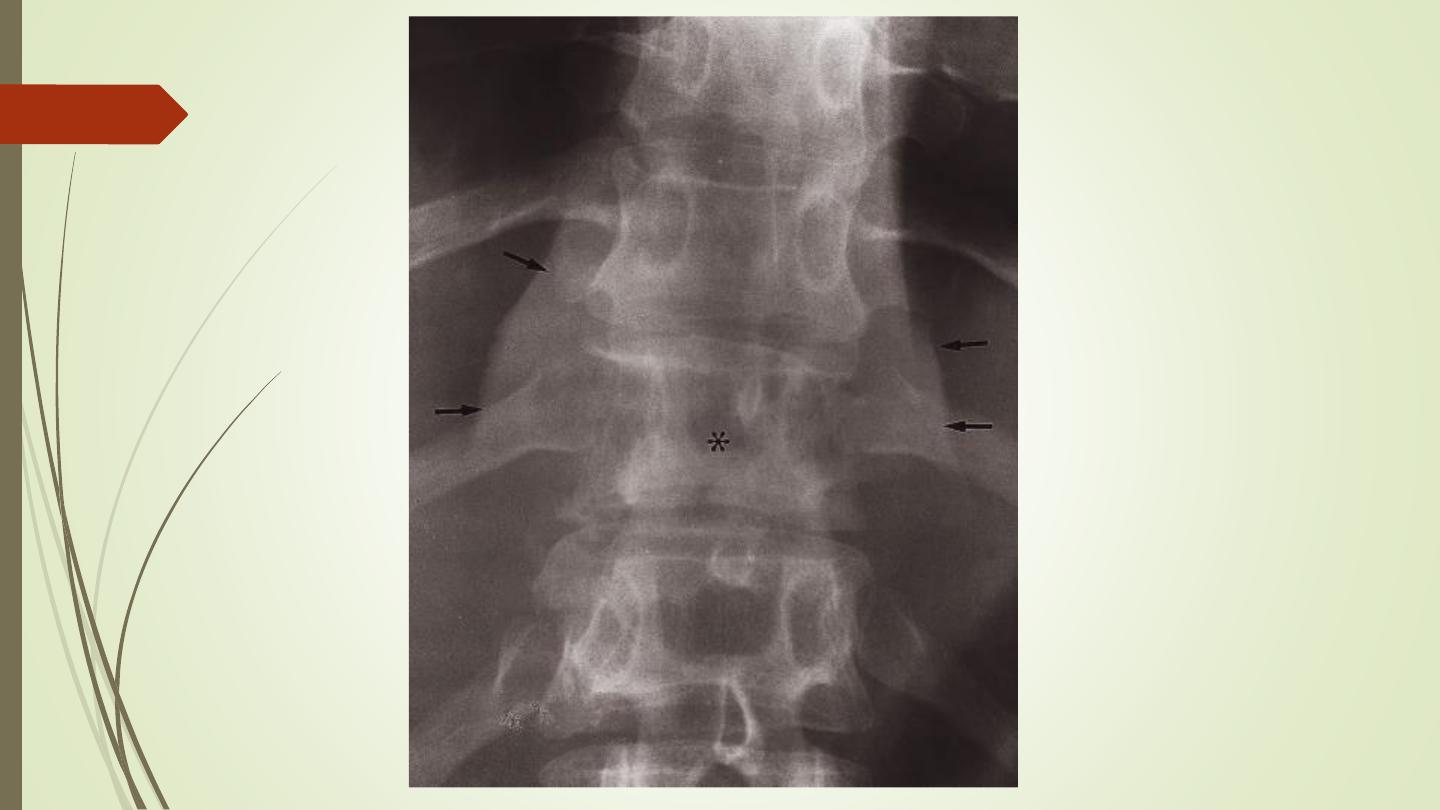
Paravertebral shadow
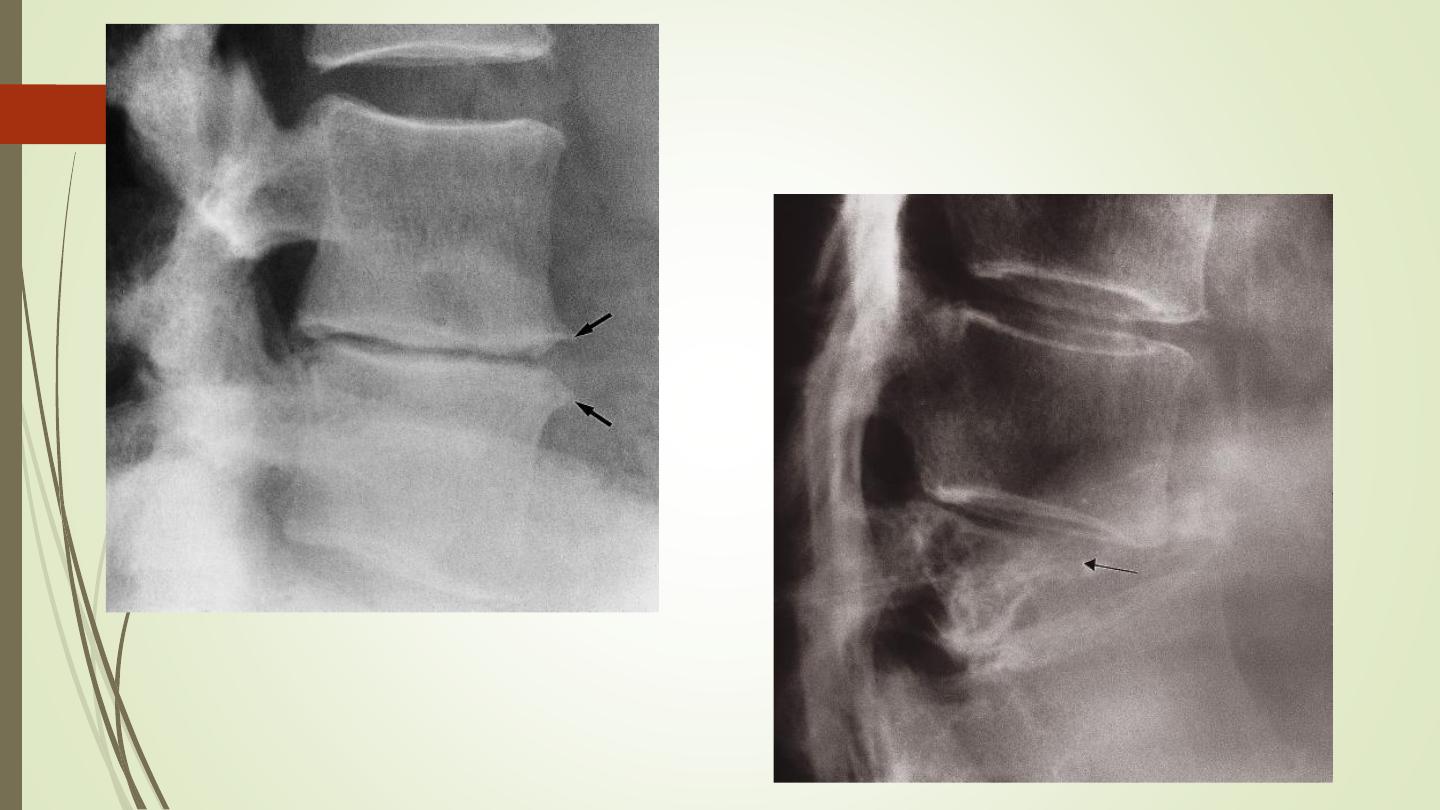

III) Pathologies:
Metastasis, multiple myeloma, lymphoma:
Metastasis can involve the pedicle, as well as vertebral body.
Collapse occur in all.
Intervertebral disc.
Radionuclide imaging
MRI
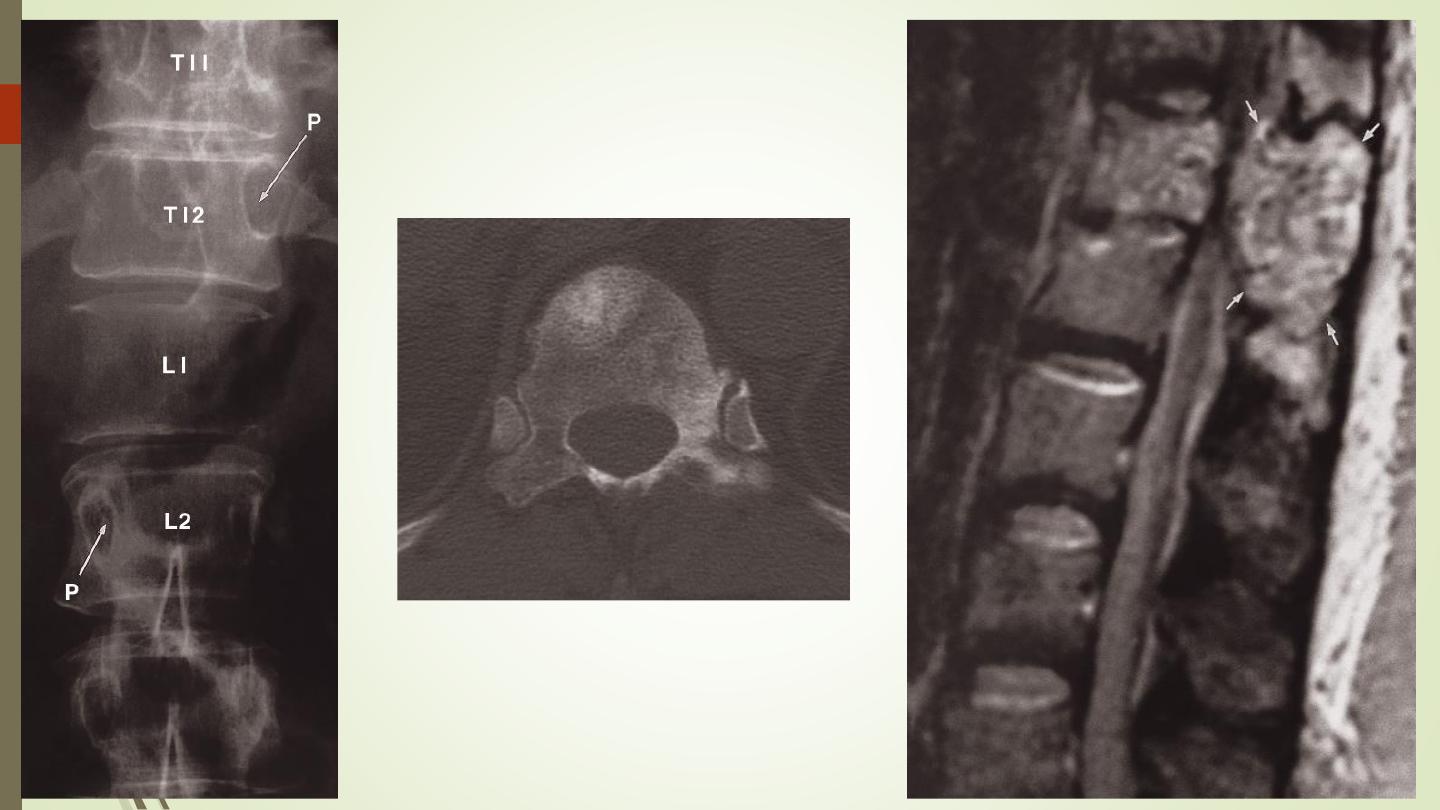
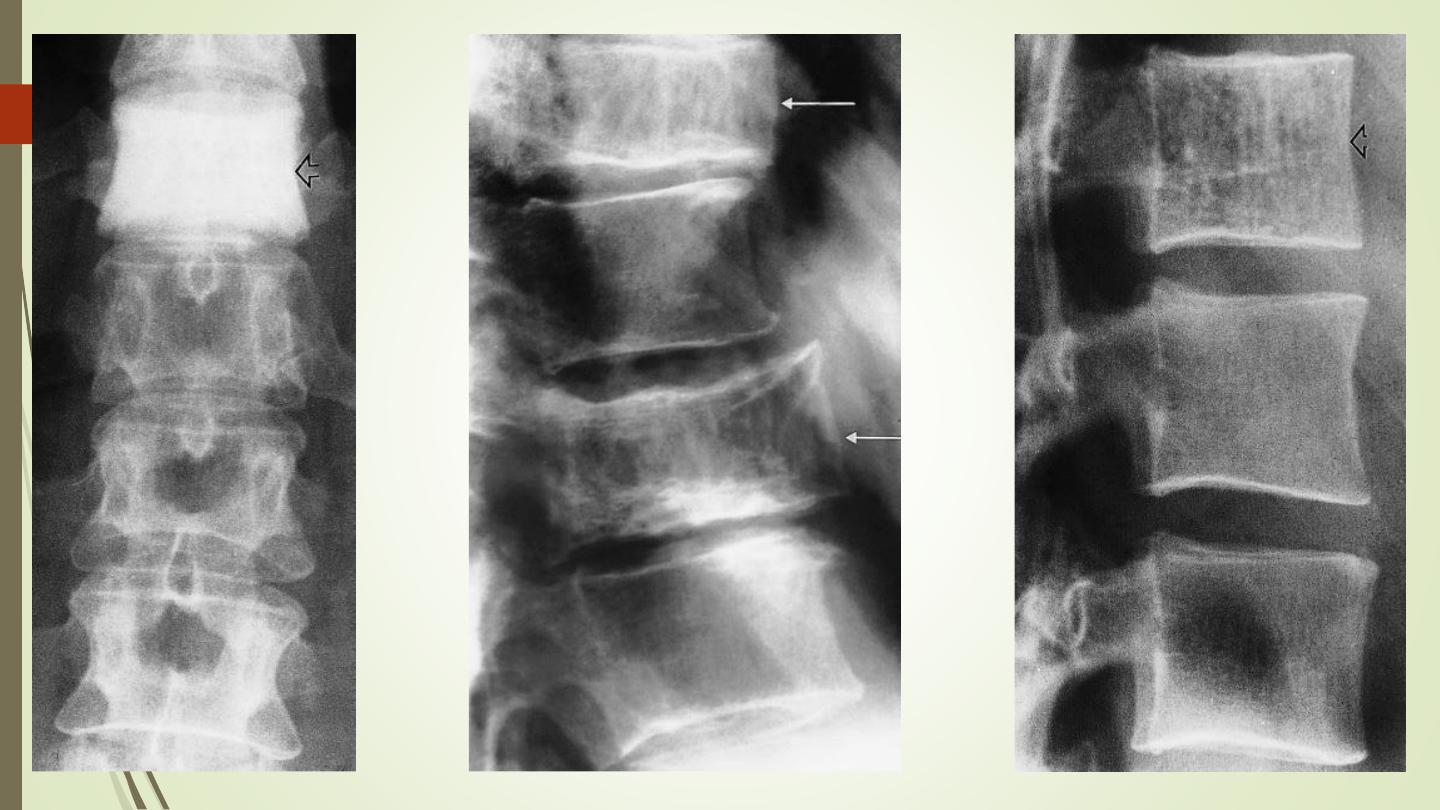
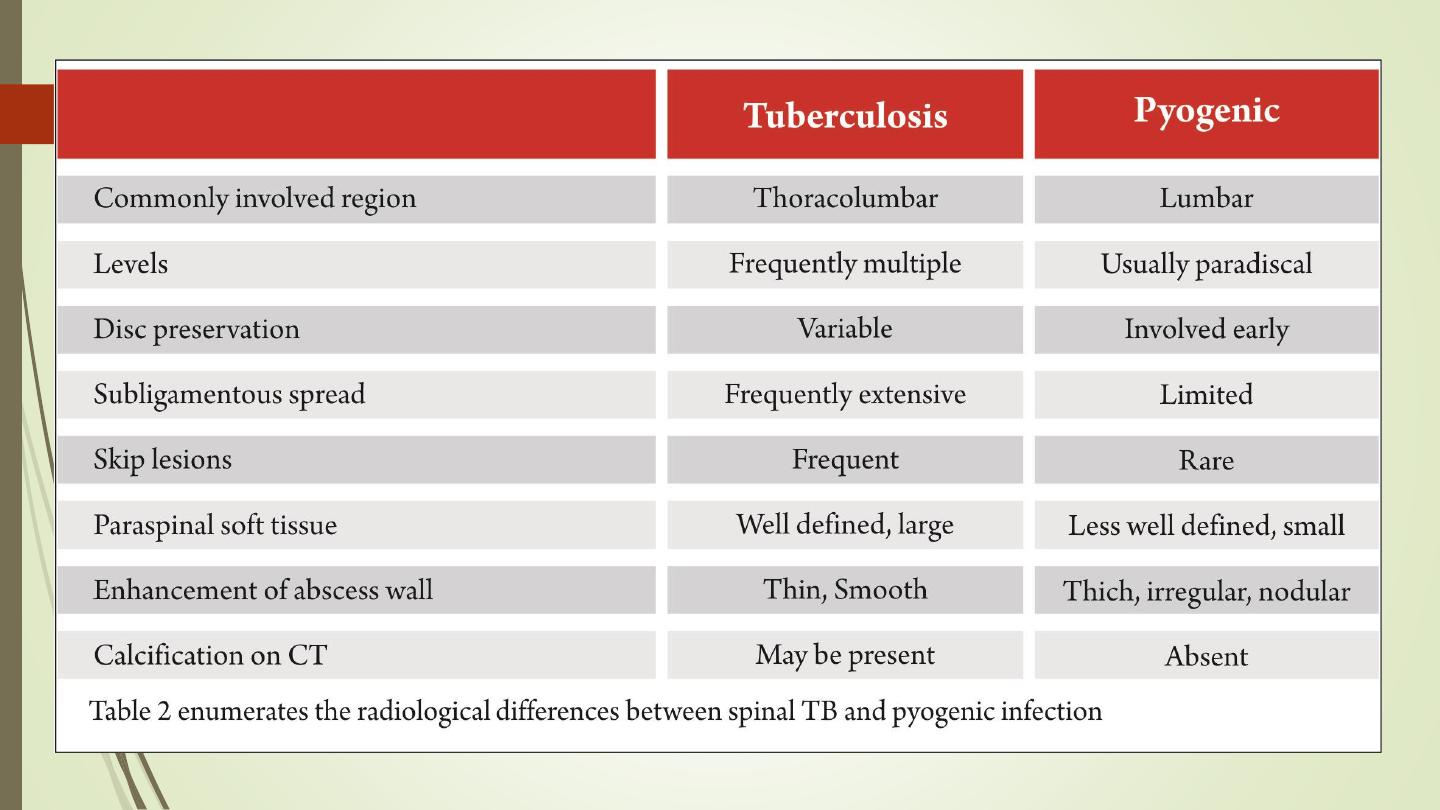
Infection:
IVD, end plates destruction, body.
Pyogenic or TB
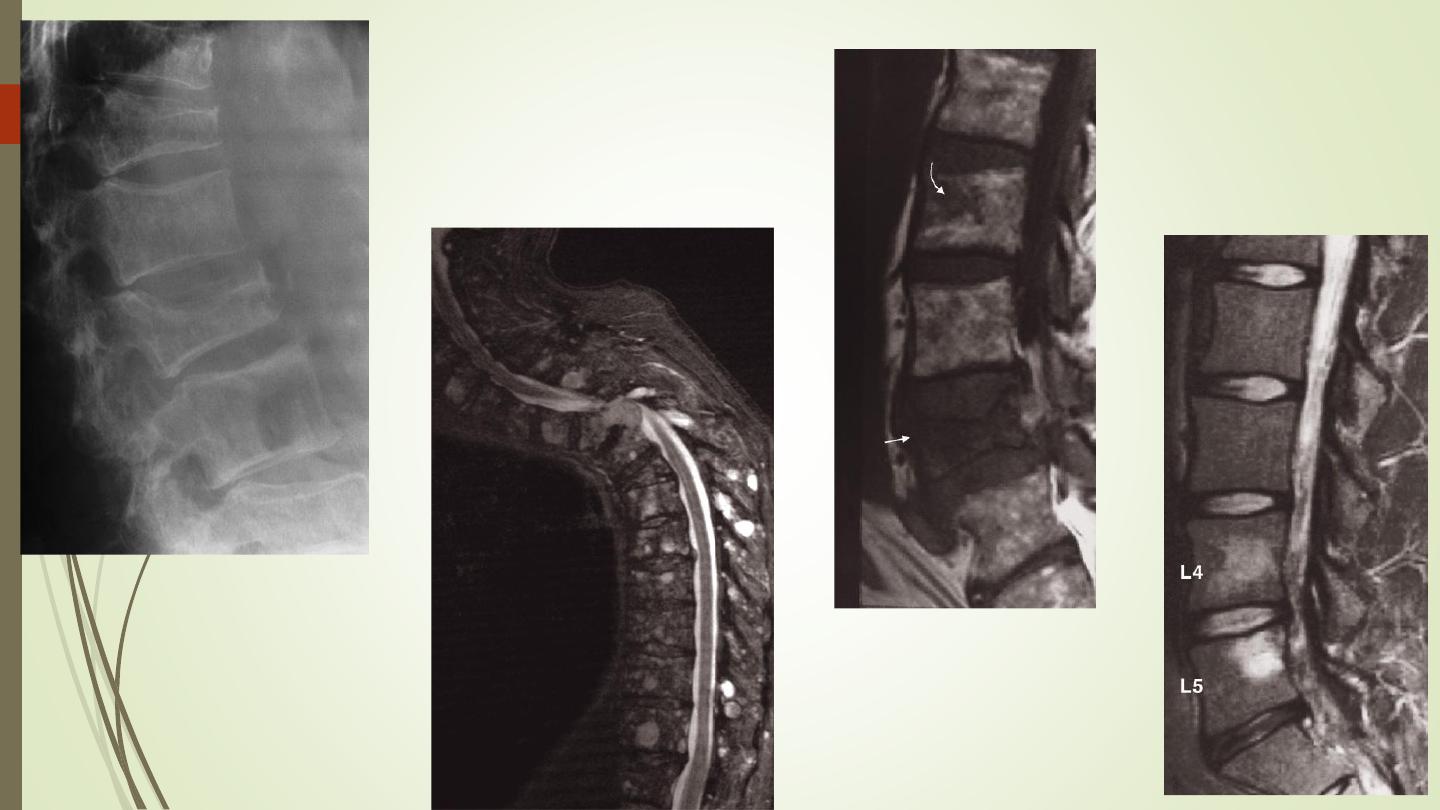
III) Pathologies:
Spinal trauma:
Plain films are the initial investigation for trauma
CT is indicated in patients with a high risk of spinal injury or with a
neurological deficit.
In the unconscious patient with a head injury, CT of the cervical
spine is carried out at the same time as a head CT
MRI: spinal cord injury, hematoma, disc bulge
Jefferson fracture: fractures of the lateral masses of C1.
hangman’s fracture: fracture of the arch of C2.
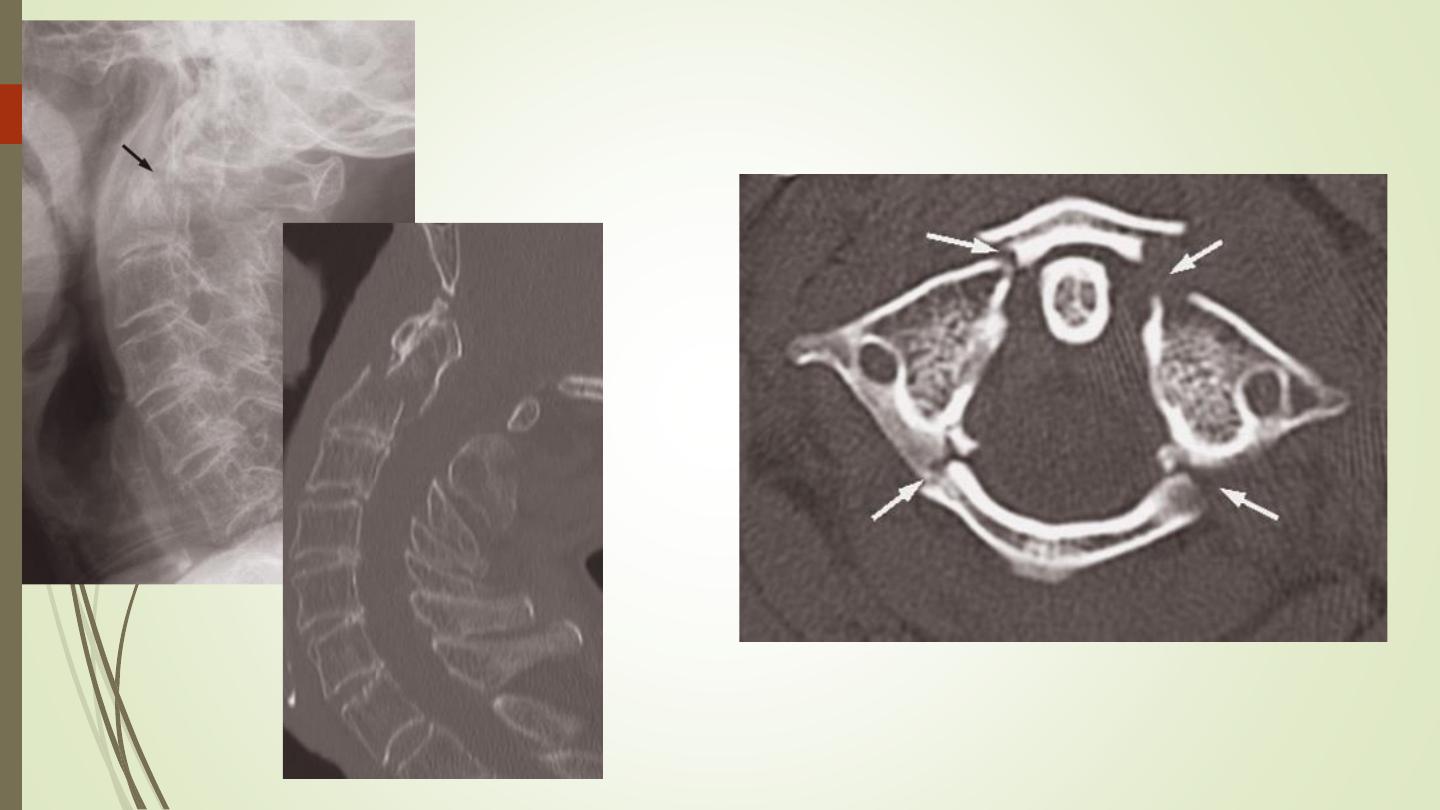
III) Pathologies:
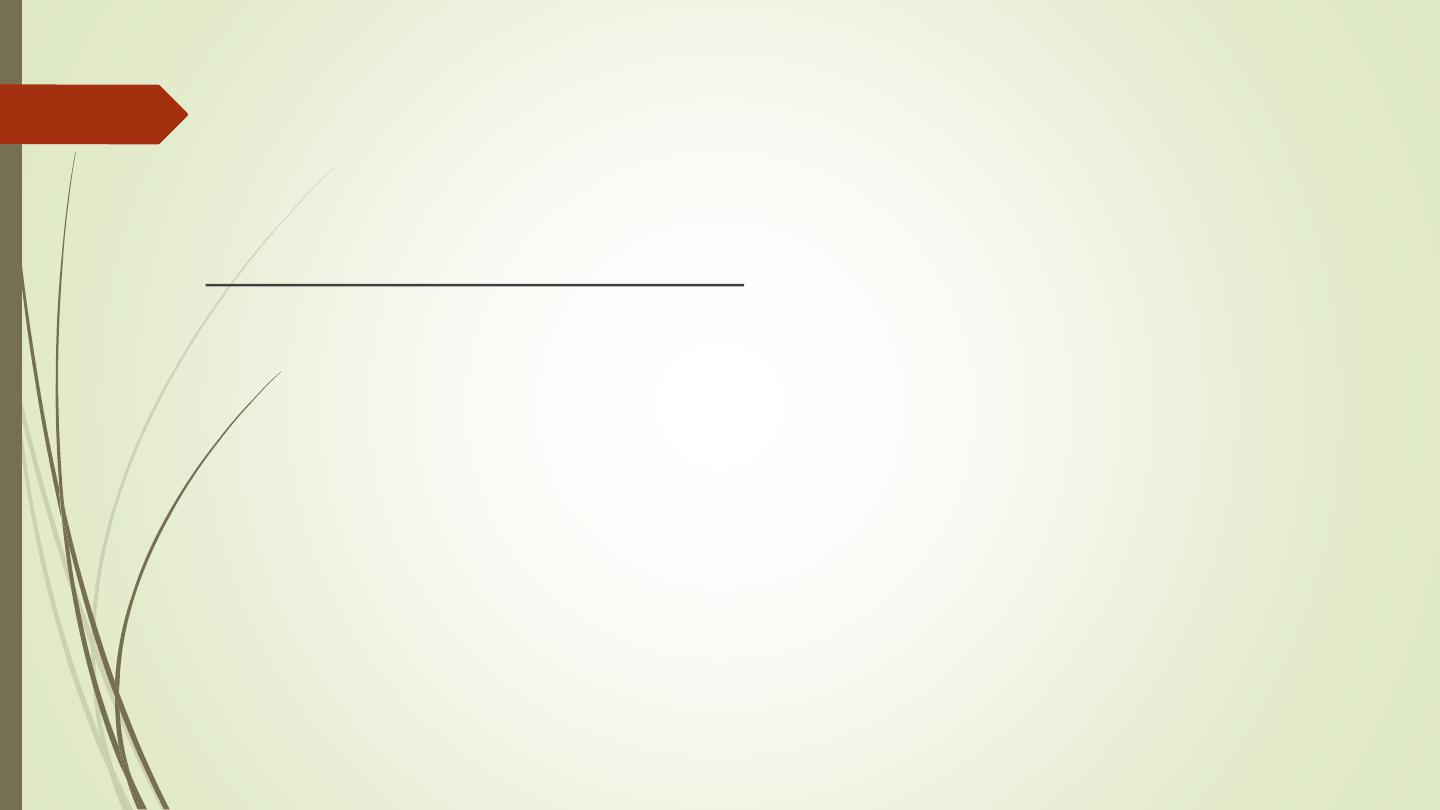
Degenerative disc disease
Spondylosis occurs maximally in the lower cervical and lower
lumbar regions.
Plain film signs: disc space narrowing, osteophytes, sclerosis.
MRI: IVD shows loss of height, reduced hydration (low T2). Disc
bulge or protrusion.
Spinal canal stenosis.
III) Pathologies:
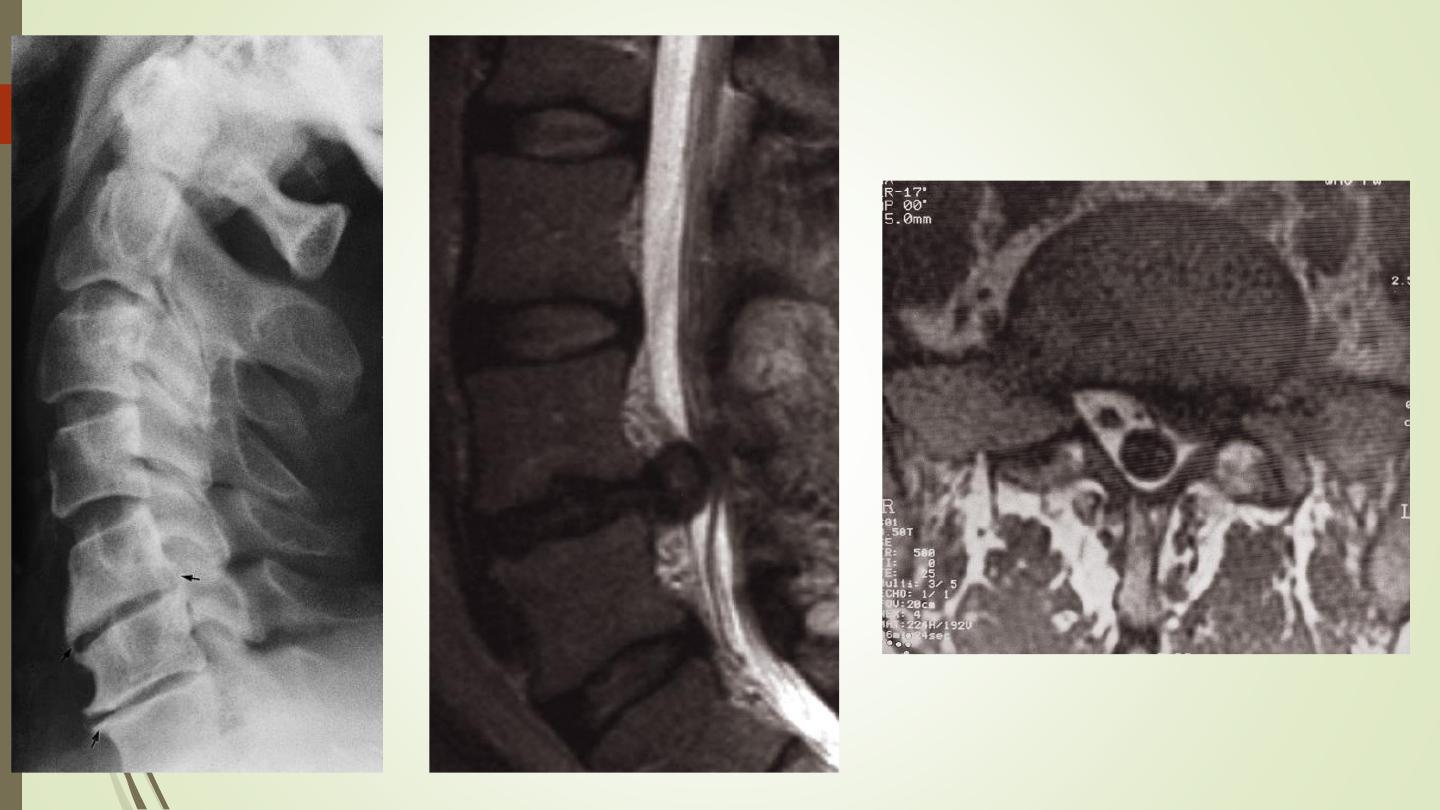
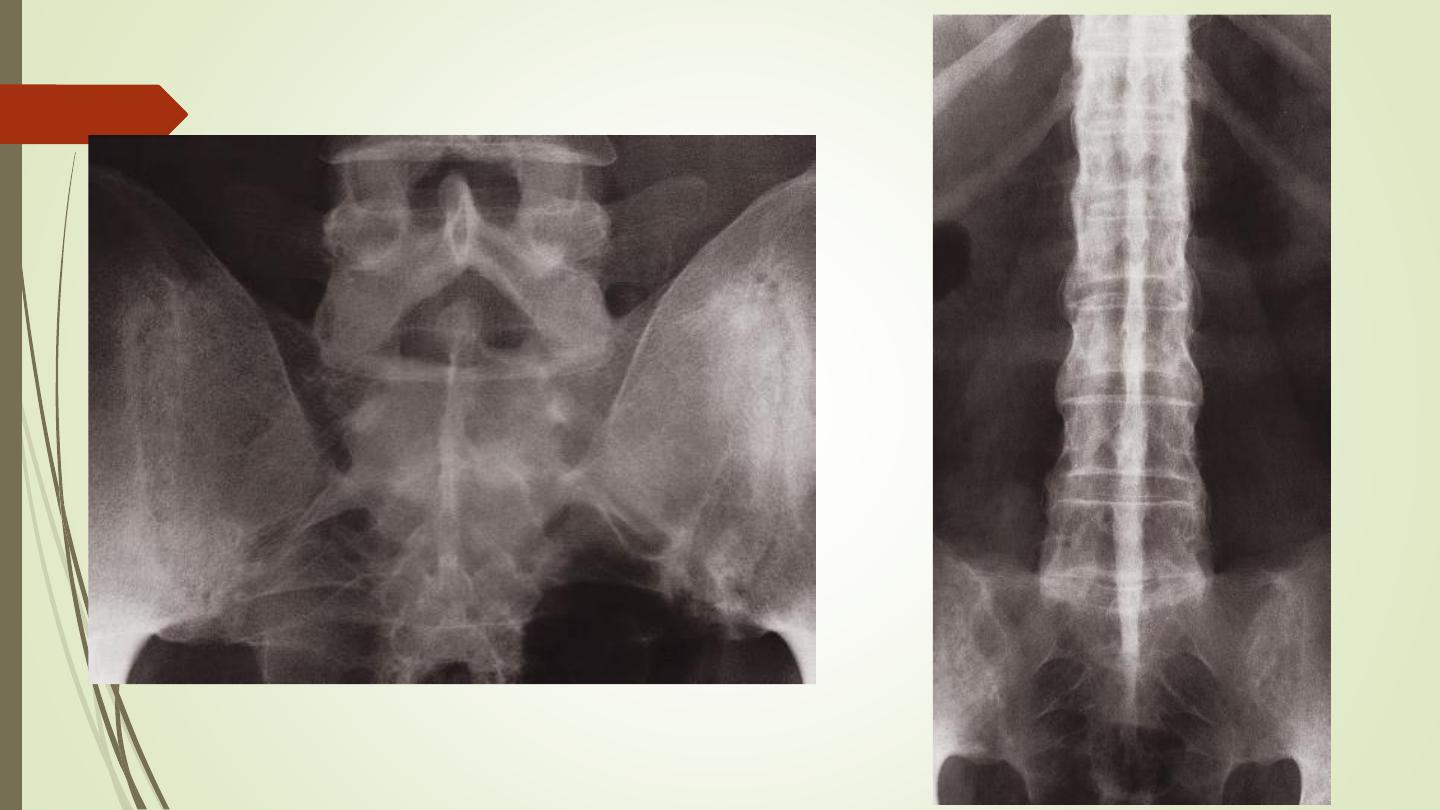
Ankylosing spondylitis
Affects principally the sacroiliac joints and the spine
The earliest radiological change is fuzziness of the joint margins, followed
by frank erosions. Eventually, the process leads to obliteration of the joint
space.
Syndesmophytes.
In advanced cases, the whole spine is rigidly fused and becomes a solid
block of bone. Known as a ‘bamboo spine’.
III) Pathologies:
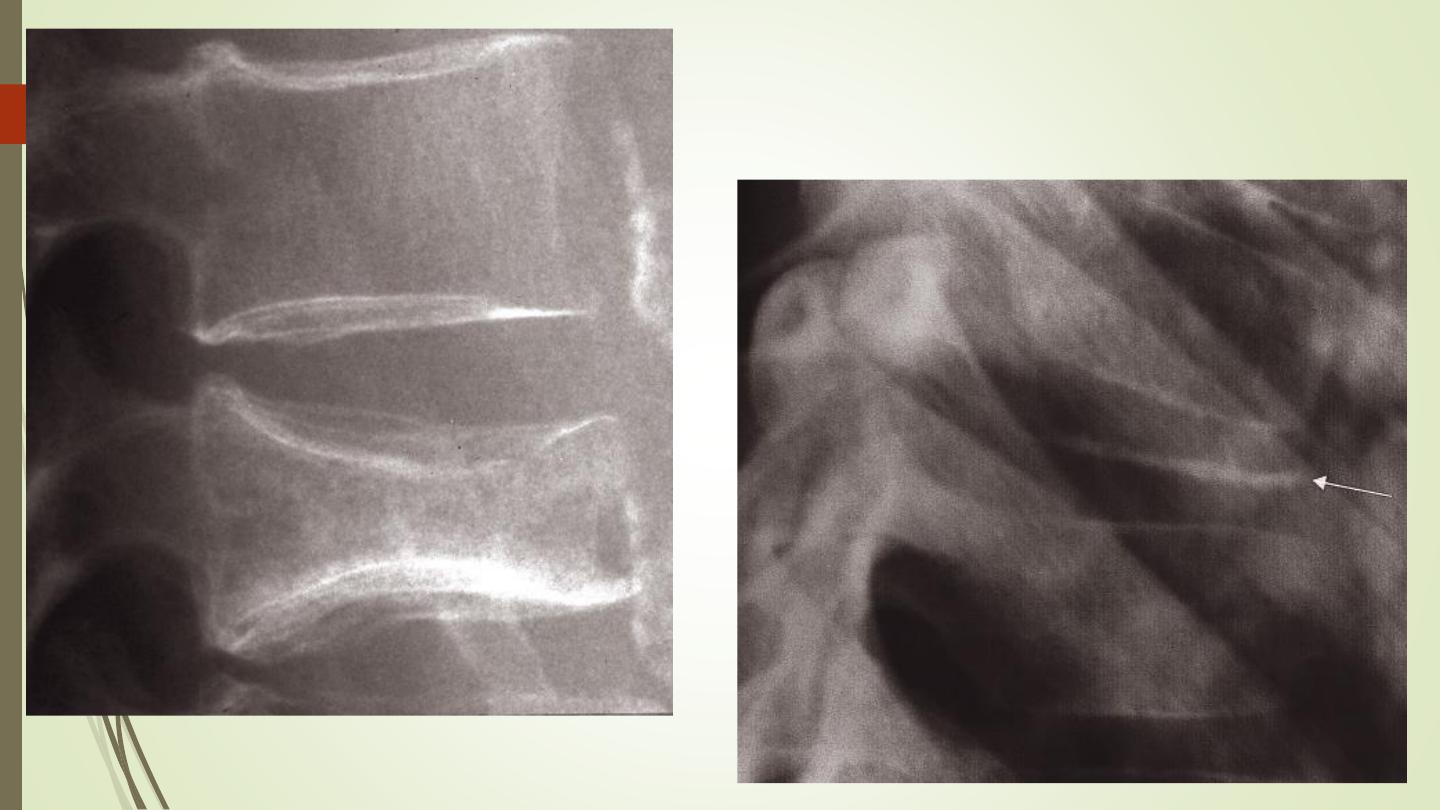
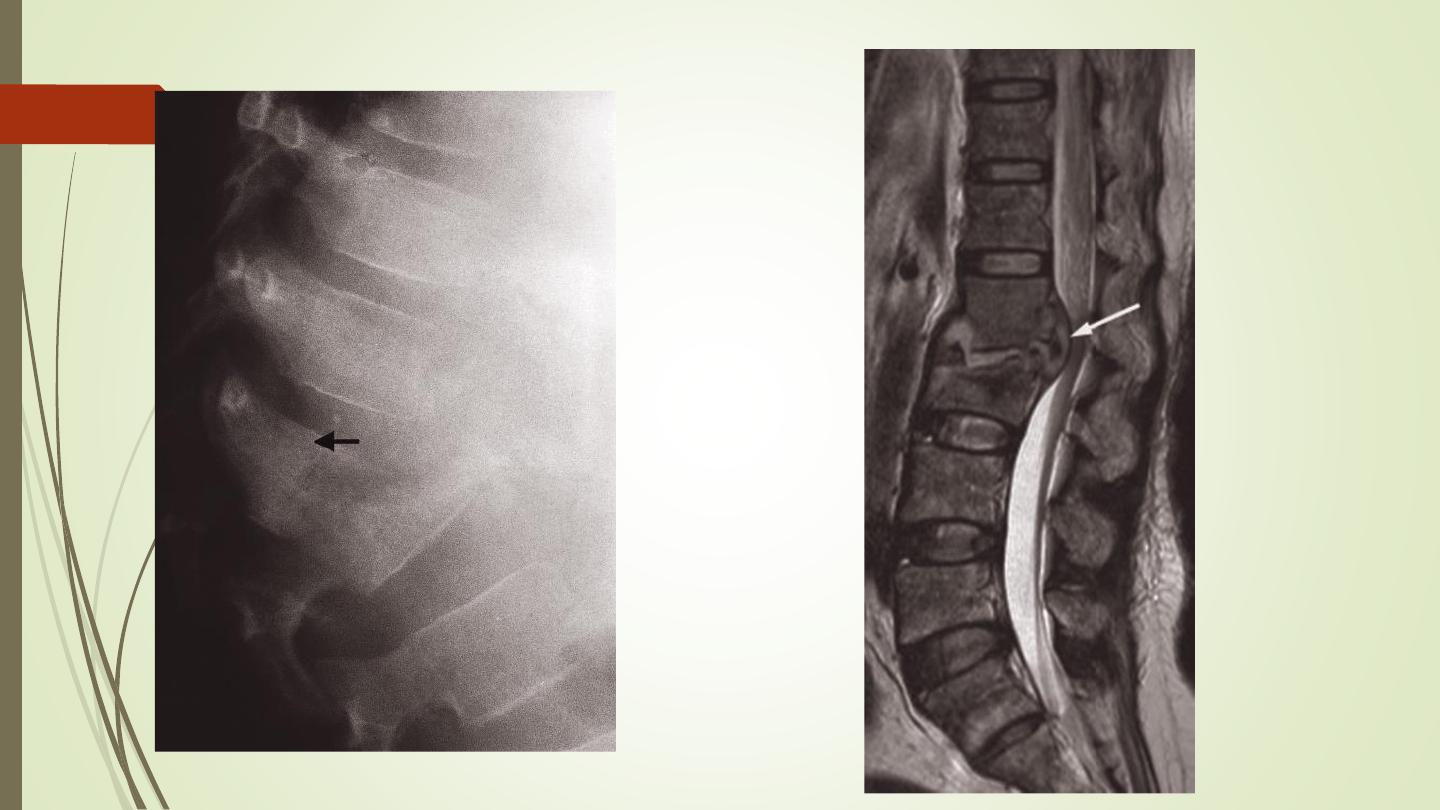
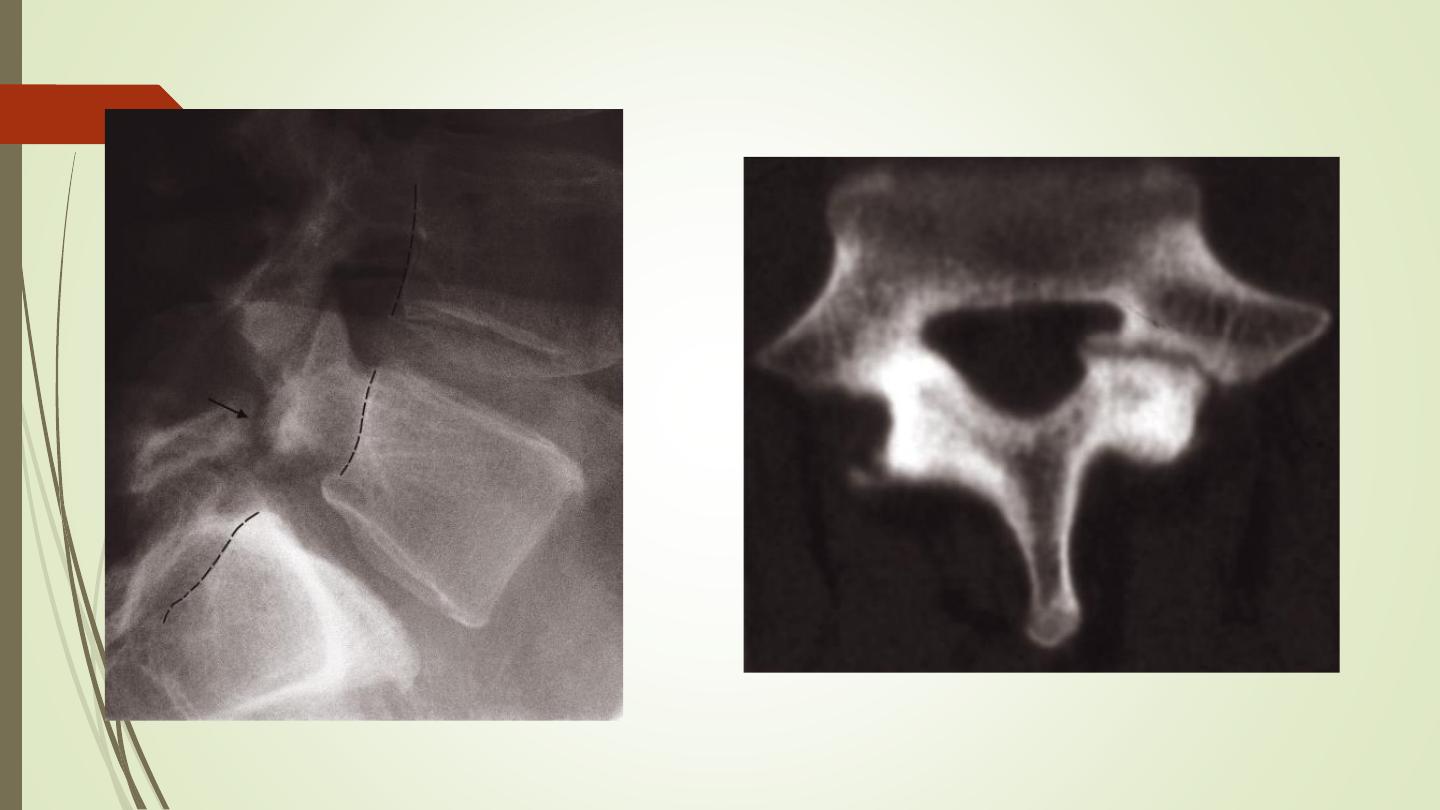
Spondylolisthesis:
Forward slip of one vertebral body on the one below.
Occurs most frequently at the lumbosacral junction and between
L4 and L5 vertebral bodies.
The defect in the pars interarticularis is thought to be a stress
fracture which can usually be identified on the lateral projection.
Spondylolysis: is the term given to a defect in the pars
interarticularis without a forward slip of one vertebral body on the
other.

Best regards
