
Cellular Physiology Lec. 4
Dr. Basim A. Al-Ka’abi
MBChB (Medicine)
MSc, PhD (Medical Physiology)

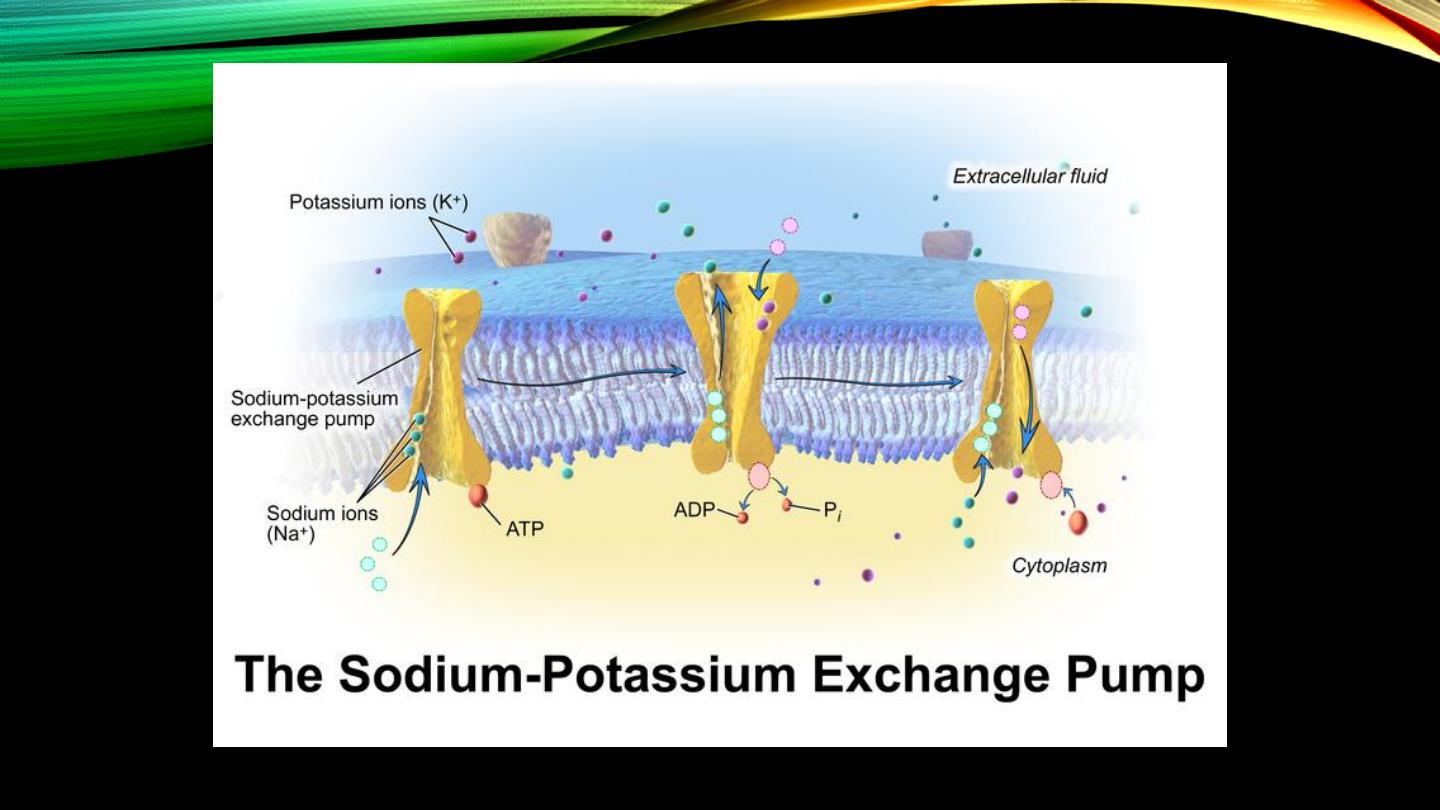
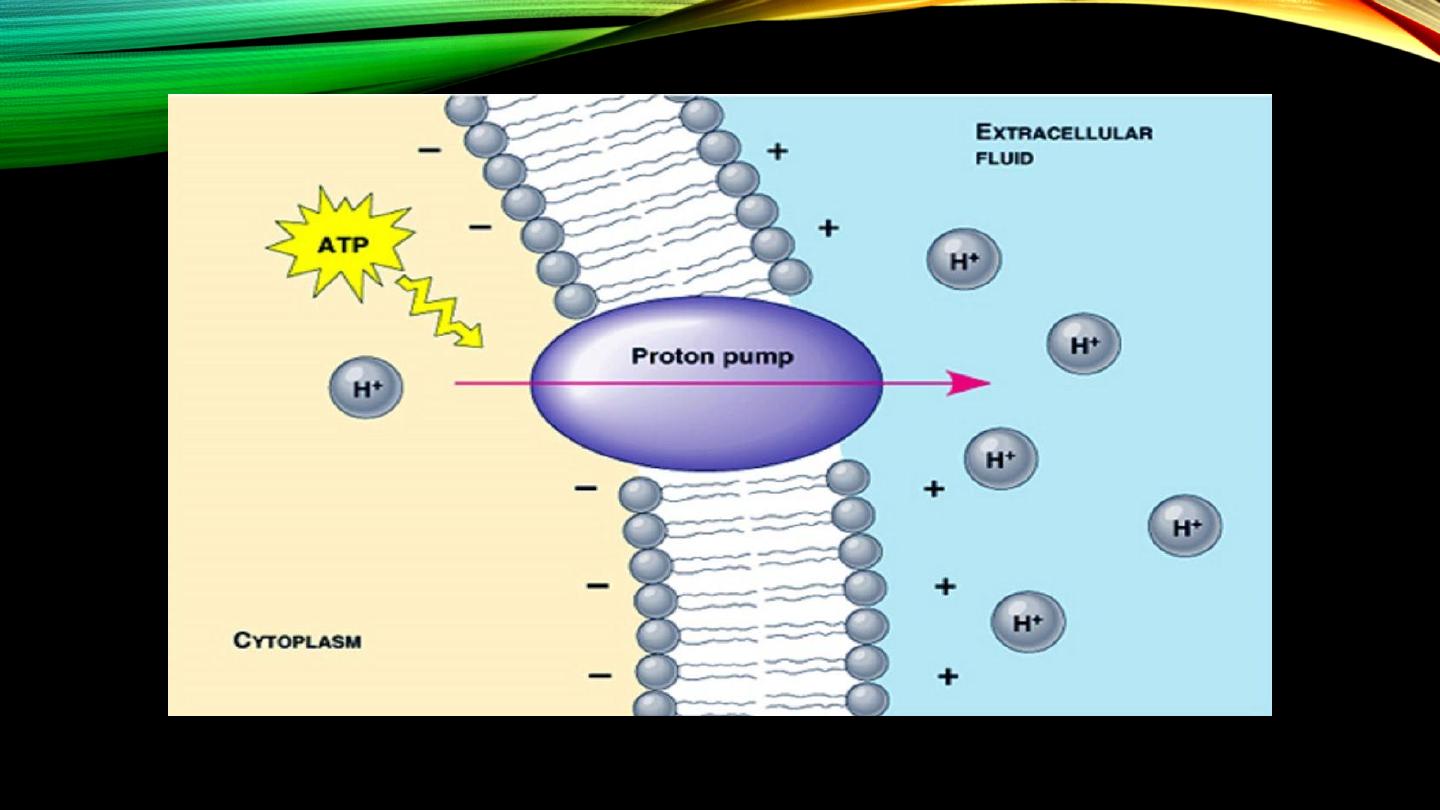
Primary active transport:
• “Uphill”
• Energy, ATP
• Examples

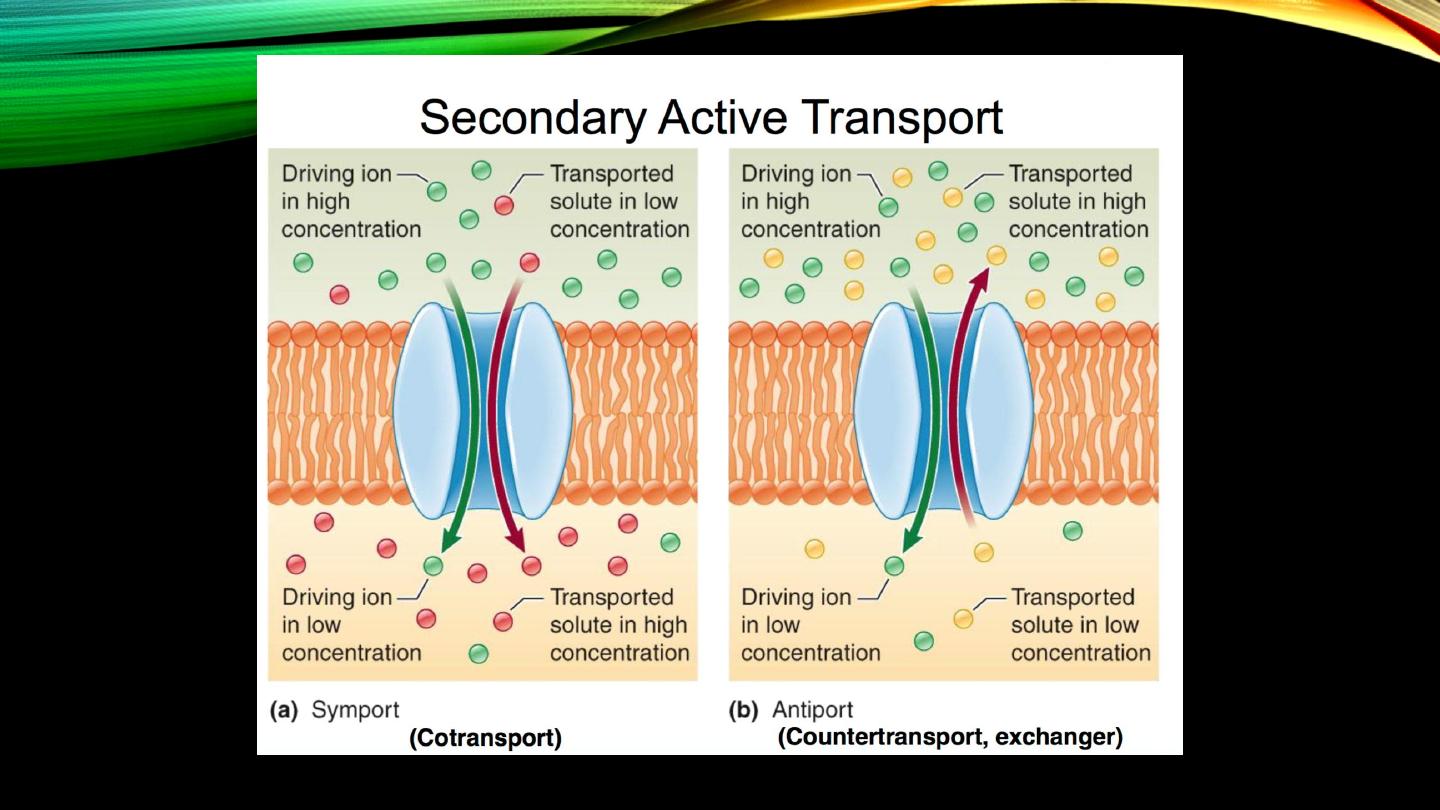
Secondary active transport:
• Coupling two or more solutes
• Na
+
(downhill), the other (uphill)
• Effect of inhibiting Na
+
/K
+
ATPase
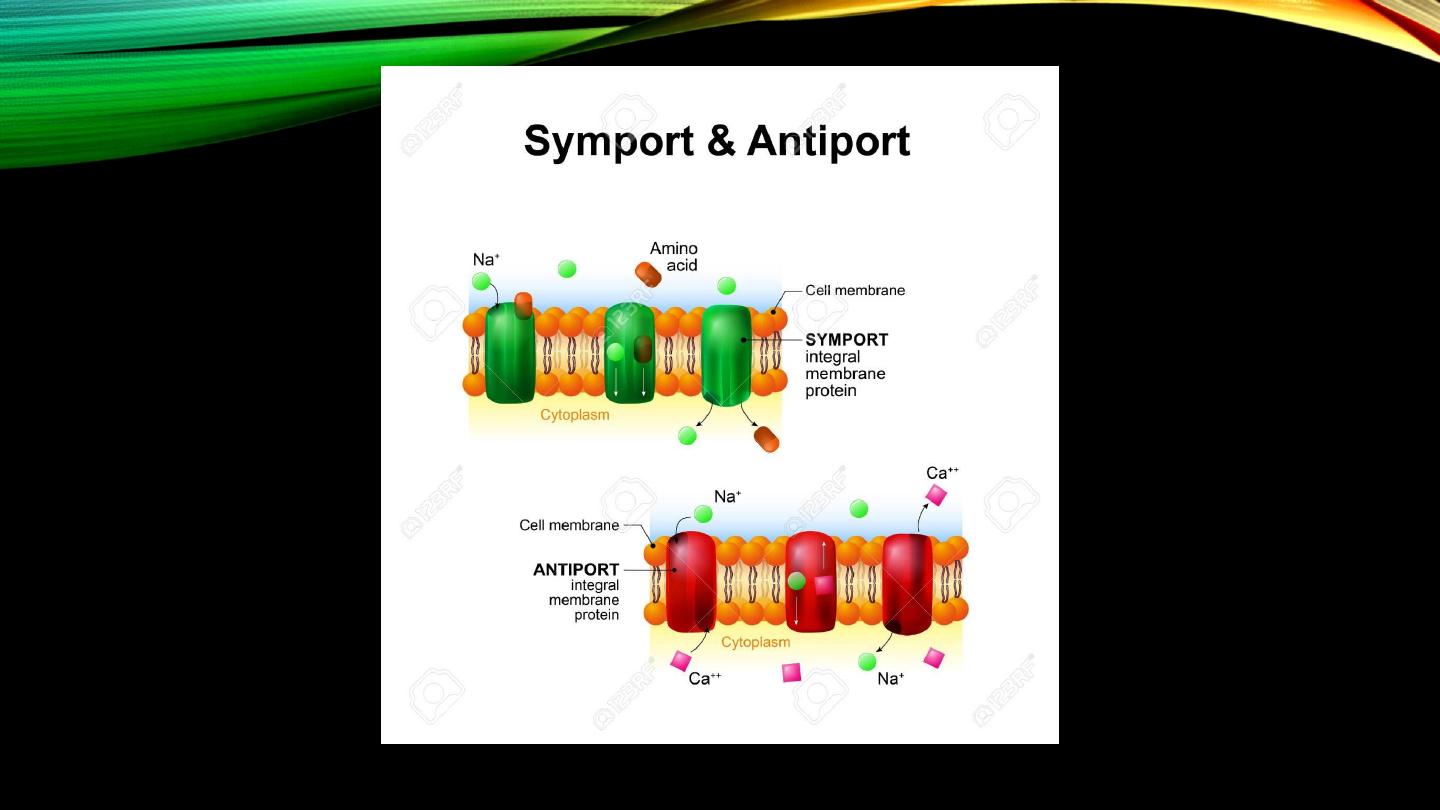
• Co-transport (symport)
• Counter-transport (antiport)

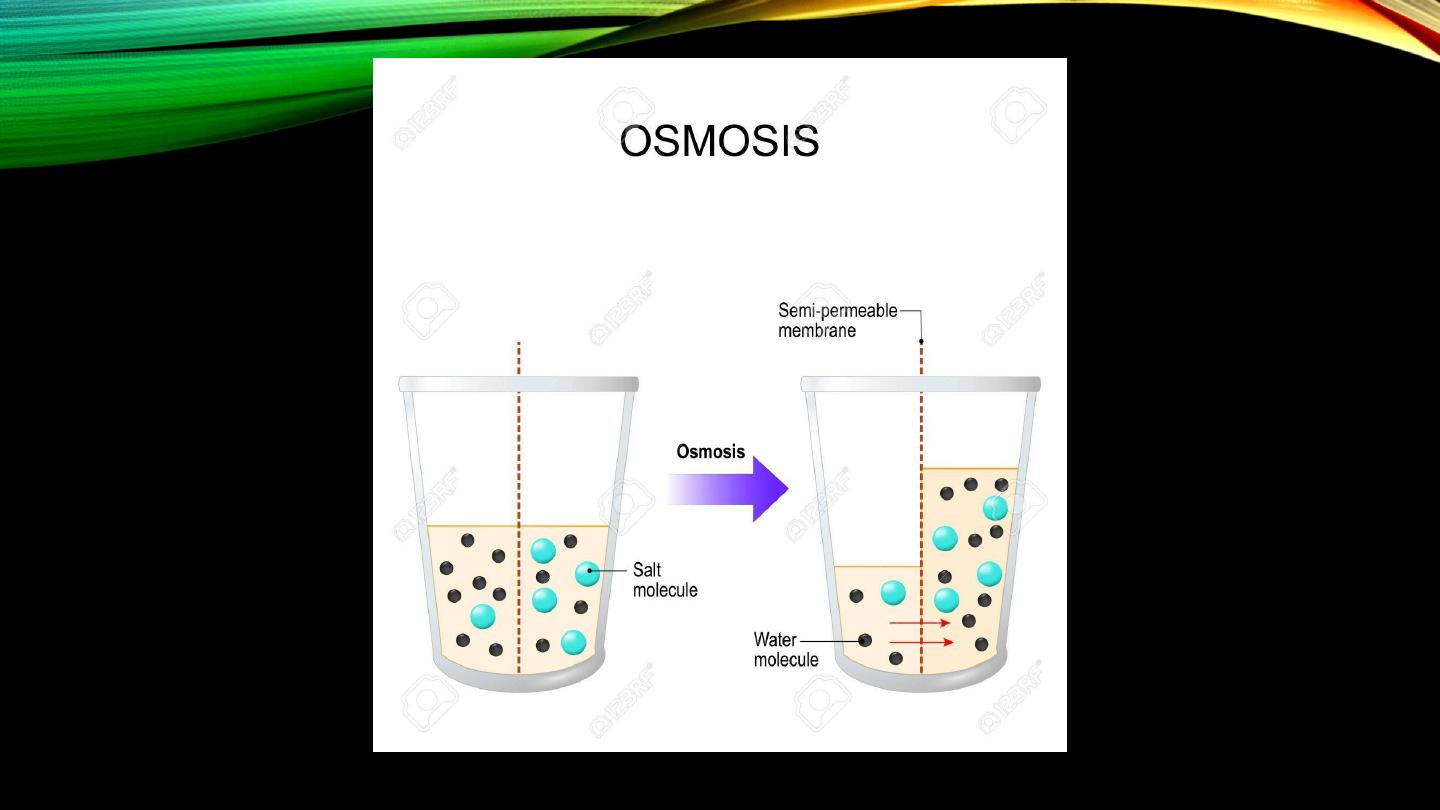
Osmosis:
• Meaning
• Effect of solute concentration on osmotic pressure
• “Osmolarity”

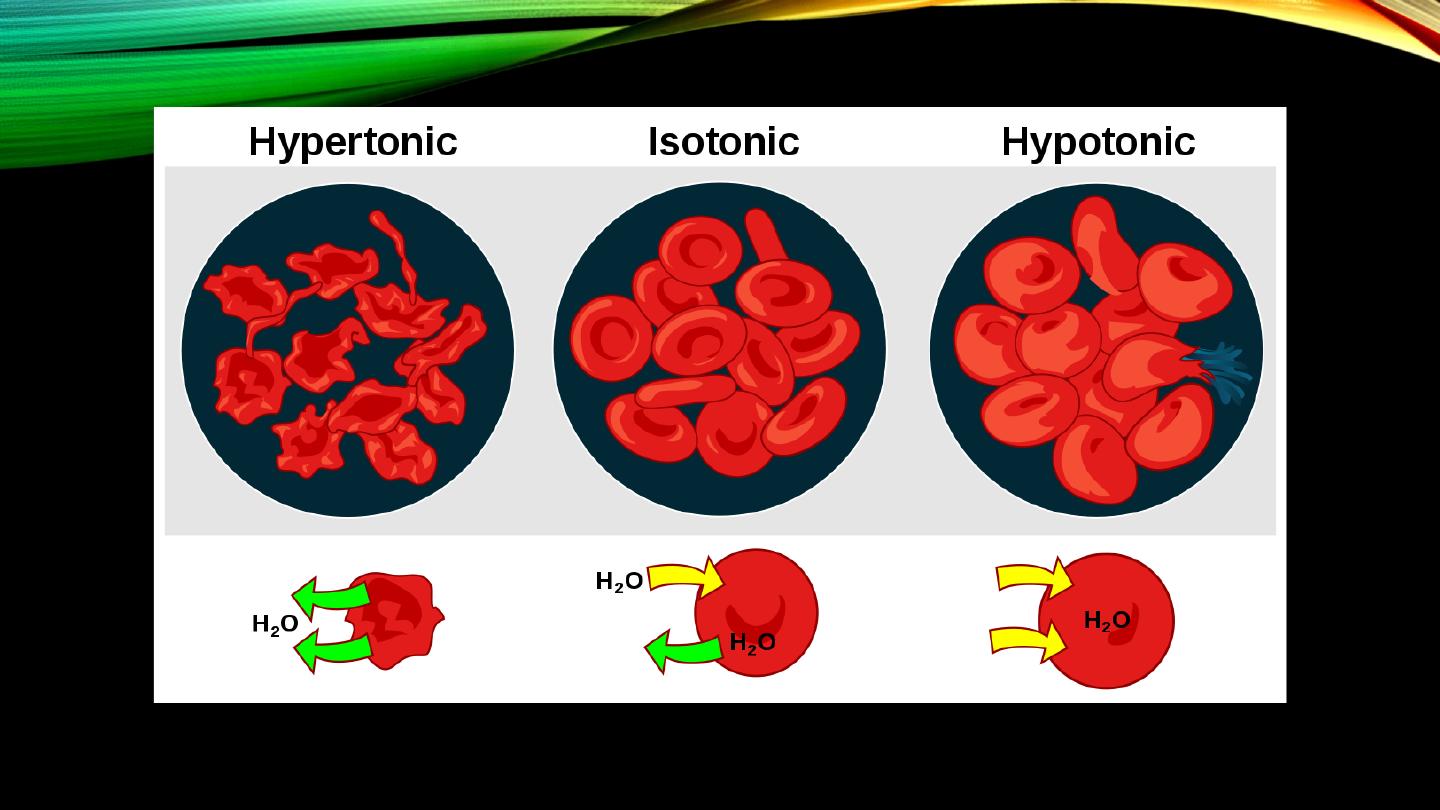
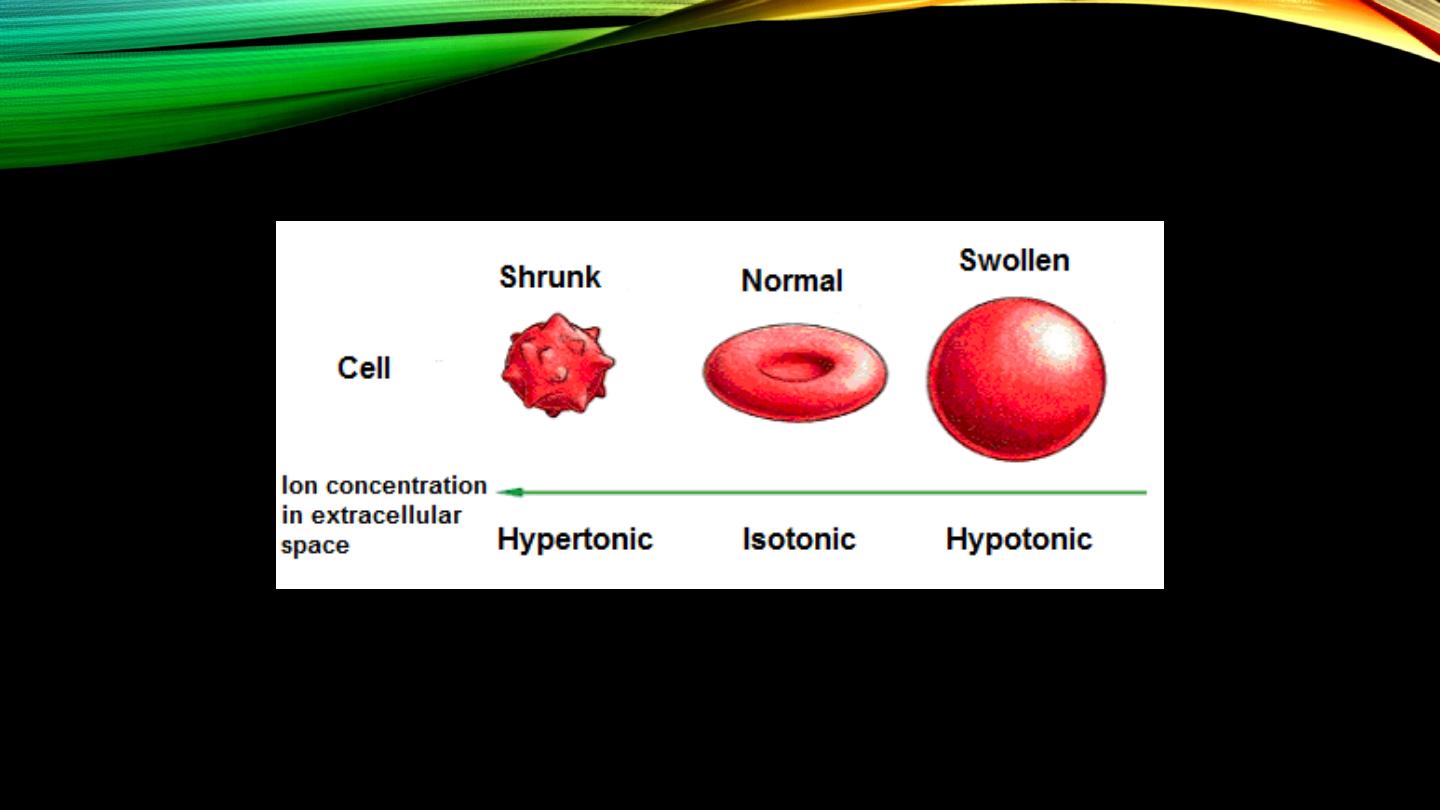
Isotonic, hyper and hypotonic fluids:
• Meaning
• Effect on cells

Edema:
• Definition
• Intracellular vs extracellular edemas
• Most common one
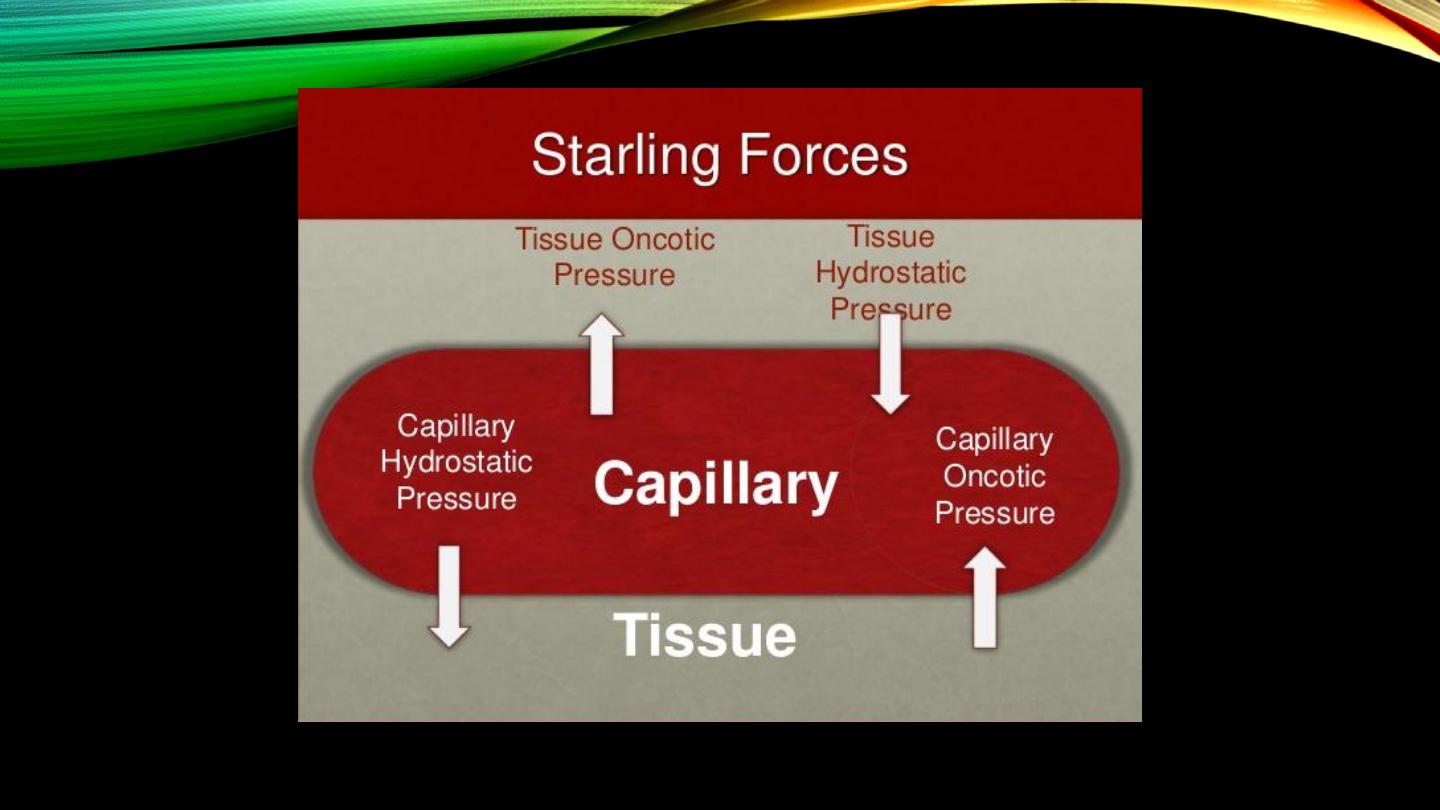

Edema (cont’d):
• Extracellular edema:
• Excessive capillary filtration, causes
• Failure of lymphatics, causes

Good Luck
