
22
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
Lecture 4:
Energy, work, and power of Body
Objectives: after the end of this lecture, the student must know:
1-
Definition of BMR and physical factors affecting it
2-
Ways of heat loss from the body
For basal conditions there are about:
25% of the body's energy used by the skeletal muscle and heart.
19% used by the brain.
10% used by kidneys.
27% used by the liver, spleen.
The body uses food energy to operate its various organs, maintain constant body
temperature, and do external work, small percentage (5%) of the body energy
excreted in the feces and urine, any energy left over is stored as a body fat.
Conservation of Energy in the body
∆u = ∆ Q- ∆W
∆u= change in stored energy
∆ Q= heat lost or gain
∆ W= work done by the body
BMR (basal metabolic rate)
: is the amount of energy needed to perform minimal
body function (such as breathing , and pumping blood through arteries under resting
condition). BMR depends primarily upon thyroid function. A person of an over active
thyroid has a higher BMR than a person with normal thyroid function.
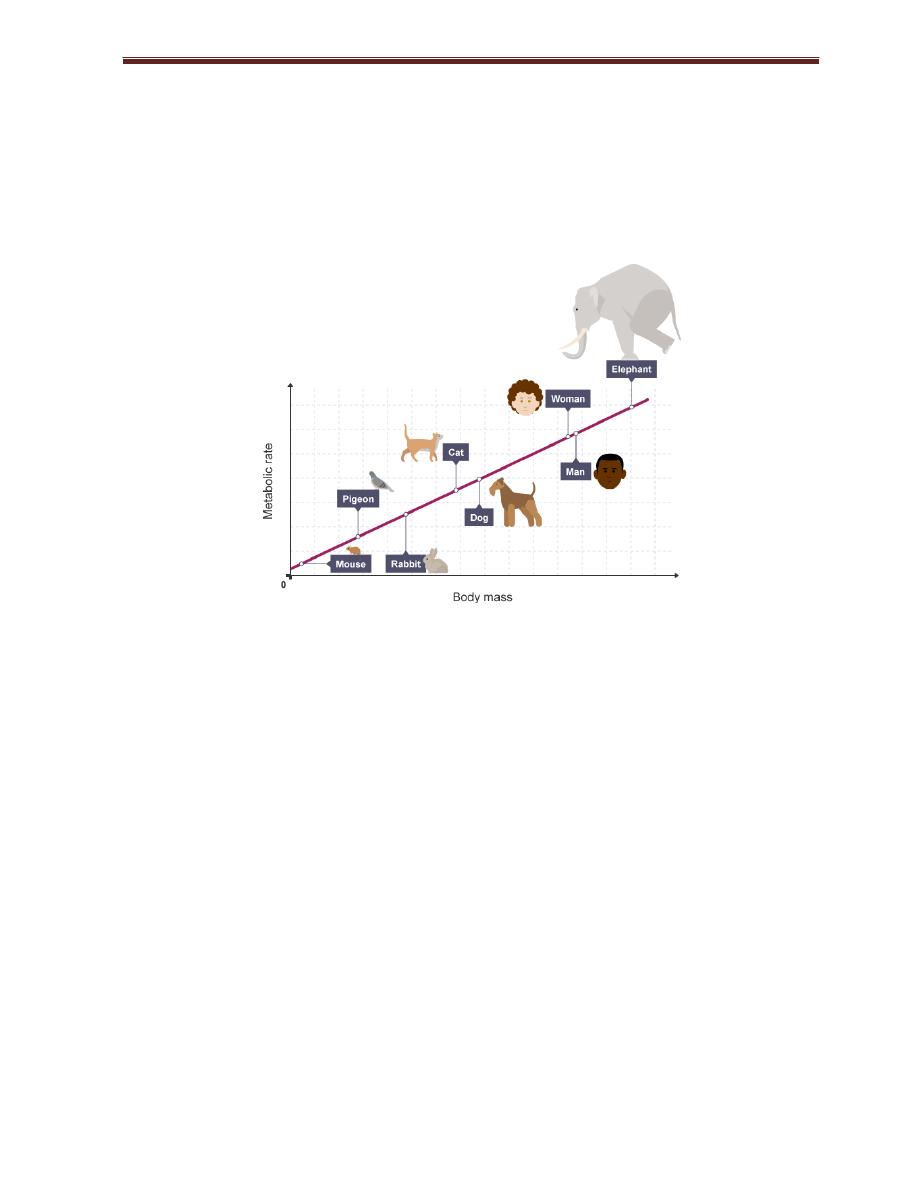
Since the energy used for basal metabolism becomes heat and dissipated from the
skin, so BMR is related to the surface area, or the mass of the body.
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
The metabolic rate depends on temperature of the body, if temperature changes by
1Cº there is a change about 10 % in the metabolic rate. For example, if a patient has
temperature of 40 Cº or 3 above normal, the BMR is about 30% greater than normal,
you can see why patients temperature sometimes lowered during heart surgery.
Figure 1:
relationship between BMR and body mass for different animals .
Work And Power
∆W = F ∆ X F= force , ∆ X= distance
P = ∆ W / ∆ t = F∆ X / ∆ t = F v , P= power
ϵ = work done / energy consumed , ϵ= efficiency
The convenient unite for expressing the rate of energy consumption of the body is
the met, the met is defined as 50 Kcal/m
2
of body surface area per hour.
For normal person 1 met is equal to the energy consumption under resting
conditions . A typical man has about 1.85 m
2
of surface area women has 1.4 m
2
and
for typical man 1 met is about 92 Kcal/hr or 107 w oxidation occur in the cells of the
body.

24
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
In oxidation by consumption heat is released within the body heat is released as
energy of metabolism. The rate of oxidation is called metabolic rate.
The oxidation of glucose a common form of sugar used for intravenous feeding. The
oxidation equation for one mole of glucose C6 H12 O6 is
C6 H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 H2 O + 6 CO2 + 686 Kcal
That is 1 mole of glucose (180) gm combines with 6 moles of O2 (129) gm to
produce 6 moles each of H2O (108) gm and CO2 (264) gm releasing 686 Kcal of heat
energy in the reaction.
When completely at rest, the typical person consumption of energy at rate of about
92 Kcal /hr or 107 w or about 1 met this lowest rate of energy consumption called
basal metabolic rate
When a man climbing a hill or walking upstairs, we calculate the work done by
multiplying person weight (gm) by vertical distance (h).
When a man walking or running at constant speed on level surface, the force act in
the direction perpendicular to his motion, thus external work done by him appears to
be zero, however his muscles are doing internal work which appears as heat in the
muscle and causes arise in its temperature.
Heat Losses From The Body
The main heat loss mechanisms are
1- Radiation
2- Convection
3- Evaporation (perspiration)
4- Some cooling of the body in lungs.

25
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
The hypothalamus of brain contains body thermostat to keep temperature close to
normal value.
If the core temperature rises, the hypothalamus initiate sweating and vasodilation
which increases blood flow to the skin and increase skin temperature which help to
get rid of extra heat.
If the skin temperature drops, the thermoreceptors on the skin inform hypothalamus
and it initiate shivering, which causes increase in the core temperature.
The difference between energy radiated by the body and the energy absorbed from
surrounding can be calculated by:
H
r
= K
r
A
r
e ( T
s
- T
w
)
Hr = energy loss or gain
Ar = surface area emitting radiation
E = emissivity of body
Ts = skin temperature
Tw =surrounding temperature.
Kr= constant= 5 Kcal/m
2
hr Cº
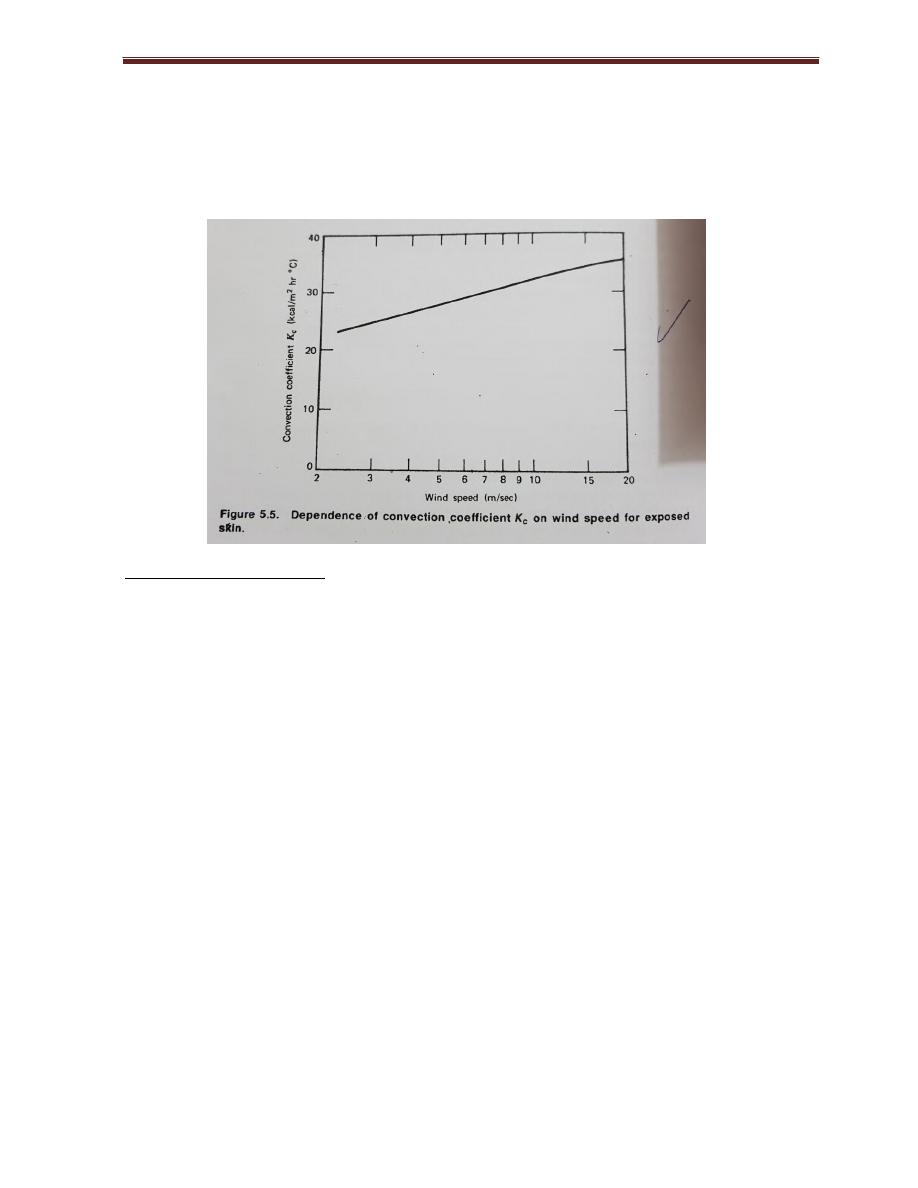
The heat loss due to convection Hc is given by
H
c
= K
c
A
c
( T
s
– T
a
)
Kc = constant depends upon the movement of air
Ac = surface area
Ta = air temperature.
When the wind constant Kc = 2.3 Kcal / m
3
hr Cº
When Ta = 25 Cº
Ts = 34 Cº
Ac = 1.2 m
2
The nude body losses about 25 Kcal /hr by convection or about 25% of body heat loss.
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
When the air is moving, the constant Kc increases according to the equation
K
c
= 10.45 – v + 10 √ v
Where v is the wind speed
Small group discussion
Qx/ What is the most accurate method to measure body temperature & why/
Qx/ What is the mechanism of thermograph and write its medical application?
Qx/ What is the effect of heating of one part of the body?
Qx/ Why we lower body temperature during heart surgery?
Qx/ Discuss the body response to exposure to hot and cold weathers.
Qx/ Example suppose you wish to loss 4.45 Kg either through physical activity or by
dieting.
Qx/ What is the effect of atmospheric pressure on the body?
Qx/ 45 years old male presented with intestinal obstruction. Explain the effect of
intestinal bacteria on the pressure inside the GIT.
Qx/ Discuss how Boyle’s law keep blood pressure constant?
Qx/ Discuss the effect of Bernoulli principle on cough
