
Blood Physiology Lec. 2
Dr. Basim A. Al-Ka’abi
MBChB (Medicine)
MSc, PhD (Medical Physiology)

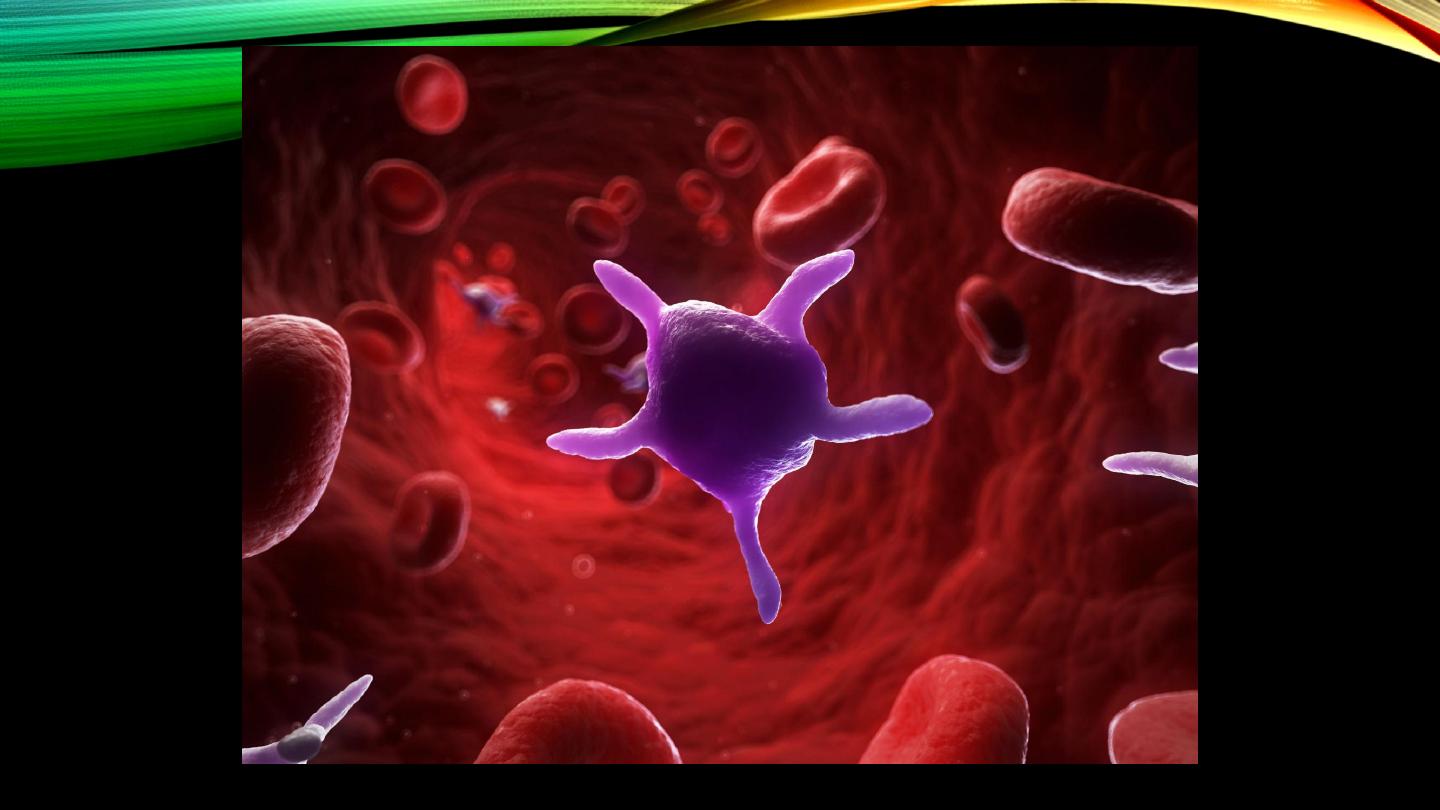
Blood cells (cont’d): Platelets:
• Shape, count, nucleus?
• Major primary function
• Active cytoplasmic factors

Reticulo-endothelial system:
• Cellular contents
• Contribution of bone marrow, spleen and LNs
• Old name

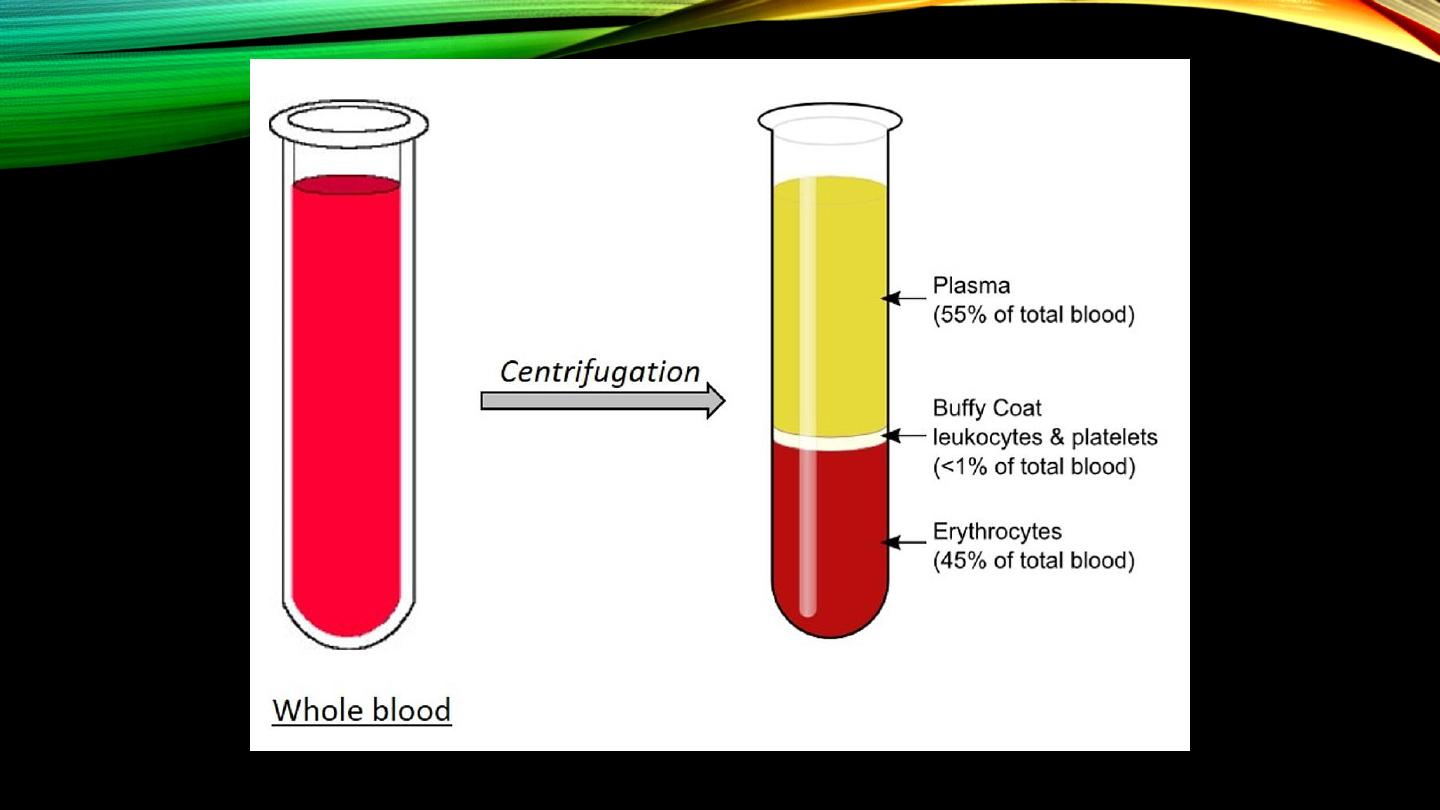
Plasma:
• Composition and pH
• Contents
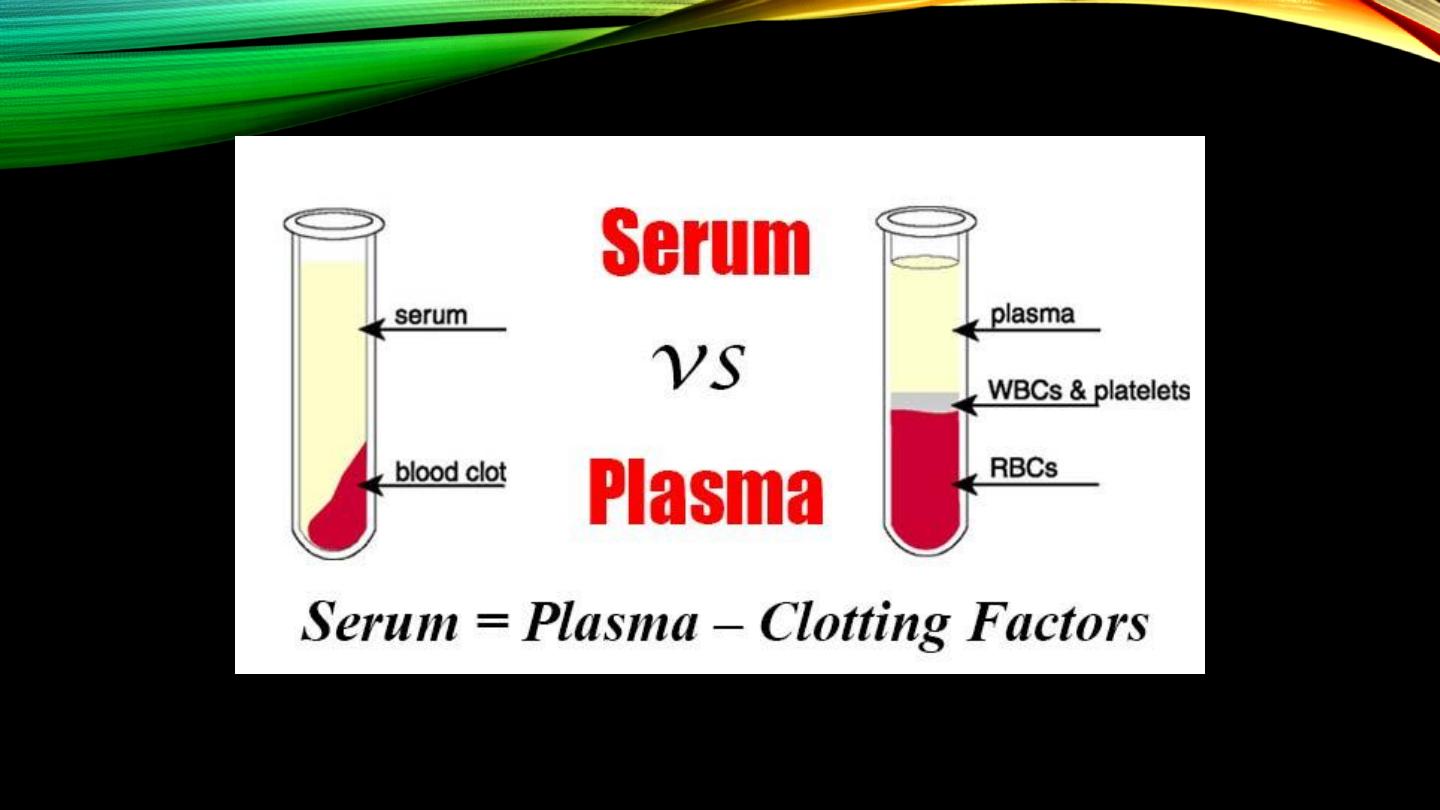
• Difference from serum

Plasma proteins:
• Types and sites of synthesis
• Total concentration in adults
• Oncotic pressure and buffering effect
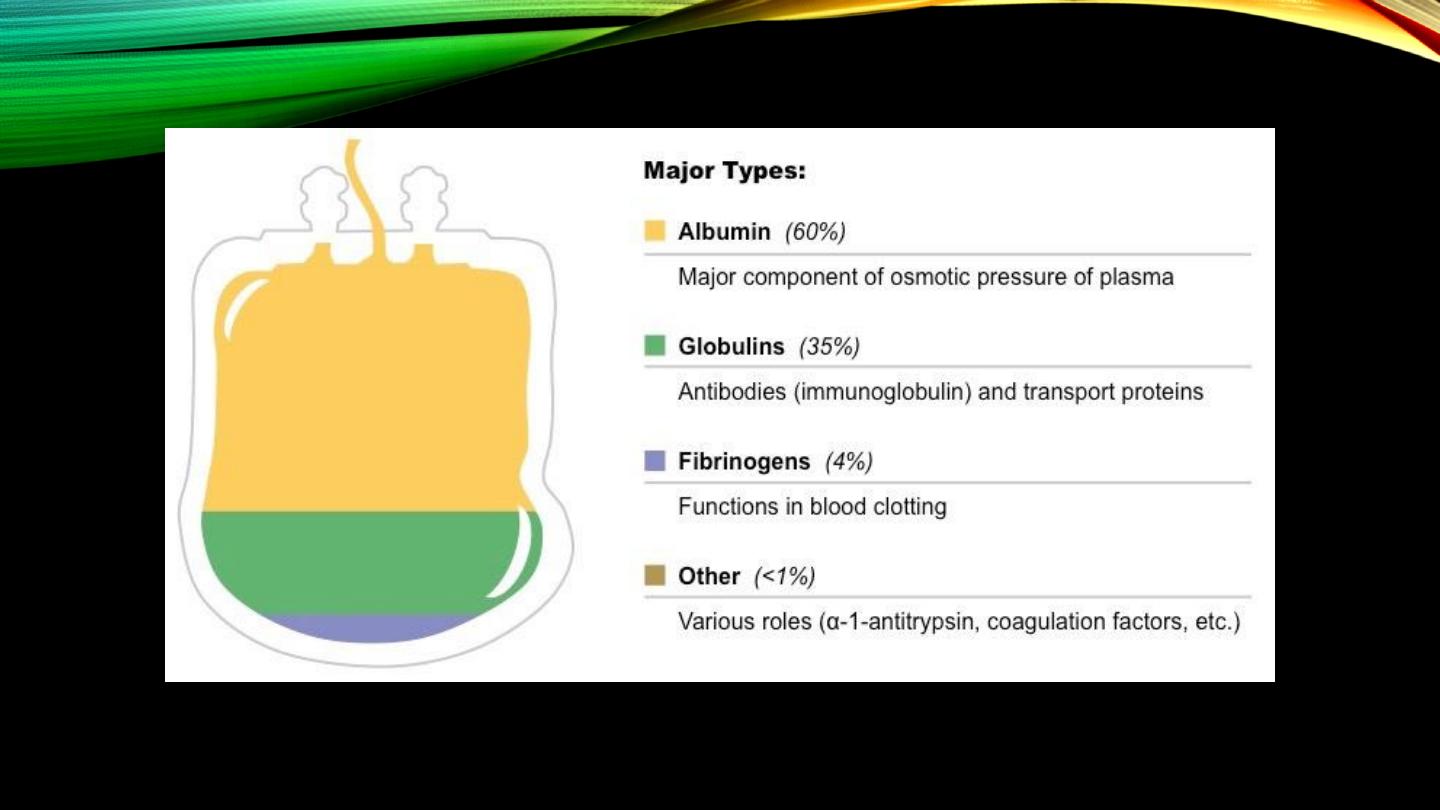

Albumin:
• Site of synthesis and concentration
• Causes of reduction
• Edema, ascites and effusion
• Carrier function

Haptoglobin:
• Hemoglobin-binding and metabolism

Ceruloplasmin:
• Copper metabolism and homeostasis
• Wilson’s disease?

Transferrin:
• Ferric iron transporter and maintainer

Ferritin:
• Soluble storage form of iron

Fibrinogen:
• Blood viscosity
• Blood coagulation

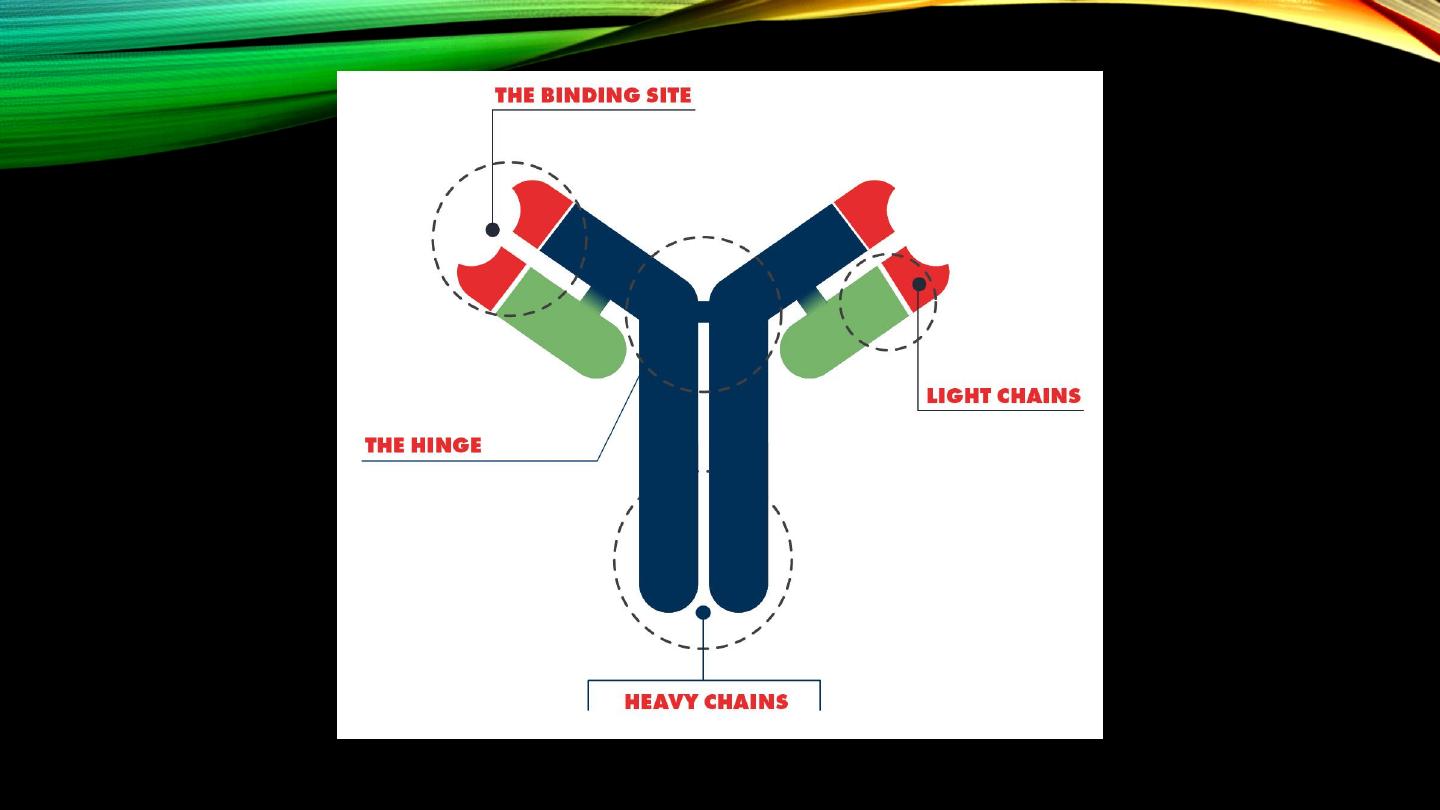
Immunoglobulins:
• “Antibodies”
• Types
• Heavy and light chains

Ions of plasma:
• Major cations
• Major anions

Enzymes of plasma:
• Mostly no metabolic roles
• Diagnosis of particular diseases

Good Luck
