Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate
Ahmed Nawres
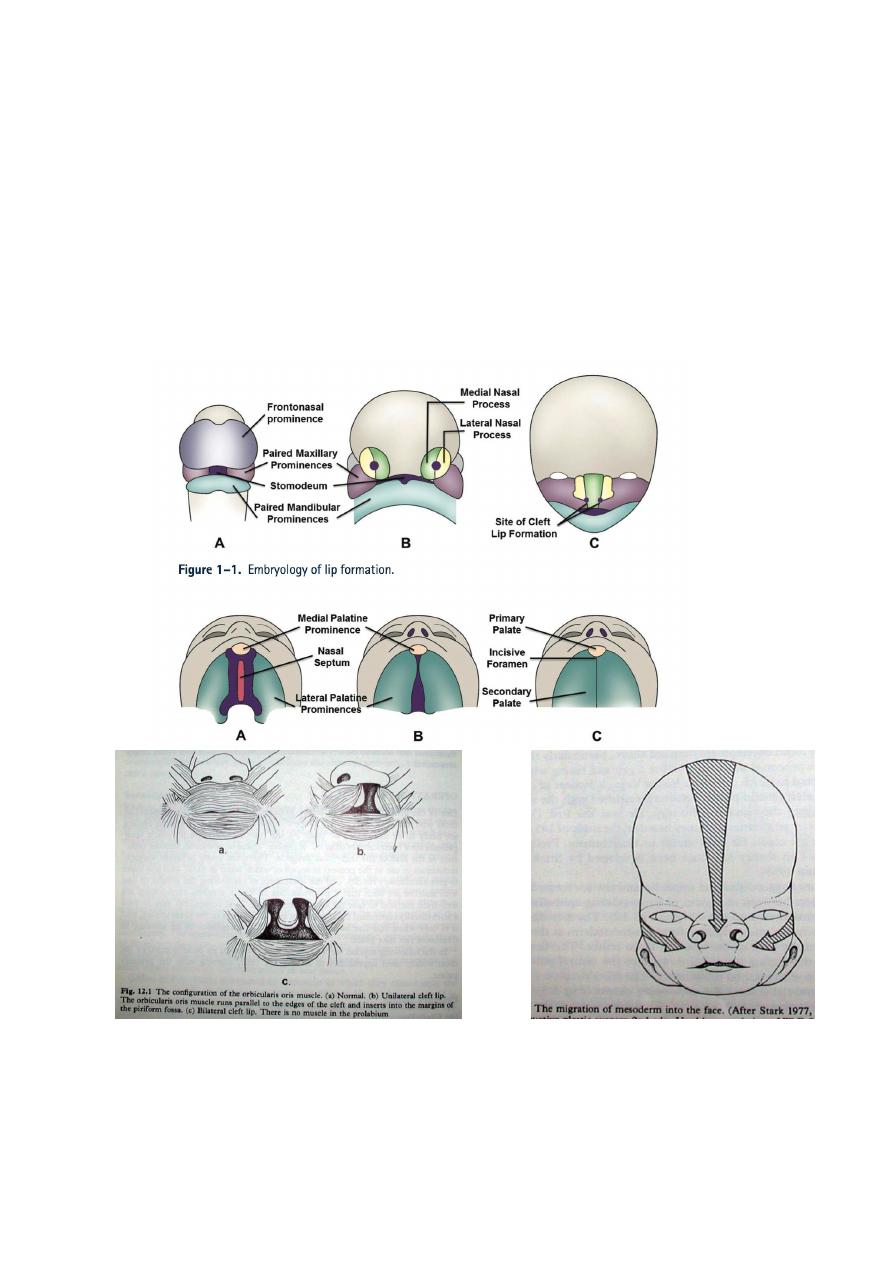
It is a congenital defect which results from failure of
mesodermal penetration and fusion of naso frontal
process & lateral maxillary process of the developing
face which is normally occur at 4
th
-7
th
week of gestation.
It is the most common facial congenital anomaly, and the
second common congenital anomaly (club foot is the
first).
Classification:
CL: Unilateral, bilateral, and some time Median.
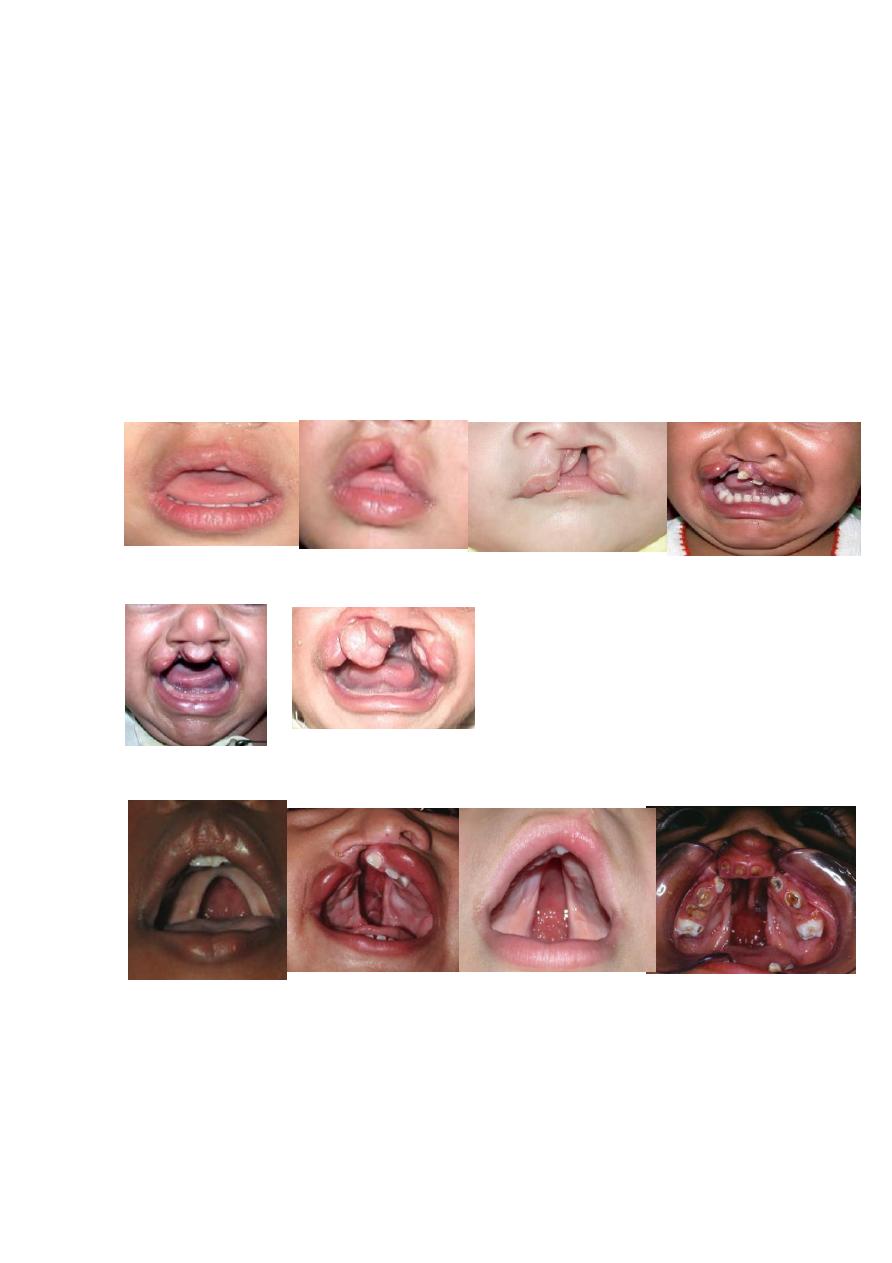
Each one could be complete, incomplete, or
microform.
Could be with or without Cleft Palate (CP).
CP: If CP alone:
Could be complete, incomplete, or sub mucus.
If CP + CL:
Could be unilateral, or bilateral. Each one may be
complete, or incomplete.
Epidemiology
Incidence of CL:
1/750 – 1/1000 live birth.

Lt CL > Rt CL>Bilateral CL→ 6:3:1.
Male > female.
Incidence of CP
1/3000 live birth.
Female>male 2:1.
Aetiology,
1: Most cases of CL/P are multifactorial.
2: Chromosomal anomalies e.g. trisomy, Vander
Woude syndrome.
have pits at lower lip, with CL with or
without CP.
3: teratogens like corticosteroids, phenytoin. Drugs used
for acne like isotretinoin (member of vit.A) ,
methotrexate, drugs used for rheumatoid arthritis, and
psoriasis increasing risk. While folic acid decrease risk.
Diazepam usage during first trimester of pregnancy also
increasing the risk of occurrence of cleft lip with or
without cleft palate.
3: Increased facial width: e.g. encephalocele, teratoma
4: Infections (maternal disease):e.g.rubella,
toxoplasmosis
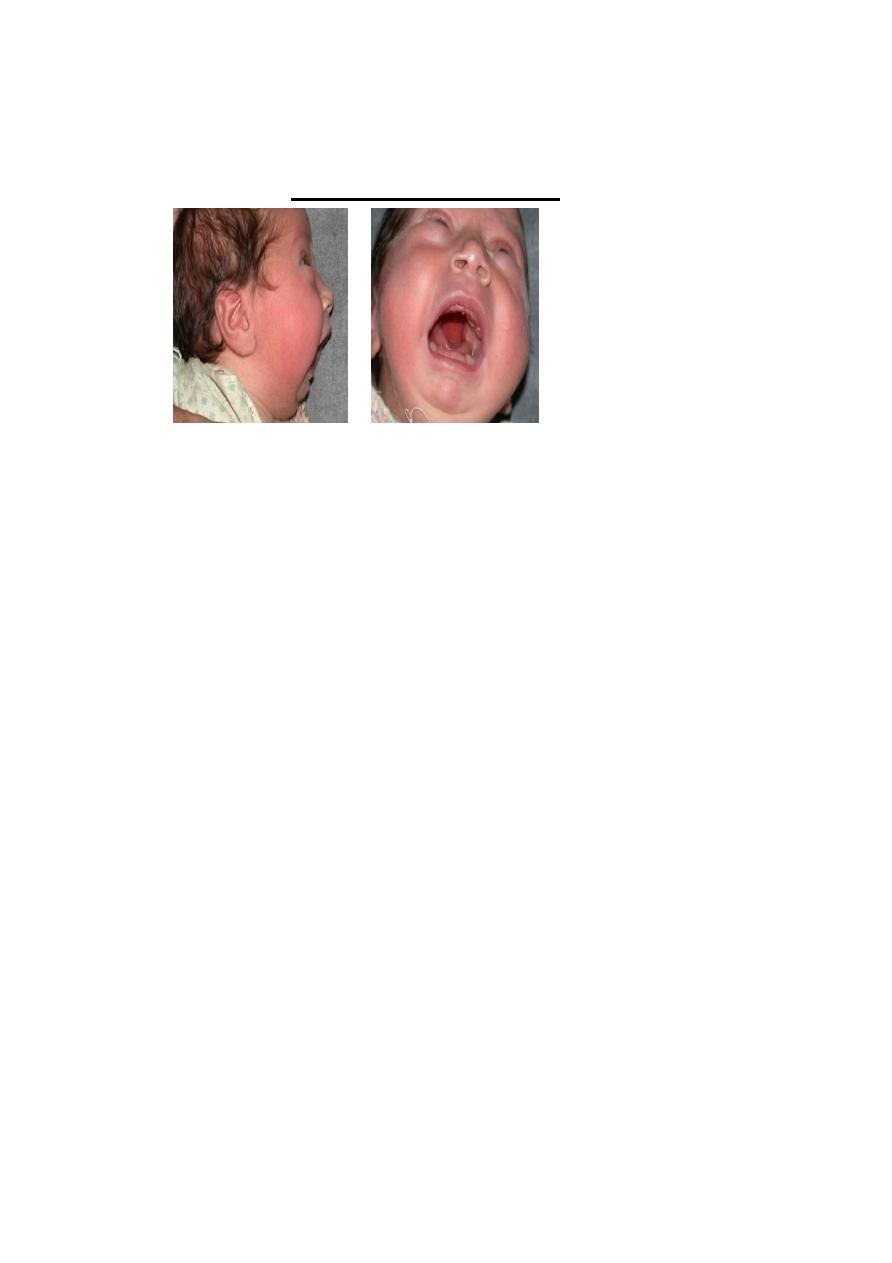
5: Syndromic: Pear Rubin Anomaly:
Insufficient amniotic fluid within the fetal membranes
pushes the fetal chin down onto the chest & the
tongue is pushed up between the palatal shelves, thus
preventing elevation of shelves, causing mechanical
obstruction. there is →high arch cleft
palate+micrognathia(small
mandible)+glossoptosis(persist in high
position)+airway problem(respiratory
obstruction).We advise feeding in sitting position
,sometime, we may need to ligate the tongue to the lip
to prevent airway obstruction.
The clinical problem in pt with CL/P
It depends on type and severity of cleft.
1: Facial appearance.
2: Speech abnormality. The pt has hyper nasal speech
due to velopharyngeal incompetence (VPI).

3: Feeding problem: due to velopharyngeal
incompetence (VPI), there will be nasal reflux while
eating or drinking. There is inability to buildup and
sustain intra oral pressure (there is normal swallowing
but inadequate suction result in decrease feeding).so we
should advice the parents:-
A: maintained upright position for the baby during
feeding.
B: enlarge the hole of the nipple.
C: special artificial feeding bottle with extra
plastic peace to close the cleft
D: breast feeding is usually not successful unless
milk production is very abundant so monitor the infant
to insure sufficient intake.
4: Hearing problem: the cleft affect on the function of
middle ear due to abnormal muscle anatomy along the
Eustachian tube orifice from which the primary muscles
of the palate originate→fluid will be accumulated in the
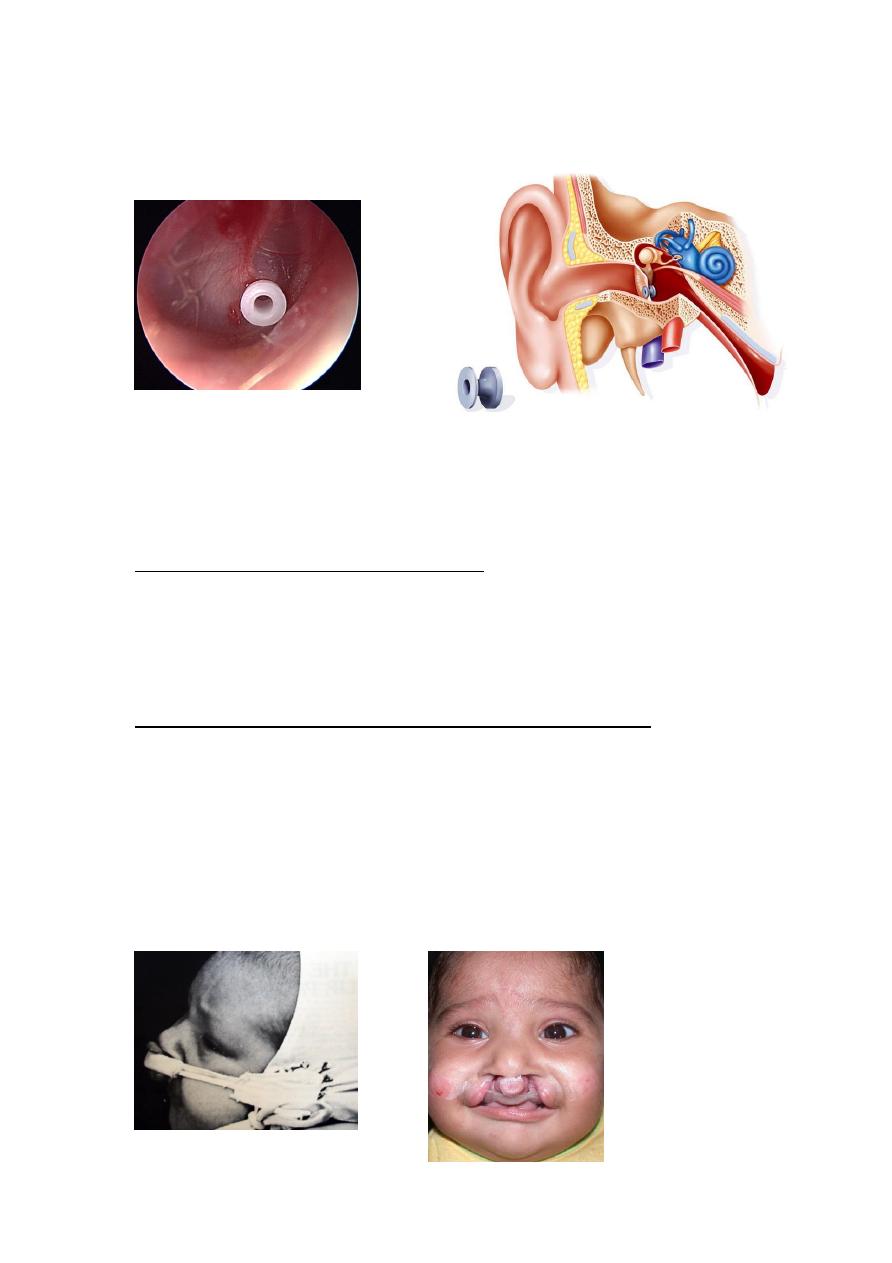
middle ear (glue ear)→hearing loss. So the baby needs
regular ENT assessment, grommet insertion.
5:
Facial growth abnormalities.
6: Psychological.
Treatment:
Teem is required which include:
Plastic surgeon, orthopedic (orthognathic surgeon,
orthodontist), speech therapist, pediatrician, ENTist,
psychologist.
Pre surgical orthodontic (orthopedic )treatment:
The Pre surgical orthodontic treatment is mainly needed
in bilateral cleft lip because of the added problem of
protruded premaxilla.
Elastic band (extra oral strapping),
molding plate (intraoral maxillary expansion
devise –Latham),
Nasoalveolar molding NAM.
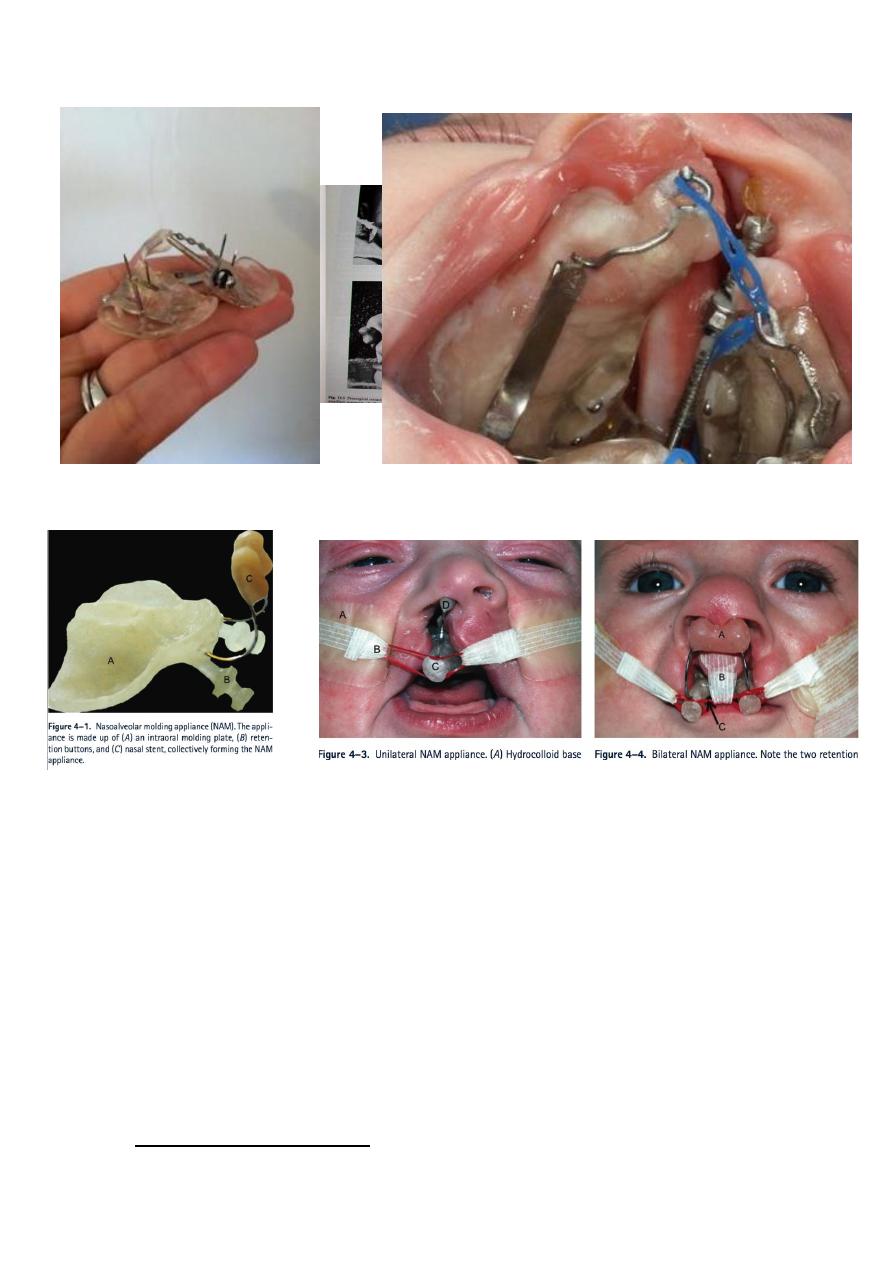
Latham device Latham device
Nasoalveolar molding device (NAM device)
Surgical intervention:
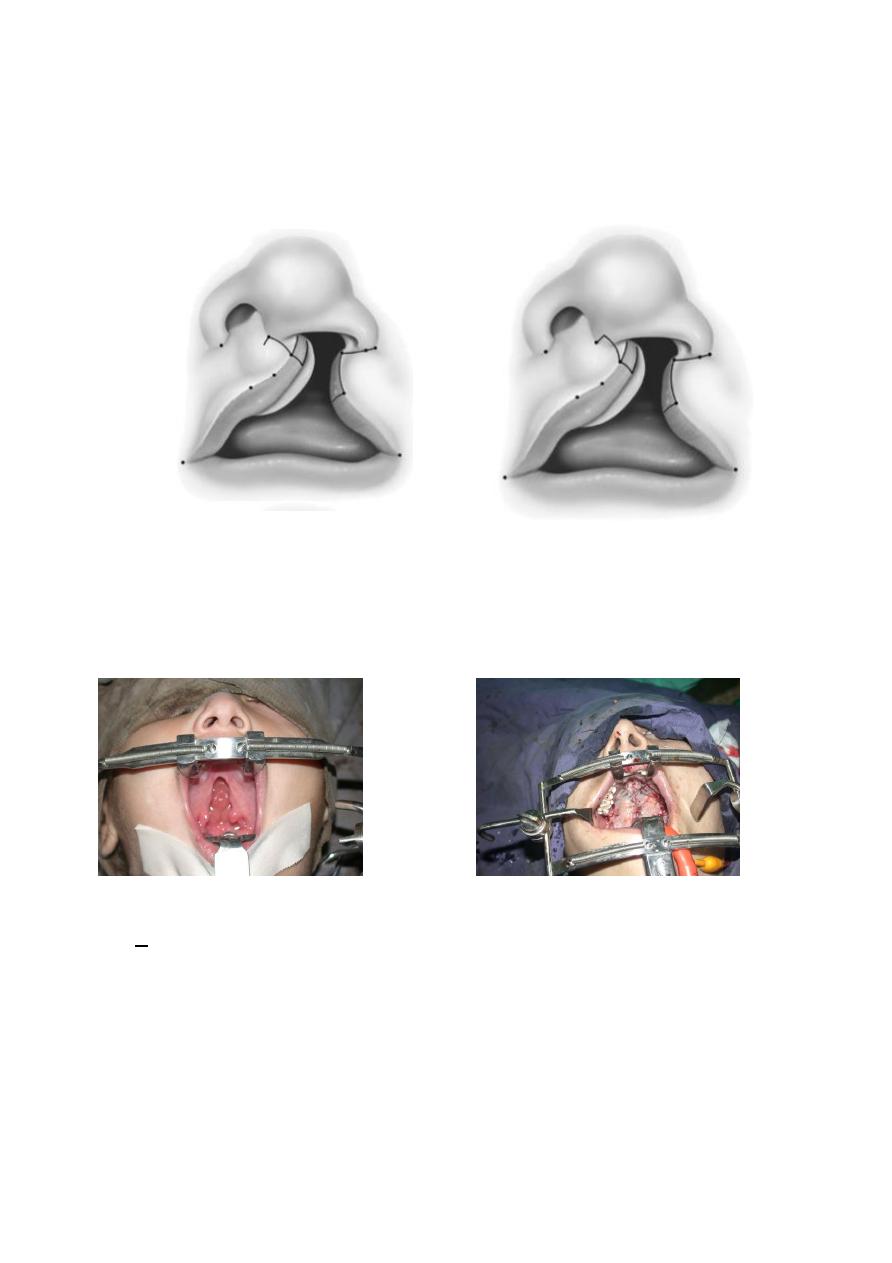
CL time of repair is: role of 10 →10 wks age, 10 pounds
wt, 10 gm HB. Most common techniques are Mohler,
and Millard.
CP: time of repair 9 months.
By elevating bilateral muco periosteal palatal flaps.
