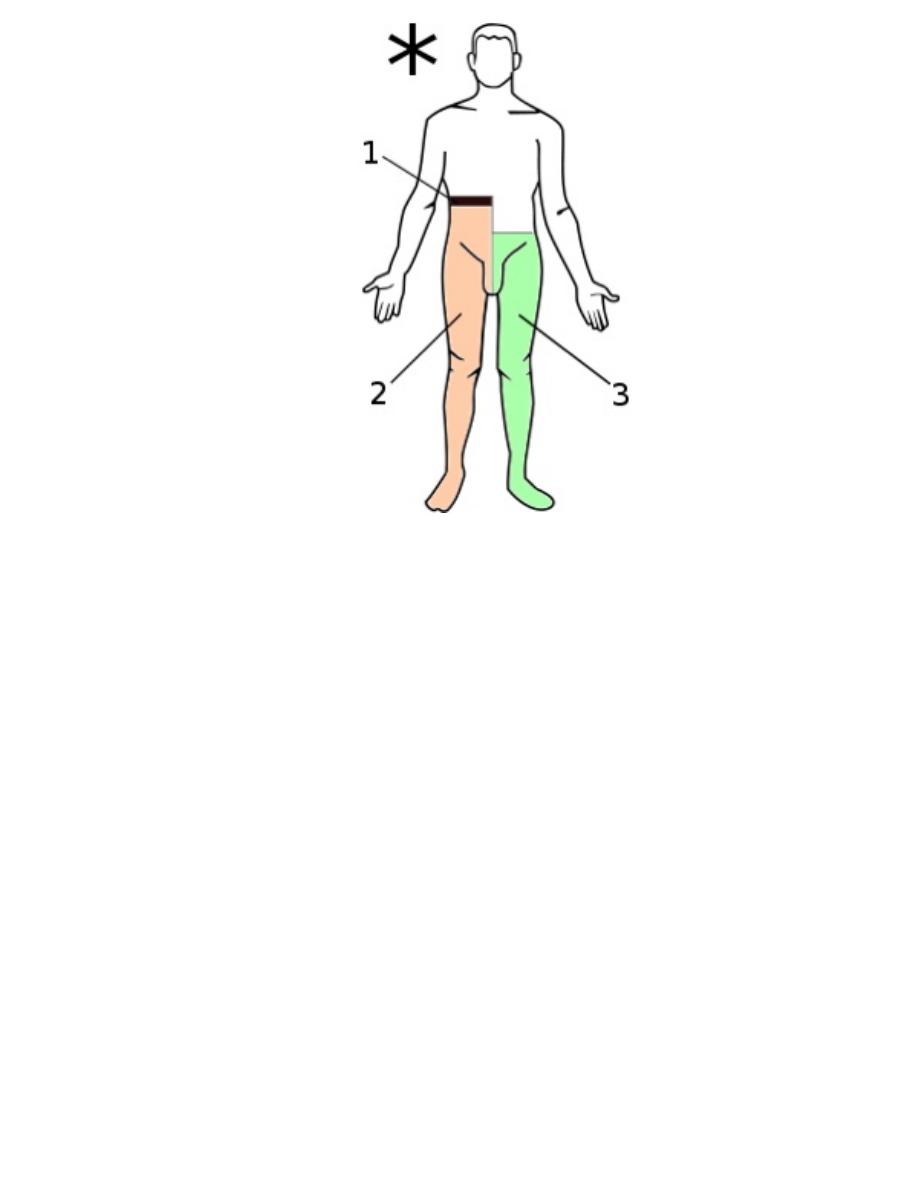
Brown-Séquard syndrome
Lesion on the patient's right
1. loss of all sensation, hypotonic paralysis
2. spastic paralysis and loss of vibration and
(position sense) and fine touch
3. loss of pain and temperature sensation
The hemisection of the cord results in a lesion of
each of the three main neural systems:

pathway of
• the
As a result of the injury to these three main brain
pathways the patient will present with three
lesions:
• The corticospinal lesion produces spastic
paralysis on the same side of the body below
the level of the lesion (due to loss of
moderation by the
). At the level of the
lesion, there will be flaccid paralysis of the
muscles supplied by the nerve of that level
(since lower motor neurons are affected at
the level of the lesion).
• The lesion to
or
ipsilateral loss of vibration and
loss of all sensation of fine touch.
• The loss of the spinothalamic tract leads to
pain and temperature sensation being lost
from the contralateral side beginning one or
two segments below the lesion.
