Flaps Ahmed Nawres
A flap, in contrast to a graft, is transferred with an
intact circulation (i.e. with an arterial input & venous
outflow); so it enable the plastic surgeon to cover
defects unsuitable for skin grafting and even bone or
functional muscle transfer can be performed.
Classification:
1
st
: According to tissue involved.
e.g. skin flap ( fascio cutaneous flap), muscle flap,
myo cutaneous flap…etc.
2
nd
: According to their blood supply:
Could be:
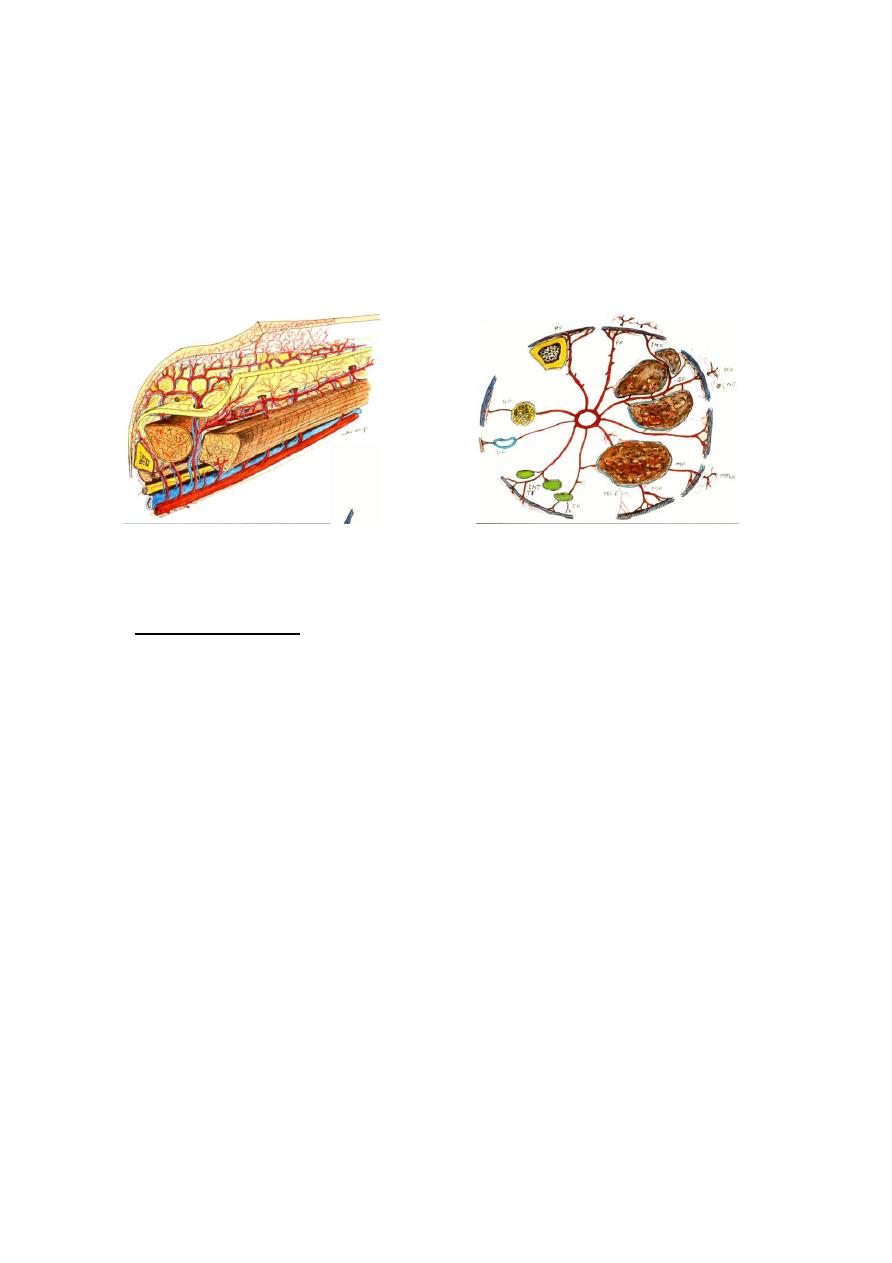
Random Flap:
Has no specific a.v.system, received bd supply
through the dermal – sub dermal plexus only.
Limited length/width ratio, 1. 5:1. some time 2:1 ,but
the safest one is 1:1 length to width ratio.
Axial F:

Has
specific a.v.system.Unlimited
length/width ratio, depend on length of
the vessel elevated.
It could be: peninsular, island, or free
flap.
3
rd
: According to where they are moved:
A: Local Flap:
→Rotate around a pivot point:

Rotation
F: cut in
a
semicircle form.
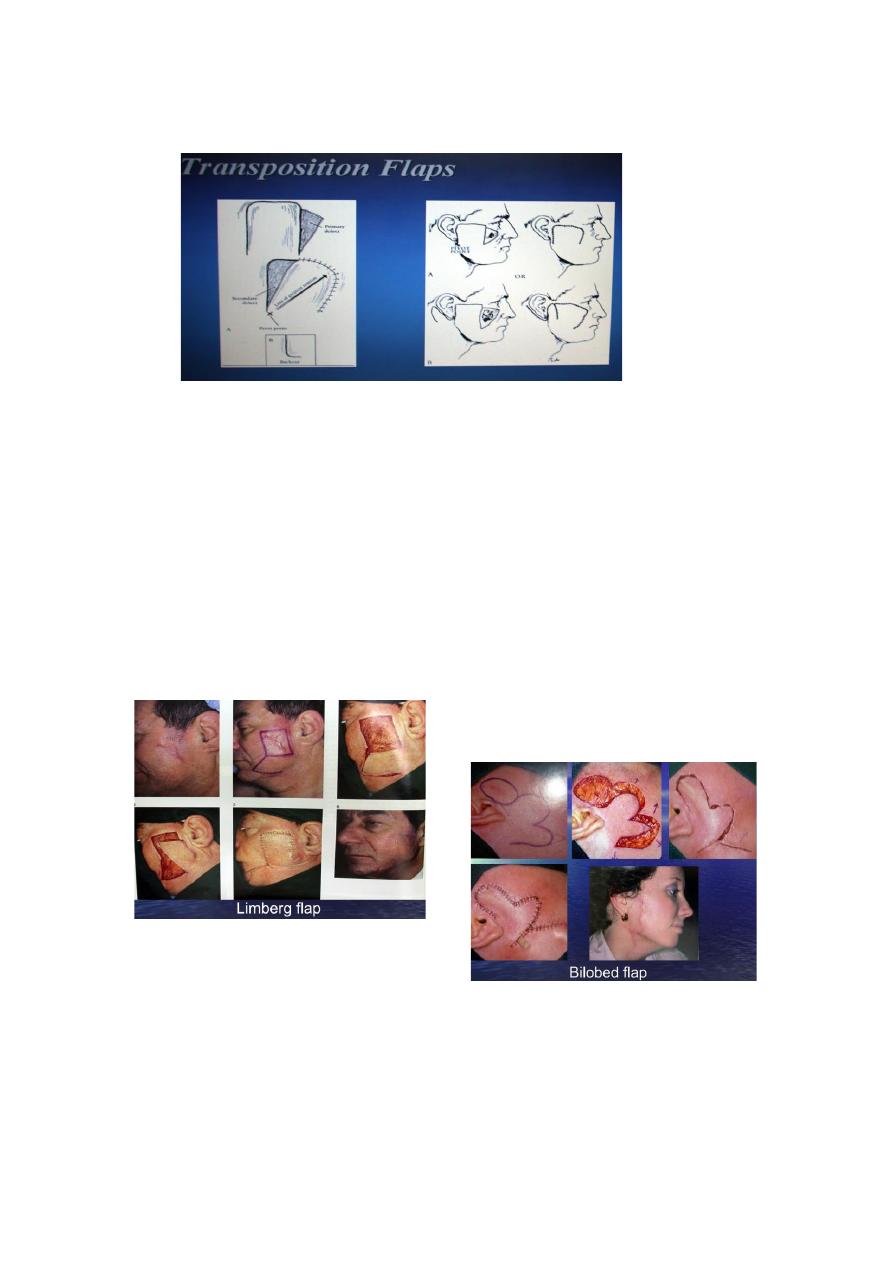
Transposition F: cut in s rectangular or square form.
Examples of transposition flaps:
Limberg flap,
Dufourmental flap,Z
plasty, Bilobed F.
Interpolation F: cut in any form and rotate around a
pivot point into a nearby but not immediately
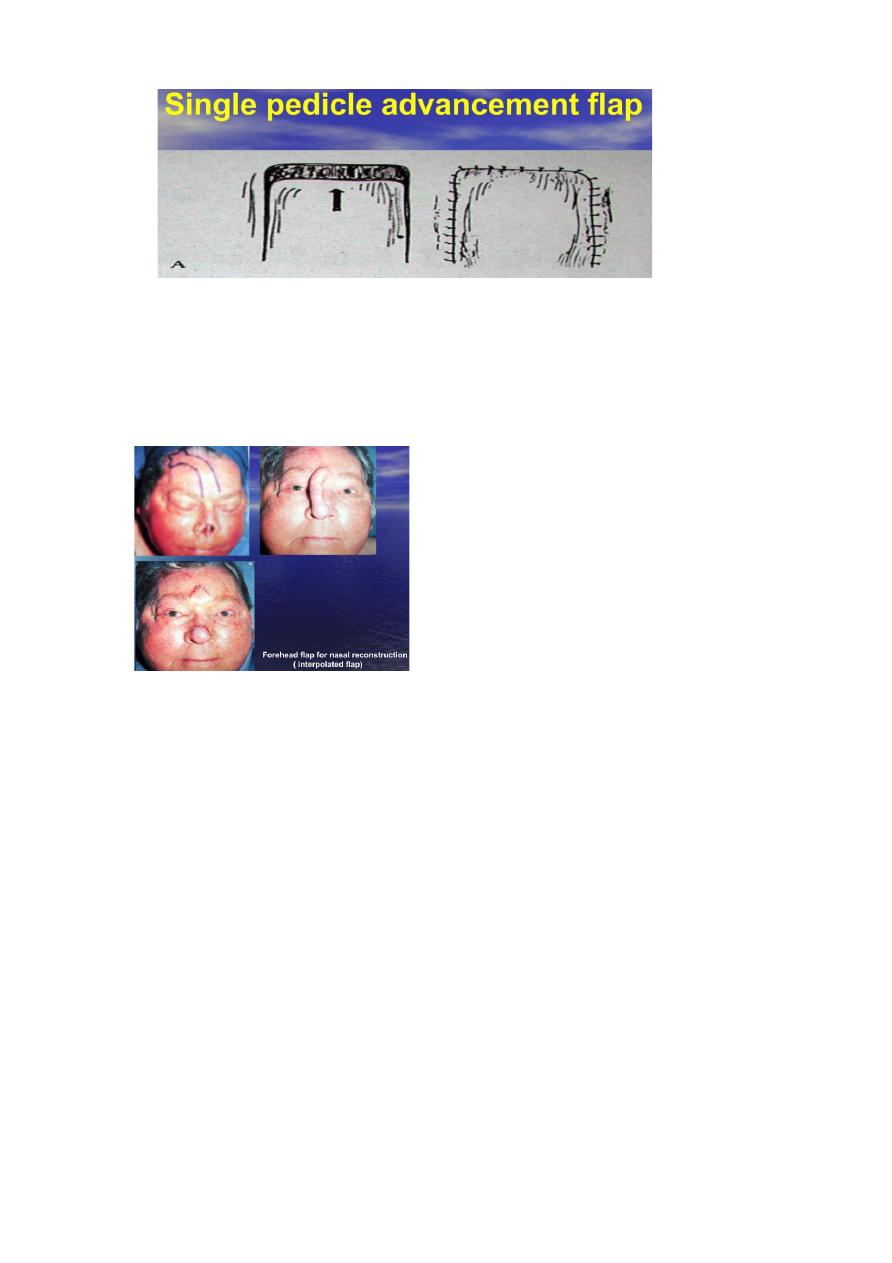
adjacent defect (ie, the donor site is separated from
the recipient site &the pedicle of the flap must pass
over or under the tissue to reach the recipient area).
→Advancement F:
directly move foreword without any rotation or
Lateral movement. It could be:
Single pedicle, Bipedicle, advancement,V-Y and
Y-V advancement flap.

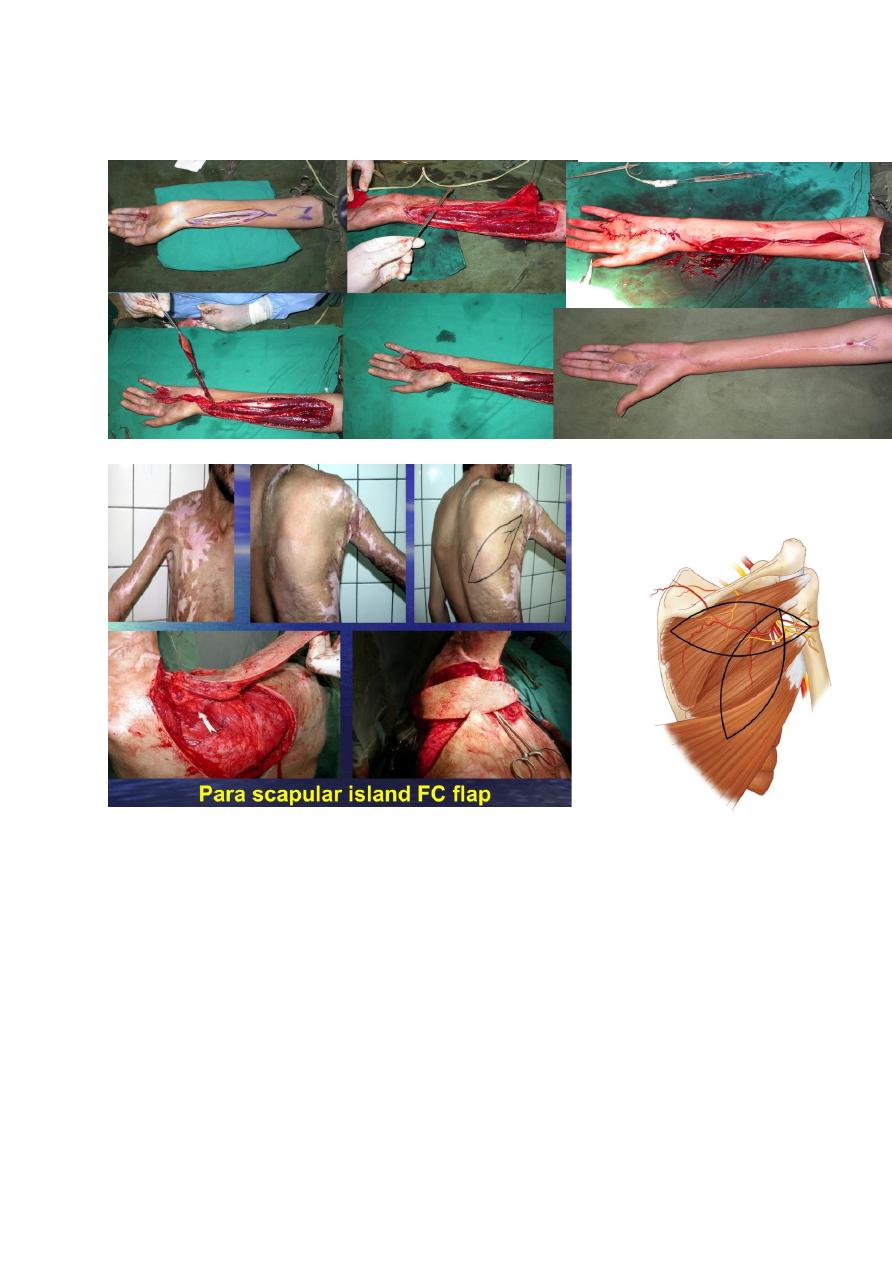
B: Distant Flap:
Could be: direct flap e.g. groin flap to the
hand, abdominal flap to the forearm, cross finger
flap, or
cross leg
flap.
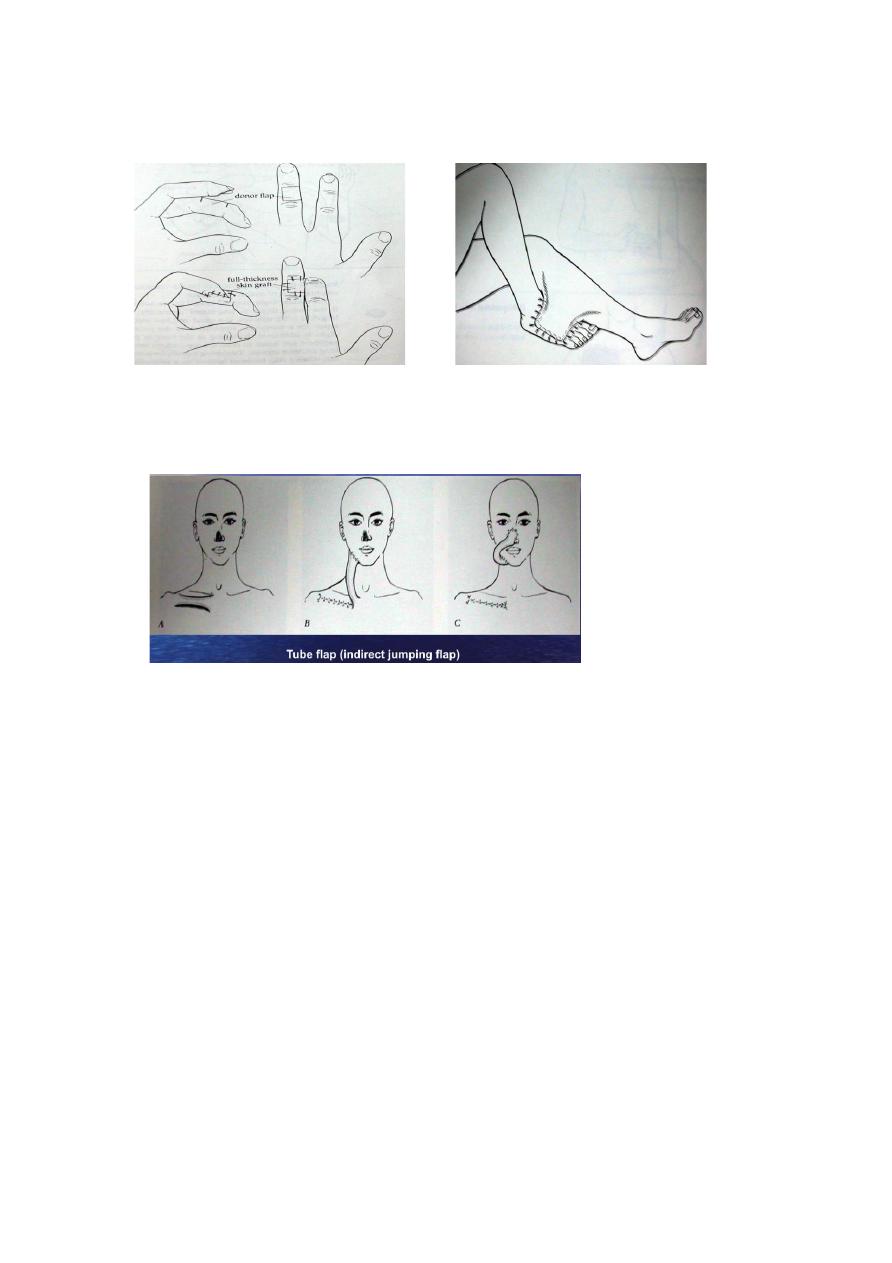
: Indirect flap (Jumping flap).

C: Free
flap:
The
vascular
pedicle is
divided
and
reanastomosed (using microscope) with the recipient
site vessels.
Uses of flaps
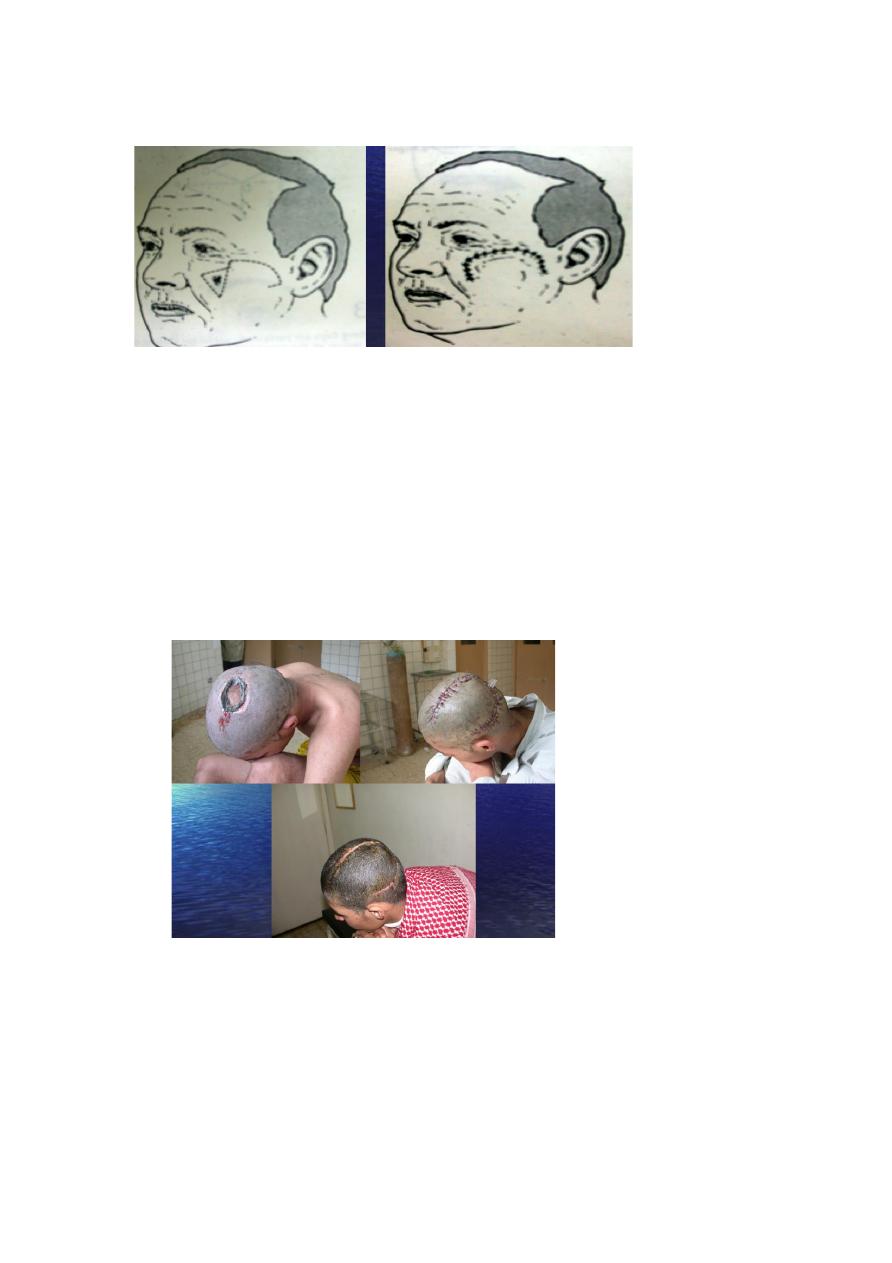
1: Closure of wound with poor vascular bed.
2: Reconstruction of facial features e.g.
reconstruction of complex facial defects.
3: Padding over bony prominence e.g. muscle flaps
are effective in filling dead space in bed sore surgery
for example.
4: Permitting operation through the flap on
underlying structures.
5: Restore sensation to anesthetic area.

6:Muscle flap is sometime effective when functioning
transfer is required.
