
Future Radar and Satellite
Technology
Daniel C. Miller
National Weather Service
Columbia, SC

The Big Idea
New radar and satellite technology
will improve NWS operations!

Outline
• Introduction
• Part I. Dual-Polarization Radar Technology
– Benefits
– What is it?
– Applications
– When?
• Part II. Next Generation Weather Satellite
– Benefits and New Features
– Applications
– When?
• Conclusion

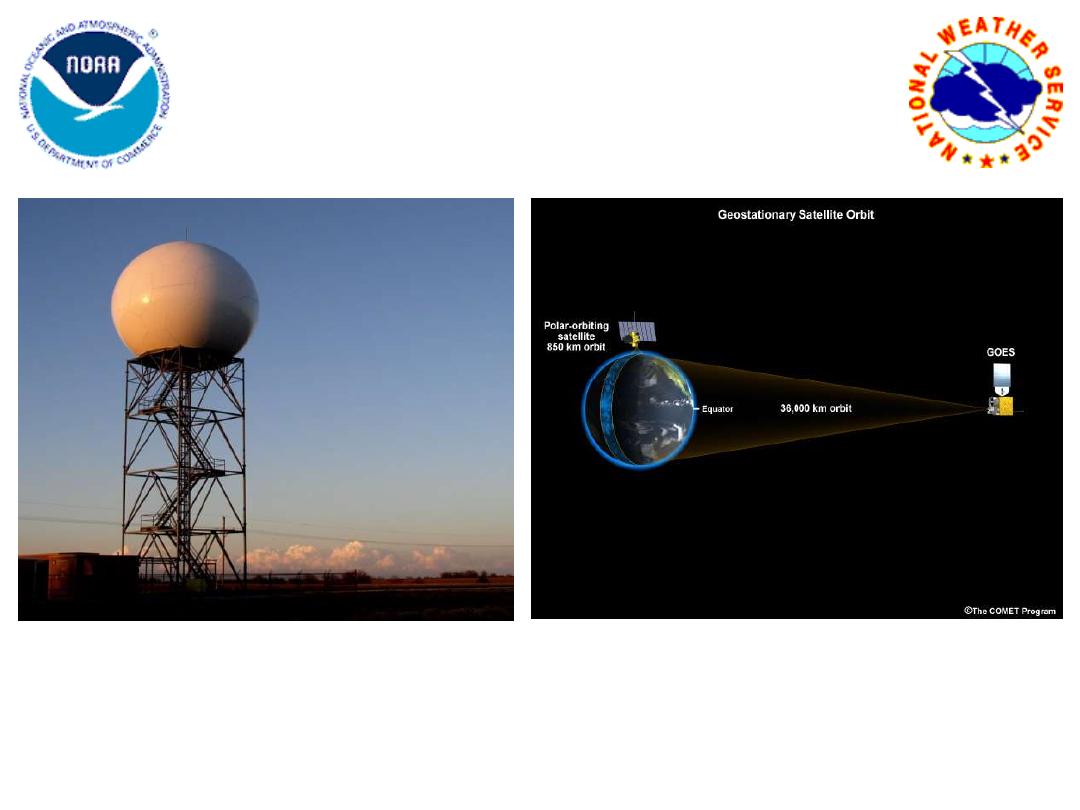
Part I. Dual-Polarization
Radar Technology
Photo courtesy of NSSL

Dual-Polarization Radar Technology
Key Benefits
• Better Determination of Precipitation Type
• Better Estimates of Rainfall Amount
• Better Detection of Hail
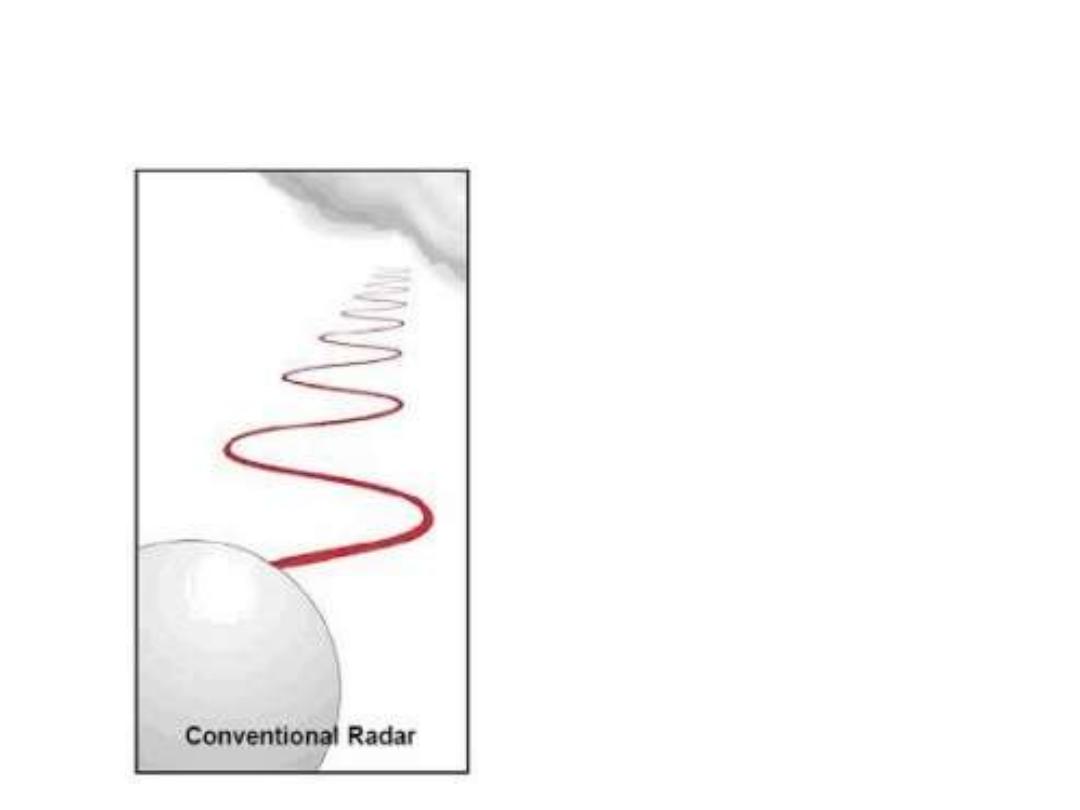
What does Dual-Polarization Mean?
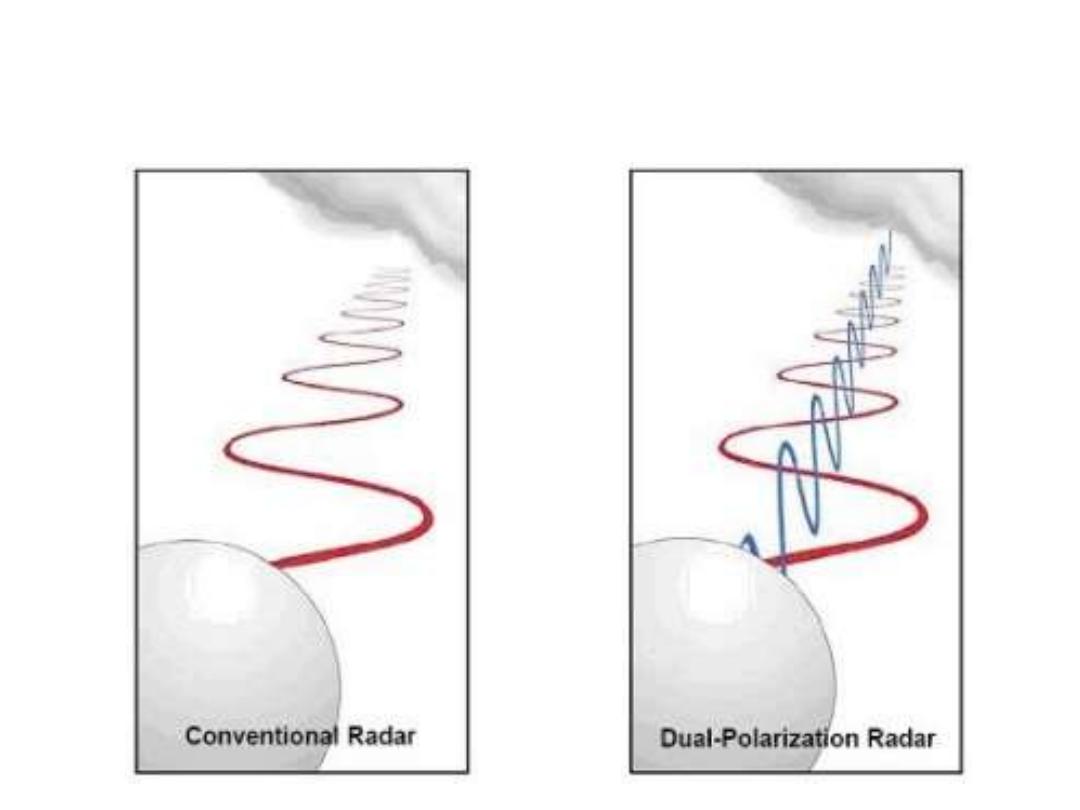
What does Dual-Polarization Mean?
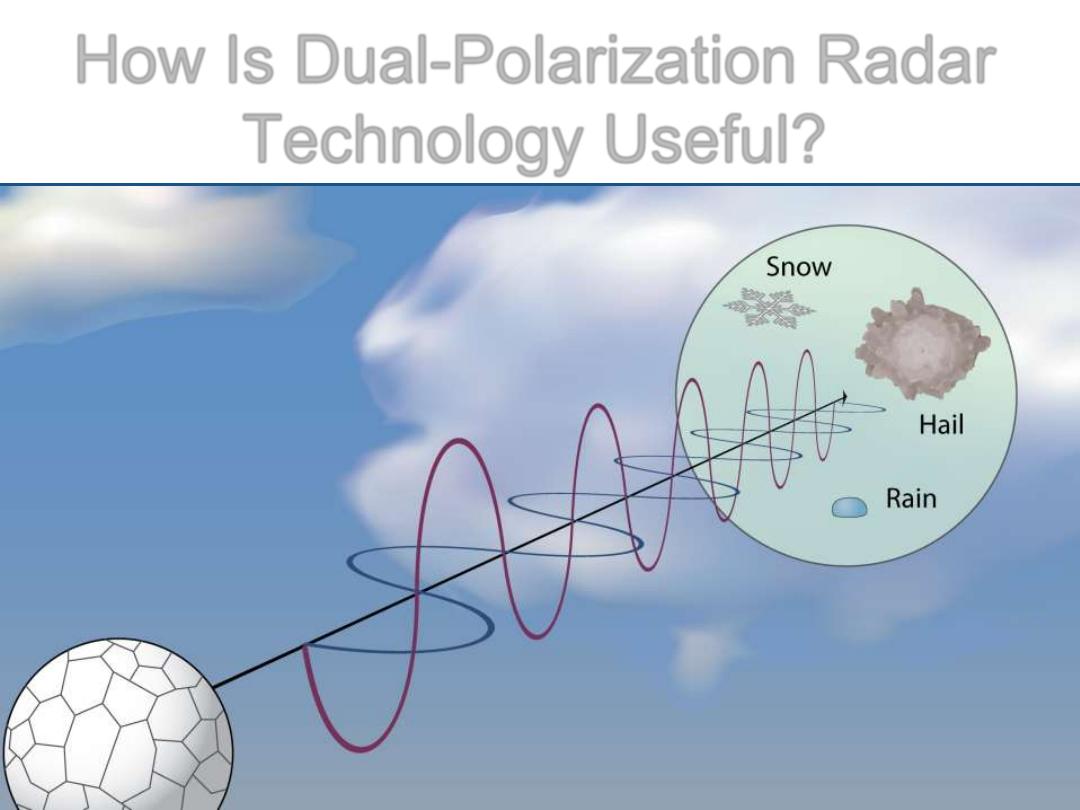
How Is Dual-Polarization Radar
Technology Useful?
Image courtesy NSSL
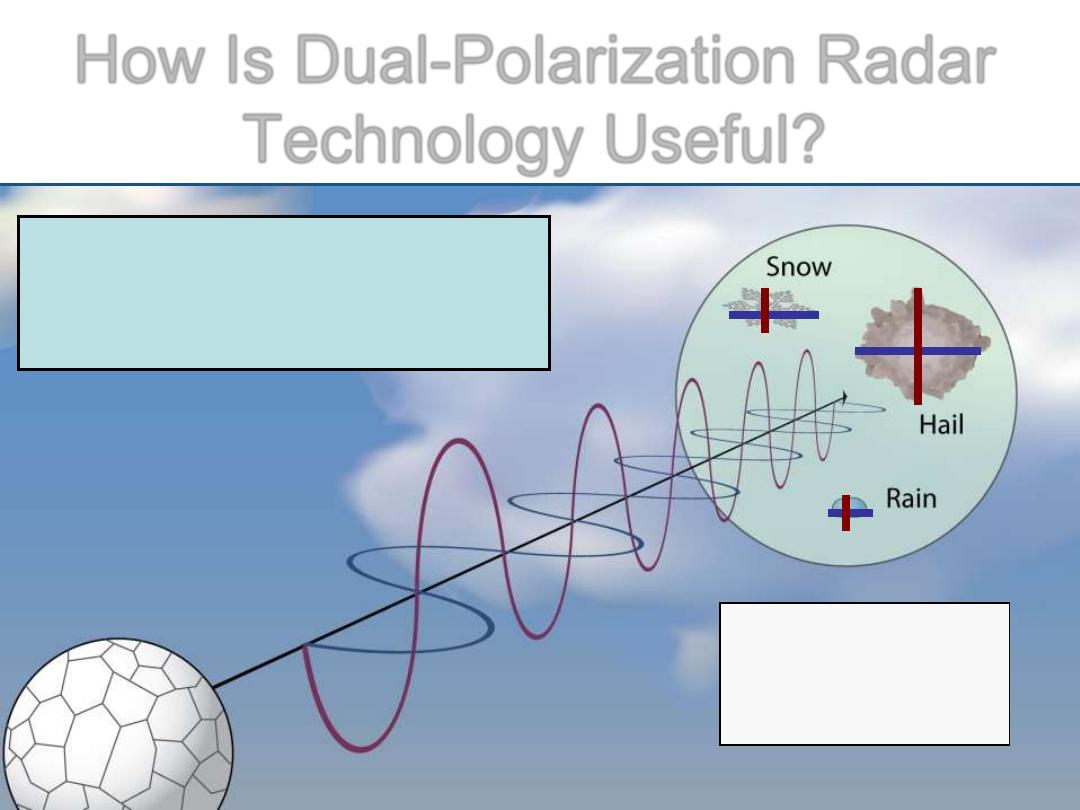
How Is Dual-Polarization Radar
Technology Useful?
Image courtesy NSSL
–
=
Size
(
|
+
–
) =
Shape
σ
(
|
+
–
)
=
Variety
Dual-Polarization Radar
tells us about the size,
shape, & variety of objects.

Summary of Benefits with Dual-
Polarization Radar Technology
• Better Determination of Precipitation Type
• Better Estimates of Rainfall Amount
• Better Detection of Hail

Part II. Next Generation
Geostationary Operational
Environmental Satellite (GOES-R)

GOES-R New Capabilities
• Higher Resolution Images
• Data Received in More Frequent Time Intervals
• A Large Suite of New Products

Comparison of GOES-R Imager
to current GOES
GOES-R
Current
Spectral Coverage
16 bands
5 bands
Visible Resolution
0.5 km
~1 km
IR/WV resolution
2 km
~4-8 km
Full disk
Every 15 min
Every 3 hr
CONUS
Every 5 min
Every 15 min
Mesoscale
Every 30 sec!
N/A
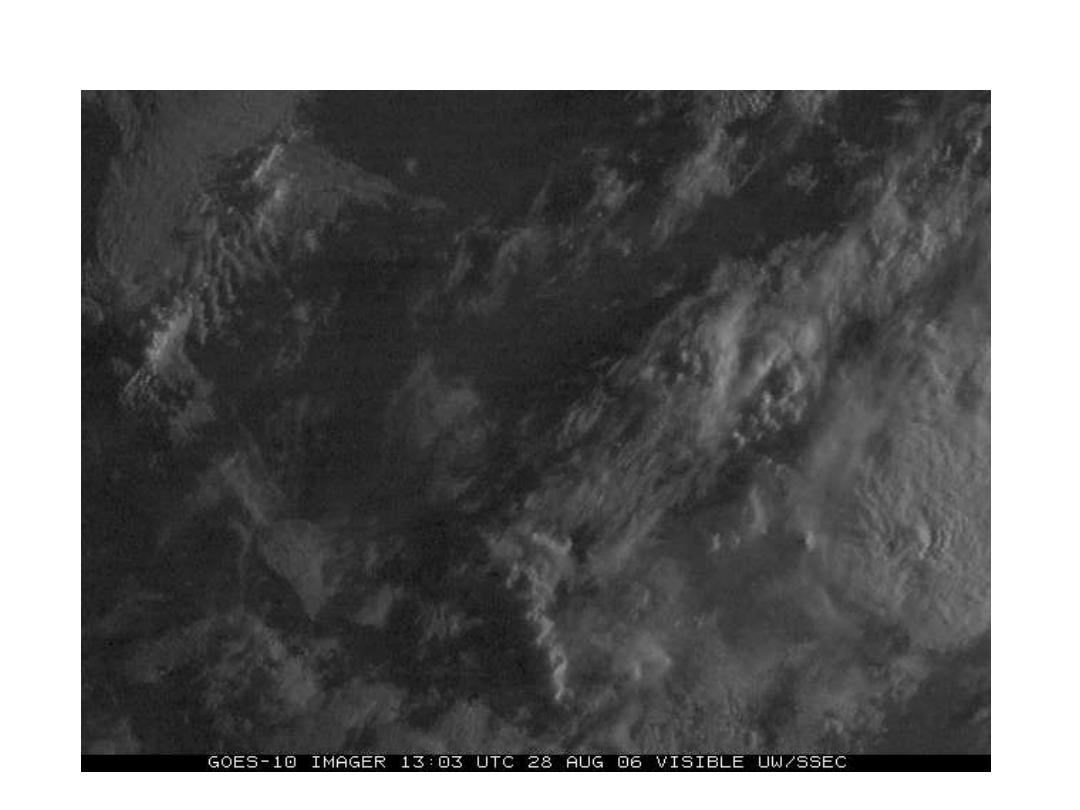

Example of Visible Loop Using 1-Min Images
Courtesy Timothy J. Schmit, NOAA/NESDIS/STAR Madison, WI

Some Applications of New GOES-R Data:
• Improved Convective Initiation Predictions
• Identification of Severe Weather Precursors
• Improved Rainfall Amount Estimates
• Better Estimates of Tropical Cyclone Intensity
• Identify Areas of Turbulence and Icing
• Improved Input to Numerical Weather Prediction Models

Some Applications of New GOES-R Data:
• Improved Convective Initiation Predictions
• Identification of Severe Weather Precursors
• Improved Rainfall Amount Estimates
• Better Estimates of Tropical Cyclone Intensity
• Identify Areas of Turbulence and Icing
• Improved Input to Numerical Weather Prediction Models

How will GOES-R improve warning
lead times?
• Rapid Cloud top cooling detection



Conclusion
• New radar and satellite technology will
result in improved forecast and warning
operations.
