Fall in elderly
Adel Gassab MohammedMD, CABMS, MSc of Medicine Specialist Endocrinologist, Thi-Qar Specialized Diabetes, Endocrine and Metabolism Center, Lecturer Diabetes, Endocrine and Metabolism Division, Department of Medicine, College of Medicine, University of Thi-Qar,
• Outline:
• Introductions of falls in elderly.• Cause and risk factors of falls.
• Consequences of falls in elderly.
• Assessment of fall in elderly.
• Preventing falls in older people.
• Summary.
• Definition of Falls
• A fall is defined as an event which results in a person coming to rest inadvertently on the ground or floor or other lower level.• Introduction
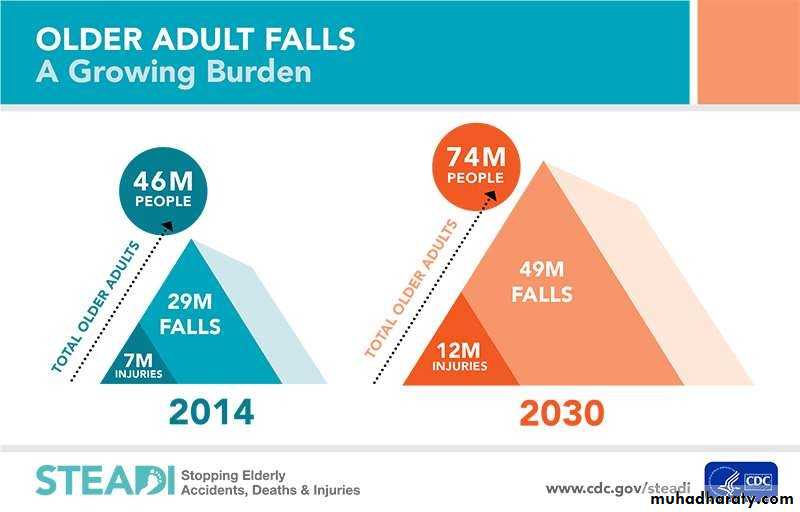
• Falls and fall-related injuries are a common& serious problem for older people.
• Fall potentially life- threatening events and may be simply the first signs of single problem.
• It lead to hospitalization and increase cost and burden on society and even lead to death .
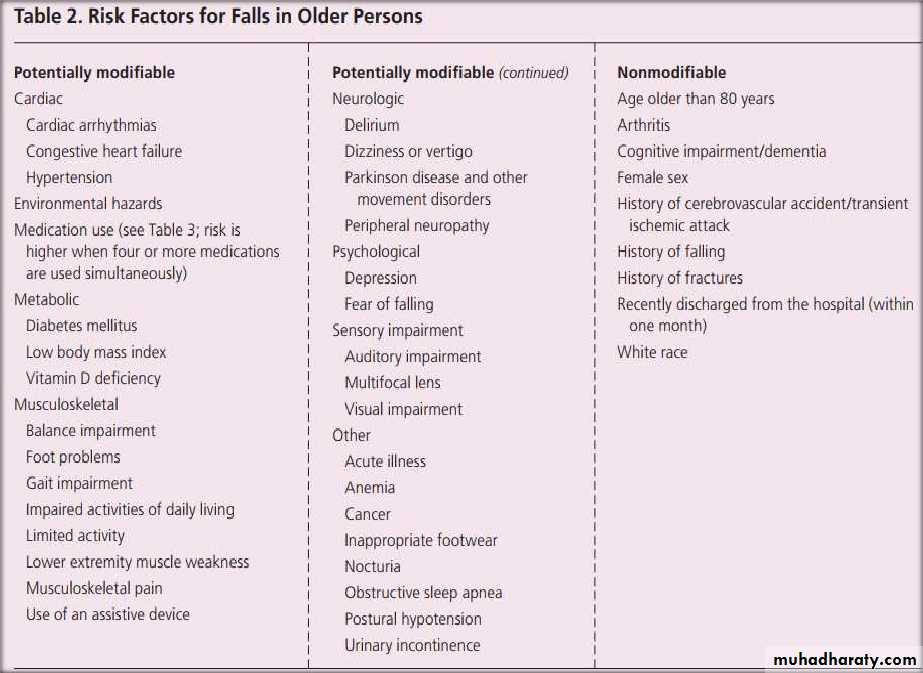
• Intrinsic risk factors:
• Age Related changes (Visual function Neurological function, Musculoskeletal function)• Diseases Female sex
• Extrinsic risk factors:
• Drugs Environmental Improper assistive
• devices
• (I HATE FALLING)
• I: Inflammation of joints (or joint deformity)• H: Hypotension (orthostatic blood pressure changes)
• A: Auditory and visual abnormalities
• T: Tremor (Parkinson's disease or other causes of tremor)
• E: Equilibrium (balance) problem
• F: Foot problems
• A: Arrhythmia, heart block or valvular disease
• L: Leg-length discrepancy
• L: Lack of conditioning (generalized weakness)
• I: Illness
• N: Nutrition (poor; weight loss)
• G: Gait disturbance
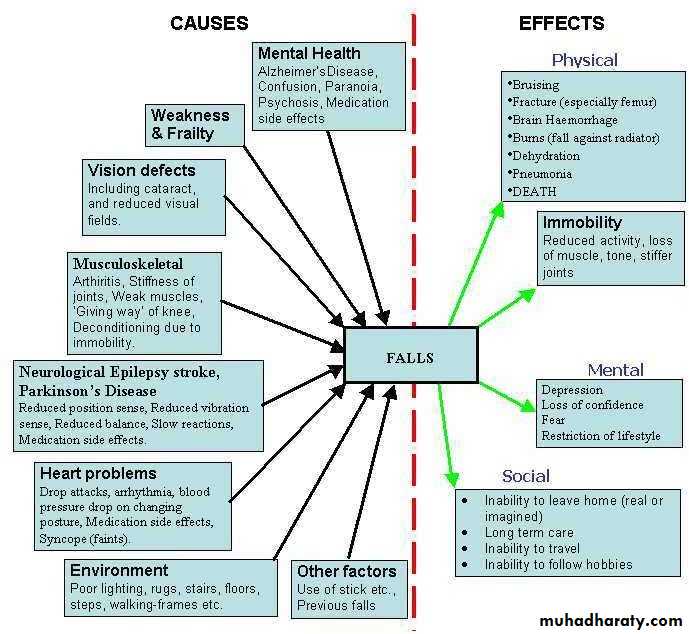
• Consequence of falls
• Physical:• Skin tear internal bleeding
• subdural hematoma Hip fracture Immobilization /
• disability
• Hospitalization
• Psychological:
• Fear of falling increased dependency Depression
• Anxiety
• loss of confidence social withdrawal
• ASSESSMENT OF FALL
• How to approach elderly with fall• History
• Examination• Investigations
• History• A thorough history is essential to determine:
• Fall ( mechanism of fall, Location, Activity, Injury related to the fall, witness/help)• Associated symptoms concurrent with a fall (change in level of or loss of consciousness, chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, vertigo or lightheadedness, Symptoms related to a change in position ,headache, weakness/tingling/numbness or acute change in mental status)
• previous falls and whether the falls were the same or different in character.
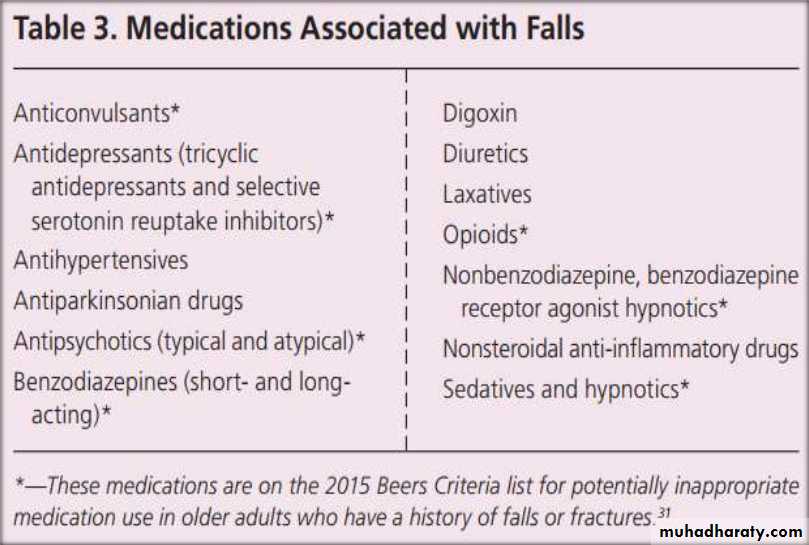
• medical history• Medications
• Functional history
• Social history
• Physical Examination
• General looking Hydration status postural changes
• Vital signs( orthostatic hypotension) Visual & Hearing abnormalities
• Cardiovascular: murmur ,presence of arrhythmias & carotid bruits
• Neurologic and mental evaluation: looking for focal deficits, assessment of lower extremity peripheral nerves,• proprioception, vibration sense, and tests for cortical, cerebellar, and extrapyramidal functions is important.
• Musculoskeletal: lower-extremity weakness, presence of contractures, limitations or pain in range of motion
• Gait and balance: abnormalities, lower extremity strength, and joint function.
• Environmental assessment: Lighting, walking surface, furniture, clothing, and equipment
• Testing and imaging
• Complete blood count, Electrolyte, Blood urea nitrogen , Creatinine , Glucose , Thyroid function, Vitamin B12 levels• X-ray
• ECG, ECHO, EEG
• Brain imaging(CT/MRI)
• DEXA(dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry)
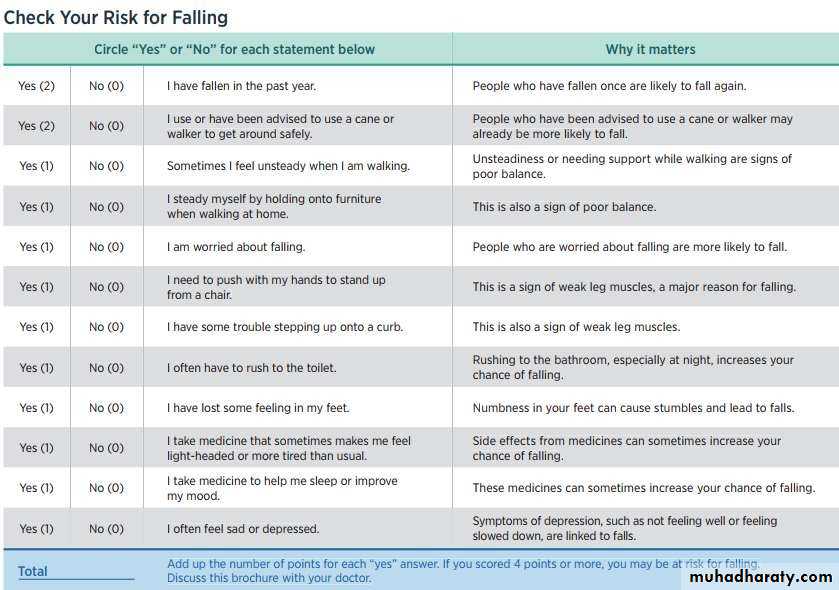
• The American Geriatrics Society and British Geriatrics Society recommend that all adults older than 65 years be screened annually for a history of falls or balance impairment.
• Evaluate gait, strength, and balance
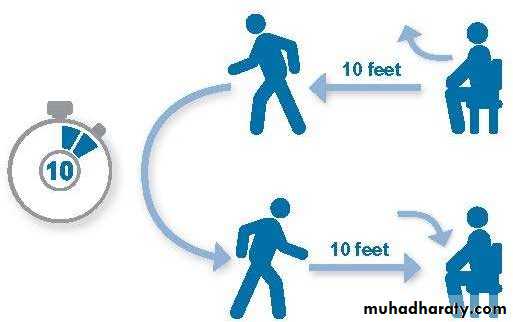
• Recommended test:• Timed Up and Go
• Optional tests:
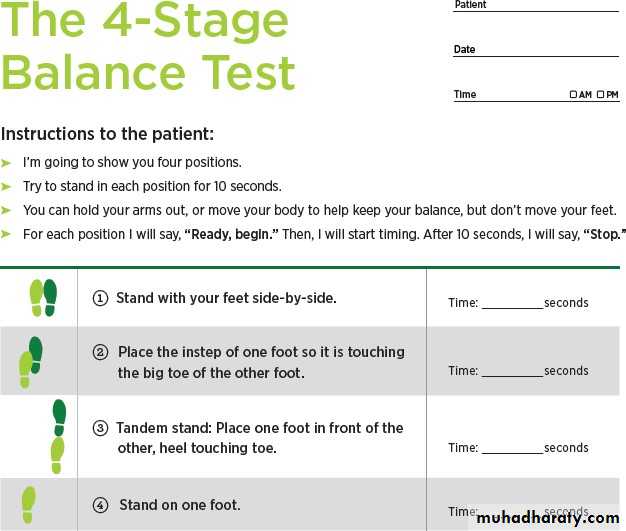
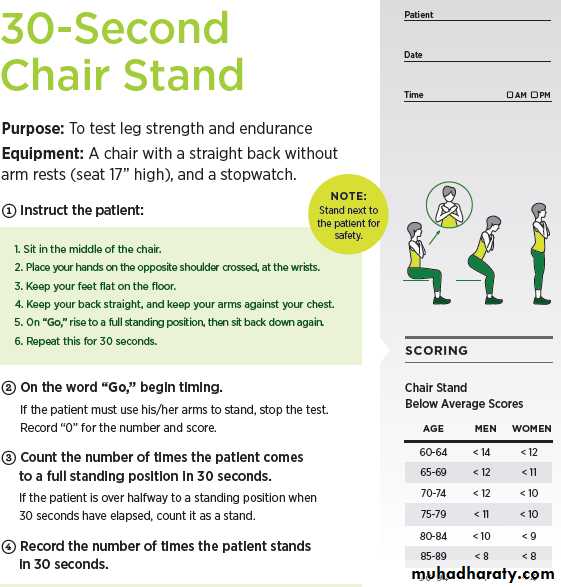
• 30-Second Chair Stand 4-Stage Balance tests
• https://youtu.be/Ng-UOHjTejY
• https://youtu.be/3HvMLLIGY6c• https://youtu.be/BA7Y_oLElGY
• PREVENTION OF FALL
• Participate in regular physical activity. Exercise makes you stronger, increases flexibility and improves balance and coordination. ...
• Remove hazards in your home. ...
• Review your medications regularly. ...
• Have your vision and hearing checked once a year. ...
• Talk to your family members and enlist their help.
Five Safe Steps to Prevent Falls Among Elderly
• Multifactorial falls risk assessment
• identification of falls history• assessment of visual impairment
• assessment of cognitive impairment and neurological examination
• cardiovascular examination and medication review.
• assessment of gait, balance and mobility, and muscle weakness
• assessment of osteoporosis risk
• assessment of the older person's perceived functional ability and fear relating to falling
• assessment of urinary incontinence
• assessment of home hazards
• Multifactorial interventions
• An intervention with multiple components that aims to address the risk factors for falling that are identified in a person's multifactorial assessment.
• MULTIFACTORIAL INTERVENTIONS
• Multifactorial interventions should include: Exercise, particularly balance, strength, and gait training• Vitamin D supplementation with or without calcium
• Management of medications Home environment modification
• Management of postural hypotension, vision problems, foot problems, and footwear.
• Improve home supports.
• Provide opportunities for socialization and encouragement.• Involve the family.
• Provide follow-up.
• Rehabilitation
• Adequate rehabilitation physically, socially, and psychologically of injured person is very important post fall.• SUMMARY