
Geomorphic Processes:
Exogenic & Endogenic
Geomorphic Processes:
Physical processes which create and modify
on the surface of the earth
Endogenous (Endogenic) vs.Exogenous (Exogenic)
Processes
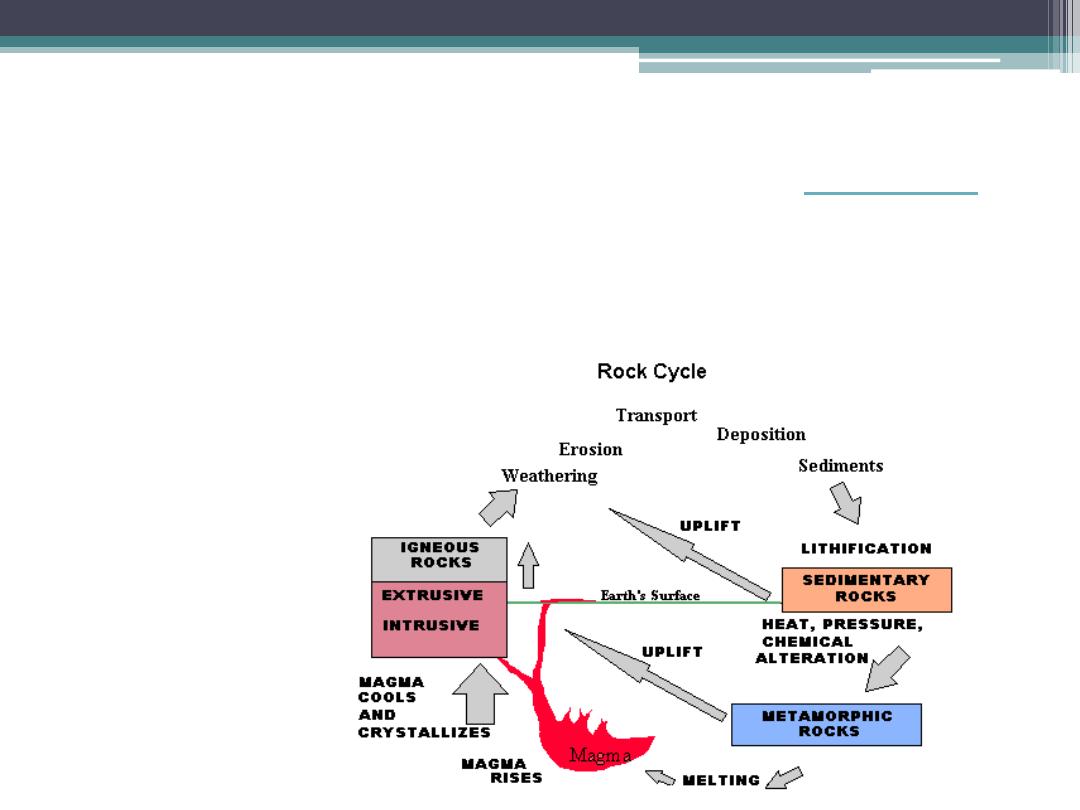
Rock Cycle

A. Endogenous Processes
Endogenous Processes are large-scale landform
building and transforming processes
– they create relief.
1. Volcanic Processes
a. Volcanism: Volcanic eruptions
Volcanoes
b. Plutonism: Igneous intrusions
2. Tectonic Processes (Also called Diastrophism)
a. Folding: anticlines, synclines, mountains
b. Faulting: rift valleys, graben, escarpments
c. Lateral Faulting: strike-slip faults
Earthquakes
evidence of present-day tectonic activity

B. Exogenous Processes
Degradation and aggradation
– they modify relief
a continuum of processes
– Weathering
Mass
Wasting
Erosion
Transportation
Deposition
these processes are carried through by Geomorphic
Agents: gravity, flowing water (rivers), moving ice
(glaciers), waves and tides (oceans and lakes), wind
1. Degradation Processes
Also called Denudation Processes
a. Weathering , b. Mass Wasting and c. Erosion
and Transportation
2. Aggradation Processes
a. Deposition
– fluvial, eolian, glacial, coastal

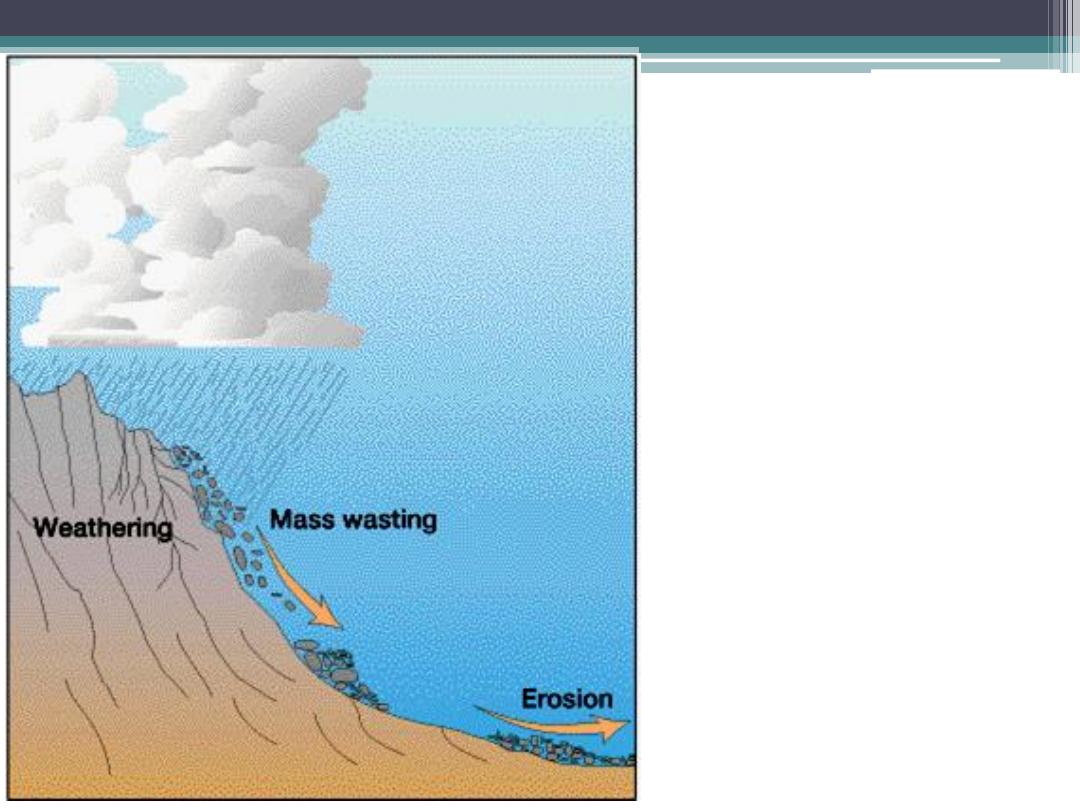
Relationship:
Weathering
Mass Wasting
Erosion
and
Transportation
Together,
these processes are
responsible for
Denudation
of Earth
’s surface

WEATHERING
mechanical and chemical weathering that fragments rock
masses into smaller components that amass on-site, before being
moved by gravity or transported by other agents
The processes begin in microscopic spaces, cracks, joints,
faults, fractures, lava vesicles and other rock cavities
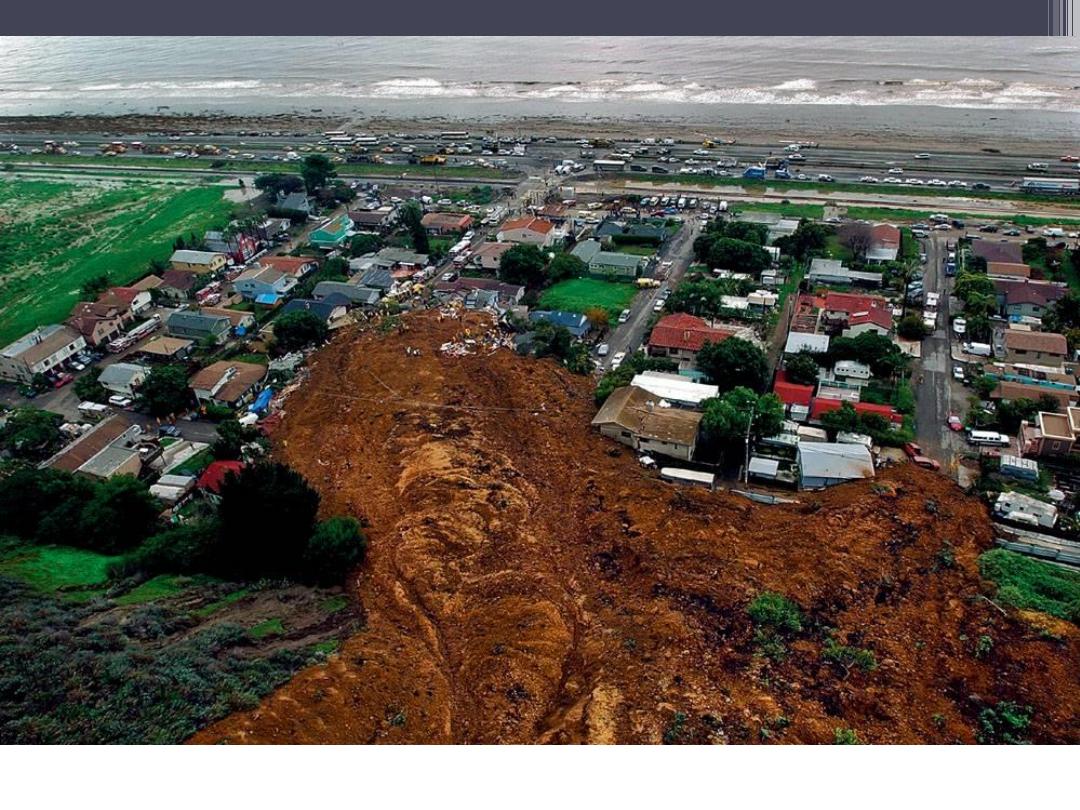

La Conchita Landslide, January 10, 2005
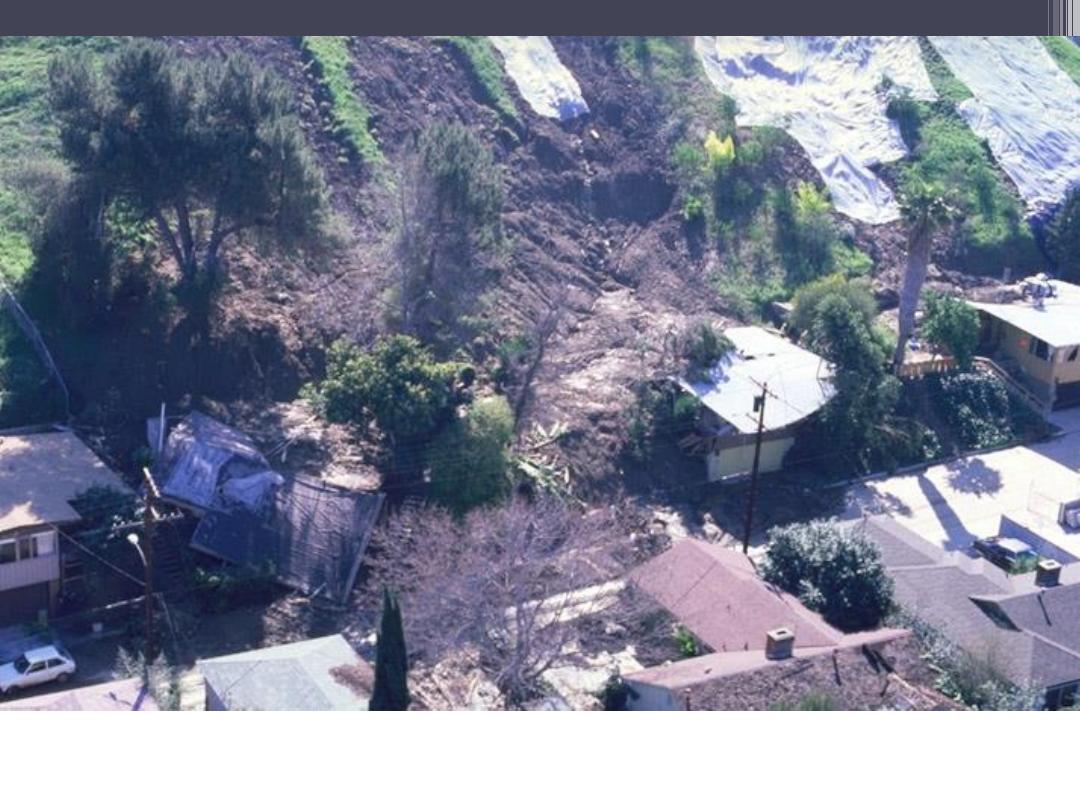

Monterey Park Debris Flow, 1980
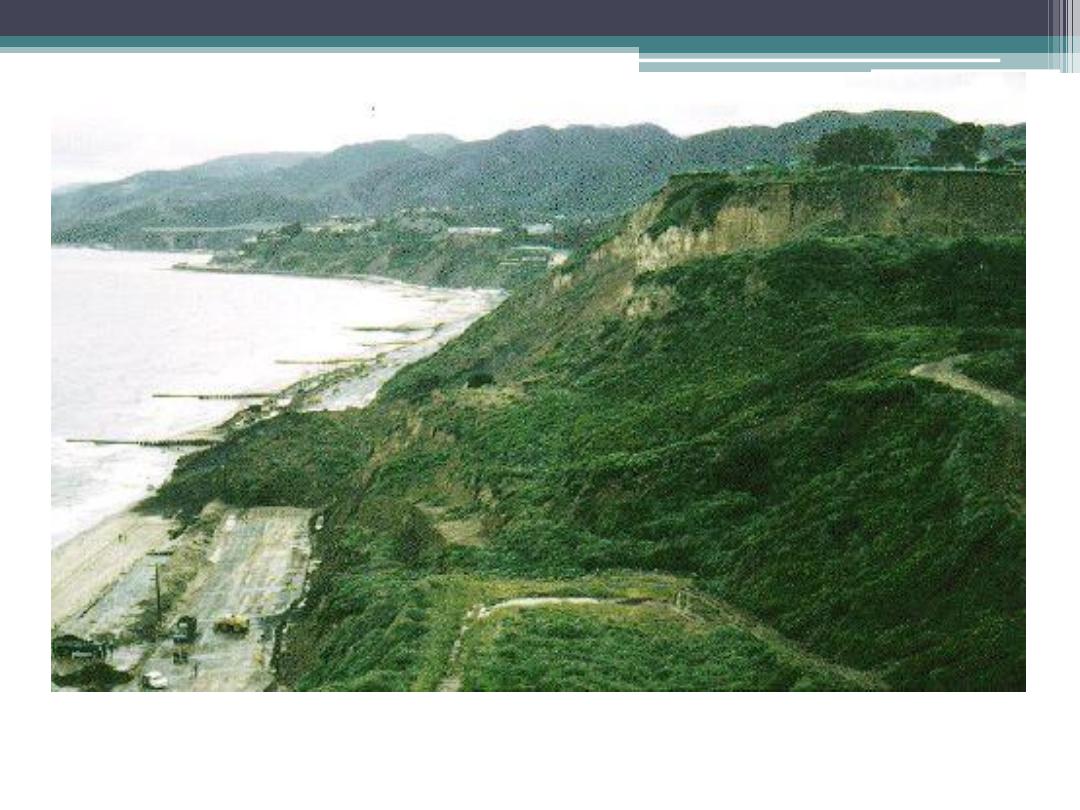

PCH near Pacific Palisades, November 1956

EROSION and TRANSPORTATION
– Various Geomorphic Agents, associated Processes,
and resulting Erosional Features
• Flowing Water –
Fluvial Morphology
Humid regions:
Perennial streams and entrenched
channels, rapids, waterfalls, plunge
pools, potholes, meandering streams,
bank erosion, oxbow lakes, etc.

•
Wind
–
Aeolian Landscapes
Dunes
• Tides and Waves –
Coastal Morphology
Sea cliffs, sea caves, sea arches, sea stacks,
wave-cut beaches, etc..
• Moving Ice –
Glacial Morphology
glacial troughs (U-shaped valleys), hanging
valleys, glacial lakes,.

DEPOSITION
– Various geomorphic agents, associated processes and
resulting Depositional Features
• Fluvial –
Humid regions: Braided streams, sand bars, floodplains
(alluvium deposits),
natural
levees, distributaries, deltas
Arid regions: Alluvial fans, bajadas,
piedmont alluvial plains, playas,
playa lakes, Salinas
(salt flats)
• Aeolian –
Sand dunes
(Barchans, Parabolic, Transverse,
Longitudinal, Star)
, and sand sheets
• Coastal –
Sea beaches and coral reefs
• Glacial –
Alpine: Glacial drifts, tills, moraines
(lateral, medial, end,
terminal, recessional, and ground)
Continental: Till plains, outwash plains, drumlins, eskers,
kames, erratic
