Viral Hepatitis
Viral Hepatitis
It caused by five hepatotropic viruses : hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viruses .HEPATITIS A
ETIOLOGY.HAV is an RNA virus.
EPIDEMIOLOGY :
1- Transmission is almost always by person-to-person contact through the fecal-oral route.2- Infection has been associated with contact with contaminated food or water and after travel to endemic areas.
Also contacts with infected persons, child-care centers, and household contacts .
3- HAV excreted in the stool from 2 wk before to 7days after the onset of jaundice. The patient is therefore contagious during this period.CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS :
Incubation period is ≈3 wk.Systemic symptoms include:
fever, malaise, nausea, emesis, anorexia, and abdominal discomfort.
Diarrhea often occurs in children.
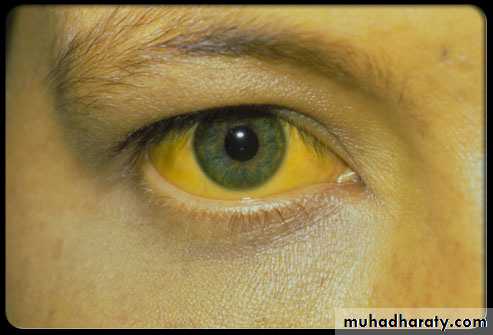
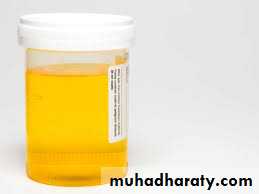
Jaundice, dark-colored urine with pale stool occur, and develop after the systemic symptoms.
Right upper quadrant pain.
The typical duration of illness is 7–14 days.
Rarely other organ systems can be affected including:1-Regional lymph nodes and the spleen may be enlarged.
2-Aplastic anemia.
Fulminant hepatitis is uncommon in children; co-infection with HCV increases the risk for fulminant hepatitis. HAV is not associated with chronic liver disease, or an intestinal carrier state.
DIAGNOSIS :
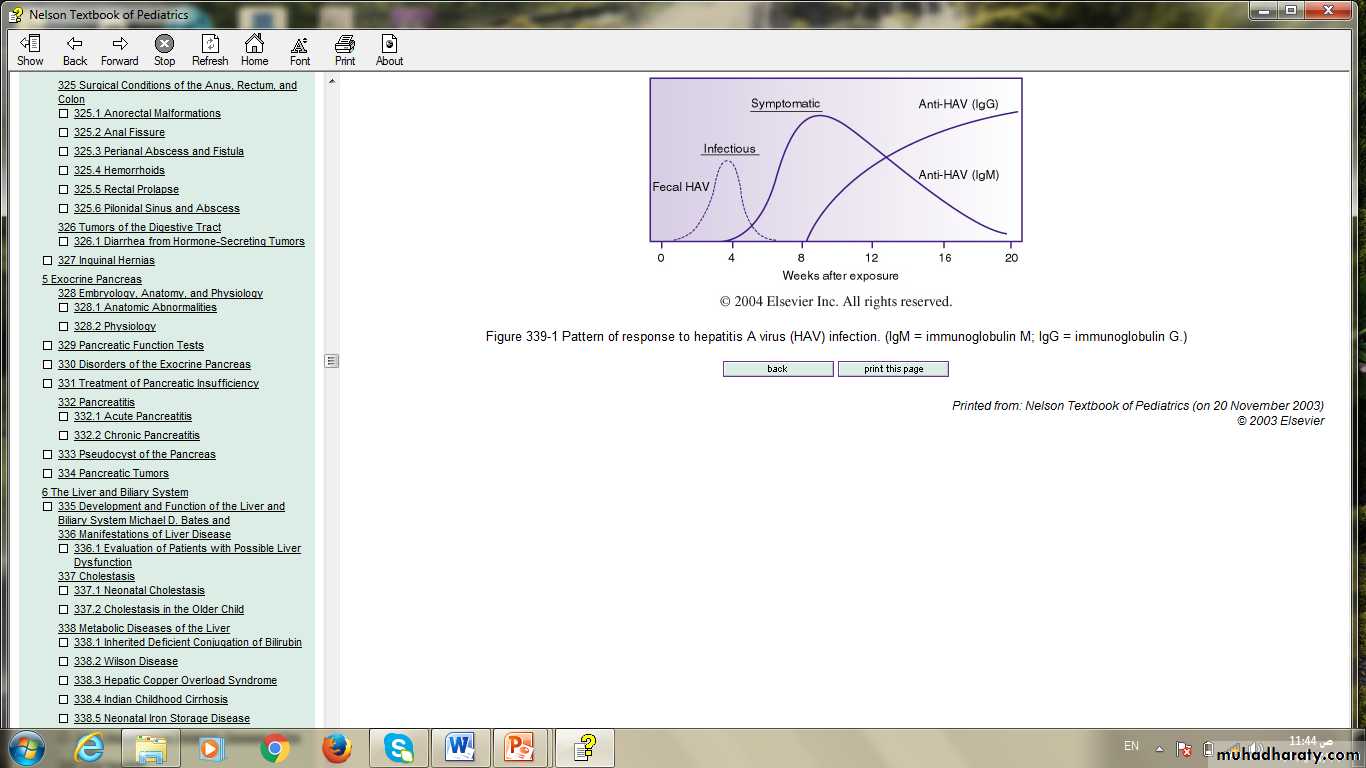
1-detection of antibodies to HAV (anti-HAV IgM & IgG) in the serum by radioimmunoassay.Pattern of response to hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection.
2- Identification of viral particles in stool .
3- Viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay.4- Liver function test:
Hyperbilirubinemia (mixed or conjugated (direct)), rise in serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) & alkaline phosphatase (ALP) .
COMPLICATIONS.
Most patients achieve full recovery.
Acute liver failure (fulminant hepatitis) rare but can occur.
Edema and Ascites due to hypoalbuminemia.
TREATMENT :
No specific treatment for hepatitis A.Supportive treatment with Intravenous hydration as needed .
PREVENTION
1- Patients should be excluded from school, child care, or work during contagious period .
2- Careful handwashing, particularly after changing diapers and before preparing food.
3-Vaccine : inactivated, HAV vaccines are approved for children >2 yr of age..
HEPATITIS B
ETIOLOGY :HBV which is double-stranded DNA virus . The surface of the virus includes particles designated hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) .
The inner portion of the virion contains hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg), the nucleocapsid that encodes the viral DNA, called hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg), which serves as a marker of active viral replication .
EPIDEMIOLOGY :
1- Transmission occurs through blood & blood products exposure, sexual contact, intravenous drugs(addict), tattoos, and intimate contact with carriers.2- Transplacental transmission from HBsAg-positive mother . The risk of transmission is greatest if the mother is also HBeAg positive .
3- HBsAg is recovered in breast milk of infected mothers.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS :
Incubation period ranges from 45 to 160 days .
*The first clinical evidence is elevation of ALT level.
*Lethargy, anorexia, and malaise.*Jaundice, usually begins ≈8 wk after exposure and lasts for ≈4 wk.
*The illness may be preceded by arthralgia or skin lesions, including urticarial, or Papular acrodermatitis.
*Extrahepatic conditions include polyarteritis, glomerulonephritis, and aplastic anemia.
“Chronic carrier state” defined as being positive for HBsAg for >6 mo, complicates up to 10% of cases.
On physical examination :
icteric skin and mucous membranes.The liver is enlarged and tender.
Splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy .
Clinical signs of altered sensorium and hyper-reflexivity indicate encephalopathy and ALF.
DIAGNOSIS
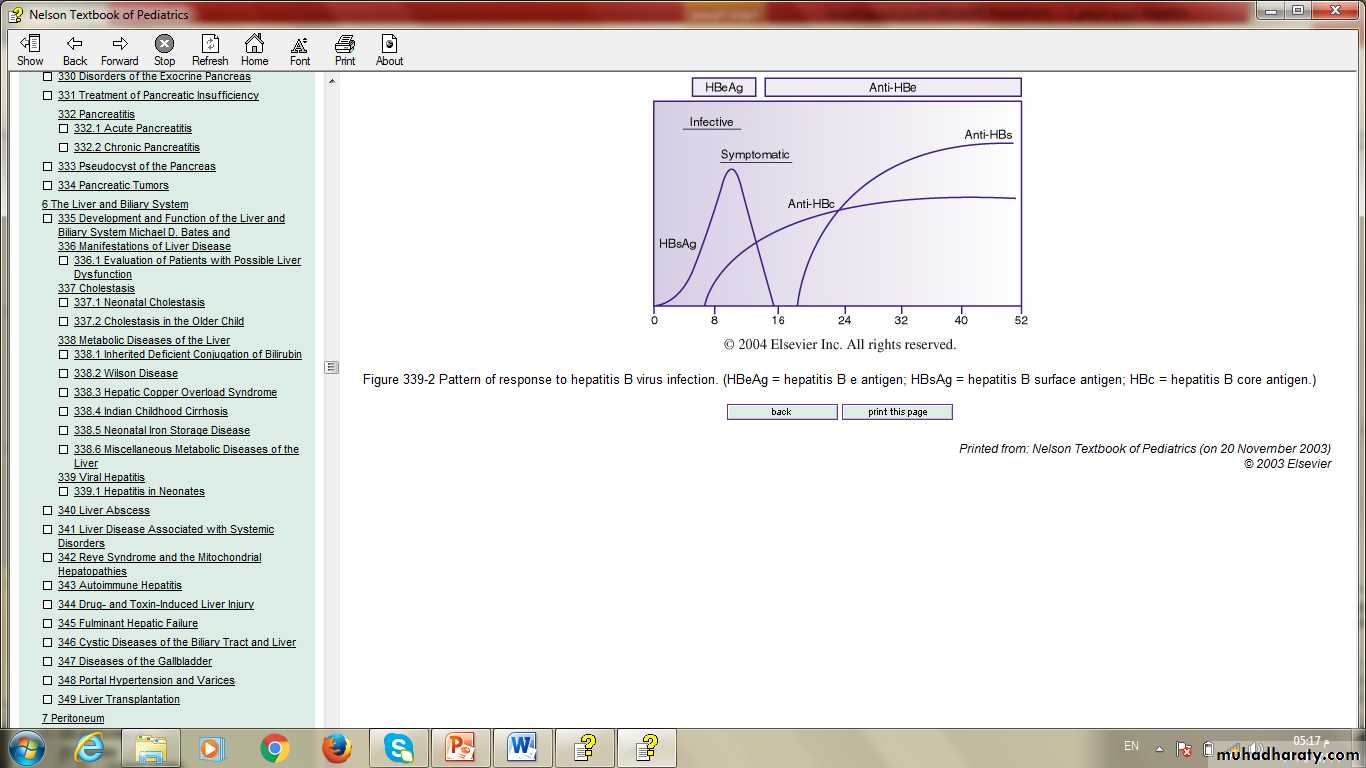
A- assay of serologic markers:1-HBsAg is the 1st serologic marker of infection to appear.
2- Antibody to HBcAg (anti-HBc IgM & IgG AB)
3- Anti-HBs and anti-HBc antibodies are detected in persons with resolved infection .While persons immunized with hepatitis B vaccine have only anti-HBs antibodies .
4- HBeAg.
B- HBV DNA can be detected in the serum .
C- Liver function test .COMPLICATIONS :
1- ALF occurs more frequently with HBV than with the other viruses.2- chronic hepatitis, which can lead to cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease, and primary hepatocellular carcinoma.
3- Membranous glomerulonephritis due to circulating immune complexes is a rare complication .
TREATMENT.
Treatment of the acute infection is supportive.Chronic hepatitis B treated with Interferon-α .
Lamivudine use in children older than age 2.
PREVENTION
1- Hepatitis B vaccine.2-Infants born to HBsAg-positive women should receive vaccine at birth accompanied by administration of Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin(HBIG) as soon after delivery as possible (within 12 hr) .
3- postexposure prophylaxis : Hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG given for household, sexual, and needle-sharing contacts, those with blood exposure & Immunocompromised patients.
HEPATITIS C
previously known as “transfusion-related non-A, non-B hepatitis .ETIOLOGY
HCV is a single- stranded RNA virus .
EPIDEMIOLOGY.
Risk factors for transmission include:*blood transfusion
*Illegal drug use with exposure to blood from HCV-infected individual .
*Sexual transmission .
*occupational exposure .
*perinatal transmission from mother to her infant .
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS :
The incubation period is 7–9 wk .Acute liver failure rarely occurs. HCV is the most likely hepatotropic virus to cause chronic infection.
Chronic HCV infection is defined by persistently elevated levels of ALT in the presence of hepatic fibrosis and by the presence of HCV RNA in blood.
DIAGNOSIS.
1- serologic test to detect the antibodies to HCV antigens (anti-HCV AB).2- PCR assay for detection of small amounts of HCV RNA.
3- Liver function test
4- liver biopsy to assess the presence and extent of hepatic fibrosis.COMPLICATIONS.
1- chronic hepatitis(60-80%).2- cirrhosis or HCC
3- acute liver failure (rarely).