
Cellular Physiology Lec. 2
Dr. Basim A. Al-Ka’abi
MBChB (Medicine)
MSc, PhD (Medical Physiology)

Cell membrane and organelles
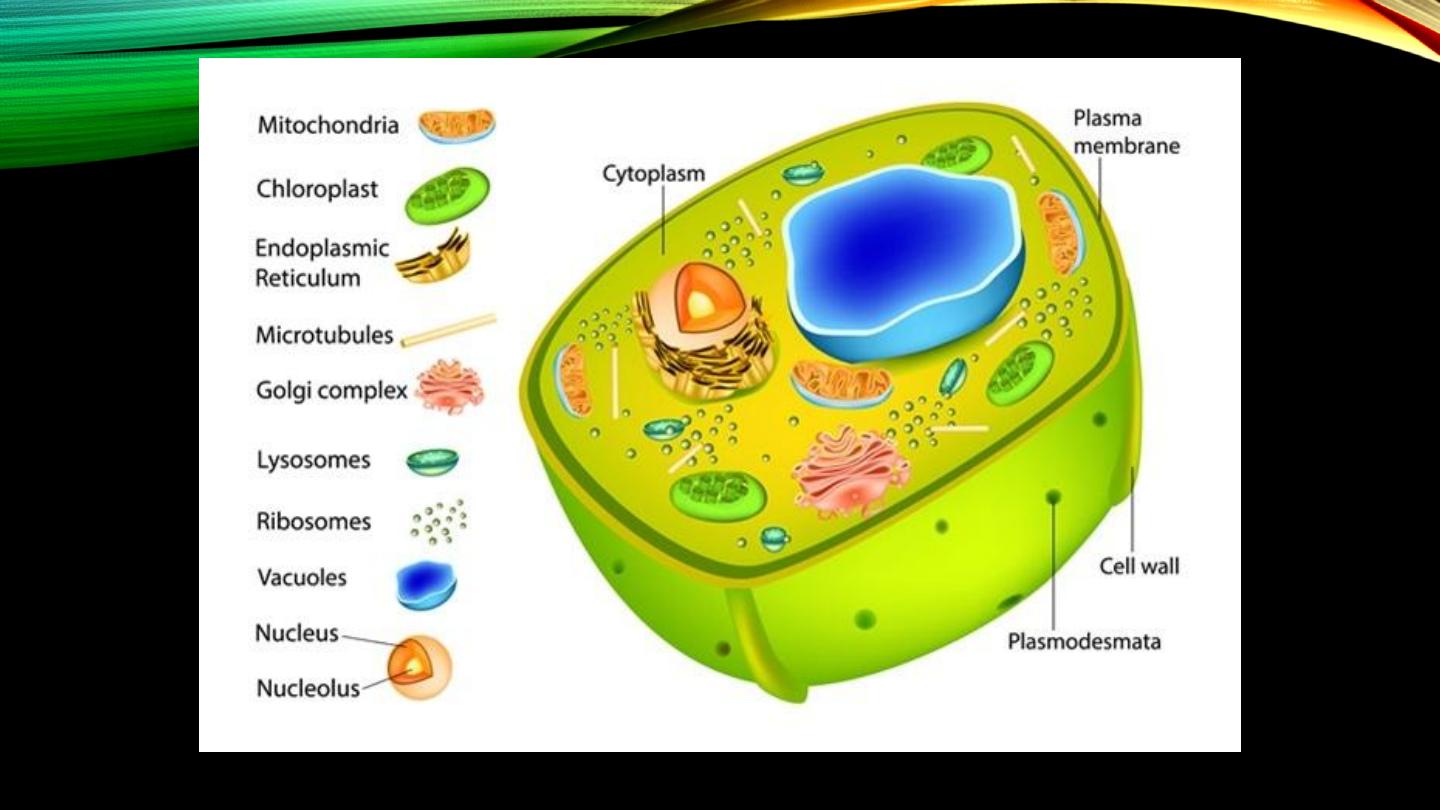

Cell membrane:
• Plasma membrane?
• Semipermeable?
• Composition

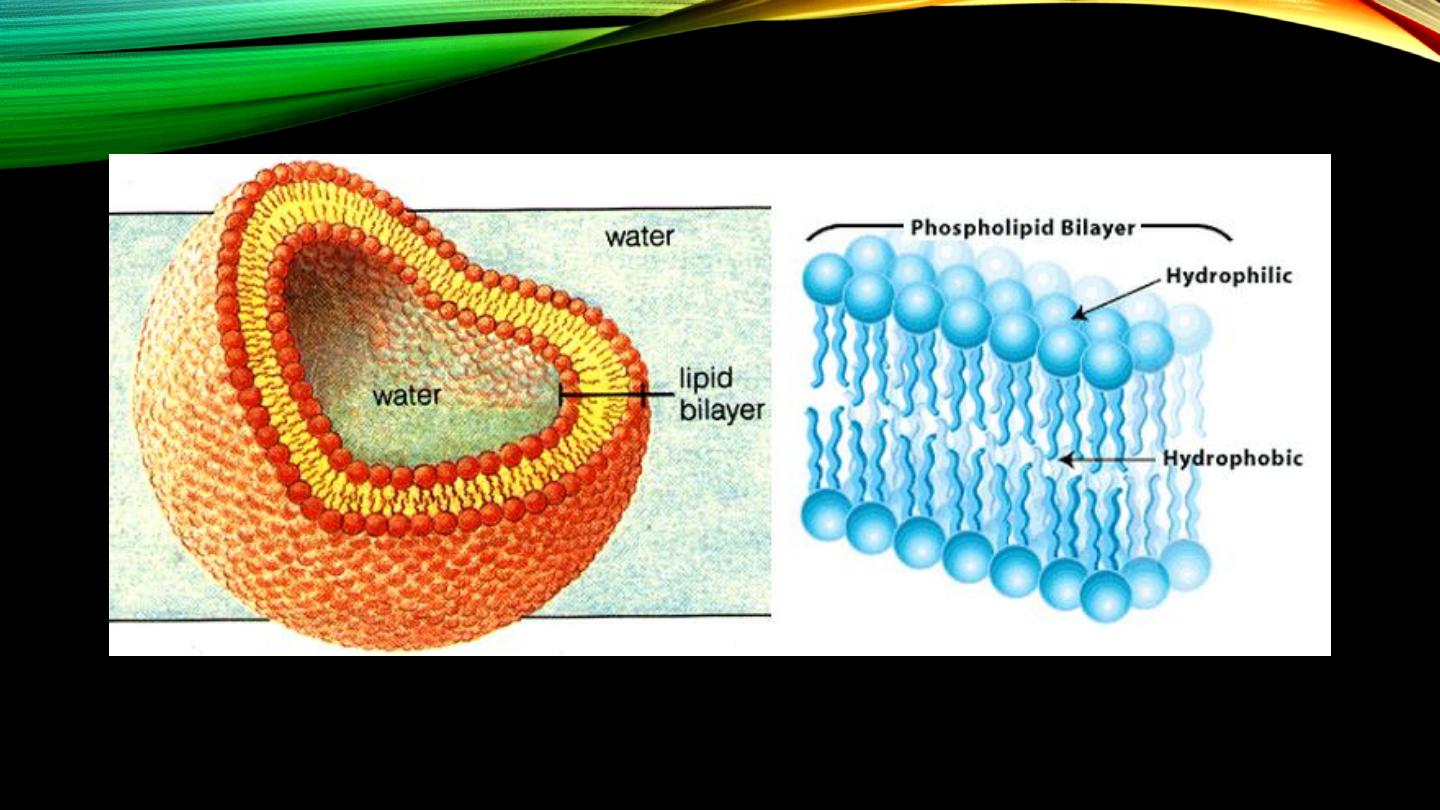
Cell membrane (cont’d):
• Lipid bilayer?
• Hydrophilic vs hydrophobic ends
• Permeability to various substances
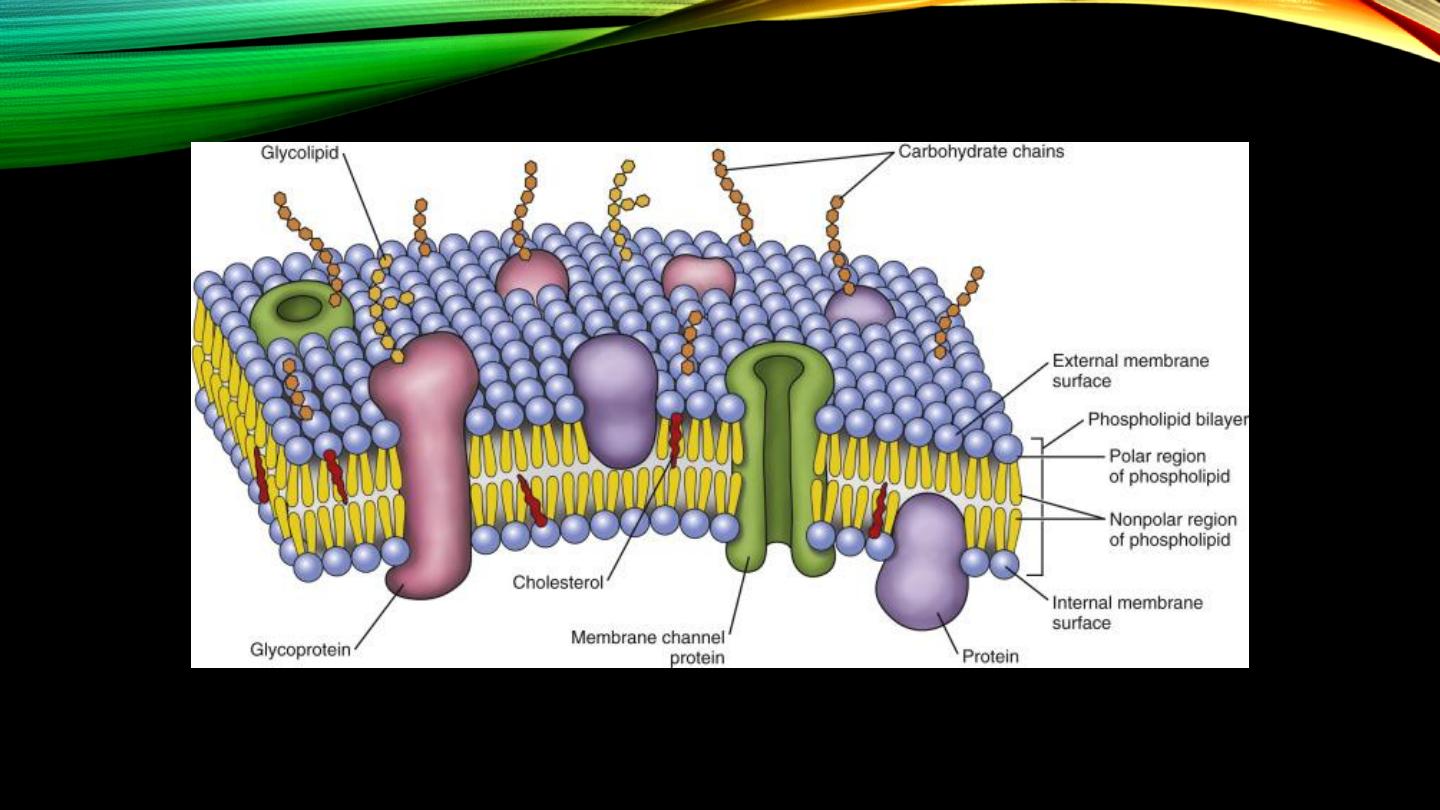

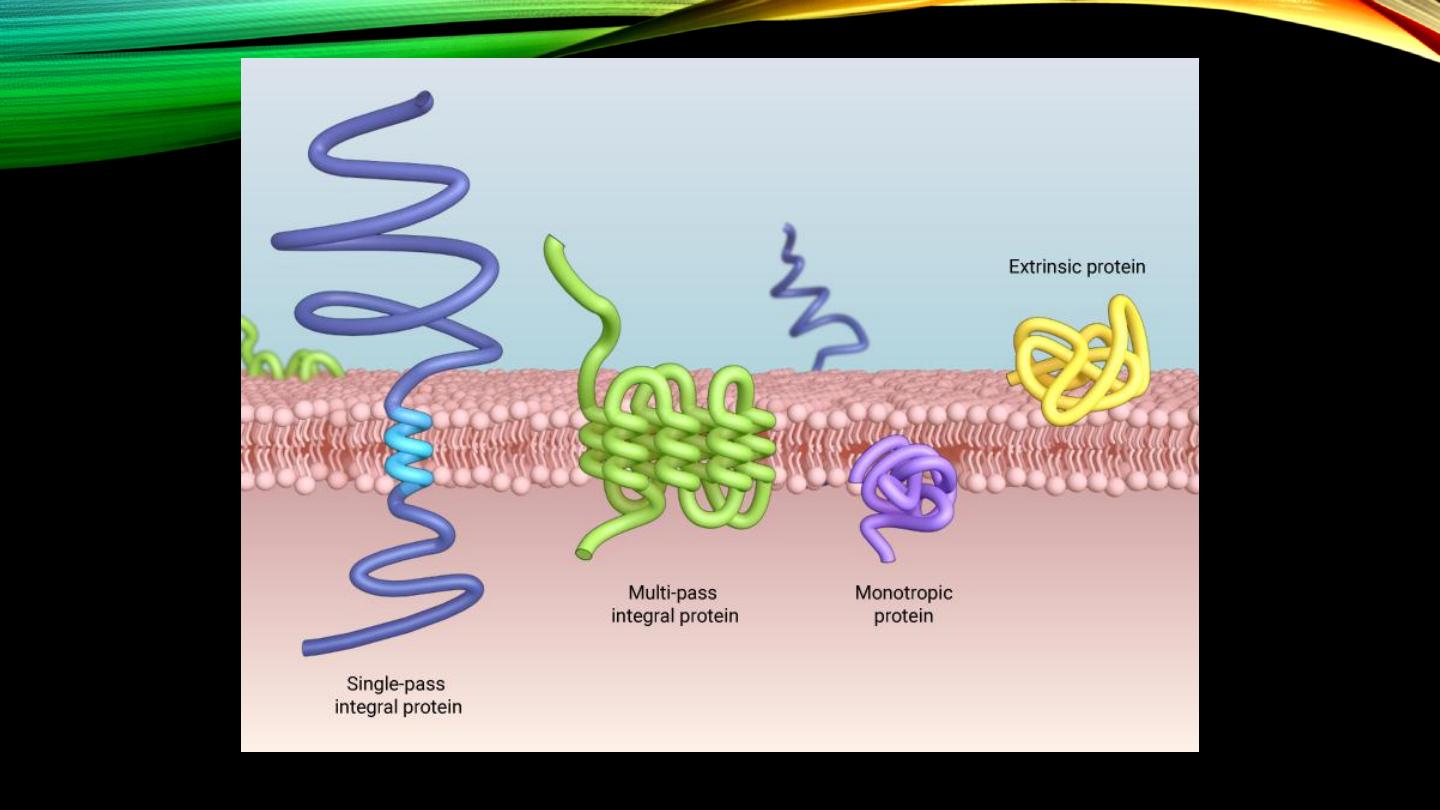
Cell membrane proteins:
• Integral proteins, function
• Peripheral proteins, function

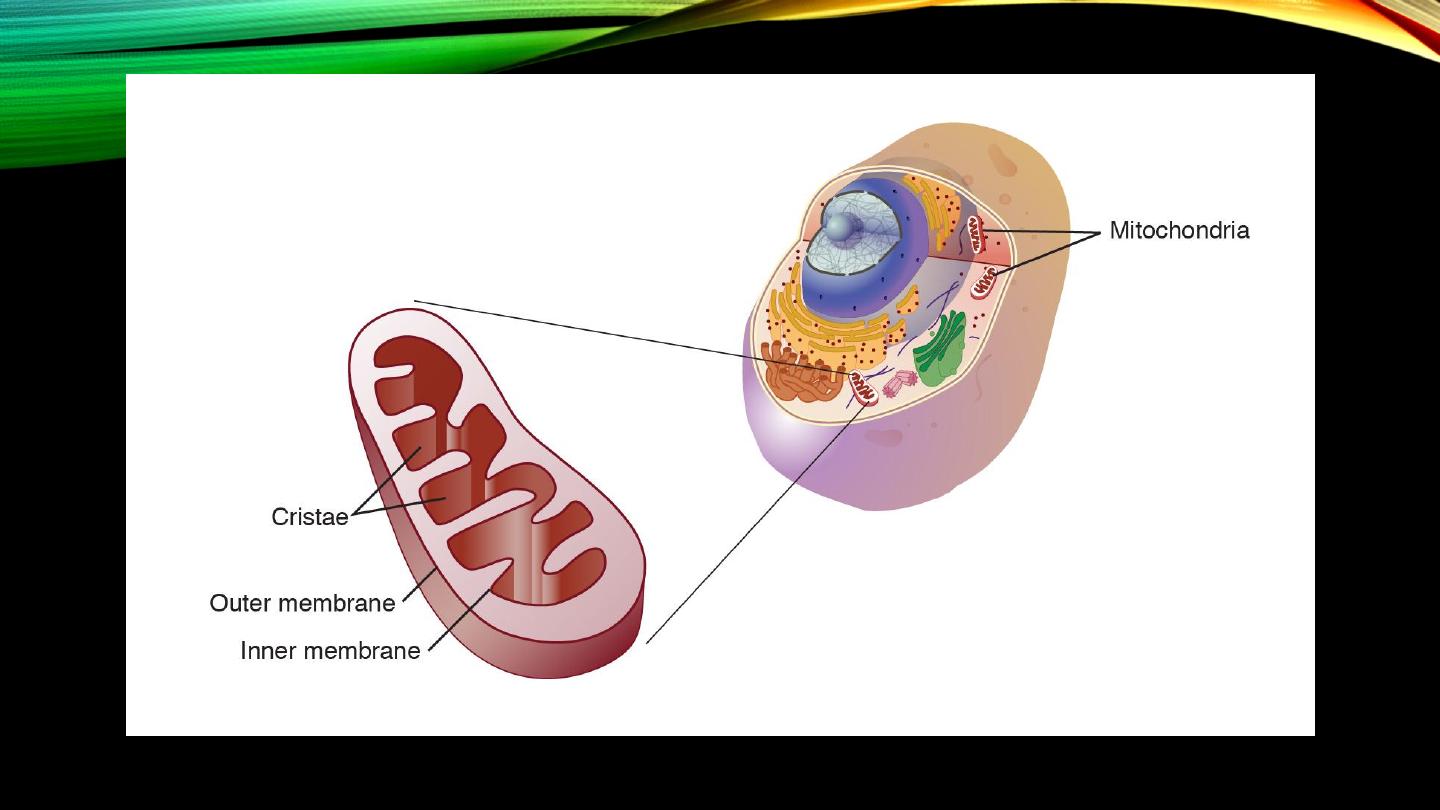
Mitochondria:
• “Powerhouses”
• Enzymatic constituent
• Required energy and number in each cell

Mitochondria (cont’d):
• “Citric acid cycle”
• Products of mitochondrial reactions, ATP
• Self-replicative?

Endoplasmic reticulum:
• Network of tubules and vesicles
• “Extensive” surface area for manufacturing substances
• Rough vs smooth ER
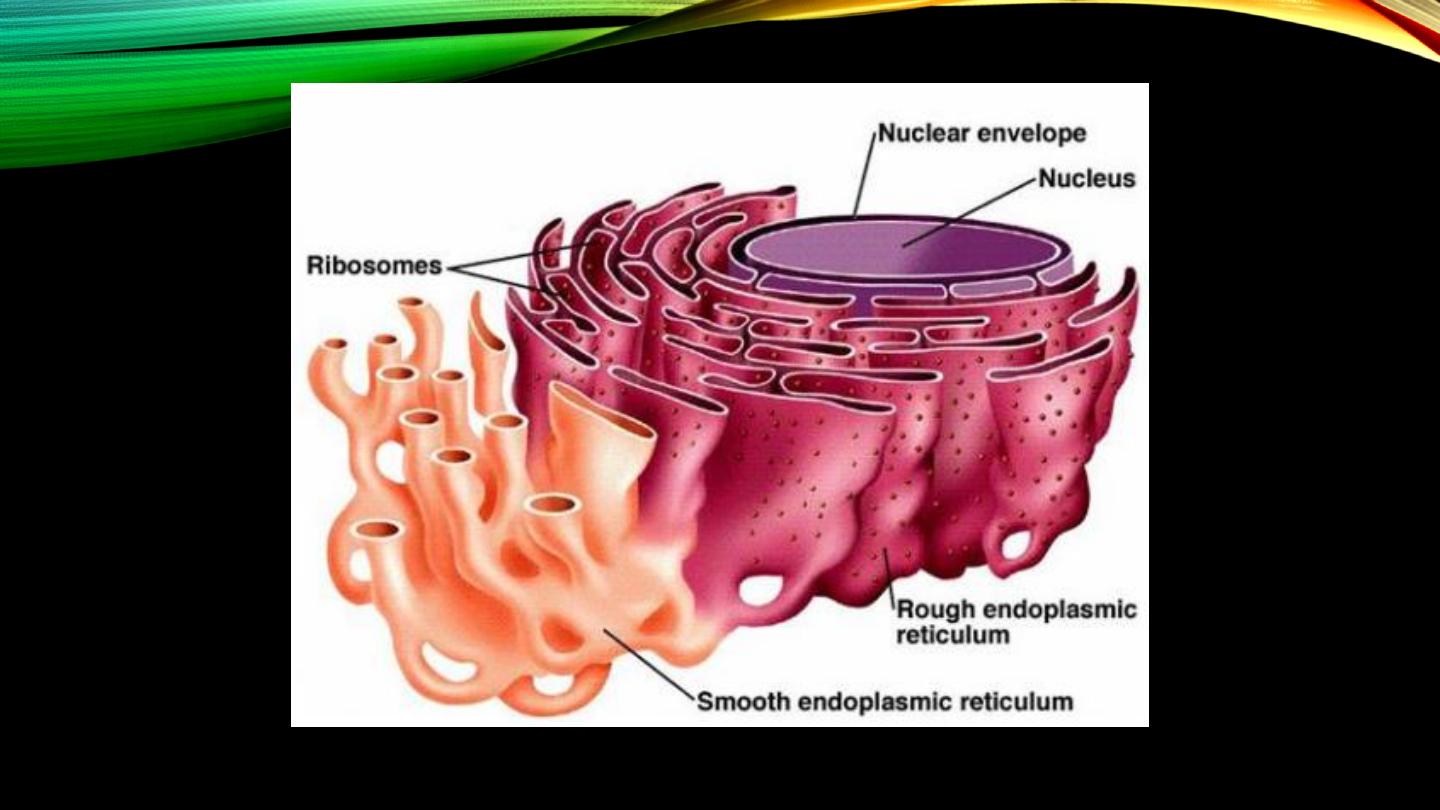

Ribosomes:
• Constituents
• ER-attached vs free ribosomes

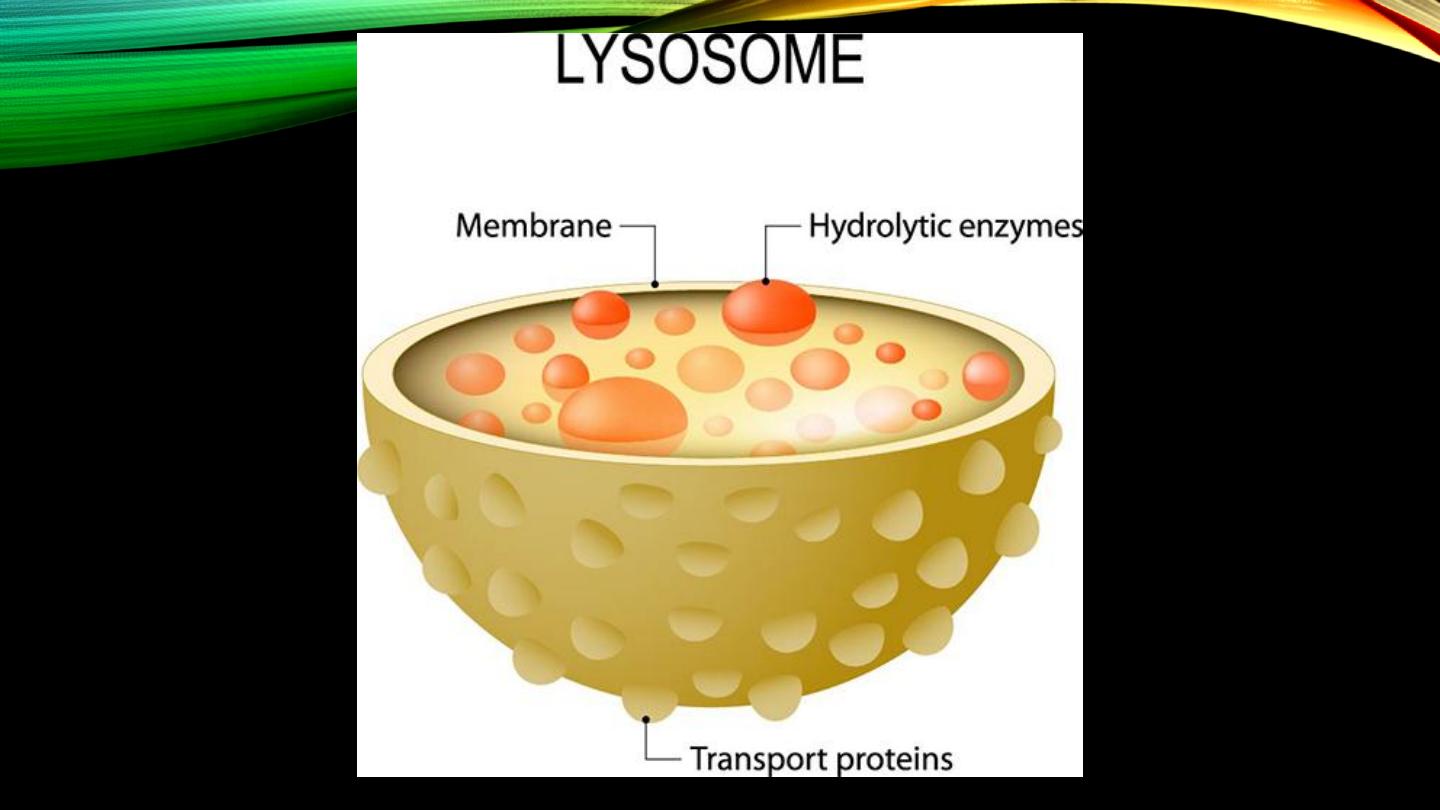
Lysosomes:
• Intracellular “digestive system”, digestive enzymes
• Function
• Membrane?

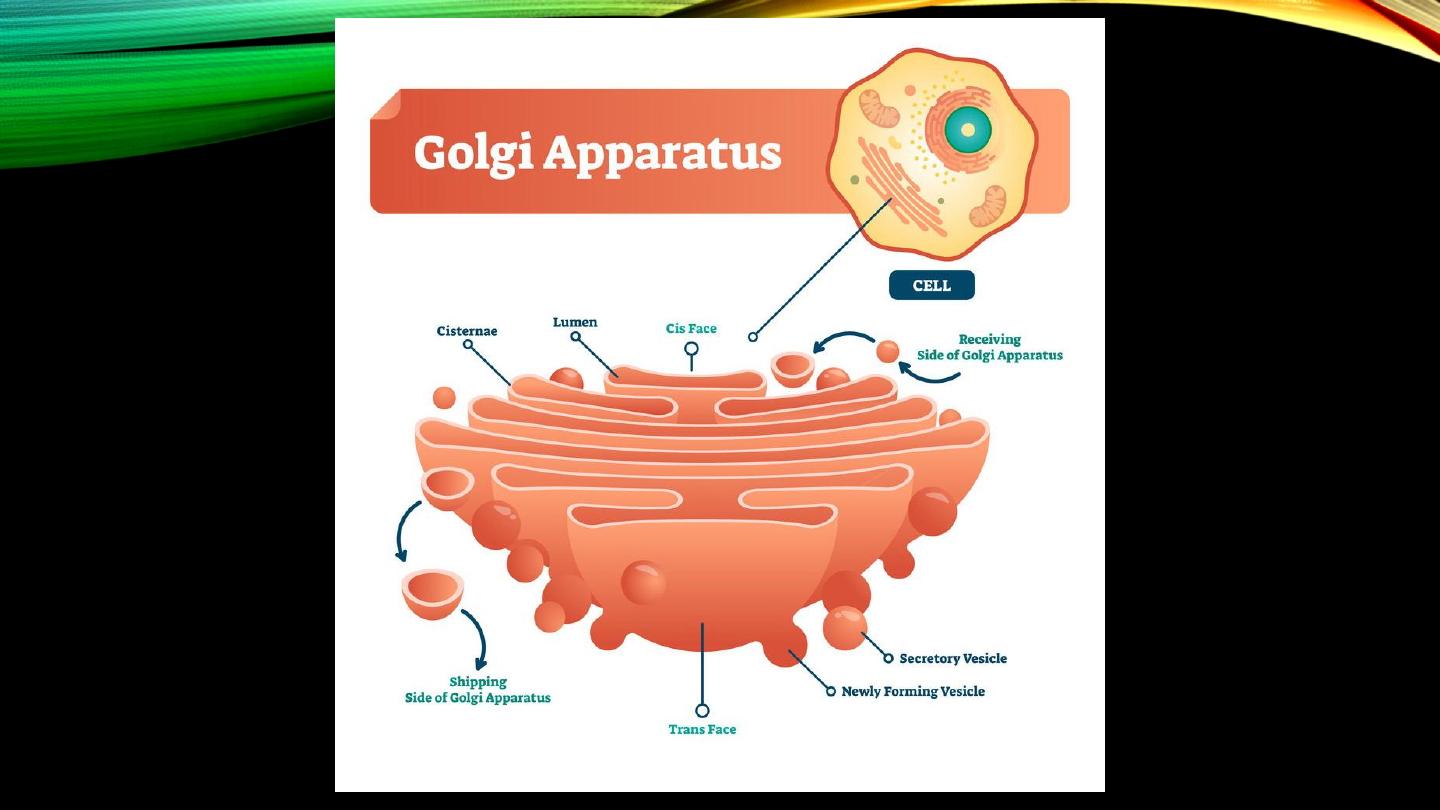
Golgi apparatus:
• Membrane-enclosed sacs
• ER-associated function
• Processing ER-entrapped substances

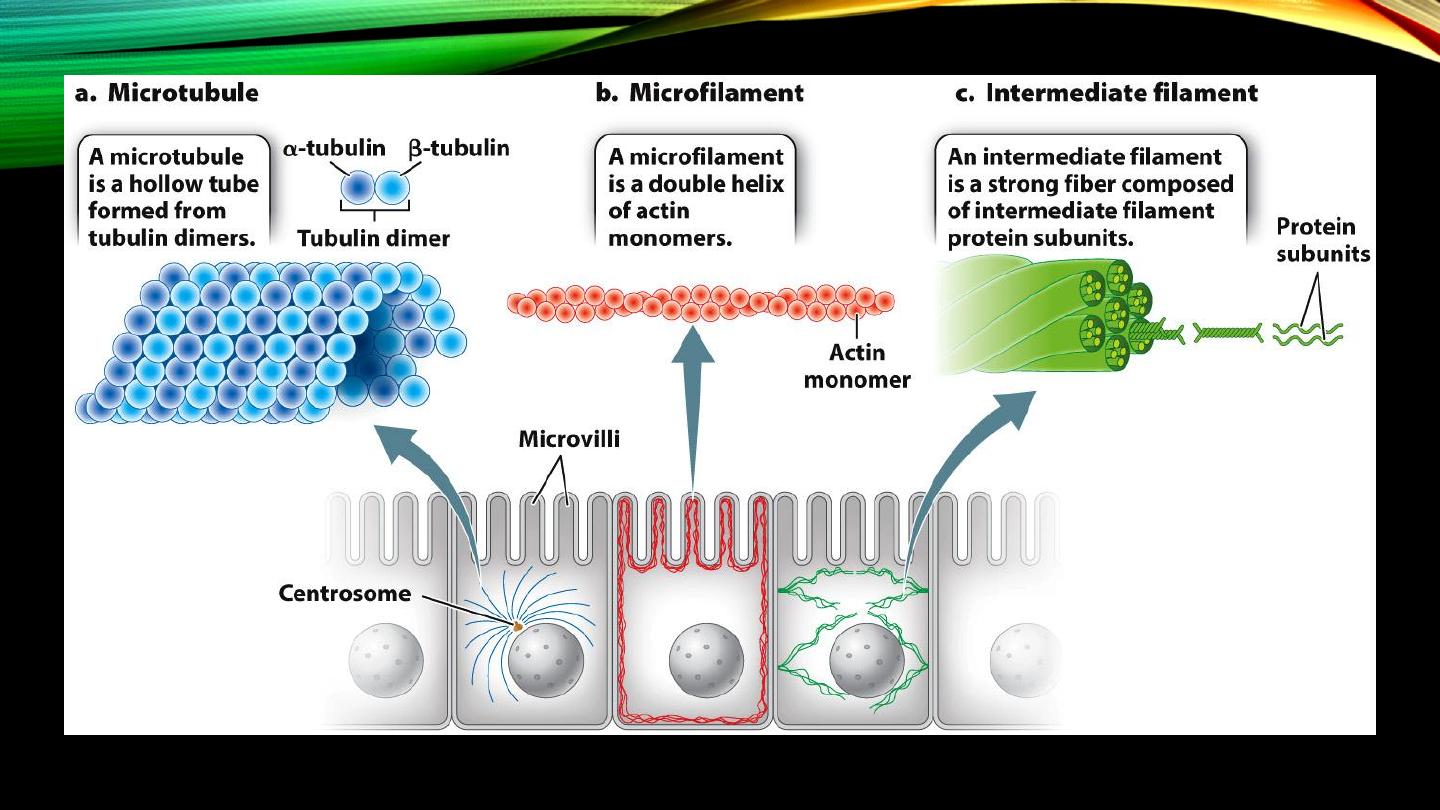
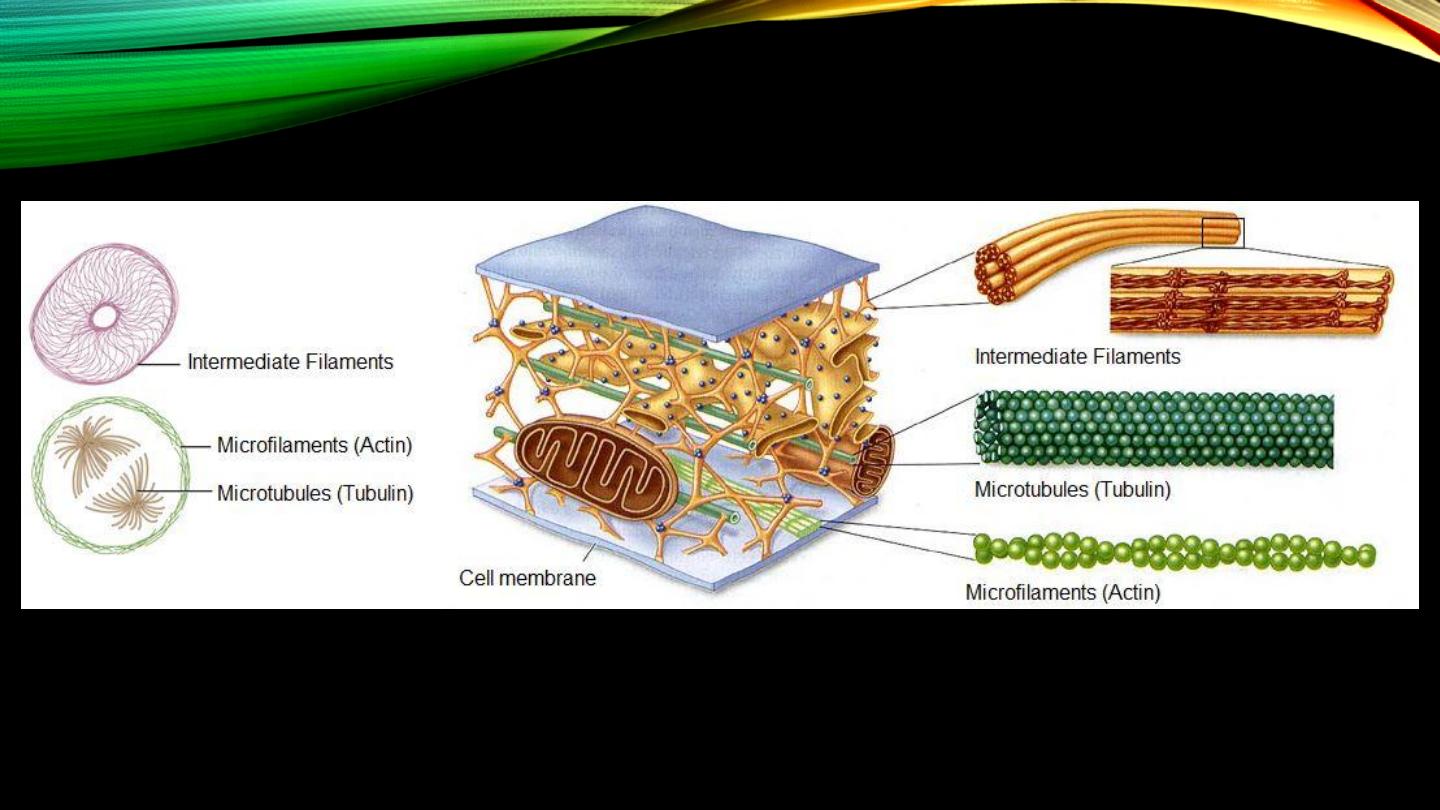
Cytoskeleton:
• Maintenance of structure
• Movement and cell shape changing

Cytoskeleton (cont’d):
• Microfilaments, actin and myosin
• Microtubules, rigid structure and tracking vesicles
• Intermediate filaments, connecting nuclear to cell mem.s

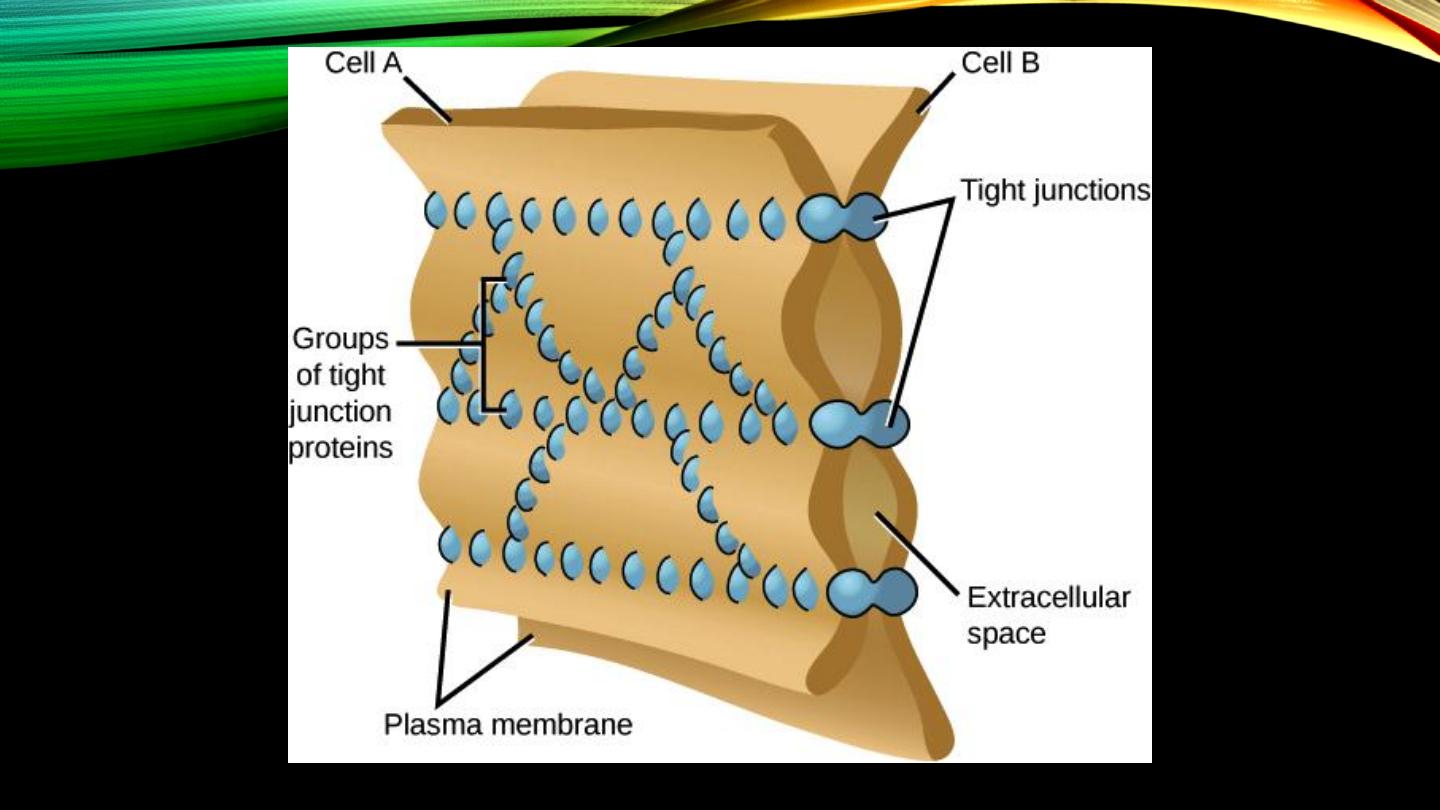
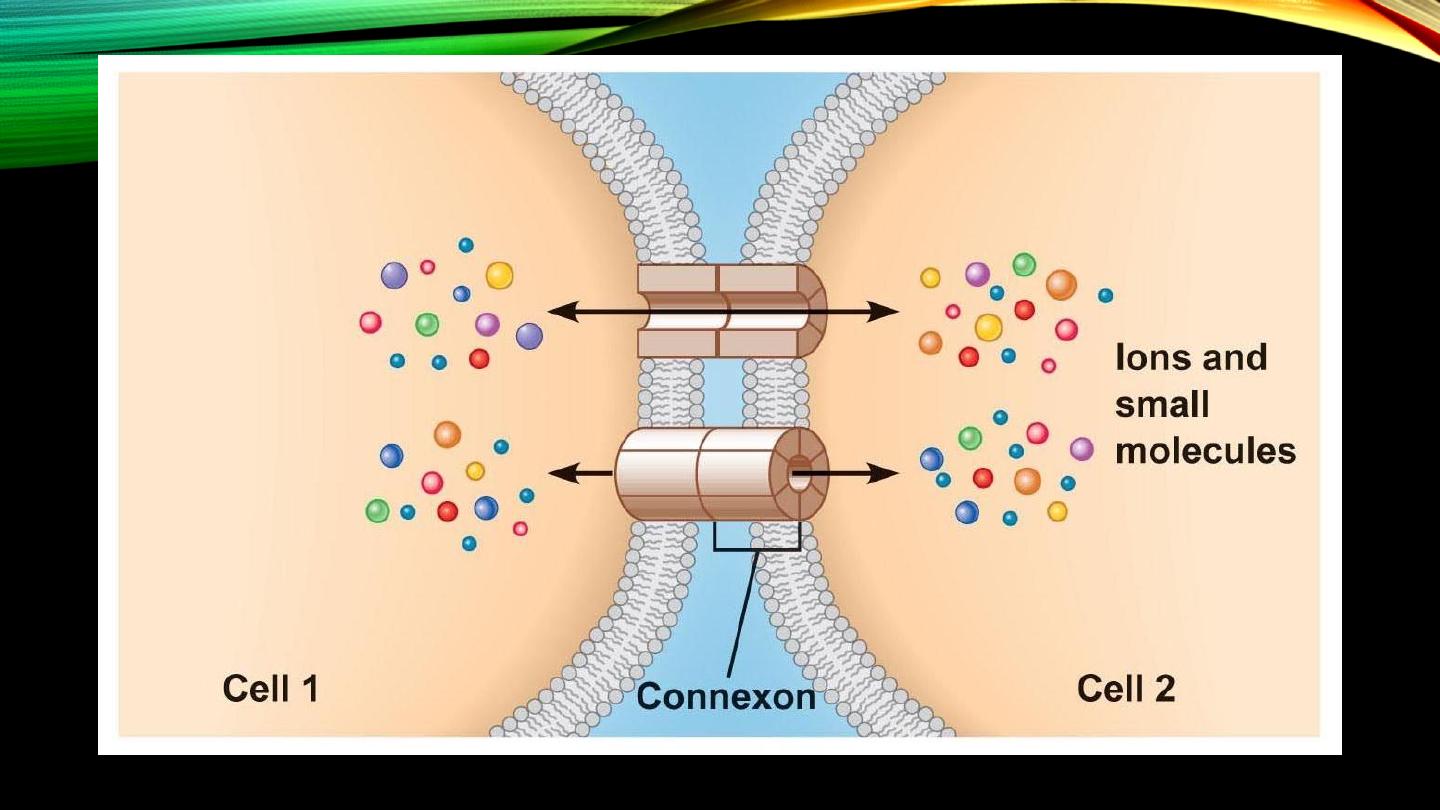
Intercellular connections:
• Tight junctions, cell-cell attachment and to surr. tissues
• Gap junctions, transfer of substances bet. cells

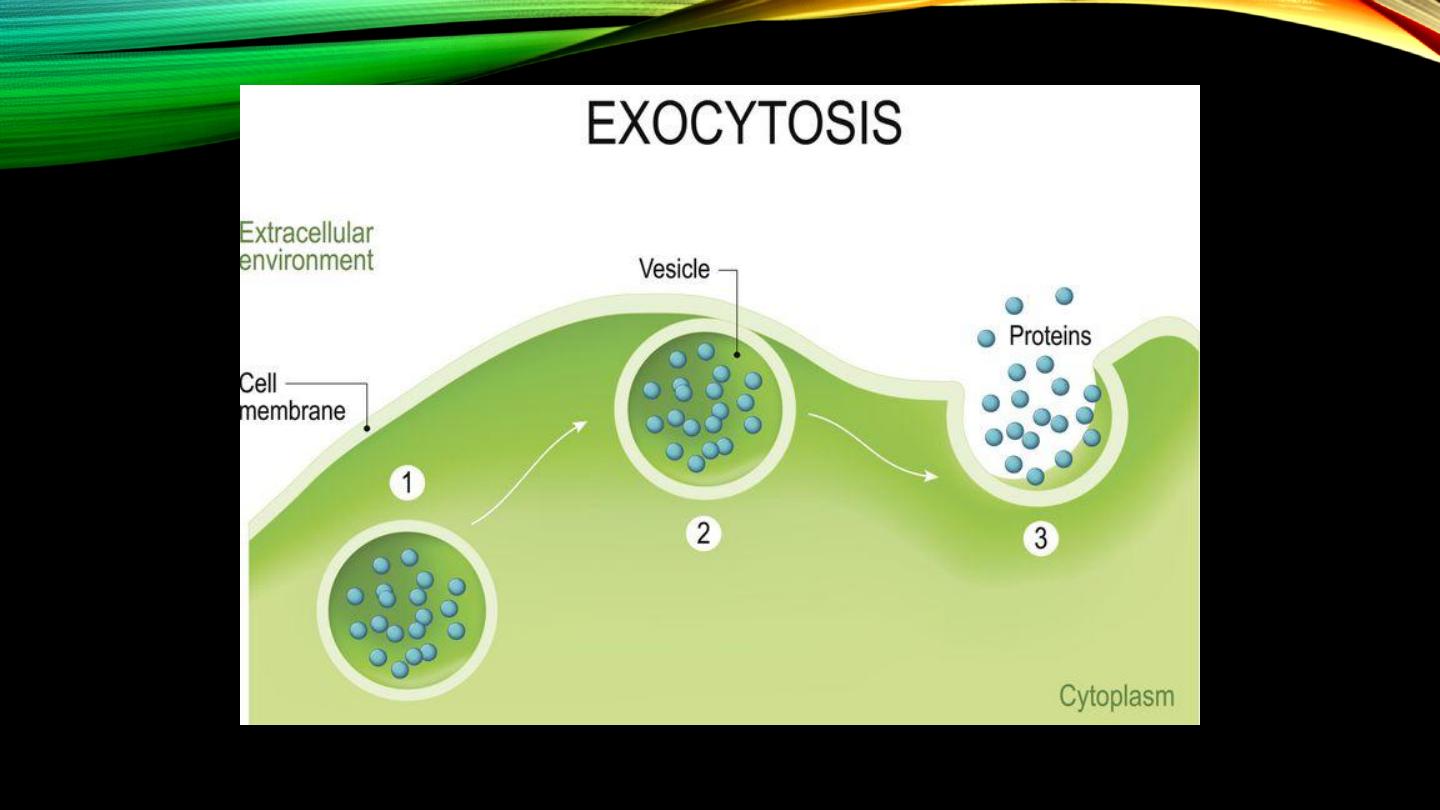
Exocytosis:
• Extruding substances from inside to outside the cells

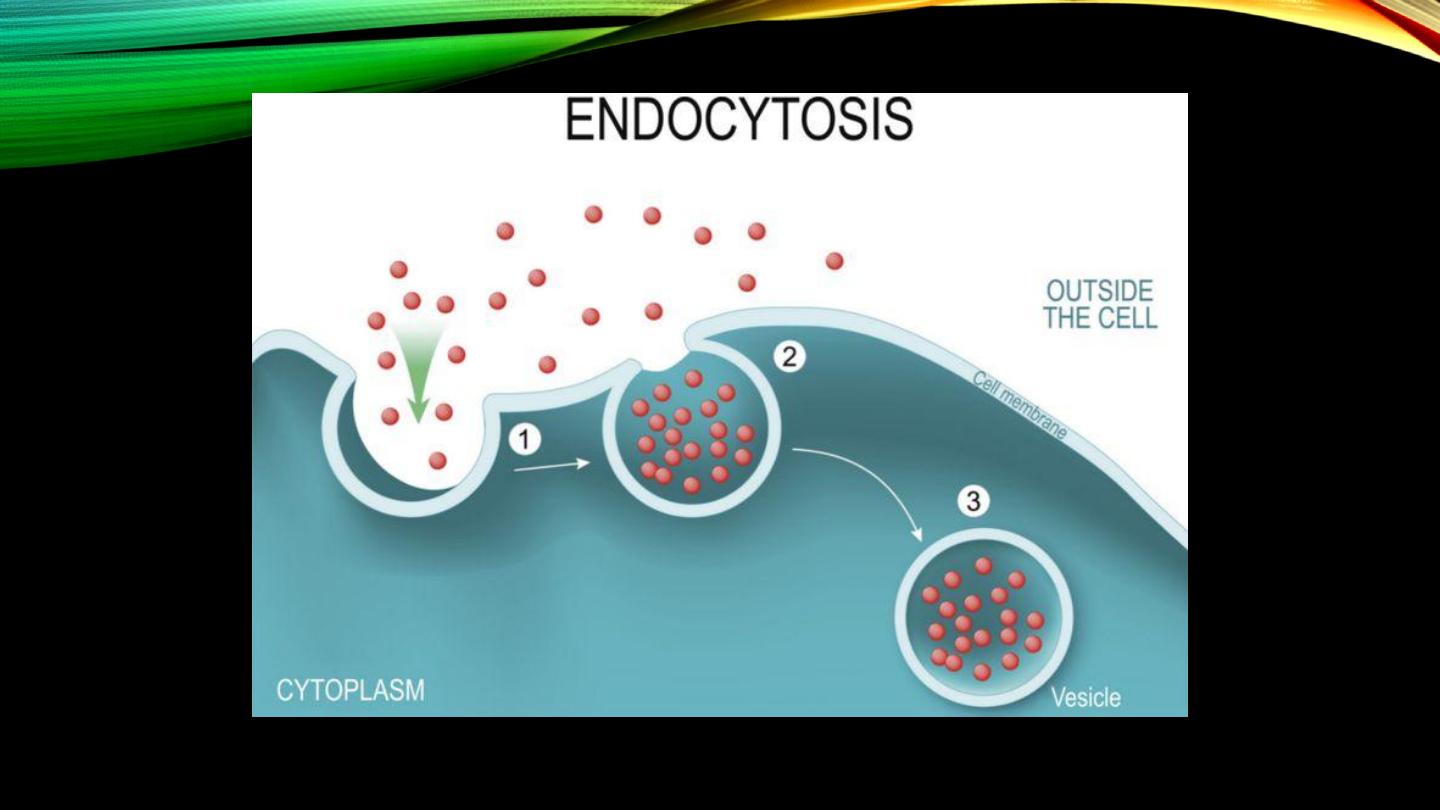
Endocytosis:
• The reverse of exocytosis
• Phagocytosis?
• Pinocytosis?

Good Luck
