Oral Histology
Lec.3 Dr. Anes AdnanDevelopment of the tooth
Part two \ Clinical considerations
Developmental anomalies affecting the morphology of teeth
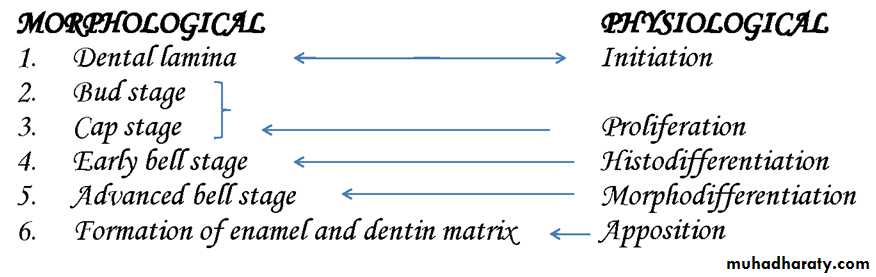
Disturbance of the epithelium and mesenchymal interactions can markedly alter the normal odontogenesis leading to the developmental anomaly of teeth. Depending on the developmental stage in which the alteration has taken place, different anomalies could take place as anomalies of number, structure, size and shape.Time / weeks
6-78
9-10
1112
varies per tooth
Time / weeks6-7
8
9-10
11
12
varies per tooth
Appositional stage
Secretion of enamel, dentin and cementum that initially secreted as a matrix that is partially calcified – serves as a framework for later calcification during varying periods of time of maturation to each tooth.Maturation Stage (Crown Stage):
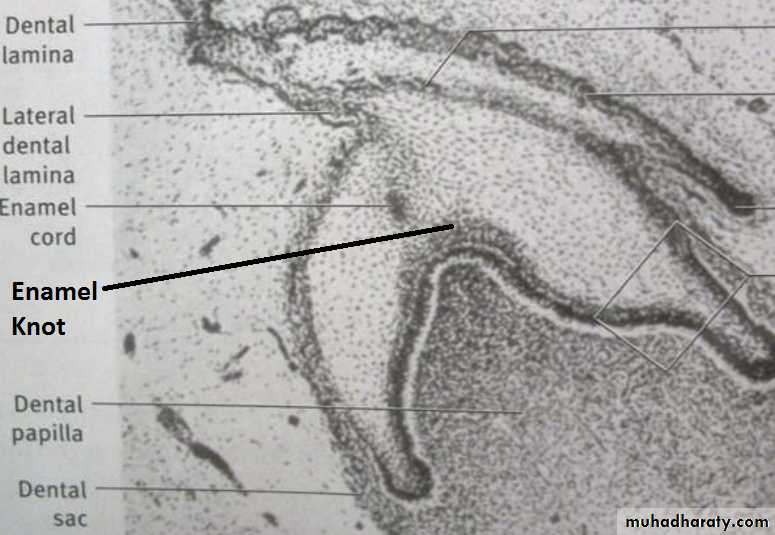
This stage is characterised by the completion of calcification. Hard tissues including enamel and dentin develop during this stage. Formation of dentin, known as dentinogenesis, is the first identifiable feature of this stage. More than 300 genes have been known to be expressed in teeth that are responsible for odontogenesis. Defects in these genes have been found to be one of the reasons for alteration of the morphology of tooth (genetics and hereditary).The cells in the center of the enamel organ are densely packed and form the enamel knot. This knot projects toward the underlying dental papilla. At the same time a vertical extension of the enamel knot, called the enamel cord will be formed.
The function of enamel knot & cord act as a reservoir of the dividing cells for the growing enamel organ. The enamel knot act as a signaling centers as many important growth factors are expressed by the cells of the enamel knot, thus play an important role in determining the shape of the tooth.
The Hedgehog signaling pathway
The signaling pathway that transmits information to embryonic cells required for proper cell differentiation. Sonic hedgehog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHH ("sonic hedgehog") gene.In early tooth development, SHH is released from the primary enamel knot, a signaling center, to provide information in tooth development and regulation of tooth cusp growth.
After the primary enamel knots are apoptosed (apoptosis = biochemical events lead to cell changes morphology and death), the secondary enamel knots are formed. The secondary enamel knots secrete SHH in combination with other signaling molecules (the others being desert hedgehog (DHH) and Indian hedgehog (IHH)) to begin the shaping of the crown of a tooth during differentiation and mineralization.
Ectodermal dysplasia:
Group of developmental inherited disorders involving the defects of ectodermal structures (hair, teeth, nails, skin and sweat glands). These disorders as a result of genetic mutation (abnormal sequences) between initiation and appositional stage.Developmental alterations (number)
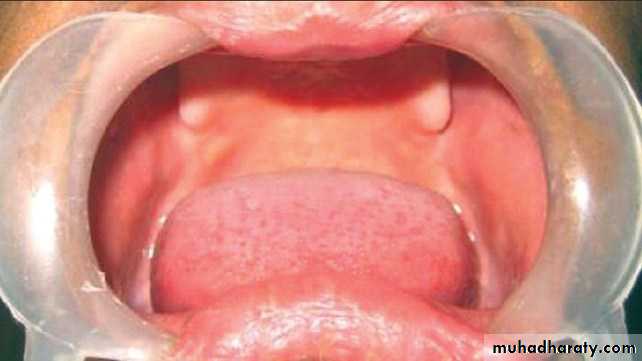
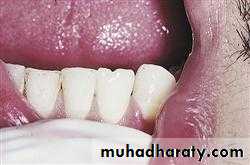
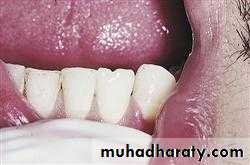
1. ANODONTIA
Anodontia is a genetic disorder characterized by the congenital absence of primary or permanent teeth. Anodontia is usually associated with ectodermal dysplasia. Since it occurring during Initiation.
Types of Anodontia
1. Complete anodontia2. Partial anodontia
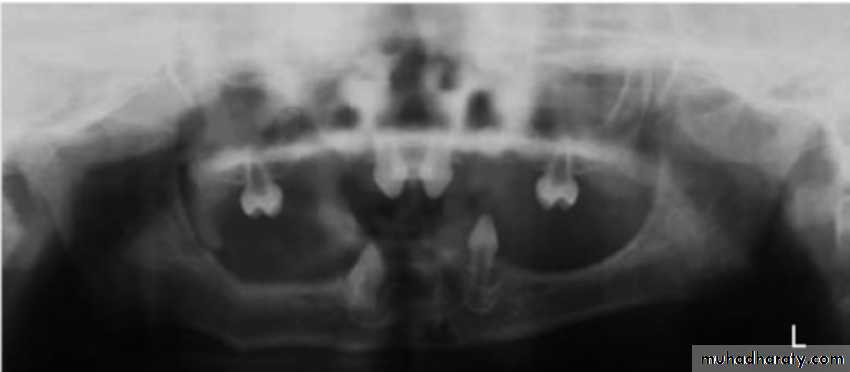
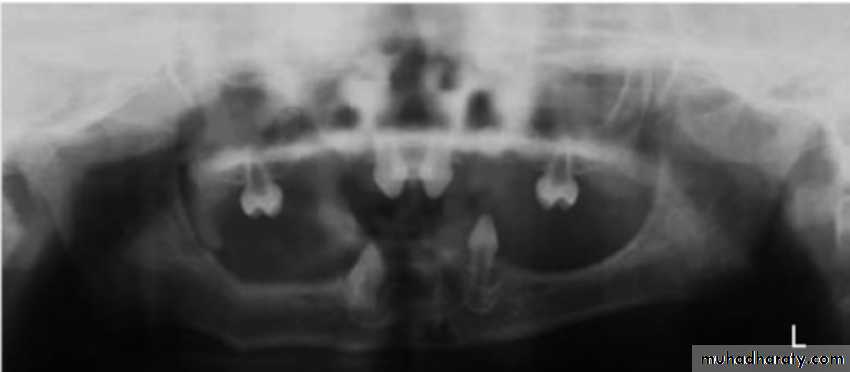
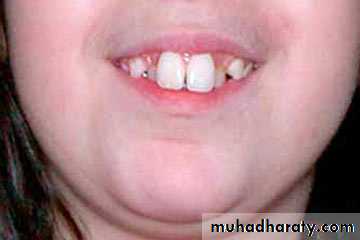
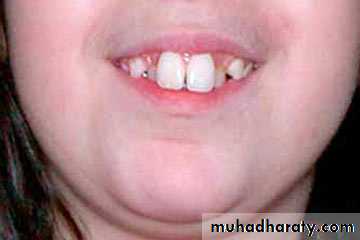
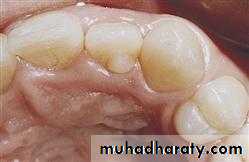
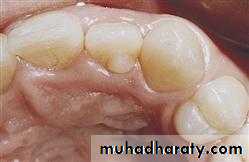
2. HYPERDONTIA
Teeth appear in addition to the regular number of teeth (supernumerary teeth). Extra primary teeth are more common. Proliferation of permanent or primary dental lamina to form many tooth germs (during initiation). Supernumerary teeth can be classified by shape and by position. The shapes include:
• Supplemental (the tooth has a normal shape for the adjacent teeth)
• Tuberculate (the tooth has tube or barrel shaped);• Conical (The tooth is wide at the base and narrows near the top ,”peg shaped");
• Compound odontome (multiple small tooth-like forms);• Complex odontome (a disorganized mass of dental tissue)
Locations of extra teeth include:Paramolar. An extra tooth grows in the back of your mouth, next to one of your molars.
Distomolar. An extra tooth grows in line with your other molars, rather than around them.
Mesiodens. An extra tooth grows behind or around your incisors.
Developmental alterations (size)
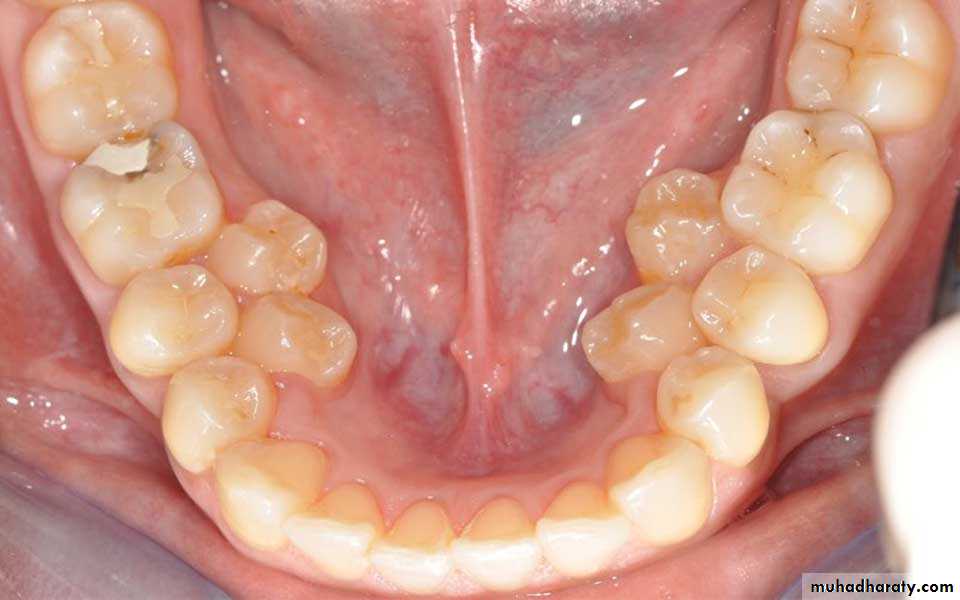
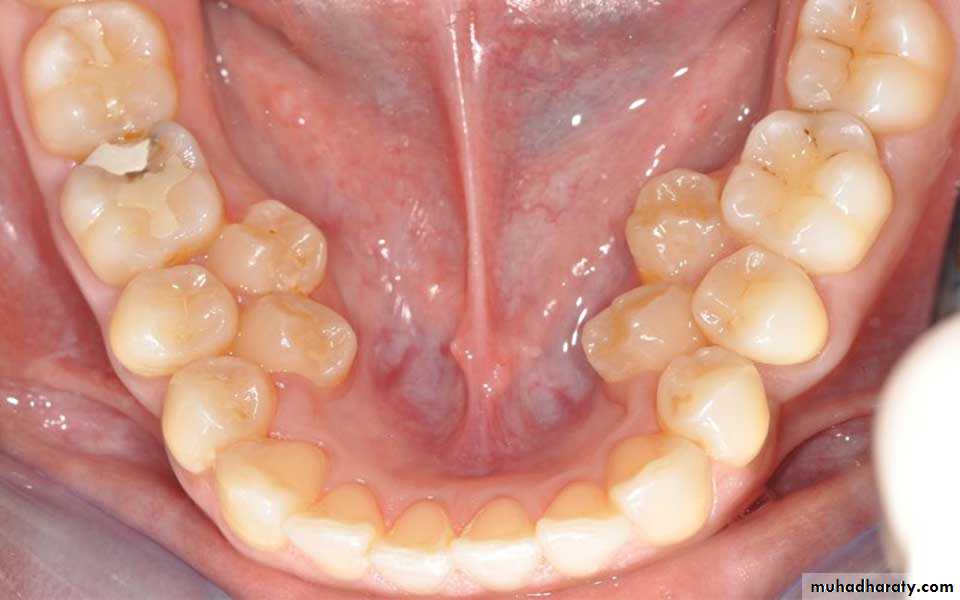
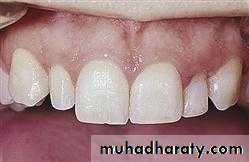
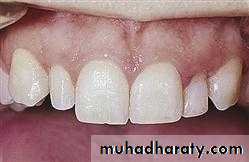
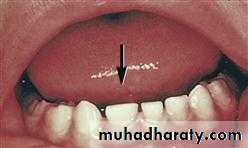
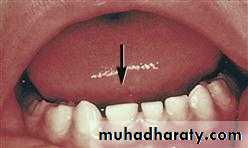
1. MICRODONTIA
The condition in which one or more teeth appear smaller than normal. all teeth are involved. Defects occurring during proliferations (bud stage). The most common teeth affected are the upper lateral incisors (peg laterals) and third molars.1) True Generalized Microdontia: all teeth are smaller than normal
(2) Relative Generalized Microdontia: slightly smaller than normal teeth.(3) Focal/Localized Microdontia: common at maxillary lateral incisor + 3rd molar.
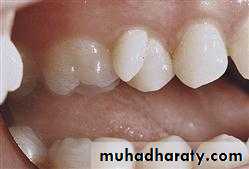
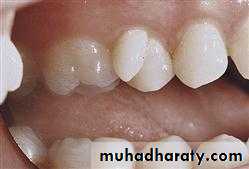
2. MACRODONTIA
One or more teeth appear larger than normal. Macrodontia of a single tooth is attributed to a disturbance between proliferation and morphodifferentiation.
(1) True Generalized Macrodontia -all teeth are larger than normal.
(2) Relative Generalized Macrodontia -slightly smaller than normal teeth.(3) Focal or Localized Macrodontia -the union of more one tooth results in single large tooth.